Are you dreaming of becoming a music producer but don’t know where to start?…
Well, you’re certainly not alone!
The road to music production success can be bumpy, especially with how saturated the music industry is.
Luckily, with the right guidance, dedication, and passion, you can make your mark in this exciting and ever-evolving industry.
In this comprehensive 10-step guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know to kick-start your music production career 一 from understanding music theory and industry roles to choosing the perfect DAW and mastering essential production skills.
Plus, we’ve included a few industry secrets to really help you skyrocket your production.
So, get ready to embark on an incredible adventure and unlock your full potential as you learn how to become a music producer.
Table of Contents
- STEP 1: Learn Different Music Theory Concepts
- STEP 2: Find the Right DAW For You
- STEP 3: Master Essential Music Production Skills
- STEP 4: Network & Collaborate
- STEP 5: Study Audio Engineering and Mixing
- STEP 6: Find Your Niche As a Music Producer
- STEP 7: Develop Your Brand and Online Presence
- STEP 8: Create a Diverse Portfolio
- STEP 9: Stay Up-to-Date
- STEP 10: Understanding the Music Industry
- Roles within the Music Industry
- Music Production Career Options
- BONUS: Creating an Optimal Recording Environment At Home
- 5 Secret Methods To Excel Your Production Process
- How to Become a Music Producer: Final Thoughts
STEP 1: Learn Different Music Theory Concepts
A solid understanding of Music Theory concepts is essential for any music producer.
Music theory is the language of music, and it allows you to understand and analyze the elements that make up a song.
As an aspiring music producer, knowing music theory helps you make informed decisions about chord progressions, melody, harmony, and rhythm.
This knowledge will enable you to create music that resonates with listeners and stands out in a saturated market.
It provides a foundation for your creative process and allows you to communicate more effectively with other musicians as well.
Music Theory Concepts You Should Know When Learning How to Become a Music Producer
When you’re first starting out your music production journey, there are a few fundamental concepts you should get familiar with.
- Scales and Modes
Understanding scales and modes is crucial for composing melodies, harmonies, and chord progressions.
Learn about major scales and minor scales, as well as different modes such as Dorian, Phrygian, and Mixolydian, to expand your musical vocabulary.

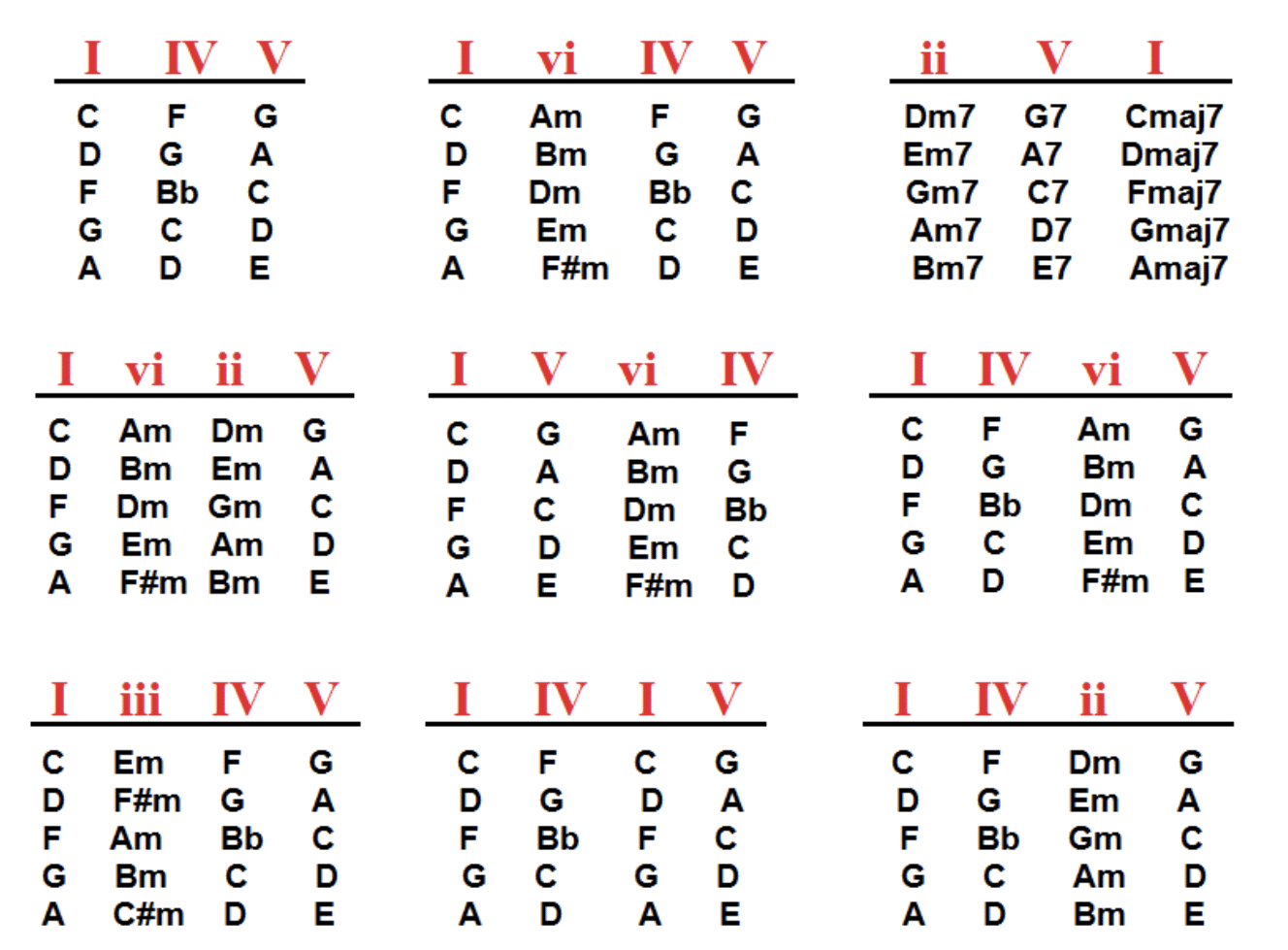
- Chords and Chord Progressions
Chords form the harmonic foundation of your music.
Learn about chord construction, inversions, and voicings, as well as common chord progressions like the I-IV-V and ii-V-I.
This way, you’ll be able to create captivating and advanced chord progressions like a pro.
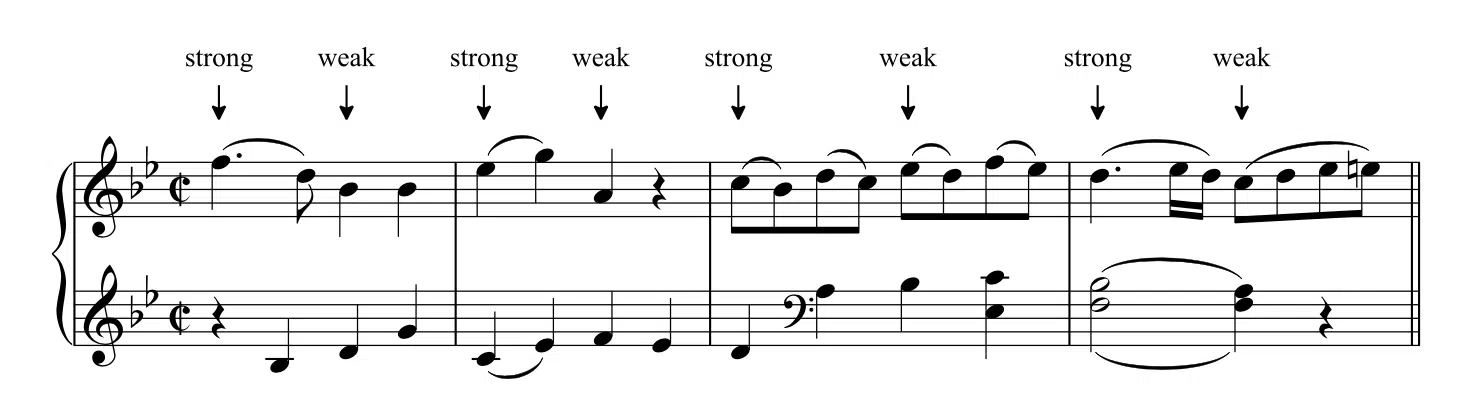
- Rhythm and Meter
Rhythm is the driving force behind any piece of music.
Understand different time signatures, note values, and rhythmic patterns to create compelling grooves and rhythmic structures in your productions.
Without understanding the fundamentals of rhythm and meter, you will surely fall behind.
- Melody and Harmony
Melody and harmony are essential components of any musical composition.
Study the principles of melodic contour, phrasing, and motif development.
Also, make sure to learn how to create harmonies that complement your beautiful melodies and enhance the overall emotional impact of your music.
You’ll need this skill if your music is going to stand out from the crowd.
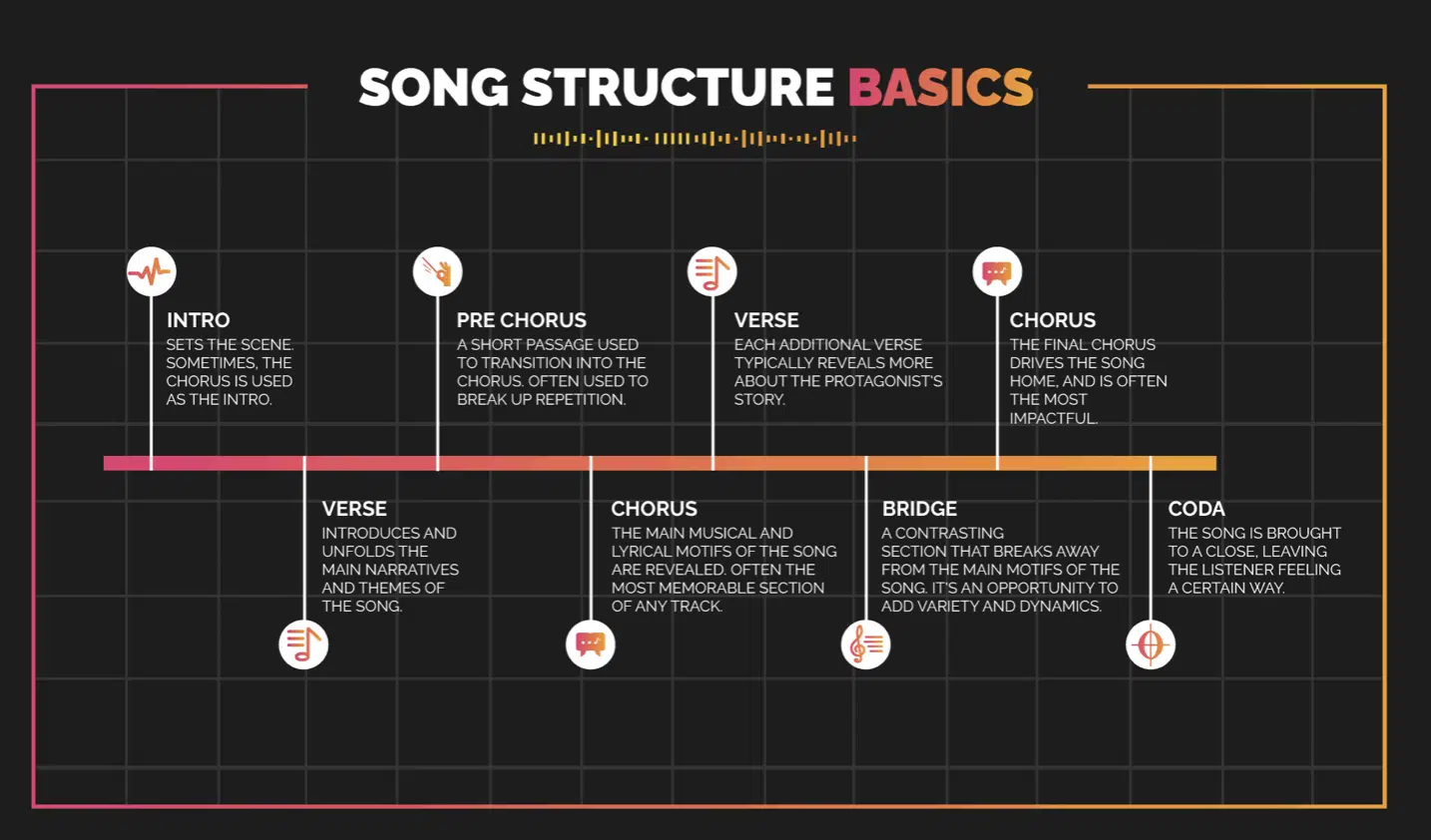
- Song Structure and Arrangement
A well-structured and arranged song is more engaging and memorable.
Familiarize yourself with common song structures, such as verse-chorus-bridge.
Also, learn to create dynamic arrangements using elements like instrumentation, dynamics, and texture.
This will help you a great deal when you’re first discovering how to become a music producer.
STEP 2: Find the Right DAW For You
A Digital Audio Workstation (DAW) is an essential tool for any music producer.
It’s the software you’ll use to create, edit, and mix your music.
With so many options available, choosing the right DAW for your needs can be a daunting task.
DAWs are the centerpiece of music production.
They allow you to record, edit, and arrange audio and MIDI tracks.
DAWs come with a range of built-in features and plugins, such as virtual instruments, effects processors, and more.
There are numerous DAWs available, each with its strengths and weaknesses.
Some popular options include Ableton Live, FL Studio, Logic Pro, and Pro Tools.
- Ableton Live 一 Known for its intuitive interface and excellent MIDI capabilities, making it a popular choice for electronic music producers.
- FL Studio 一 User-friendly and comes with a vast array of plugins and virtual instruments.
- Logic Pro 一 A Mac-exclusive DAW with a comprehensive set of features and tools
- Pro Tools 一 The industry standard for professional recording studios.

How to Choose the Right Digital Audio Workstation
Choosing the right Digital Audio Workstation (DAW) is crucial because it serves as the primary tool for your music production process.
Your choice of DAW will significantly impact your workflow and the quality of your productions, so it’s important to find one that suits your needs and preferences.
To pick the right digital audio workstation for you, consider the following:
Workflow 一 Each DAW has its unique workflow and interface.
Try out various DAWs through trial versions or free lite editions to find one that suits your working style.
For example, Ableton Live is popular for its intuitive and flexible workflow, which makes it ideal for electronic music producers.
Pro Tools is favored by many professionals for its powerful editing and mixing capabilities.
FL is loved by many hip-hop producers, for its unique and flexible piano roll.
Compatibility 一 Ensure that the DAW you choose is compatible with your computer’s operating system (Windows, macOS, or Linux) and hardware.
Check the system requirements and ensure that your computer meets or exceeds them for optimal performance.
Budget 一 DAWs are available at various price points, from free options like GarageBand and Cakewalk to premium software like Logic Pro and Cubase.
Consider your budget and choose a DAW that offers the best value for your investment.
Genre and Production Style 一 Some DAWs cater better to specific music genres or production styles.
For instance, FL Studio is favored by many hip-hop and electronic music producers due to its user-friendly interface and powerful step sequencer.
Expandability 一 Consider the availability of third-party plugins and virtual instruments for the DAW you’re interested in.
While most DAWs support common plugin formats like VST and AU, some have unique features and compatibility options that may influence your choice.
Many DAWs offer trial versions or free editions with limited features, so test out different options to find one that feels comfortable and intuitive.
Don’t be afraid to switch to another DAW if your current choice isn’t working for you – the key is finding a tool that supports and enhances your creative process.
STEP 3: Master Essential Music Production Skills
To become a successful music producer, you’ll need to learn music production and master a range of skills.
From sound design to mixing and mastering, these music producer skills will enable you to create professional-sounding tracks that captivate listeners:
Sound Design
Involves creating unique sounds and textures for your music by manipulating audio samples or synthesizing new sounds from scratch.
This skill allows you to craft distinctive sonic landscapes that set your music apart from the competition.
Experiment with different synthesis techniques, sample manipulation, and effects processing to develop your signature sound.
Mixing & Mastering
In order to become a music producer, you must know the fundamentals of mixing and mastering.
- Mixing 一 The process of balancing the individual elements of a track, such as volume levels, panning, and frequency content, to create a cohesive and polished sound.
- Mastering 一 The final stage of music production, where the mixed track is optimized for distribution across various platforms.
Both mixing and mastering are crucial to creating professional-sounding music, so invest time in learning these skills and refining your techniques.
Working With Digital Musical Instruments
Aspiring music producers often work with digital instruments, such as software synthesizers, samplers, and drum generators.
Understanding how to use these tools effectively can greatly expand your creative possibilities.
Spend time exploring different virtual instruments, learning their unique features, and incorporating them into your productions.
MIDI Programming
MIDI programming allows you to create and edit virtual instrument performances, drum patterns, and automation data.
Master the MIDI editing features in your DAW and learn how to create realistic and expressive MIDI performances using techniques like:
- Quantization
- Velocity editing
- Humanization
With the help of MIDI, you’ll become a master of music production in no time.
STEP 4: Network & Collaborate
Networking is an essential aspect of building a successful music production career.
By connecting with other music professionals, you can gain access to new opportunities, collaborations, and resources, as well as expand your knowledge and skills.
Make sure to attend industry events, conferences, and Music Producer workshops to network with other music professionals.
Also, stay current on new trends and technologies, and gain valuable insights from industry experts and other music producers.
Examples of popular music industry events include NAMM, SXSW, and the ASCAP “I Create Music” Expo.
Online Opportunities
Engage in online forums, social media platforms, and music collaboration websites to connect with other musicians, producers, and music professionals from around the world.
Examples of online forums and communities include Gearslutz, KVR Audio, and the Reddit music production community.
The most prolific music production program in the entire music industry is the Unison Audio Affiliate Program.
It’s already helped almost a quarter of a million producers create their best music… so if you’re just learning how to become a music producer, this program can skyrocket your workflow and skill set.
Make sure to share your work, provide feedback, and collaborate on projects to expand your network and grow your skills.
Collaborate with Other Artists and Producers
Collaboration can lead to creative growth, skill development, and new opportunities in the music industry.
Working with other artists and producers allows you to learn from their unique perspectives, techniques, and experiences.
This could lead to a richer and more diverse music production skillset.
Get Involved
Get involved in your local music scene by attending open mics, jam sessions, and local music events.
Collaborate with local musicians and producers to build relationships, share ideas, and create new music together.
Look for local Facebook groups, Meetup events, or community organizations that host music-related gatherings and workshops.
Leverage online platforms and tools for remote collaboration, such as Kompoz and BandLab.
These platforms enable you to work with musicians and producers from around the world, expanding your creative horizons and building an international network.
Additionally, consider joining Discord servers, Facebook groups, or other online communities focused on music production and collaboration.
STEP 5: Study Audio Engineering and Mixing
Aspiring music producers need to understand that audio engineering and mixing are crucial for creating professional-sounding music.
By developing these skills, you’ll be able to craft polished, well-balanced mixes that showcase your creative vision.
Plus, they’ll help you ensure your music sounds great across different listening devices and environments.
Begin by studying the fundamental concepts of audio engineering and mixing, such as:
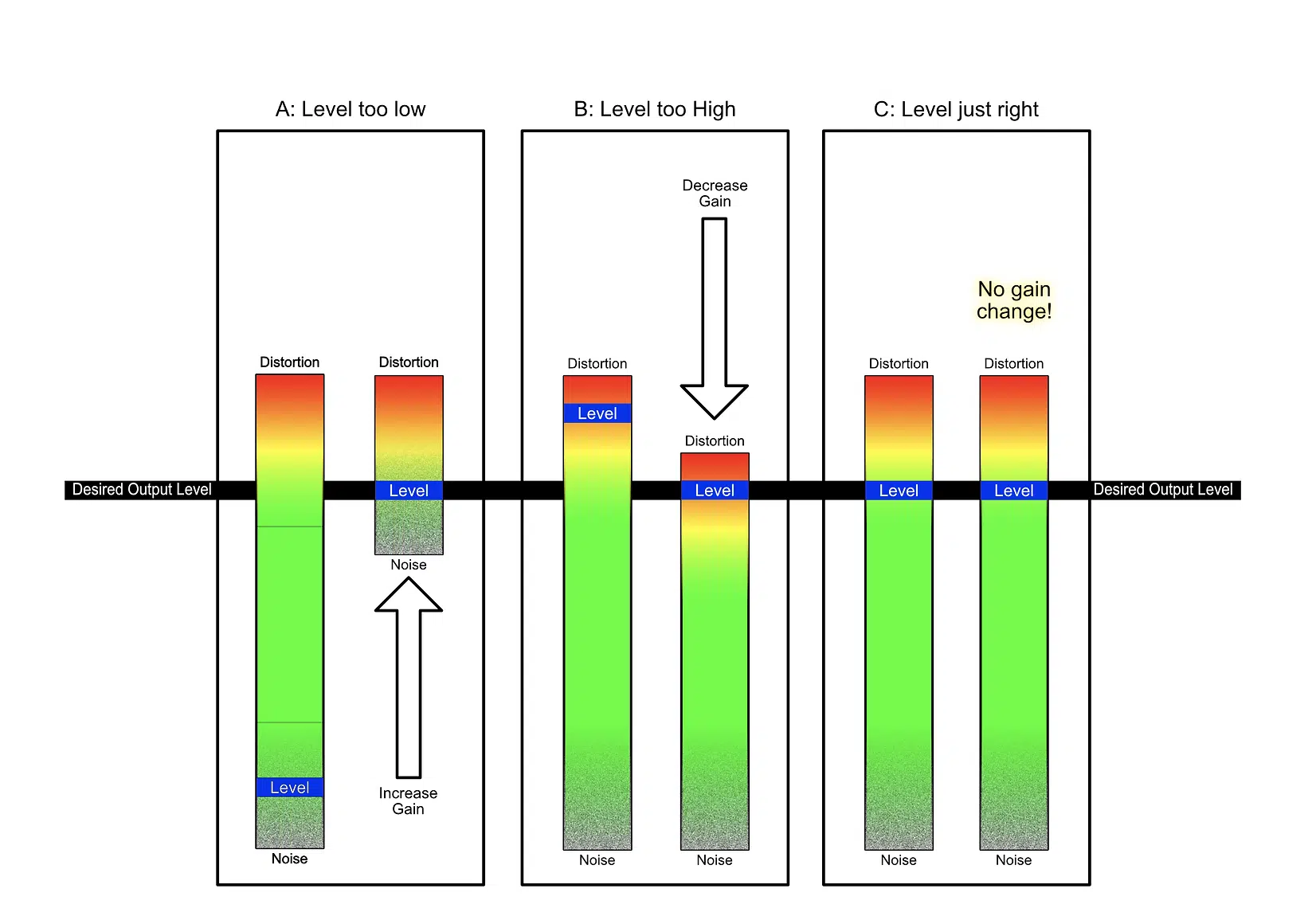
1. Gain staging
The process of setting the levels of each element in a mix to optimize the signal-to-noise ratio and avoid clipping or distortion.
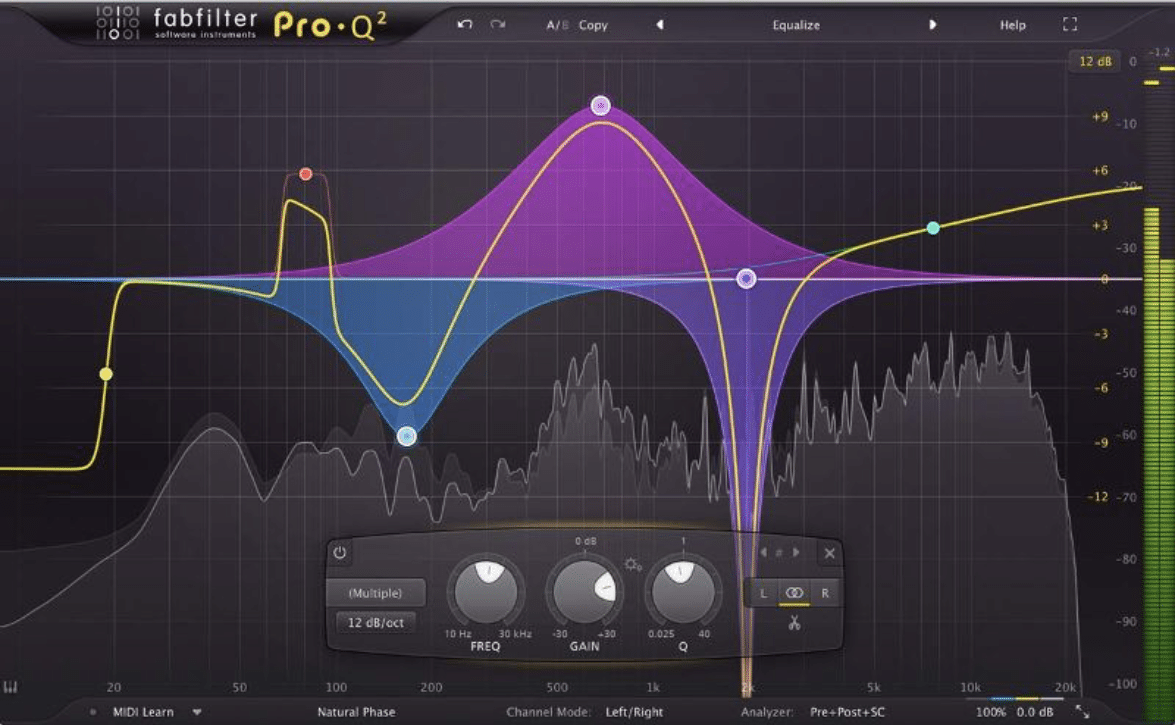
2. Equalization
A tool used to adjust the frequency balance of a sound, allowing for boosting or cutting specific frequencies to shape the tone of an instrument or mix.
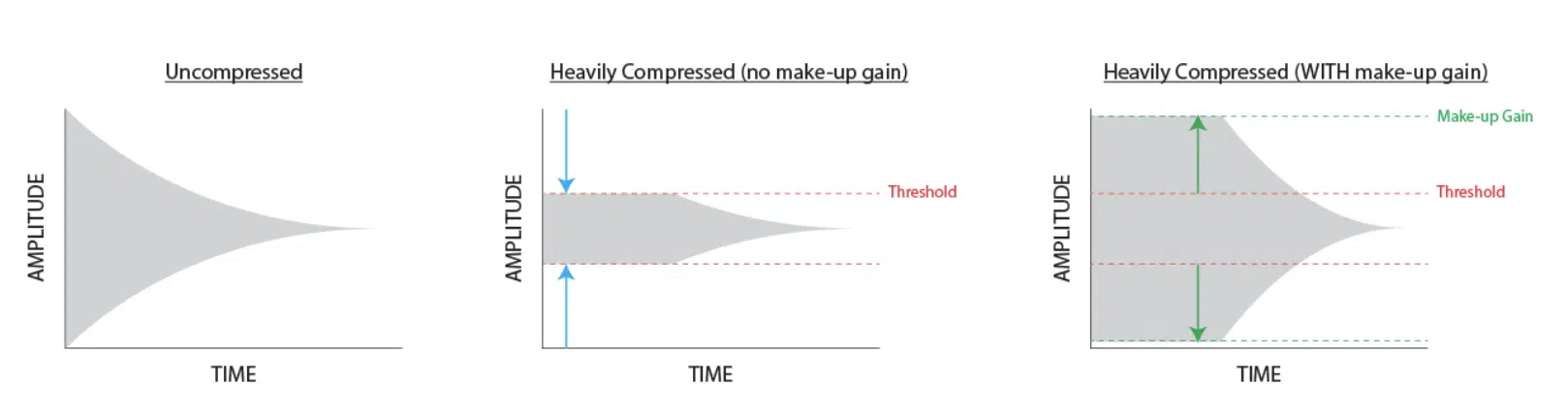
3. Compression
A dynamic processing tool used to reduce the dynamic range of a sound or mix, making quieter elements louder and louder elements quieter.
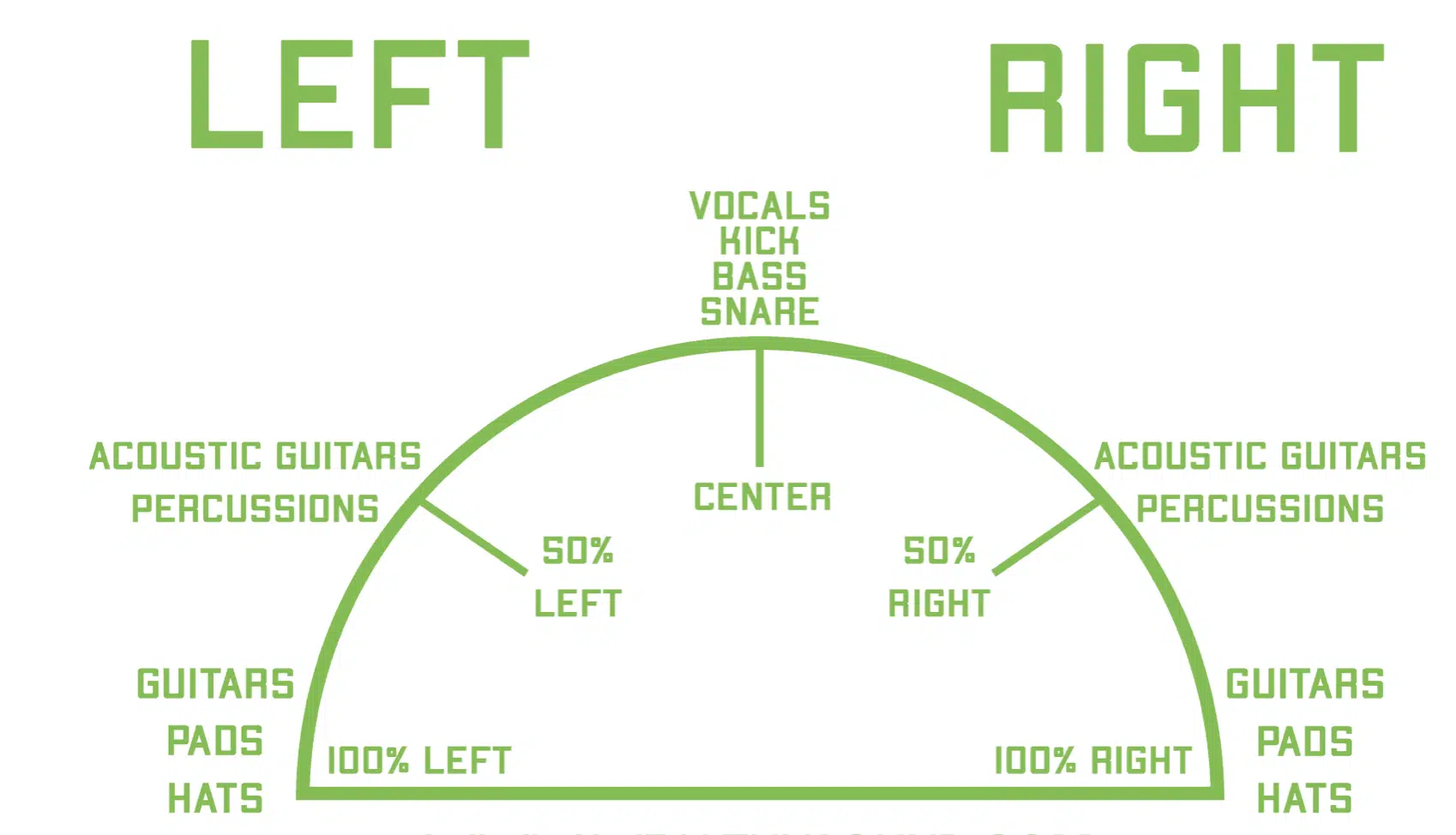
4. Panning
The placement of sounds in the stereo field; allowing for sounds to be positioned left, right, or center in a mix.
5. Reverb
An effect that is used to simulate the acoustic space of a particular environment, adding depth and dimension to sounds by creating a sense of space around them.
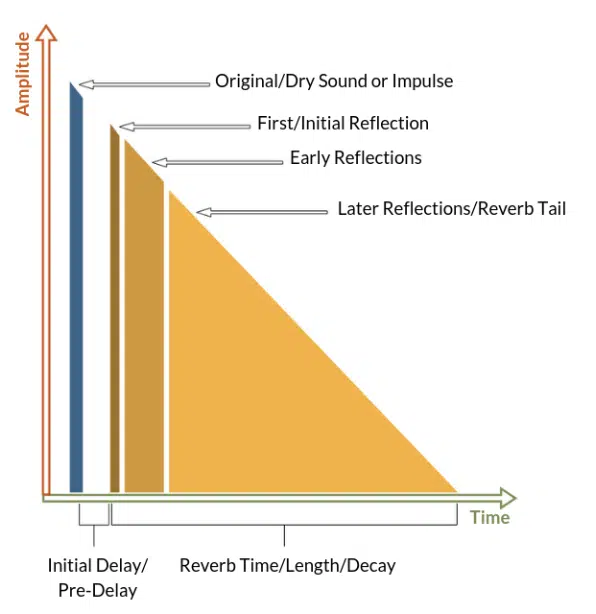
Familiarize yourself with the different types of audio processing tools and plugins available, such as EQs, compressors, limiters, and spatial effects.
It is an absolute must when you’re learning how to become a music producer.
Also, seek mentorship from experienced audio engineers and mixers to gain valuable insights and guidance.
You can find potential mentors through:
- Your professional network
- Online forums
- Social media platforms
- Reaching out to engineers whose work you admire
Observe their techniques, ask questions, and apply what you learn to your own projects.
Hands-on Practice and Experimentation
The key to mastering audio engineering and mixing is hands-on practice and experimentation.
Apply the techniques and concepts you’ve accrued to your own music projects, and don’t be afraid to make mistakes as you’re learning to become a music producer.
Make sure to set aside time to practice these concepts so you can quickly master them and feel more confident in your production skills.
Use reference tracks from professional artists and producers to compare your mixes and identify areas for improvement.
As you gain experience as a music producer, you’ll develop your own mixing workflow and unique sound that sets your music apart.
STEP 6: Find Your Niche As a Music Producer
In order to really shine as a music producer, you’ll need to find your unique lane.
That way, you won’t get looked over or drowned out in this saturated field.
To find your niche, you’ll need to identify:
- Your musical strengths ✓
- Your personal interests ✓
- Your passions ✓
- Your overall goal ✓
If you’re a little weary about where to start, just ask yourself the following questions:
- Am I drawn to a specific genre(s) or style(s)?
- Am I particularly good at a certain instrument/pattern?
- Do I excel in sound design or creating infectious hooks?
Understanding your strengths (and weaknesses) as a music producer can guide you toward a specialized area of music production that sets you apart from others.
A good tip would be to research the music industry landscape and identify niches with high demand and low competition.
Carving out a niche in an underserved area can help you stand out and increase your chances of success in a crowded market.
Building a Reputation Within Your Niche
Focus on building a reputation within your chosen niche by:
- Consistently producing high-quality music
- Engaging with the community
- Collaborating with other artists and producers in that space
As you become known for your unique music producer skills and style, you’ll attract more opportunities and increase your chances of success.
STEP 7: Develop Your Brand and Online Presence
Your personal brand is the unique combination of your skills, style, and personality as a music producer.
It should reflect who you are at your core, and emphasize your creativity and unique music style.
Start by:
- Choosing a production name/identity
- Defining your brand’s core values
- Harnessing your personal mission
- Identifying your target audience
Again, consider your musical strengths and interests as a music producer, and how you want to be perceived in the industry.
Designing a Cohesive Visual Identity
When learning how to become a music producer, it’s important to create a cohesive visual identity.

This can include:
- Your logo
- Color schemes
- Typography
Consistency in your visual identity across all platforms helps establish brand recognition and sets you apart from the competition.
Consider working with a graphic designer or using online tools like Canva or Adobe Creative Cloud to create professional-looking visual assets.
Building a Strong Online Presence
Establishing a strong online presence as a music producer by creating a professional website, social media profiles, and music streaming accounts is an absolute must.
The world is mostly digital now, so don’t expect to be noticed if no one can actually find you.
Use platforms like Squarespace, Wix, or WordPress to build your website, and set up profiles on SoundCloud, Spotify, and Apple Music for your music.
Consistently share your work, updates, and achievements across these platforms to maintain engagement and increase your visibility as a music producer.
Also, once you’ve established your identity, get some music business cards made up that contain all your social media platforms.
You can even incorporate a QR code for easy accessibility.
STEP 8: Create a Diverse Portfolio
A diverse music producer portfolio showcases your ability to work in various genres and styles.
It demonstrates your versatility to potential clients, recruiters, and collaborators.
This can open up more opportunities and help you appeal to a broader range of projects and clients.
Include examples of your best work, such as:
- Original compositions ✓
- Remixes ✓
- Collaborations ✓
- Production projects ✓
Make sure to include your very best work, as first impressions are everything for a music producer.
Organizing and Presenting Your Portfolio
Organize your portfolio by category, genre, or project type to make it easy for potential clients or collaborators to find relevant examples of your work.
Ensure your music producer portfolio is easy to navigate, visually appealing, and showcases your best work.
If not, you may lose a client just because they got frustrated and annoyed.
Make sure to update your portfolio regularly to reflect your growth and current skills as a music producer.
Also, actively promote your portfolio as a professional music producer by sharing it with your network, on social media, and in online music communities.
Attending industry events and conferences always looks good, so whenever possible you should be present.
Engage in online forums and groups to showcase your work and connect with potential clients, music producers, or collaborators.
STEP 9: Stay Up-to-Date
Staying informed about the latest music news, trends, and emerging technologies is super crucial when you’re learning how to become a music producer.
It helps you look committed and dedicated and can give you a leg up over the competition.
You can do this by subscribing to reputable music publications, blogs, and podcasts.
Examples include Billboard and Music Business Worldwide.
And, of course, our Unison blog which posts daily about relevant, beneficial topics can help you become a music producer in no time.
Staying current with industry developments can help you adapt to changes and identify new opportunities as a music producer.
Participate in Industry Events
Attend industry events, workshops, and conferences to learn about new trends, technologies, and best practices.
These events can also provide valuable networking opportunities and insights from industry professionals.
Examples of popular music industry events include the NAMM Show, AES Convention, and the Amsterdam Dance Event (ADE).
Join Professional Organizations
Consider joining professional organizations and music production programs to stay connected with the industry and access valuable resources, networking opportunities, and professional development programs.
It’ll help you learn how to become a music producer in many different ways, from many different sources.
A great place to start would be the Audio Engineering Society (AES) or the Music Producers Guild (MPG).
Many successful music producers first started out with these concepts, so don’t overlook them.
Also, participate in online forums, social media groups, and subreddits dedicated to music producers.
These communities can provide helpful tips, resources, and discussions on the latest industry developments.
As well as opportunities to connect with other music producers and share your work.
Examples of online communities include Gearslutz, KVR Audio, and the Reddit music production community.
Never be afraid to ask for feedback from recording engineers, an audio mixer, a vocal producer, or anyone you encounter in your music forums.
STEP 10: Understanding the Music Industry
In order to break into the music industry, you must first understand what it really is and how it’s recently changed.
This way, you won’t have unrealistic expectations, and you can successfully make your way in.
The industry has evolved significantly in recent years, with technological advancements and changes in consumer behavior playing a key role in this transformation.
Here are some notable developments that have shaped the contemporary music landscape:
Digital Streaming

The rise of digital streaming platforms like Spotify, Apple Music, and Tidal has led to a significant shift in how people consume music.
Physical sales have declined, and digital streaming has become the primary source of revenue for the industry.
This change has also affected how artists and music producers approach music production and promotion, with an increased focus on creating content tailored for streaming platforms.
Make sure to display your work on multiple audio channels, music licensing platforms, and music publishing platforms and learn their personal requirements before uploading.
A record label is no longer the staple of music production, so becoming prominent (or even “viral”) is super attainable.
Plus, you’ll have complete creative control and freedom, so in a way, it’s much better.
Social Media and Influencer Culture
Social media platforms like Instagram, TikTok, and YouTube have provided artists and future music producers with new avenues to promote their music and connect with fans.
Make sure you post your own tracks daily and put out good, intriguing, professional content.
You’ll want to showcase your production skills as much as possible, across as many platforms as you can.
Staying active is super important in today’s climate.
The influencer culture has also led to an increased emphasis on personal branding and image.
You can now successfully use social media to cultivate your unique brand identity.
Roles within the Music Industry
If the social media route isn’t really your thing, then you’ll need to fully understand different roles within the industry.
It will help you navigate the professional landscape as a music producer and identify potential collaborators and career opportunities.
Here’s why you should know each role and how you can initially get your foot in that world:
Music Producers 一 A music producer oversees the creative and technical aspects of music production.
Knowing this role helps you understand the skills required to become a music producer and allows you to collaborate effectively with other producers.
To get started, attend music production workshops and courses, and connect with established producers to learn from their experiences.
Sound Engineers 一 Sound engineers are responsible for capturing and manipulating audio for music, film, television, and other media.
Understanding this role enables you to work effectively with sound engineers during a recording session in recording studios and live performances.
To gain exposure to this field, consider interning (like many aspiring music producers do) or shadowing at a recording studio or live venue.
Audio Mixers 一 Audio mixers blend and balance the various elements of a music track to create a polished and cohesive sound.
Knowing this role allows you to communicate effectively with mix engineers during the mixing process.
To get started, attend music producer workshops or courses focused on audio mixing, and reach out to professional mix engineers for guidance and mentorship.
Mastering Engineers 一 Mastering engineers optimize the final mix of a song for distribution across different platforms.
Understanding this mastering role helps you ensure that your music is properly prepared for release.
To enter this world, consider taking courses on audio mastering or interning at a record label or recording studio.
Music Production Career Options
Once you’ve established your brand as a music producer and you’ve successfully learned how to become a music producer, it’s time to decide which path you’re going to take.
As a music producer, you can certainly go the social media route (as we discussed), but if you’re looking for something more stable, let’s check out a few options in the industry:
1. Record Producer
Record producers work closely with artists and bands to develop their sound, choose songs, and oversee the entire recording process.
To enter this career, consider:
- Working as an assistant producer
- Interning at a record label or recording studio
- Producing your own music to build your portfolio
Examples of famous record producers include Quincy Jones, Max Martin, and Rick Rubin.
2. Live Sound Engineer
Live sound engineers work at concerts, festivals, and other live events to ensure optimal sound quality for the audience and performers.
To enter this field, consider:
- Volunteering at local venues
- Interning with a touring sound engineer
- Enrolling in a live sound engineering course
They mix live sound, set up and operate PA systems, and troubleshoot audio issues.
3. Film & Video Game Composer 一 Film and game composers create original music and scores for movies, TV shows, video games, and other media.
To enter this field, consider:
- Studying composition and orchestration
- Developing your skills in various DAWs and virtual instruments
- Creating a demo reel showcasing your work
Examples of renowned film composers include Hans Zimmer, John Williams, and Ennio Morricone.
BONUS: Creating an Optimal Recording Environment At Home
An optimal recording environment (home studio) is key if you want to learn how to become a music producer.
Let’s be honest, it’s where you’re going to be spending the majority of your time, so it has to be up to your personal standards.
It helps you capture high-quality audio and create a comfortable workspace for your newfound music production process.
Consider the following factors when setting up your recording environment:
- Acoustic Treatment 一 Proper acoustic treatment can significantly improve the sound quality of your recordings.
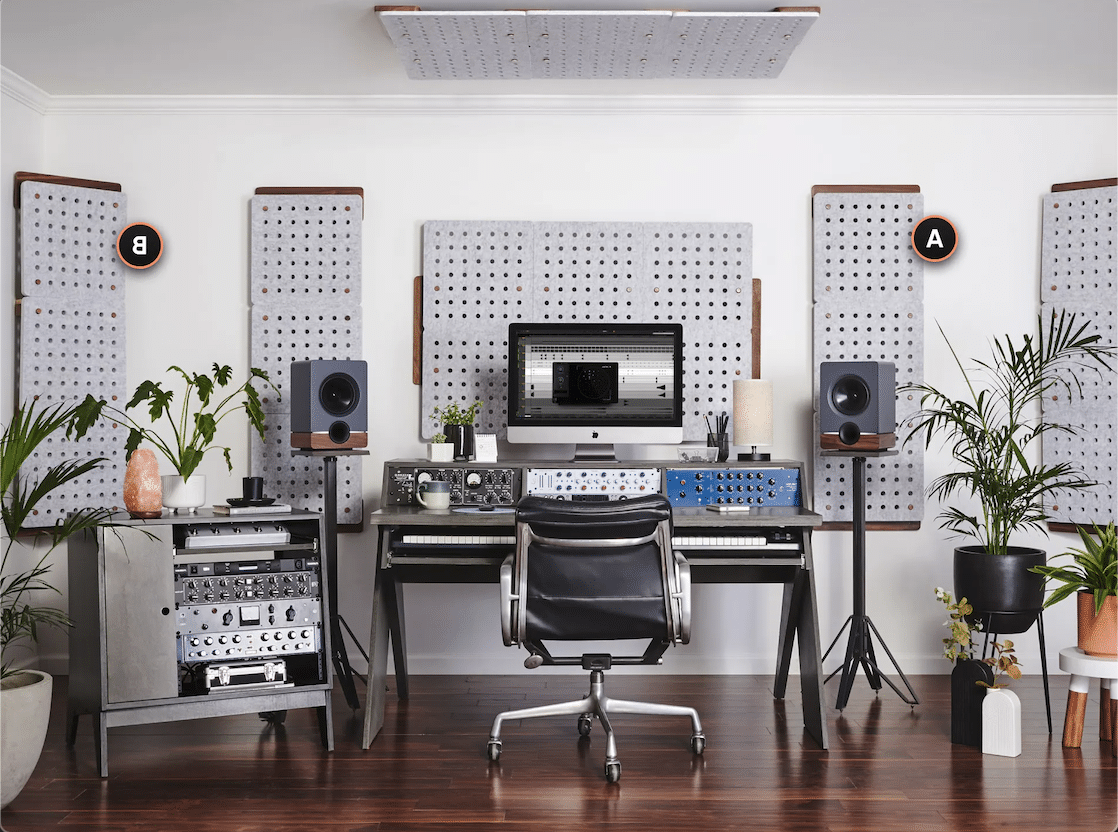

Use bass traps, acoustic panels, and diffusers to reduce unwanted reflections, standing waves, and room modes.
- Isolation 一 Soundproofing helps minimize external noise and prevents sound leakage between rooms.
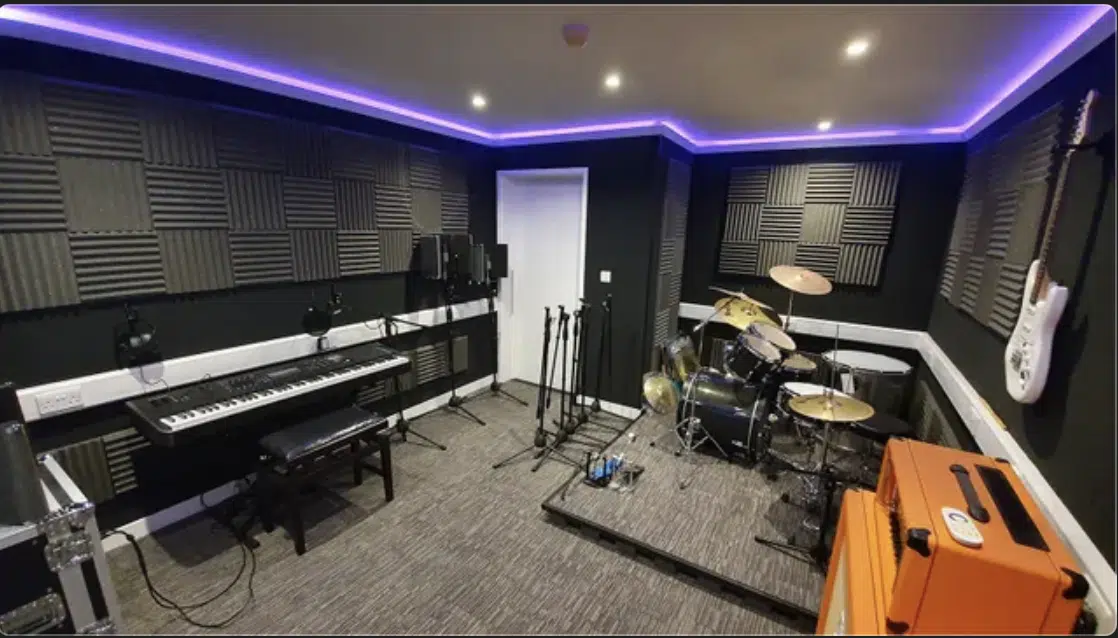

Use weatherstripping, door seals, and insulation materials to create a quieter and more controlled recording space.
- Ergonomics 一 Arrange your studio equipment and furniture in a way that promotes comfort, efficiency, and proper posture.
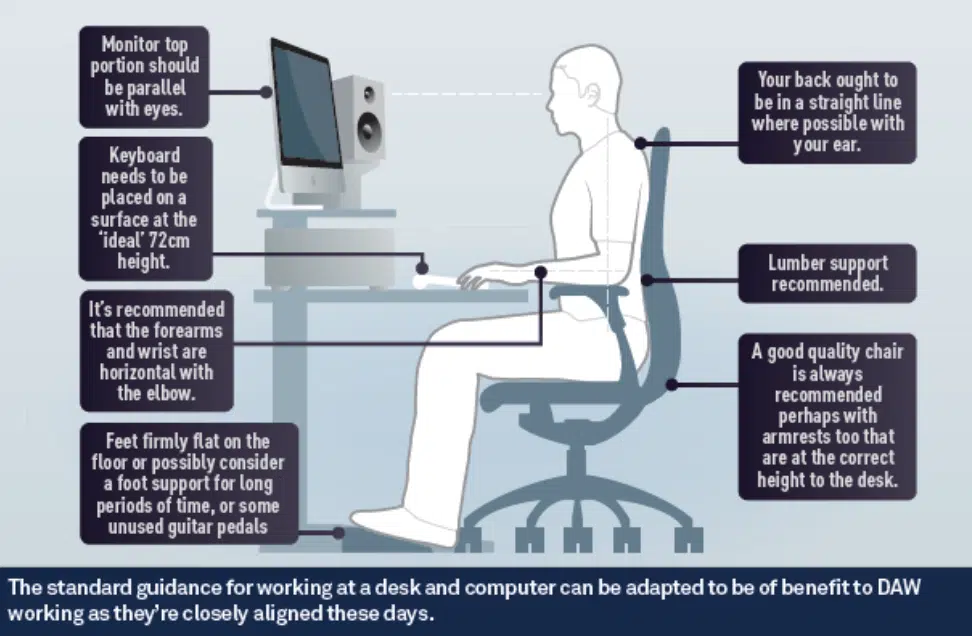
Position your monitors, computer, and MIDI controllers within easy reach, and invest in a comfortable and supportive chair.
- Lighting and Ambiance 一 Create a pleasant and inspiring atmosphere by choosing the right lighting and decorations for your studio.
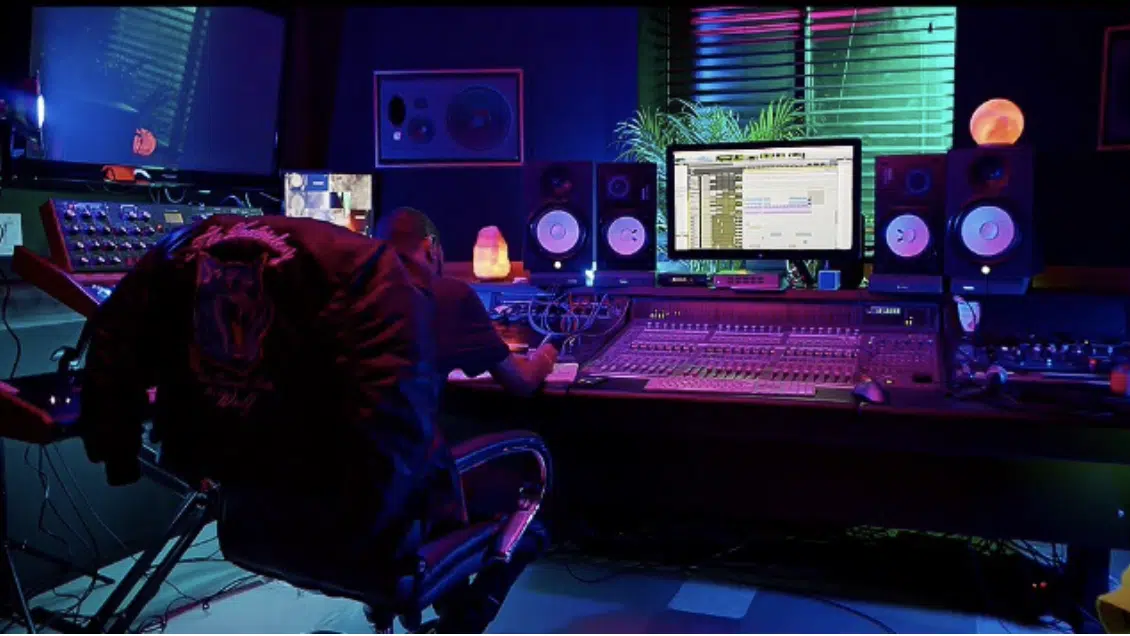

Opt for adjustable, non-glare lighting and consider adding plants, artwork, and other personal touches to make the space more inviting.
5 Secret Methods To Excel Your Production Process
When you’re learning how to become a music producer, it can feel like you’re a little fish in a big pond.
So, we’ve decided to let you in on 5 industry secrets that can help you excel as a music producer and do what you love.
#1: Enter Remix Competitions
Participate in online remix competitions to hone your music producer skills and gain exposure.
Many competitions offer prizes and opportunities to work with established artists or labels, helping you build your reputation in the industry.
This is a great opportunity to showcase your music producer skills, make contacts, and acquire potential jobs.
#2: Volunteer at Music Events
Volunteer at music events, festivals, and conferences to gain insider knowledge about how to produce music and network with professionals in the industry.
As a music producer, volunteering can also give you unique access to industry panels, workshops, and behind-the-scenes experiences.
You’ll have a chance to connect with people who have extensive experience working with artists, producers, and music legends.
#3: Listen to Unconventional Genres
Study and experiment with unconventional genres and styles of music to expand your creative horizons and develop unique production techniques.
This can help you stand out in the competitive music production landscape.
Musical genres are not so clear-cut anymore; a music producer can create their own hybrid at any time.
A music producer’s responsibilities are to find creative workarounds.
Who knows, you might create the next big one!
#4: Offer Free Services
It may sound a little counterproductive, but hear me out…
When you offer your music producer services for free or at a discounted rate, it can help you build your portfolio, network, and gain real-world experience.
Remember, the goal is to have your music circulating in as many different places as possible, you don’t need a music production degree to know that.
Collaborate with local artists, indie filmmakers, or nonprofit organizations to create music for their projects.
Anything to get your music out there is super beneficial.
#5: Capitalize on Emerging Platforms
Stay on the cutting edge of new music platforms and technologies (e.g., blockchain and VR/AR music experiences) to gain a competitive advantage in the industry.
Early adopters of emerging platforms often have increased visibility and access to new opportunities.
So, make sure to look online every day to get a jump on emerging trends, legal and business frameworks, technical aspects, and leisure and media industries.
Staying ahead will get you far, as the world is moving faster than ever.
How to Become a Music Producer: Final Thoughts
Now that you’ve explored the ins and outs of how to become a music producer, it’s time to take action and put your newfound knowledge into practice.
Remember, success in the industry doesn’t happen overnight; it takes dedication, hard work, and persistence.
Stay focused, keep learning, and never be afraid to take risks.
With passion, creativity, and the right strategies in place, you’re well on your way to becoming a professional music producer.
In order to begin your music production journey and really learn how to become a music producer, you’ll need to begin with the right template…
Luckily, we have the most accurate and organized structures of 2 beloved hit tracks (Jack Harlow’s “First Class,” and Pop Smoke’s “The Woo”) inside the FREE Unison Famous Beatmaker Template.
It’s an amazing place to start, as they are pro-level, fully accurate, polished to perfection templates.
You can use any sounds you want to tweak, customize, and truly make each template your own.
So, go forth and conquer the world of music production – the sky’s the limit!
Until next time…







Leave a Reply
You must belogged in to post a comment.