Have you ever wondered what makes a song irresistibly catchy, tapping into the very essence of what makes us move?
If so, you’ve come to the right place.
Today, we’re taking an in-depth look at the difference between rhythm and beat 一 two fundamental elements that breathe life into music and captivate our senses.
Though they may seem similar, understanding the nuances and the difference between rhythm and beat, can elevate your music production or performance to new heights.
So, let’s delve into the difference between rhythm and beat, and unlock the secrets to creating unforgettable, harmonious music.
Table of Contents
- What Is The Beat? Building Your Foundation
- Quarter Notes and Time Signatures
- Importance of the Beat in Music
- What is Rhythm? The Life of Your Song
- Rhythm Patterns & Timing
- Rhythm and Beat in Digital Music Production
- Tips To Create A Strong Rhythm and Beat
- The Difference Between Rhythm and Beat: Summing It Up
- Beat:
- Rhythm:
- Final Thoughts
What Is The Beat? Building Your Foundation
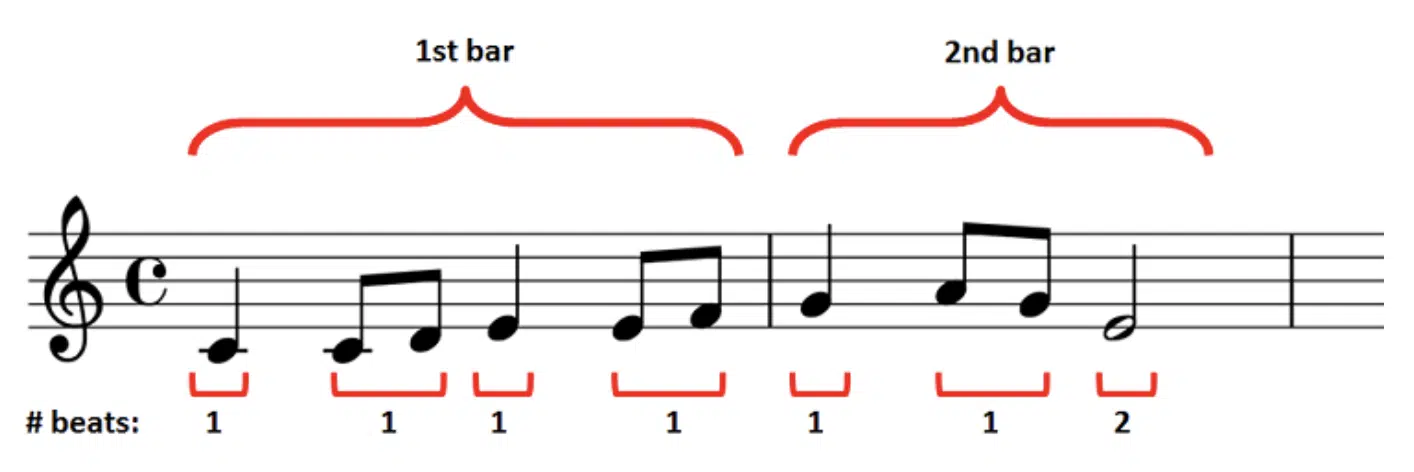
The beat is the heartbeat of your music, providing a steady pulse that drives the song forward.
It’s the constant, underlying element that gives structure and a sense of unity to the composition.
In most songs, the beat remains constant, acting as a reliable reference point for other musical elements to latch onto.
To feel the beat in a song, tap your foot or clap along — what you’re following is the beat, because the beat remains consistent.
When it comes to creating unique music, the beat serves as the foundation upon which other elements such as melody, harmony, and rhythm are built.
As a music producer, understanding how to establish and maintain a solid beat is essential for crafting a well-structured and engaging track.
Quarter Notes and Time Signatures
When we talk about beats, we often discuss them in terms of quarter notes, which are the basic units of measurement in music.
Each beat (or, steady pulse) typically corresponds to one quarter note, and a series of these notes form the framework for the song’s signature.

The time signature is a crucial aspect of music that indicates how many beats are in a measure and which note value gets the beat.
For instance, a 4/4 time signature means there are four beats in a measure, with each beat being a 1/4 note long.
Conversely, a 3/4 time signature has three beats per measure, each represented by a 1/4 note.
Understanding the role of quarter notes and time signatures in your music is essential for establishing a solid beat structure.
This way, it’s easier for listeners to follow along and for musicians to practice and play in time.
Importance of the Beat in Music

In music, the beat serves several critical functions, especially in drums and other percussive instruments.
These instruments often provide the rhythmic backbone of a song, helping to establish and maintain a steady tempo.
By playing with a consistent beat, musicians can ensure that their music flows smoothly, creating a sense of unity and coherence throughout the piece.
Maintaining a steady beat is also crucial for keeping other song elements—such as melody, harmony, tempo, and rhythm—in sync.
When all of these components align with the beat, the music becomes way more engaging and enjoyable.
What is Rhythm? The Life of Your Song
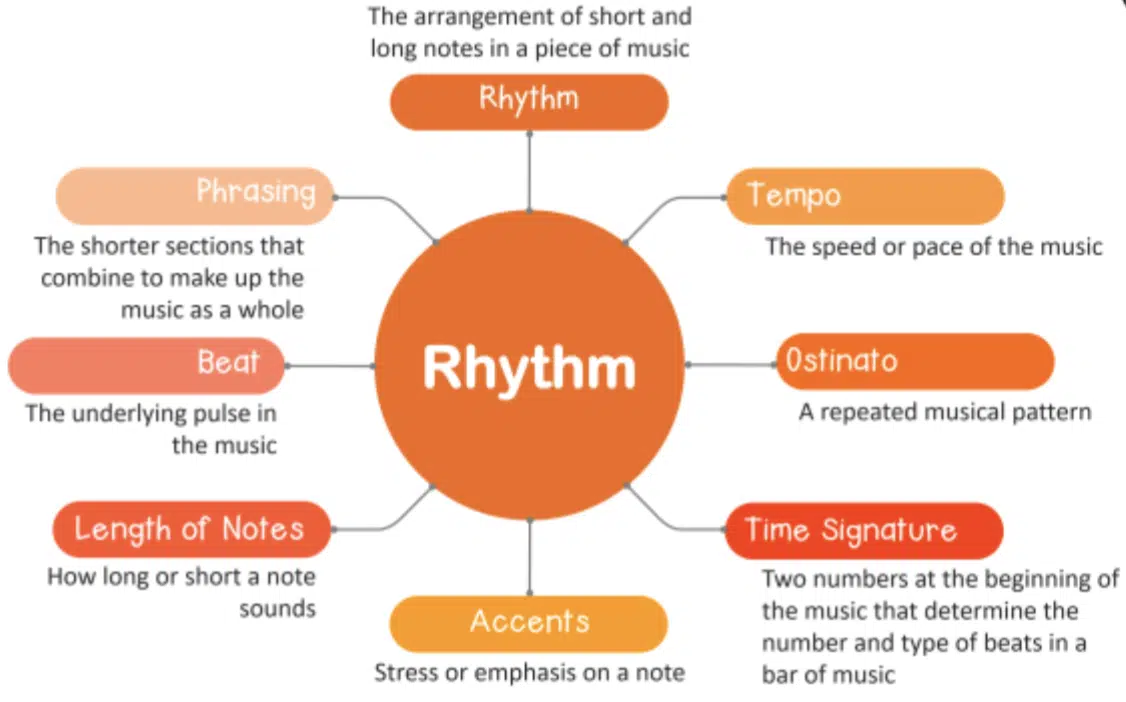
Rhythm refers to the pattern of sounds and silences in music, created by the arrangement and duration of musical notes.
Unlike the beat, which is steady and consistent, rhythm can vary throughout a song, providing interest and movement.
Rhythm is what brings a song to life, adding depth and character to the melody and harmony.
In Music Theory, rhythm is a complex concept that encompasses various elements of a song, including:
-
Note durations

The length of time a musical note is played or sustained.
In sheet music, note durations are represented by different music symbols, such as whole notes, half notes, quarter notes, and so on.
Each symbol indicates the relative length of the note compared to others, dictating the rhythm and flow of a piece of music.
-
Rests
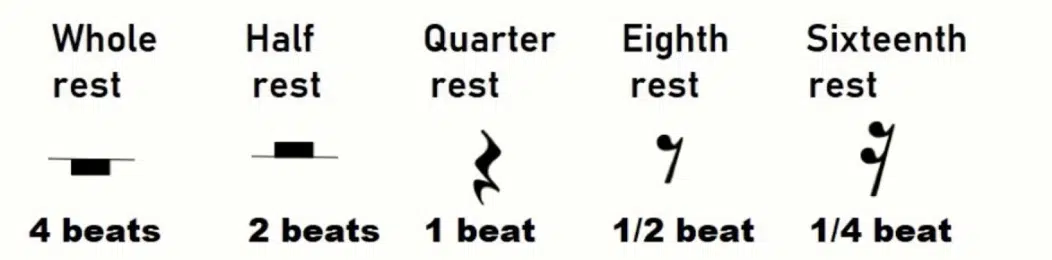
Rests are symbols used in sheet music to signify periods of silence or pause(s) in a piece.
Like note durations, rests come in different lengths, such as whole rests, half rests, quarter rests, and so on.
They play an essential role in creating the overall rhythm and structure of a musical composition, providing necessary breaks and spaces between notes.
-
Accents
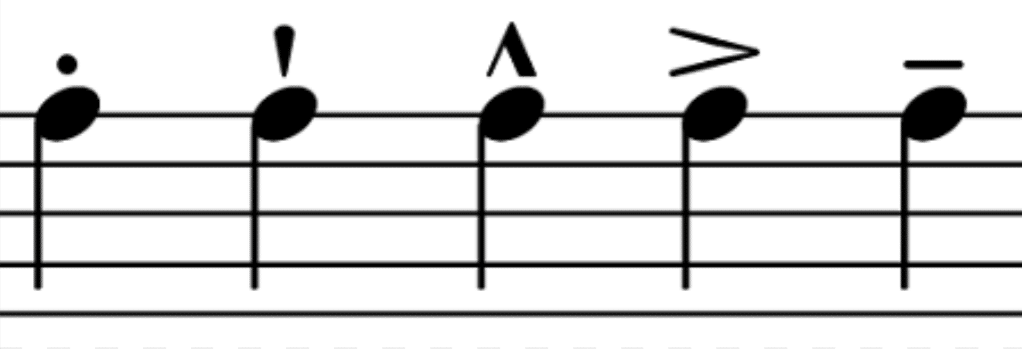
Marks added to musical notes indicate a stronger or more emphasized attack compared to surrounding notes.
They help shape the dynamics and expression of a piece, adding variety and interest to the rhythm.
Accents can generally be achieved through increased volume, a more forceful attack, or a combination of both.
-
Syncopation

A rhythmic technique in which notes are played off the main beats, or “on the offbeats.”
This creates an unexpected or surprising shift in the rhythmic pattern, adding complexity and intrigue to the music.
Harmonic or melodic elements also contribute to the overall feel of a musical piece, working together with rhythm to create a rich tapestry of sound.
When you play music on the piano or other instruments, these elements are intertwined.
So you might find yourself focusing on the 1st beat of each measure to anchor your performance.
By manipulating these elements, you can create intricate and engaging rhythmic patterns that make your music truly shine.
Rhythm Patterns & Timing
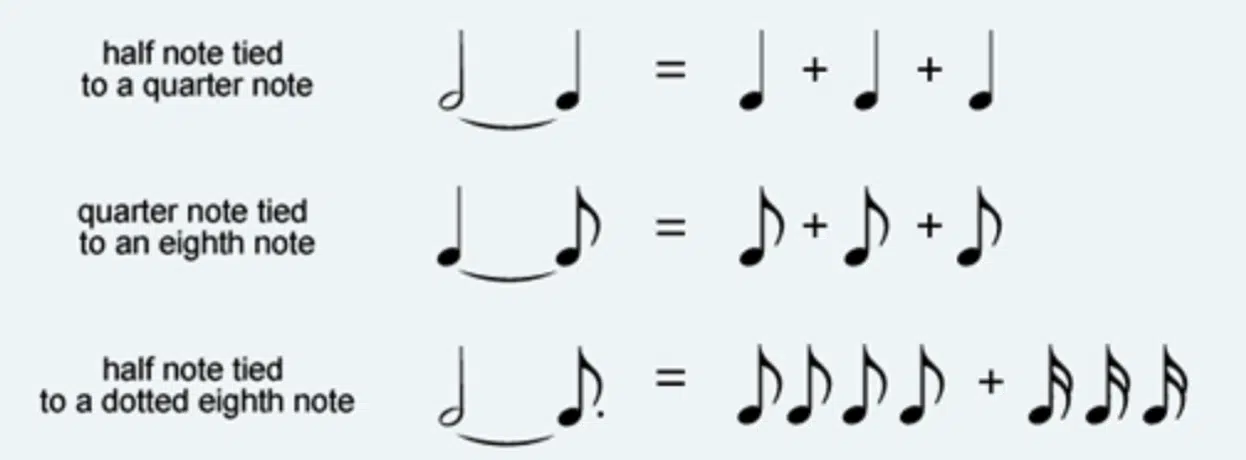
Rhythm patterns are the arrangements of notes and rests within a specific time frame, creating a unique and recognizable flow.
These patterns can be simple or complex, depending on the genre and the desired effect.
Timing, on the other hand, is the precise placement of these patterns within the song’s beat structure, ensuring that the rhythm aligns with the underlying pulse.
To create captivating rhythm patterns, you can experiment with various combinations of notes and rests.
Try adjusting their durations and placements to create a sense of movement and intrigue.
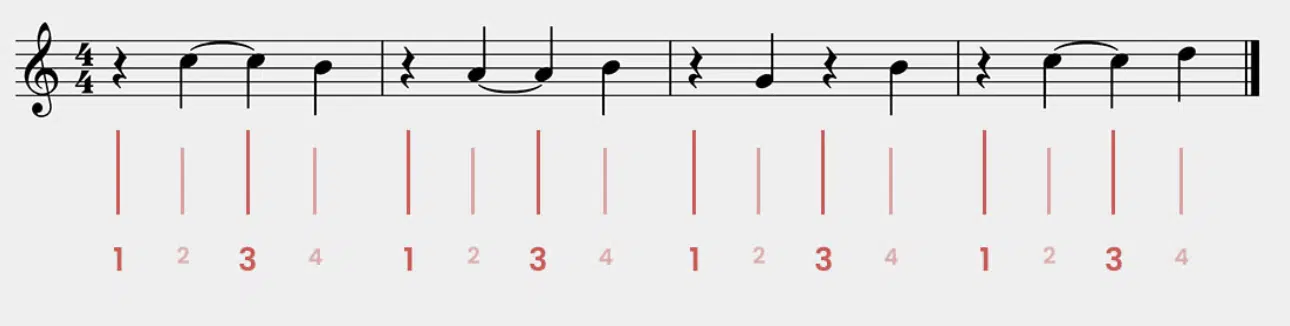
Syncopation can add an unexpected twist to a rhythm pattern, making it more engaging and dynamic.
Even simple nursery rhymes showcase different rhythmic patterns, with beats remaining consistent as the backbone of the melody.
For instance, when singing or playing a nursery rhyme, you may notice how the melody often emphasizes the first beat, while two notes of equal duration might be used to create a sense of forward motion.
Rhythm and Beat in Digital Music Production
In the realm of digital music production, technology plays a significant role in shaping and manipulating rhythm and beat.
With advanced software and hardware tools, you can experiment with a vast array of rhythmic possibilities, fine-tuning beats and patterns to create compelling, cutting-edge tracks.
These innovations have expanded the creative horizons and allowed us to push the boundaries of rhythm and beat in ways that were once unimaginable.
-
Drum Machines
Drum machines are electronic instruments that emulate the sound of drums and other percussion instruments.
They allow you to program beats and rhythm patterns, offering a vast array of customizable options, including tempo, time signature, and sound selection.
-
Digital Audio Workstations (DAWs)
DAWs are the central hub for digital music production, providing tools for recording, editing, and arranging both rhythmic and melodic elements.
Popular DAWs like Ableton Live and FL Studio offer built-in drum machines, samplers, and sequencers to help producers craft intricate rhythm and beat patterns.
-
MIDI Controllers
MIDI controllers enable you to manipulate virtual instruments and effects within your DAW.
By using devices such as drum pads, keyboards, or grid controllers, you can input and edit rhythmic elements with precision and ease.
Tips To Create A Strong Rhythm and Beat
- Start With A Solid Foundation: As with any musical endeavor, establishing a solid beat structure is crucial. Take advantage of your DAW’s built-in metronome and grid system to ensure that your rhythm patterns align with the underlying pulse of the song.
- Experiment With Sound Design: Don’t be afraid to explore unconventional samples, synths, and effects to create unique and captivating rhythm patterns.
- Quantization And Swing: DAWs often provide quantization tools that can help tighten up or loosen your rhythm patterns, depending on the desired feel. Experiment with swing settings to add a human touch or a distinctive groove to your beats.
- Layering And Arrangement: To create depth and interest in your digital music production, consider layering multiple rhythmic elements and sounds. This can help you build complex and engaging rhythm patterns that captivate listeners.
By embracing the more creative approaches and techniques, you can unlock new creative potential and take your understanding of rhythm and beat to exciting new heights.
The Difference Between Rhythm and Beat: Summing It Up

Before we wrap up, let’s take a moment to clearly outline the key differences between rhythm and beat.
This summary will help solidify your understanding of these essential musical concepts and serve as a quick reference for future music production endeavors.
Beat:
- The steady, consistent pulse of a song
- Provides the foundation for other musical elements
- Remains constant throughout a piece
- Often represented by quarter notes and determined by the time signature
Rhythm:
- The arrangement/duration of musical notes and rests that create patterns
- Adds movement, depth, and character to the music
- Can vary throughout a song, providing interest and dynamics
- Involves elements such as note durations, rests, accents, and syncopation
By understanding and recognizing the distinctions between both the beat and rhythm, you’ll be better equipped to create music that is both entrancing and harmonious.
You’ll also need to know them if you’re going to create captivating melodies, conquer music modes and basic types of chords.
Final Thoughts
As we’ve explored throughout this guide, the difference between rhythm and beat is a crucial concept for anyone involved in music production or performance.
By understanding and mastering these elements, you can create memorable, harmonious, and captivating music that resonates with your listeners.
A great way to hone your skills and develop a solid foundation in rhythm and beat is by utilizing resources like the Unison Essential MIDI Melodies.
This collection of 12 expertly crafted MIDI files can serve as an invaluable starting point for your musical creations, providing you with inspiring patterns and ideas to build upon.
Simply plug & play into your music, and manipulate it however you’d like.
Now that you have a deeper understanding of the difference between rhythm and beat, you’re well-equipped to experiment, innovate, and create musical masterpieces.
Until next time…






