Picture this: you’ve just spent hours recording the perfect vocal take, only to find that your final mix is plagued by harsh sibilance and irritating high frequencies.
It’s enough to make even the most seasoned music producer cringe. But fear not! Dealing with sibilance doesn’t have to be a headache.
Enter the De Esser – the unsung hero of the music production universe.
In today’s article, we’ll dive deep into the fascinating realm of de-essing, revealing the tips, tricks, and techniques that can transform your vocal tracks from amateurish to professional in no time.
Say goodbye to those pesky “esses” and “tees” that ruin an otherwise flawless performance.
With the power of de-essers at your fingertips, you’ll be ready to conquer the sibilance beast and elevate your productions to new heights.
By the time you’ve finished reading, you’ll be armed with the knowledge and confidence to tackle even the most stubborn sibilance issues and make your vocal recordings shine like never before.
Let’s dive in…
Table of Contents
- What is DeEssing?
- How To Use a De Esser
- Types of De Essers
- De Essing & The Mixing Process
- De Essing Vocal Recordings
- Using De Essers on Vocal Tracks
- Techniques for Precise De Essing
- De Essing Beyond Vocals
- Frequency Range: Why it’s Important
- Preserving the Natural Sound of Your Mix
- Best De Esser Plugins
- Advanced De Essing Techniques
- Conclusion
What is DeEssing?
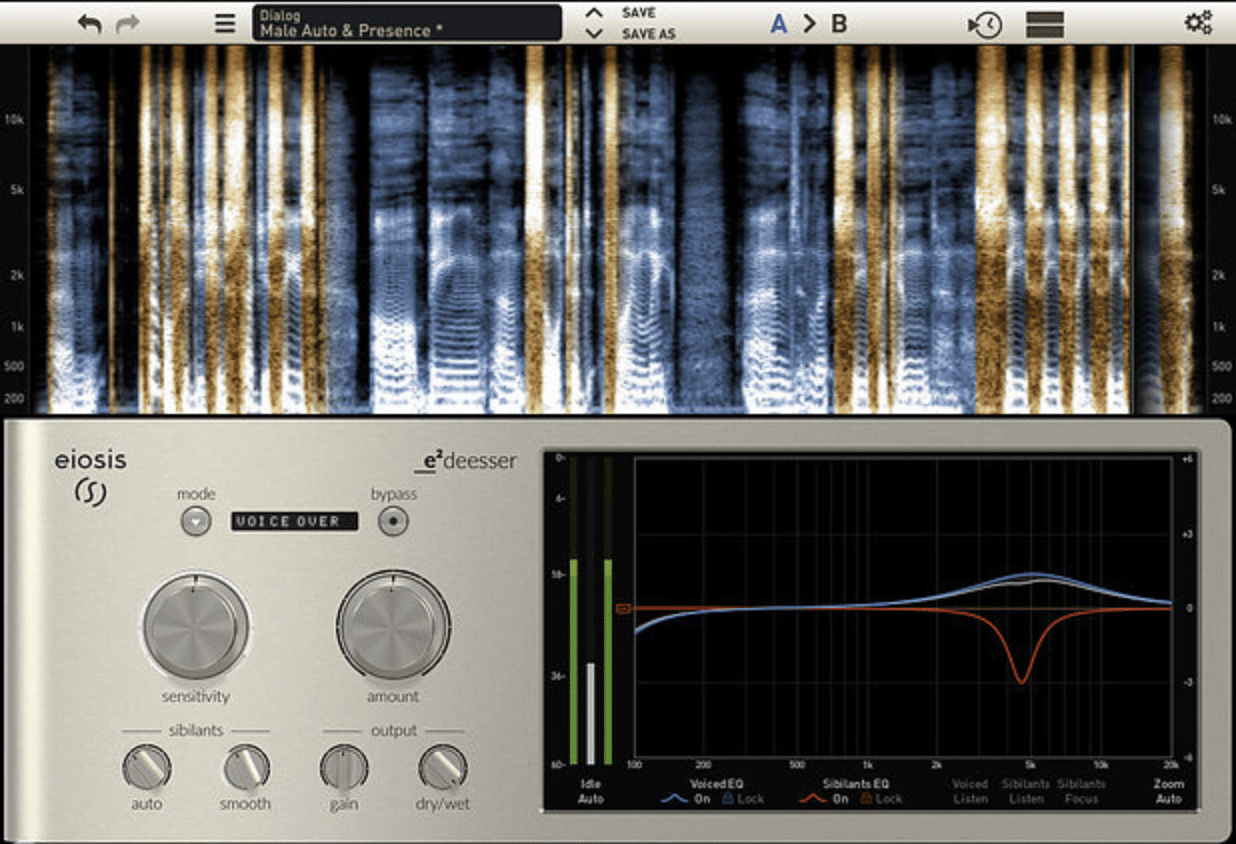
De essing is a technique used in audio processing to reduce or remove harsh sibilance or sibilant sounds that can occur in vocal recordings.
These sounds are usually caused by the excessive emphasis of certain consonants, like “s” and “sh.”
De essing is a vital tool in the music production process, as it helps to create a more polished and professional sound in your mixes.
De essing typically involves using a de esser plugin or a dynamic EQ to target specific frequency ranges where sibilance is most likely to occur.
By compressing or reducing these frequencies, you can effectively eliminate the harshness and ensure your vocal tracks sound smoother and more pleasant to the ears.
De essing is crucial for creating high-quality vocals, as it allows you to tackle the harshness and sibilance that can be distracting or even painful to listen to.
When sibilance is left untreated, it can create an unpleasant listening experience and detract from the overall quality of your mix.
Moreover, sibilance can also interfere with other elements of your mix, making it difficult to achieve a balanced and harmonious sound.
By properly de essing your vocal tracks, you can create a more professional and polished sound that will captivate your listeners and elevate your music production skills.
How To Use a De Esser
A de esser works by acting as a specialized compressor that focuses on a specific frequency range where sibilance typically occurs.
When the input signal’s level in that range exceeds a set threshold, the de esser applies gain reduction to attenuate the harshness.
This way, you can maintain the overall integrity of your vocal track while minimizing the distracting sibilance.
De essers usually provide several essential controls to help you fine-tune the process, such as threshold, frequency range, and gain reduction settings.
Types of De Essers
There are two main types of de essers:
- Split band
- Wide band
Each type has its unique characteristics and advantages, so it’s essential to understand the differences to choose the best one for your mix.
-
Split Band De Essing
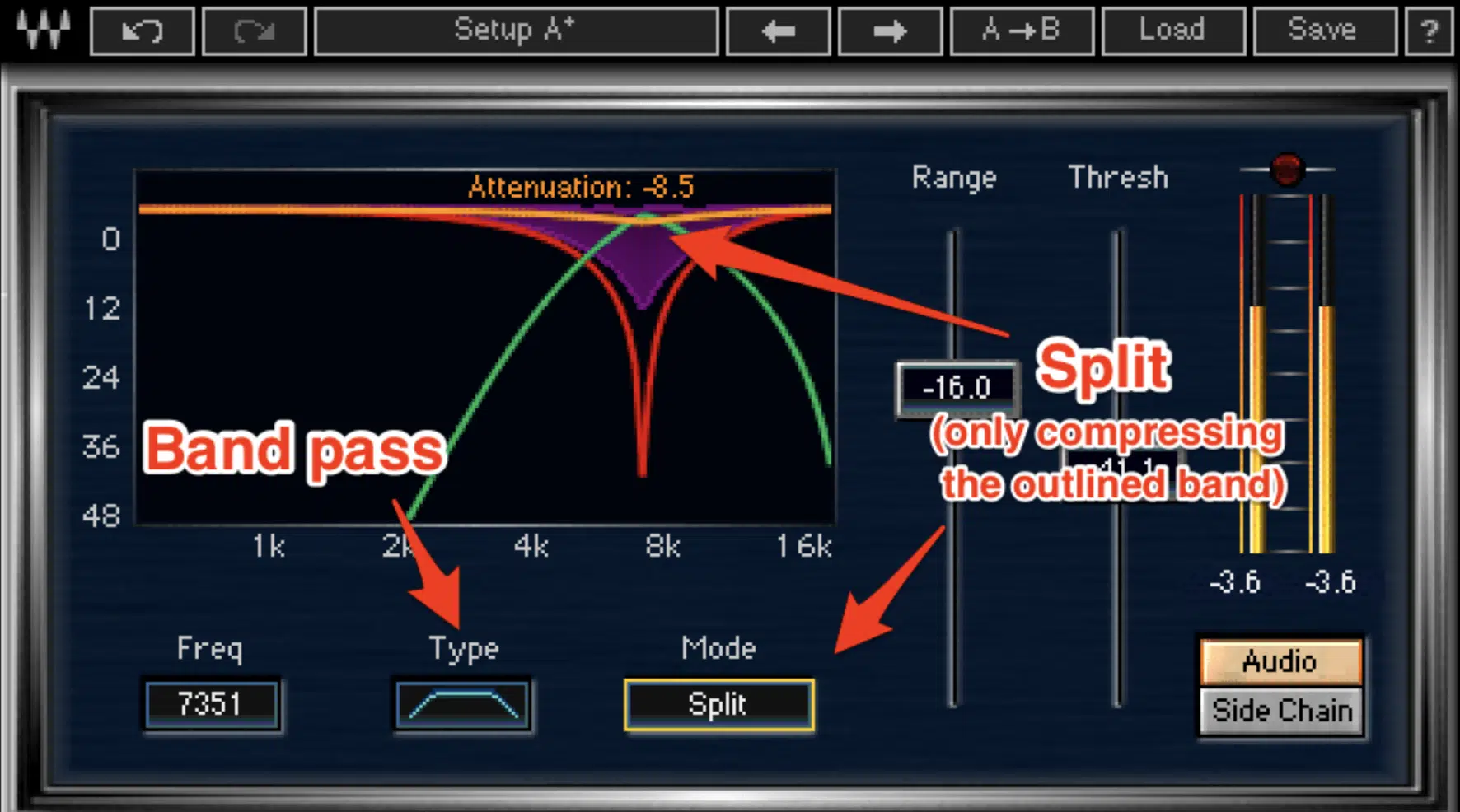
Split band mode works by dividing the input signal into two frequency bands:
- One band contains the problematic sibilant frequencies
- The other contains all the remaining frequencies
Split band processing only compresses the sibilant band, leaving the rest of the signal untouched.
This selective processing helps maintain the natural sound of your vocal recordings and prevents over-compression of the entire frequency spectrum.
-
Wide Band Mode
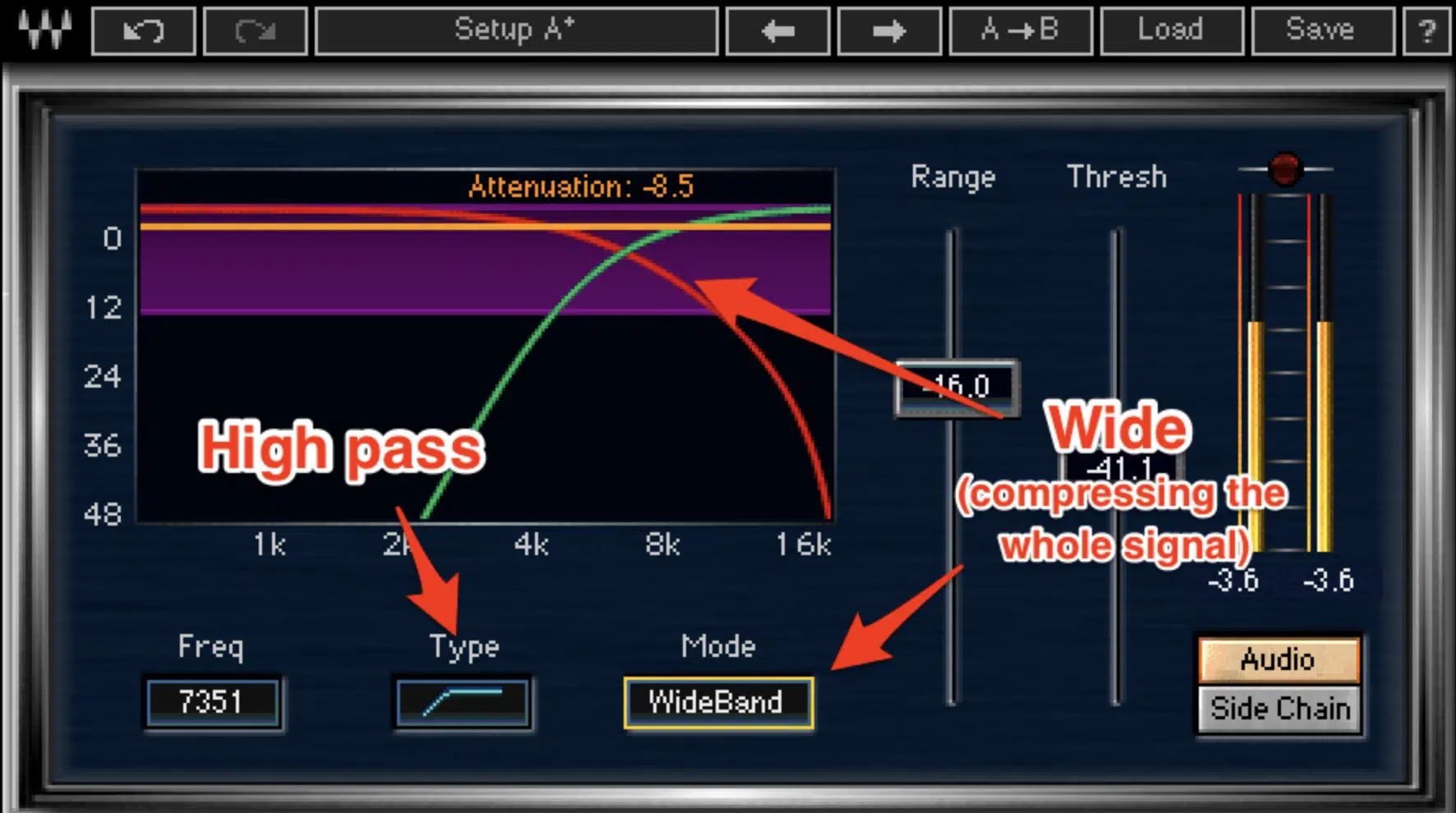
Wide band de essers, on the other hand, apply compression to the entire signal when sibilance is detected.
While this approach may be more straightforward, it can sometimes lead to a more noticeable effect on your overall sound.
This is because other elements of the mix might be affected.
Wide band de essers can be useful in certain situations, such as when sibilance is pervasive throughout the entire vocal track.
Choosing the Best Mode for Your Mix
To choose between split band and wide band de essing, consider the specific needs of your vocal track.
If the sibilance is focused within a narrow frequency range, split band de essing may be more appropriate.
On the other hand, if the harshness is spread across a wider frequency range, wide band de essing can be more effective.
De Essing & The Mixing Process
De essing is an essential part of the mixing process, ensuring that your vocal tracks sound polished and professional.
Integrating de essing into your workflow can also benefit other elements of your mix, such as hi hats and cymbals.
Integrating De Essing into Your Effects Chain
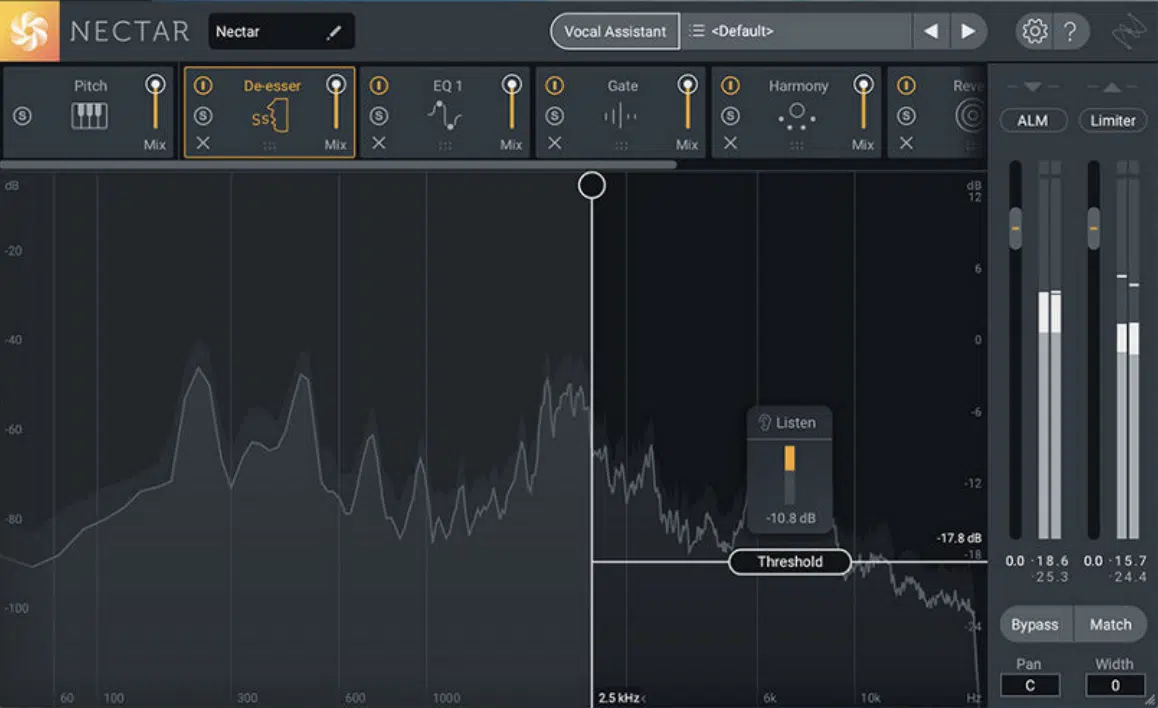
The position of the de esser in your effects chain can significantly impact the overall sound.
Generally, I recommend to place the de esser early in the chain, before EQ and compression.
This approach allows you to address sibilance issues before applying further processing, helping you achieve a cleaner mix.
Balancing De Essing with Other Audio Effects
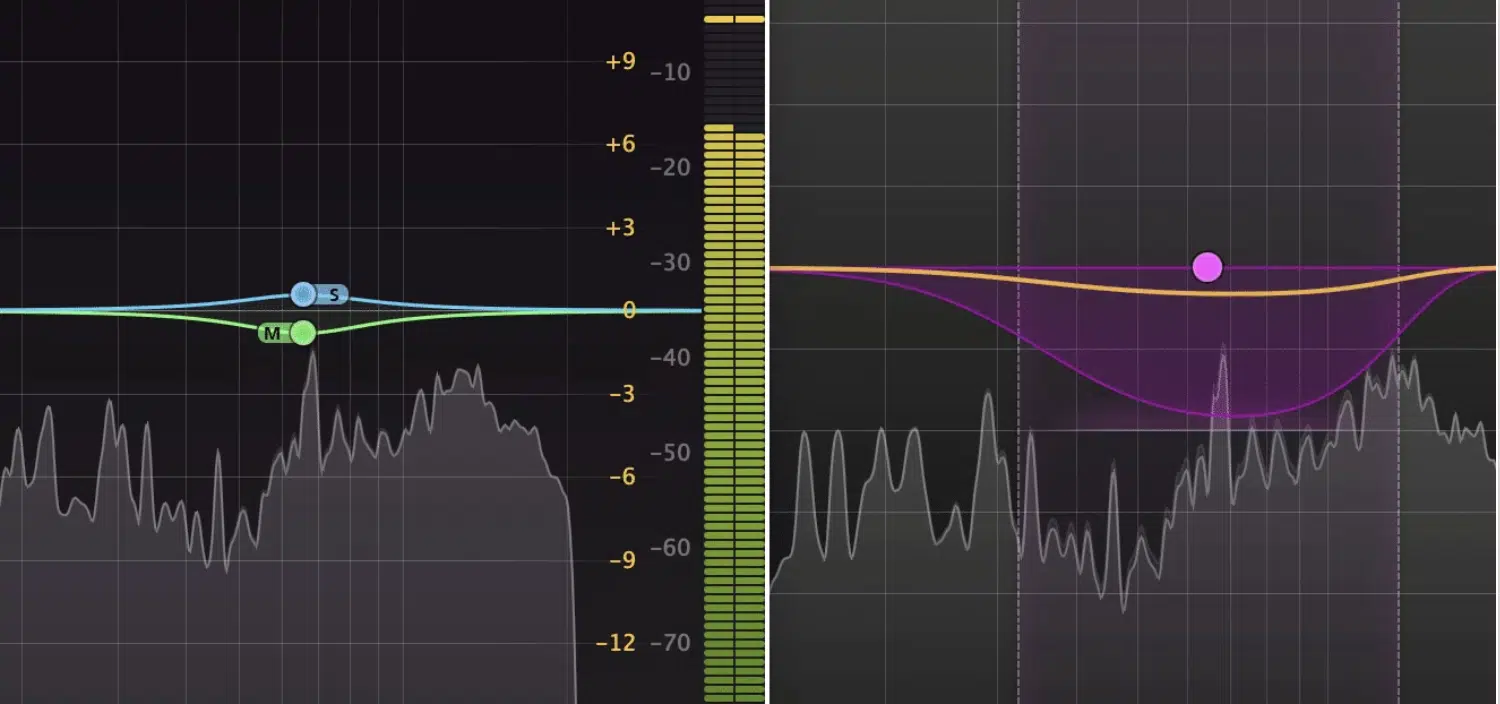
It’s essential to balance the use of de essing with other audio effects, such as EQ, compression, and reverb.
Over-processing a vocal track can lead to an unnatural sound, so use these effects judiciously and always listen critically to the results.
To achieve a balanced mix, listen to your track on various playback systems and at different volume levels.
This will help you identify any remaining sibilance issues and make the necessary adjustments.
Additionally, make sure to periodically bypass your de esser plugin to ensure that you’re not over-processing the vocal track and compromising its natural sound.
De Essing Vocal Recordings
Before you start de essing, it’s essential to identify the problematic frequencies in your vocal recording. There are several ways to do this:
-
Use a Spectrum Analyzer
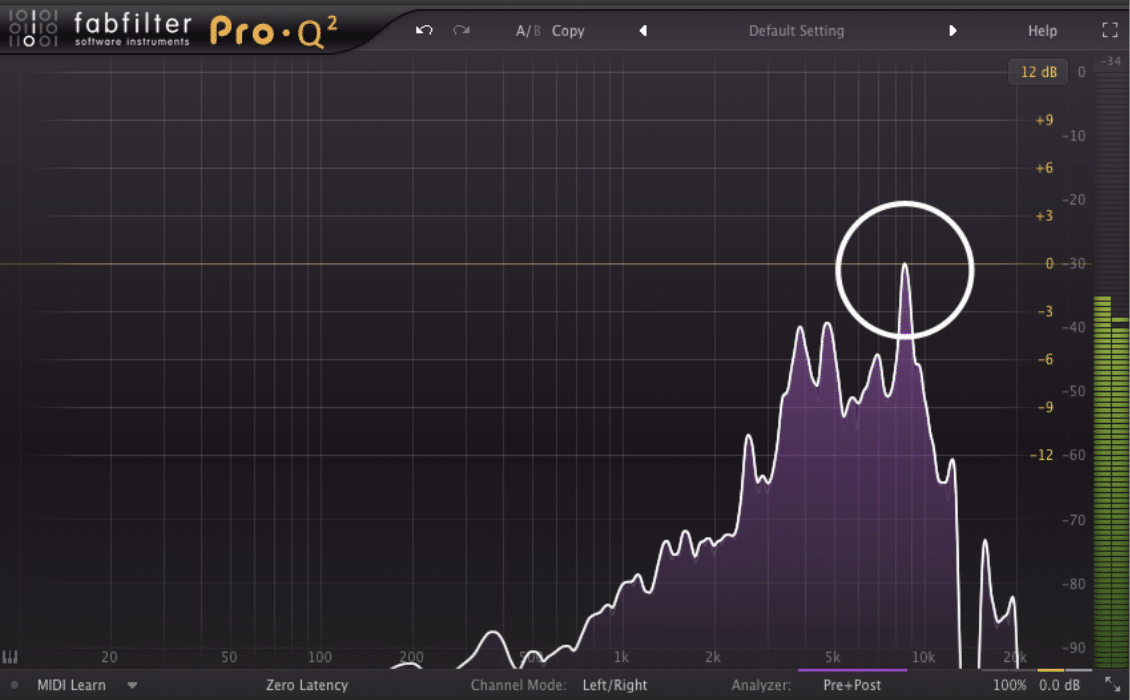
Analyzing the frequency spectrum of your vocal track can help you visually identify the areas where sibilance is most prominent.
-
Solo the Track
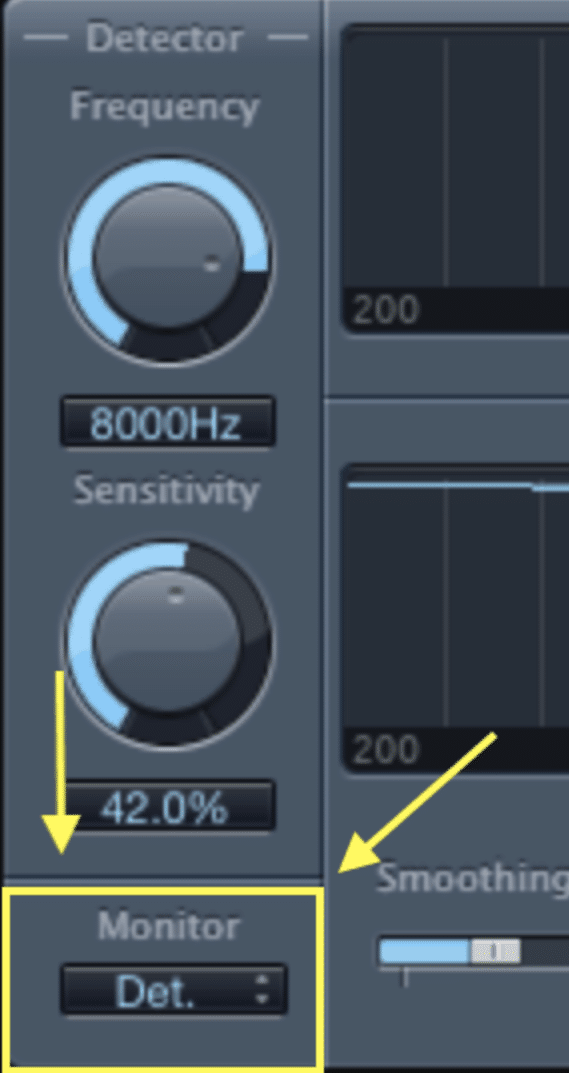
By listening to the vocal track in isolation, you can better focus on the sibilance and determine its specific frequency range.
-
Sweep an EQ
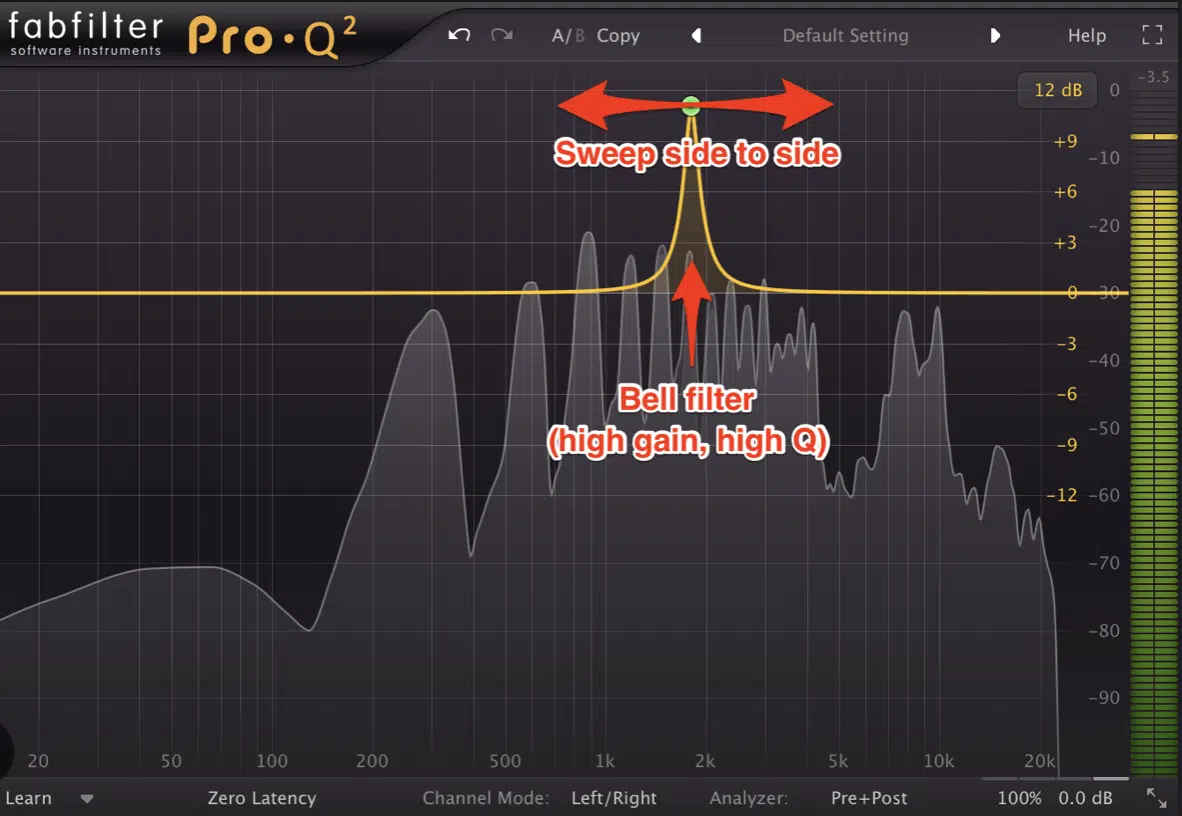
Boost a narrow band on an EQ and sweep it through the sibilant frequency range (5 kHz to 10 kHz) until you notice the harshness becoming more pronounced.
This can help you pinpoint the exact frequency that needs attenuation.
Using De Essers on Vocal Tracks
Once you’ve identified the problematic frequencies, it’s time to apply de essing to your vocal track.
Follow these steps:
- Insert the de esser plugin on your vocal track.
- Set the threshold control so that the de esser only engages when sibilance is present.
- Adjust the frequency range to target the specific sibilant frequencies you identified earlier.
- Set the gain reduction or range control to reduce the sibilance to an acceptable level without compromising the natural sound of the recording.
Remember to keep an eye on the gain reduction meter to ensure you’re not over-processing the signal.
It’s also a good idea to compare the processed and unprocessed signals by bypassing the de esser plugin to ensure you’ve achieved the desired result.
Reducing Sibilance and Harsh High Frequencies
In addition to using a de esser plugin, you can employ other techniques to prevent and/or reduce sibilance and harsh high frequencies in your vocal recordings:
“Adjust the Mic” Technique: Experiment with different microphone positions, angles, and distances to minimize sibilance during the recording process.
Use a Pop Filter: A pop filter can help reduce sibilance and plosive sounds, improving the overall quality of your vocal recording.
Apply EQ: Gently attenuate the problematic high frequencies using a parametric EQ.
Be cautious not to remove too much high-end, as this can result in a dull and lifeless vocal sound.
Techniques for Precise De Essing
-
Manual De Essing
Manual de essing involves manually adjusting the gain or volume of individual sibilant regions in your vocal track.
This technique can provide more control and precision compared to using a de esser plugin, but it can also be super time-consuming.
To manually de ess a vocal track:
- Zoom in on the waveform display in your DAW and locate the sibilant regions.
- Use your DAW’s gain automation or clip gain feature to reduce the volume of each sibilant region until it sits well in the mix.
Manual de essing can be particularly effective when dealing with an isolated problematic section or when you need to preserve the natural sound of a vocal recording.
However, it may not be practical for extensive de essing tasks, as it can be labor-intensive and time-consuming (as I’ve mentioned).
-
Using Dynamic EQ for De Essing
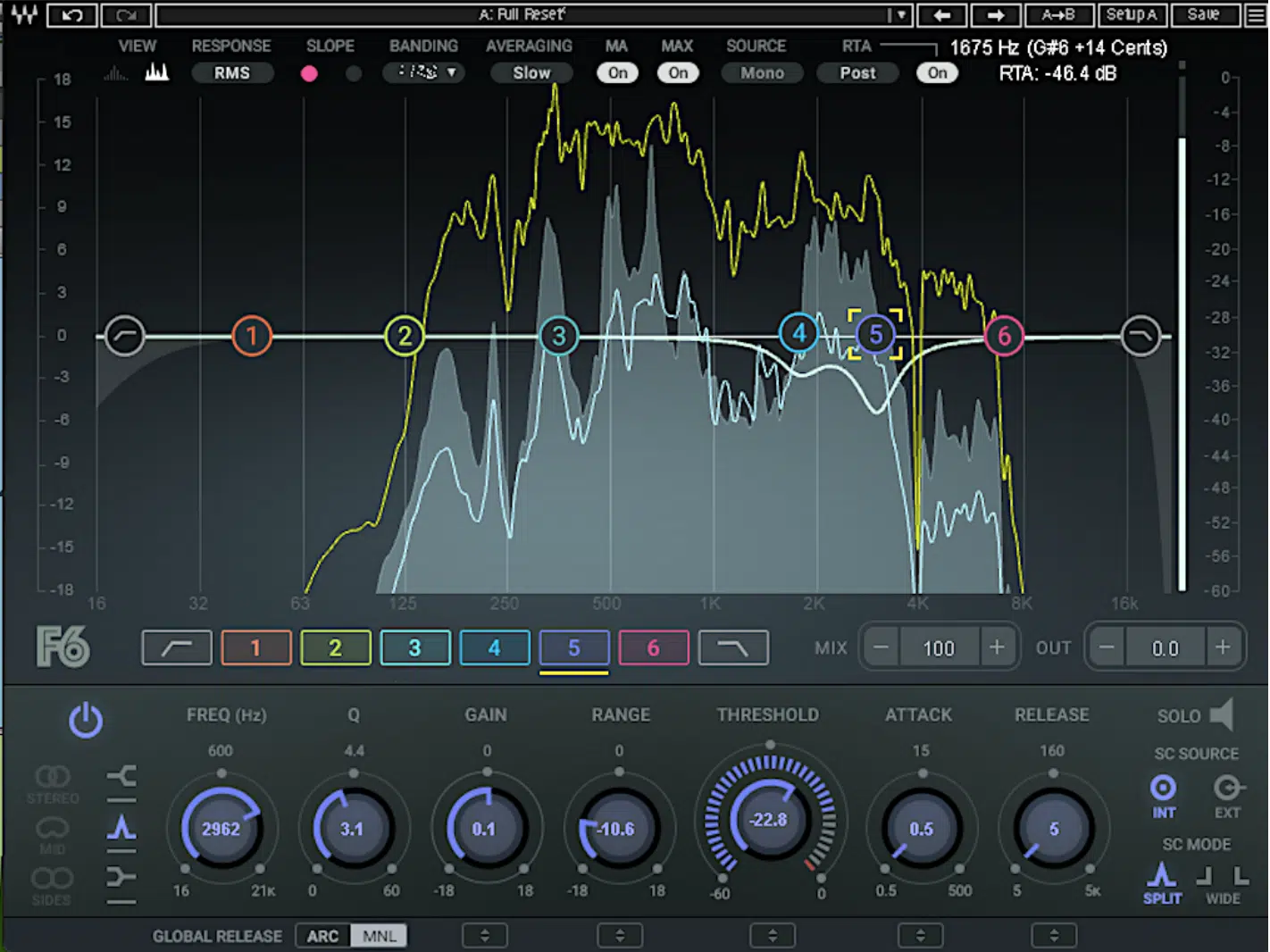
Dynamic EQ is another powerful technique for precise de essing.
It combines the benefits of both equalization and compression 一 allowing you to target specific frequency bands and apply gain reduction only when the signal exceeds a certain threshold.
To use dynamic EQ for de essing:
- Insert a dynamic EQ plugin on your vocal track.
- Set a narrow Q and boost the problematic frequency range (usually between 5 kHz and 10 kHz) to identify the sibilance more clearly.
- Apply gain reduction by setting the threshold, so it only engages when sibilance is present.
- Fine-tune the attack and release times to ensure the processing is smooth and natural-sounding.
Dynamic EQ can provide more surgical control over the de essing process and is particularly useful when dealing with complex or tonally rich vocal tracks.
De Essing Beyond Vocals
While de essing is primarily used for vocal sounds in audio production, it can also be applied to other elements in your mix that exhibit harshness or excessive high frequencies.
Hi Hats and Cymbals
Hi hats and cymbals (even guitars) can sometimes have harsh high frequencies that can clash with other elements in your mix.
De Ess or use dynamic EQ can help you tame these harsh frequencies and create a more balanced and cohesive sound.
Full Mixes and Mastering
In some cases, you may find that your entire mix or master has an overall harshness due to an accumulation of high frequencies.
Applying gentle de essing to the full mix or during the mastering stage can help smooth out the overall sound without affecting the individual elements too drastically.
Frequency Range: Why it’s Important
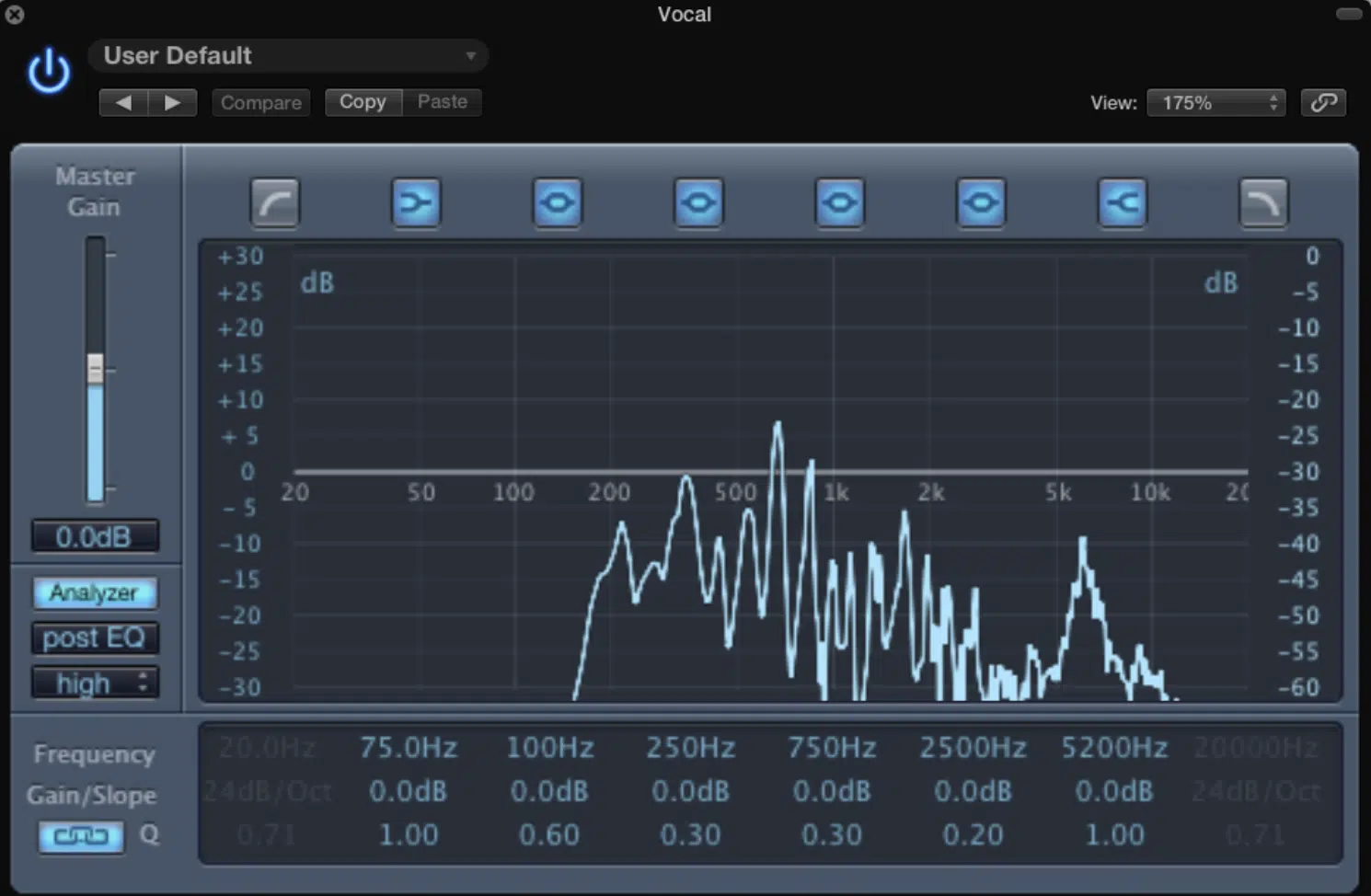
When using a de esser, it’s crucial to select the appropriate frequency range for the sibilance you’re targeting.
Sibilant frequencies usually fall between 5 kHz and 10 kHz, but they can vary depending on the vocalist and recording conditions.
By carefully selecting the frequency range, you can effectively reduce sibilance without negatively impacting other aspects of your mix.
To find the problematic frequencies, you can use a spectrum analyzer or rely on your ears.
Some de essers also offer a ‘listen’ or ‘solo’ feature that allows you to hear the targeted frequency range, making it easier to pinpoint the issue.
Preserving the Natural Sound of Your Mix
The overall goal of de essing is to reduce harsh sibilance while maintaining the natural sound of the vocal performance.
Striking the right balance between de essing and preserving the character of the recording is crucial for achieving professional-sounding mixes.
-
Avoid Over-De Essing
Over-de essing can result in a “lispy” or muffled vocal sound…
To avoid this, use moderate settings on your de esser and be cautious when applying gain reduction.
It’s better to lean on the side of subtlety and apply additional de essing if necessary, as opposed to overdoing it from the start.
-
Maintain a Natural Sound in Vocal Recordings

One way to maintain a natural sound in vocal recordings is to use manual de essing techniques, such as gain automation or clip gain adjustments.
By carefully adjusting the volume of individual sibilant sounds, you can achieve precise control over sibilance without affecting the overall character of the performance.
Best De Esser Plugins
There are numerous de esser plugins available in the market, each with its unique features, strengths, and weaknesses.
Some popular de esser plugins among music producers include:
-
FabFilter Pro-DS
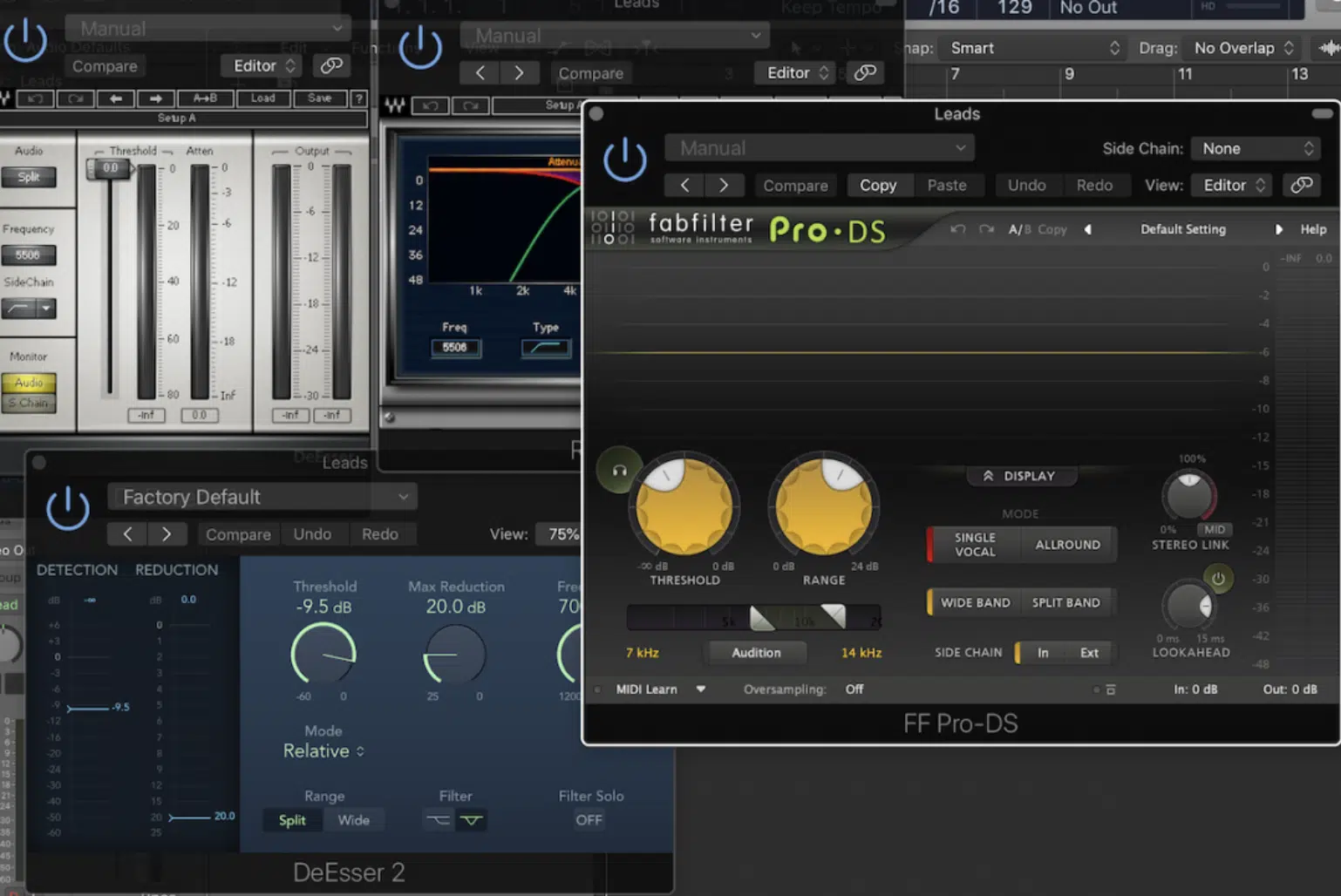
A go-to de esser plugin for many music producers, FabFilter Pro-DS excels in tackling sibilance with its intelligent ‘Single Vocal’ and ‘Allround’ modes.
The plugin’s user-friendly interface offers precise control over sibilance reduction.
Plus, the real-time waveform display and adjustable side-chain filter make it a breeze to identify and address problematic frequencies.
This results in polished and professional-sounding vocal tracks.
Offers an intelligent single vocal and all-round mode, adjustable side-chain filtering, and real-time waveform display.
-
Waves Sibilance
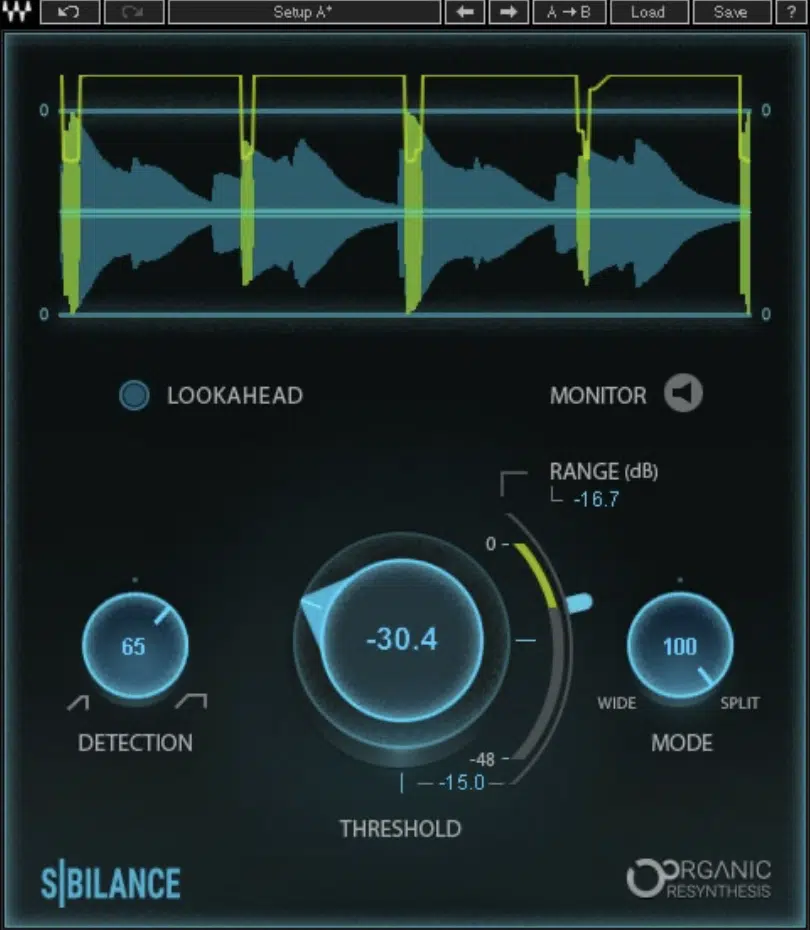
Waves Sibilance is known for its simplicity and effectiveness.
With its easy-to-use interface and phase compensation feature, this plugin ensures great-sounding results with minimal effort.
Waves Sibilance is a powerful de esser plugin that uses the cutting-edge Organic ReSynthesis technology to minimize sibilance while maintaining the natural character of the vocals.
Its precision processing and intuitive interface make it an excellent choice for taming harshness without introducing unwanted artifacts, ensuring your vocal tracks retain their authentic sound.
-
Softube Weiss Deess
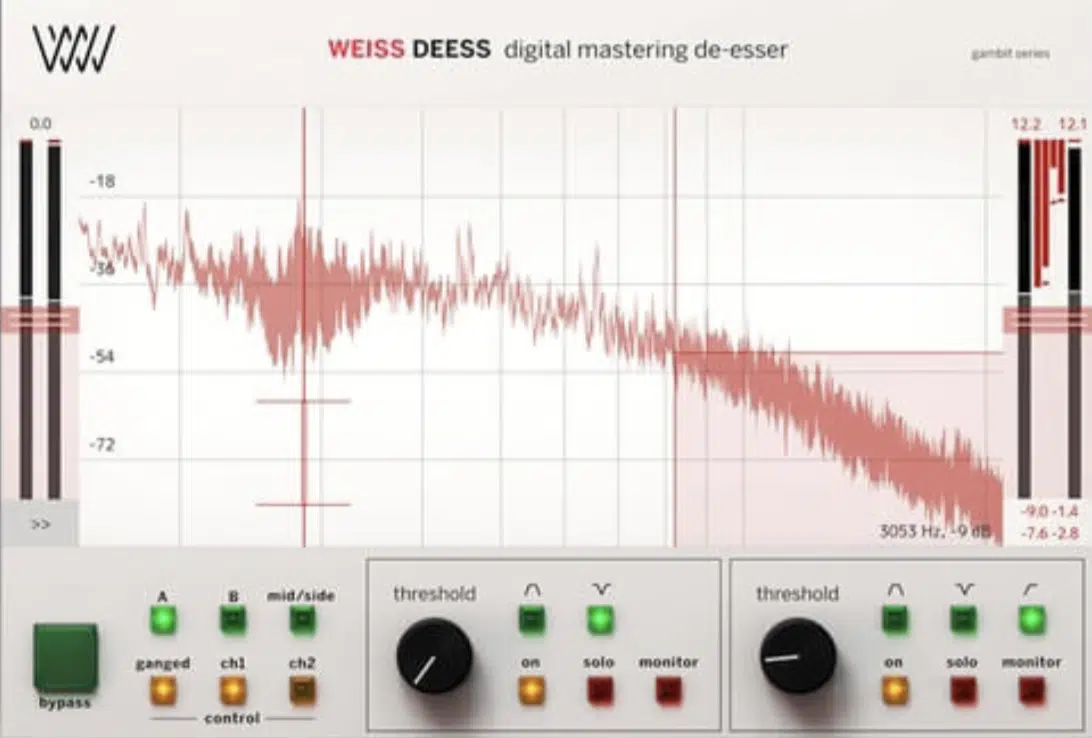
Drawing inspiration from the iconic Weiss DS1-MK3 mastering processor, Softube Weiss Deess offers state-of-the-art de essing capabilities for music producers.
Focused on delivering surgical precision and unparalleled sound quality, this plugin features dual-band and wide-band modes to effectively address sibilance.
The Softube Weiss Deess’s transparent sound and intuitive interface make it a top choice for both mixing and mastering applications in music production.
Choosing the Right Plugin for You
When deciding on a DeEsser plugin, consider the following factors:
- Interface: Ask yourself if the plugin’s interface is user-friendly and easy to navigate.
- Flexibility: Does the plugin offer a range of features and controls to fine-tune your de essing process?
- Compatibility: Make sure the plugin is compatible with your DAW and OS.
- Price: Determine whether the plugin fits within your budget and offers good value for money.
By evaluating these factors, you can select the plugin that best suits your needs and helps you achieve polished, professional-sounding vocal tracks.
Advanced De Essing Techniques
If you’re a more experienced producer, or just want to push the bounds and challenge yourself, there are more advanced de essing techniques available.
The following are a few of my personal favorite:
1. Parallel De Essing
Parallel de essing involves mixing a heavily de-essed version of your vocal track with the original, unprocessed track.
This technique can help maintain the natural sound of the recording while still effectively reducing sibilance.
To set up parallel de essing:
- Duplicate your vocal track in your DAW.
- Apply aggressive de essing to one of the tracks, reducing the sibilance significantly.
- Blend the processed track with the unprocessed track, adjusting the levels until you achieve the desired balance of sibilance reduction and naturalness.
Note: If you’d like to learn more about the world of parallel manipulation, check out our Parallel Compression article.
2. Mid/Side De Essing
Mid/side processing allows you to process the center (mid) and sides (stereo) of a signal separately.
By applying de essing only to the mid or side channels, you can preserve the stereo image and achieve a more natural-sounding result.
To implement mid/side de essing:
- Insert a mid/side-capable de esser plugin or a mid/side processor with a de esser on your vocal track.
- Target only the mid or side channel, depending on where the problematic sibilance resides.
- Adjust the de esser settings to reduce the sibilance without affecting the overall stereo image.
3. Multiband Compression for De Essing
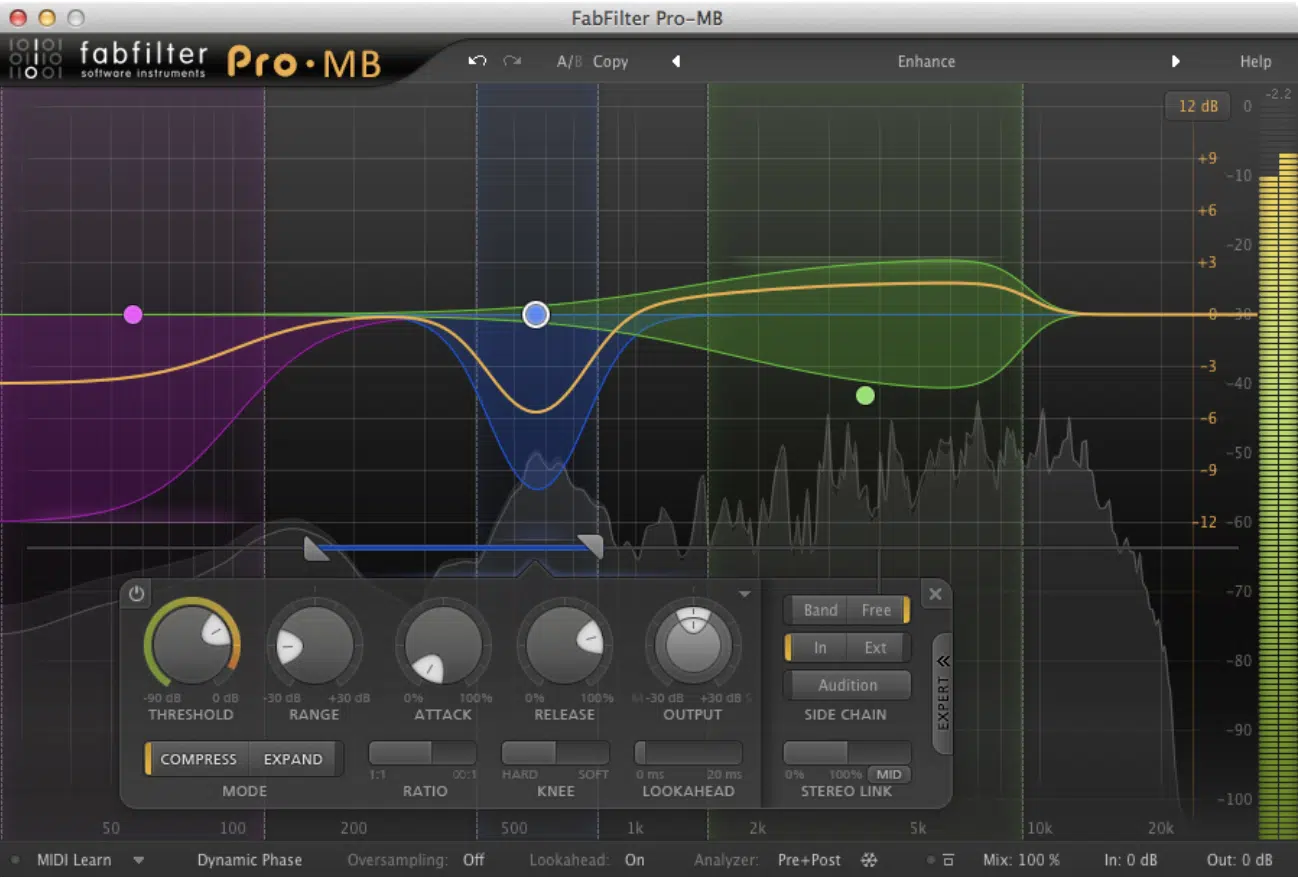
Multiband compression allows you to compress specific frequency bands independently, making it a useful alternative to traditional de essing.
To use multiband compression for de essing:
- Insert a multiband compressor plugin on your vocal track.
- Create a narrow band focusing on the problematic sibilant frequency range (5 kHz to 10 kHz).
- Set the compressor’s threshold, ratio, attack, and release settings to effectively reduce the sibilance without affecting other frequency bands.
By incorporating these advanced techniques into your de essing arsenal, you can further refine your production skills and achieve professional-sounding results.
Yes, even when it comes to the most challenging mixes.
Conclusion
De essing is an essential skill, as it can significantly improve the quality of your vocal recordings and overall mixes.
By understanding the different types of de-essers, techniques, and applications, you can tackle sibilance and harshness with confidence and precision.
So, go ahead and dive into the world of de-essing – you will achieve better sounding mixes every single time.
To hear vocals that are already perfectly pristine, and have no need for de-essing techniques, check out our Unison Vocal Series – Aaron Richards “Talk About It.”
It includes:
- 80 Unique Vocal Lines
- 137 Unique Adlibs
- 120 Unique Vocal Chops available in Dry&Wet (totalling 240)
- 2 In-Depth Vocal Processing Video Tutorials
- Bonus 1: Unison Theory Blueprint PDF (54 Page Chord/Melody Writing Guide)
- Bonus 2: Unison Vocal Secrets PDF (25 vocal processing tricks)
- Bonus 3: Unison Loop Pack (200 WAV Loops, 10 for each of the 20 main genres of music)
By using these vocals, you’ll be able to add the missing piece to your tracks and get your music stuck in your listeners’ head.
Until next time…







Leave a Reply
You must belogged in to post a comment.