As a music producer, you might have come across the term “sample rate” and wondered how it impacts your sound quality.
Well, it’s time to lift the veil and discover the true potential of sample rates in the realm of digital audio.
Welcome to your all-in-one guide, where we’ll explore everything you need to know about sample rates and their role in your music production journey.
This informative and engaging guide will take you through the fundamentals of sample rates, bit depths, and their interplay in shaping your digital audio recordings.
Regardless of your experience level, you’ll find valuable insights and professional tips, tricks, and techniques to help you make the right choices when it comes to sample rates in your projects.
So, prepare to enhance your music production expertise, elevate your sound to new heights, and unlock the key to achieving exceptional audio quality.
Let’s dive deep into the fascinating world of sample rates…
Table of Contents
- What Is a Sample Rate?
- How Digital Audio Works
- Common Sample Rates in Music Production
- Factors to Consider When Choosing a Sample Rate
- Bit Depth: Broken Down
- Sample Rates vs. Bit Depth
- The Human Hearing Range and Sample Rate
- Advanced Topics in Sample Rates
- Sampling Rate & Frequency Content
- Working With Higher Sample Rates
- Sample Rate Cheat Sheet
- The Future of Sample Rates & Audio Technology
- Conclusion
What Is a Sample Rate?
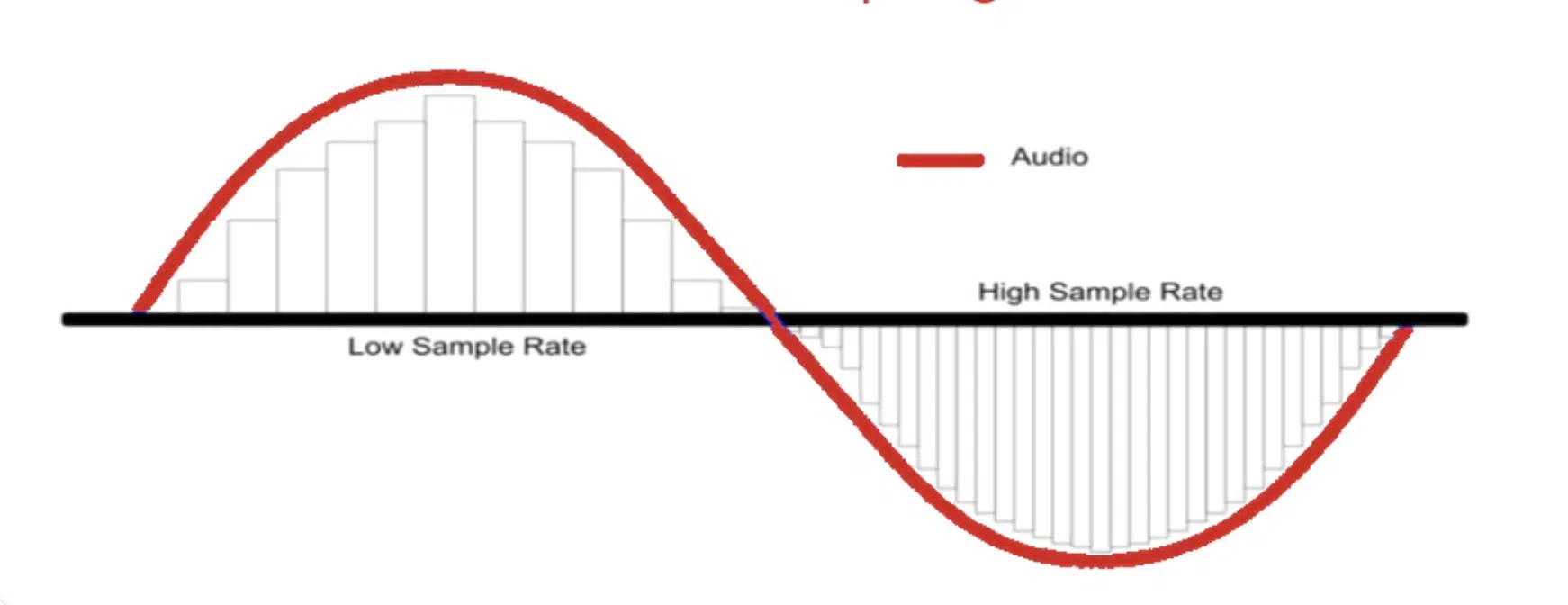
The sample rate, measured in Hertz (Hz), Kilohertz (kHz), or samples per second, refers to the number of times an audio signal is sampled in a given second.
In digital audio, sound waves are converted into a series of discrete data points, known as samples.
The sample rate determines the number of these samples taken per second, effectively capturing the original audio sound and turning it into a digital signal.
How Digital Audio Works
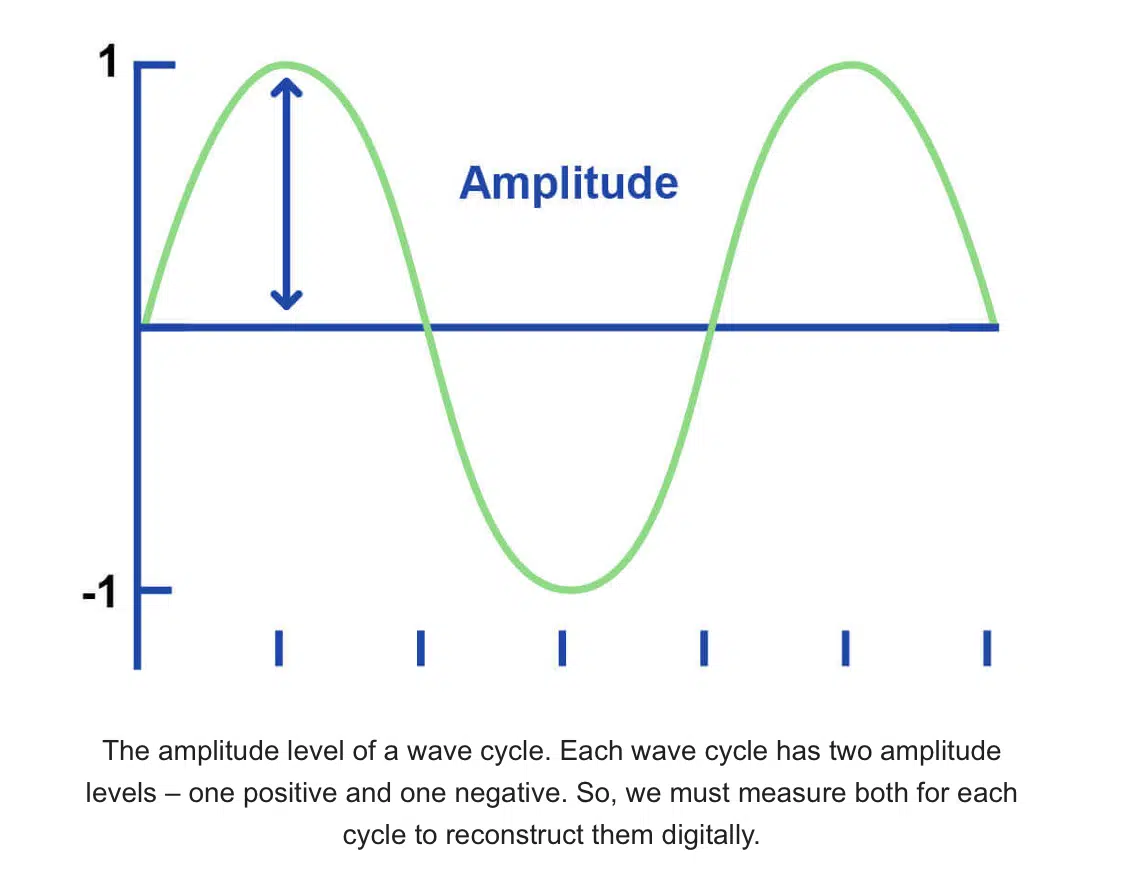
When we record an analog signal, such as sound waves, it’s continuous and smooth.
However, in digital audio, the continuous signal must be converted into a series of discrete values, representing the amplitude values of the sound wave at specific moments in time.
This process is known as digital conversion, and the resulting data points are the audio samples.
The higher the sample rate, the more samples are taken per second, resulting in a more accurate representation of the original audio sound.
The Relationship Between Sample Rate and Sound Quality
The sample rate plays a critical role in determining the audio quality of your digital recordings.
A higher sample rate captures more samples per second, resulting in a more accurate representation of the original sound wave.
However, higher sample rates also result in larger audio files and increased processing power requirements.
Therefore, striking the right balance between audio quality and practical considerations is essential.
Common Sample Rates in Music Production
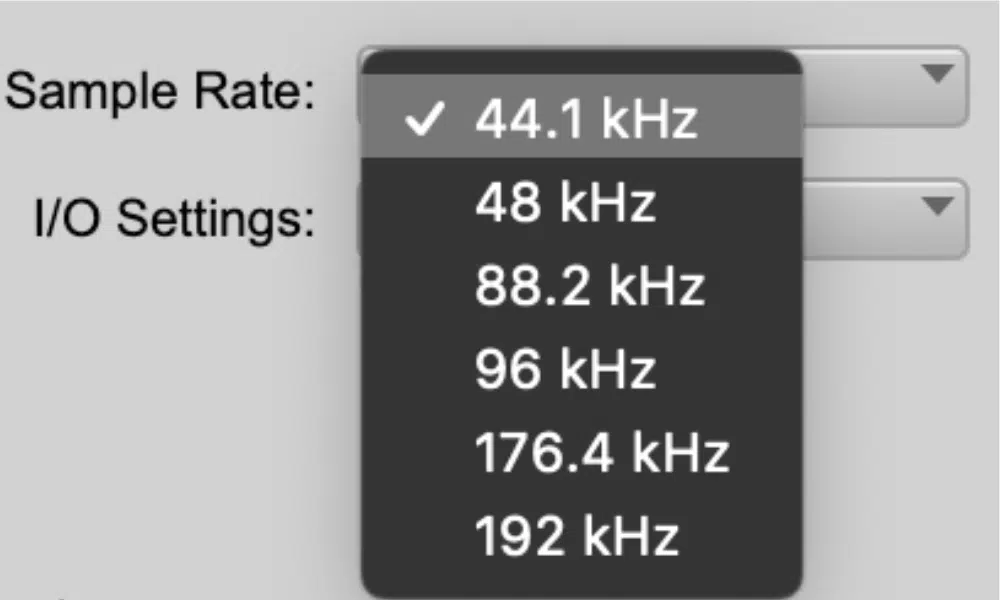
-
44.1 kHz
The 44.1 kHz sample rate is the standard for audio CDs and is widely used in music production.
It was chosen because it allows for the accurate representation of audio frequencies up to 22.05 kHz (half of the 44.1 kHz), which is just beyond the upper limit of human hearing.
Using the 44.1 kHz sample rate ensures that your audio files will sound great while keeping file sizes manageable.
-
48 kHz
The 48k Hz sample rate is commonly used for video and film production, as well as professional audio applications.
It offers a slightly higher frequency range than 44.1 kHz, allowing for the capture of frequencies up to 24 kHz.
While the difference in sound quality between 44.1 kHz and 48 kHz is generally considered “negligible,” some audio engineers prefer to work at 48 kHz for added flexibility in post-production.
-
88.2 kHz and 96 kHz
Higher sample rates, such as 88.2 kHz and 96 kHz, are often used in professional music production and mastering.
These sample rates capture a broader frequency spectrum, which can provide increased audio resolution.
However, using higher sample rates also results in larger file sizes and increased processing power requirements.
Some audio professionals argue that the improvements in sound quality at these sample rates are non-detectable, while others believe they provide a much more accurate representation of the original audio sound.
-
192 kHz
The 192 kHz sample rate represents the upper limit of commonly used sample rates in music production.
It offers exceptional audio resolution, capturing frequencies up to 96 kHz – well beyond the range of human hearing.
While some people may choose to work at this sample rate, the increased audio quality comes with significant trade-offs in terms of file size and processing power.
In most cases, you’ll find that lower sample rates, such as 44.1 kHz or 48 kHz, provide a more practical balance between quality of sound and resource requirements.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Sample Rate
Before you decide which sample rate you’d like to work with, there are a few different factors to consider, such as:
-
Audio Resolution
As discussed earlier, the sample rate directly affects the audio resolution of your digital recordings.
A higher sample rate captures more samples per second, resulting in a more accurate representation of the original sound wave.
When selecting a sample rate for your projects, consider the level of audio detail you require and whether the increased resolution provided by a higher sample rate is worth the trade-offs in file size & processing power.
-
File Size
Higher sample rates result in larger audio files, as more samples are captured per second.
This can quickly eat up storage space on your computer or hard drive, especially when working with multiple tracks and large projects, which, as we all know, is absolutely infuriating.
Before choosing a sample rate, consider the available storage space and the potential impact on your workflow.
-
Processing Power
Working with higher sample rates requires more processing power from your computer or DAW.
This can lead to increased CPU usage, which may result in slower performance or even crashes if your system isn’t up to the task.
Be sure to factor in your computer’s innate capabilities when selecting a sample rate.
-
End-Use and Compatibility
Another important factor to consider when choosing a sample rate is the intended end-use of your audio files.
If you’re producing music for streaming services, CDs, or other specific platforms, you’ll need to ensure that your chosen sample rate is compatible with those formats.
Additionally, collaborating with other producers may require you to work at a specific sample rate to ensure seamless file sharing and compatibility.
Be sure to thoroughly examine your situation before proceeding with a sample rate.
Bit Depth: Broken Down
Bit depth, another essential aspect of digital audio, refers to the number of bits used to represent the amplitude values of an audio sample.
In simpler terms, bit depth determines the dynamic range and accuracy of the digital representation of the original analog signal.
Bit depth plays a crucial role in determining the dynamic range and overall quality of your audio recording.
A higher bit depth captures more amplitude values per audio sample, allowing for a more accurate representation of the original sound wave, improved sound quality, and reduced noise.
This ultimately results in greater dynamic range, and provides a cleaner and more detailed signal.
Common Bit Depths in Music Production
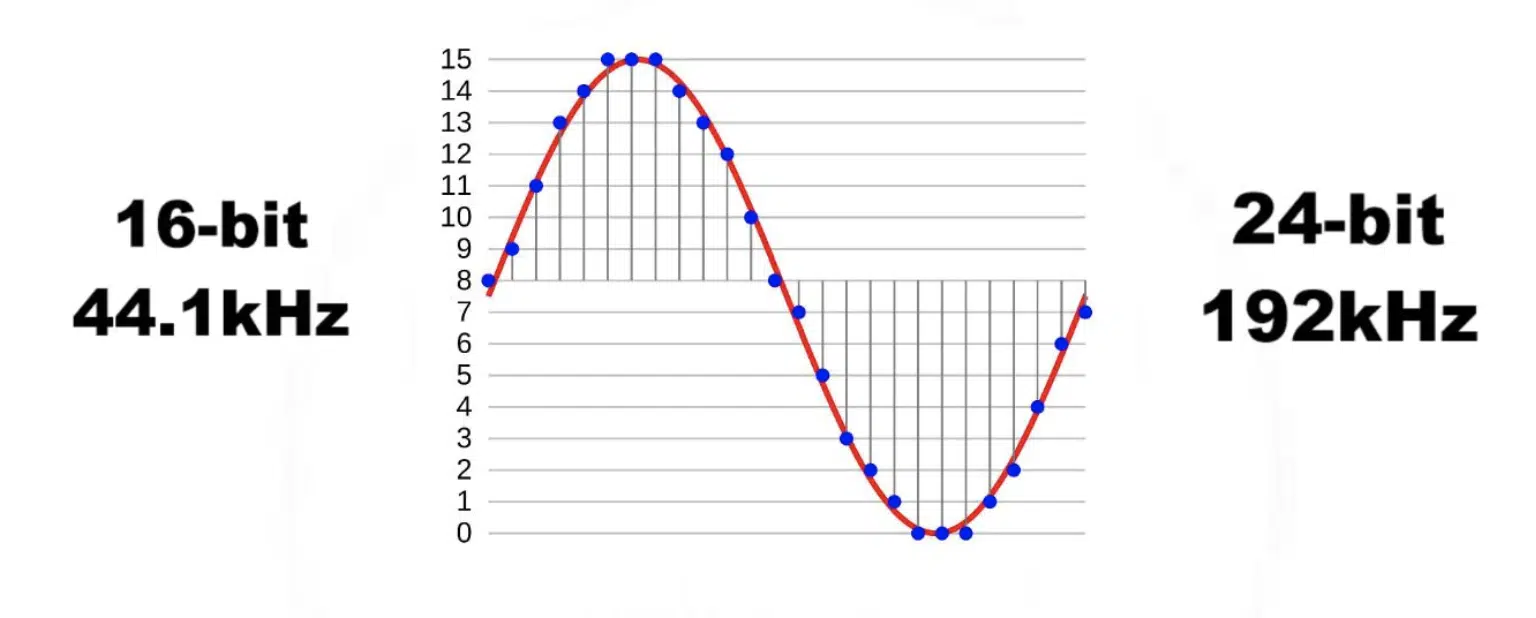
In music production, the most common bit depths are:
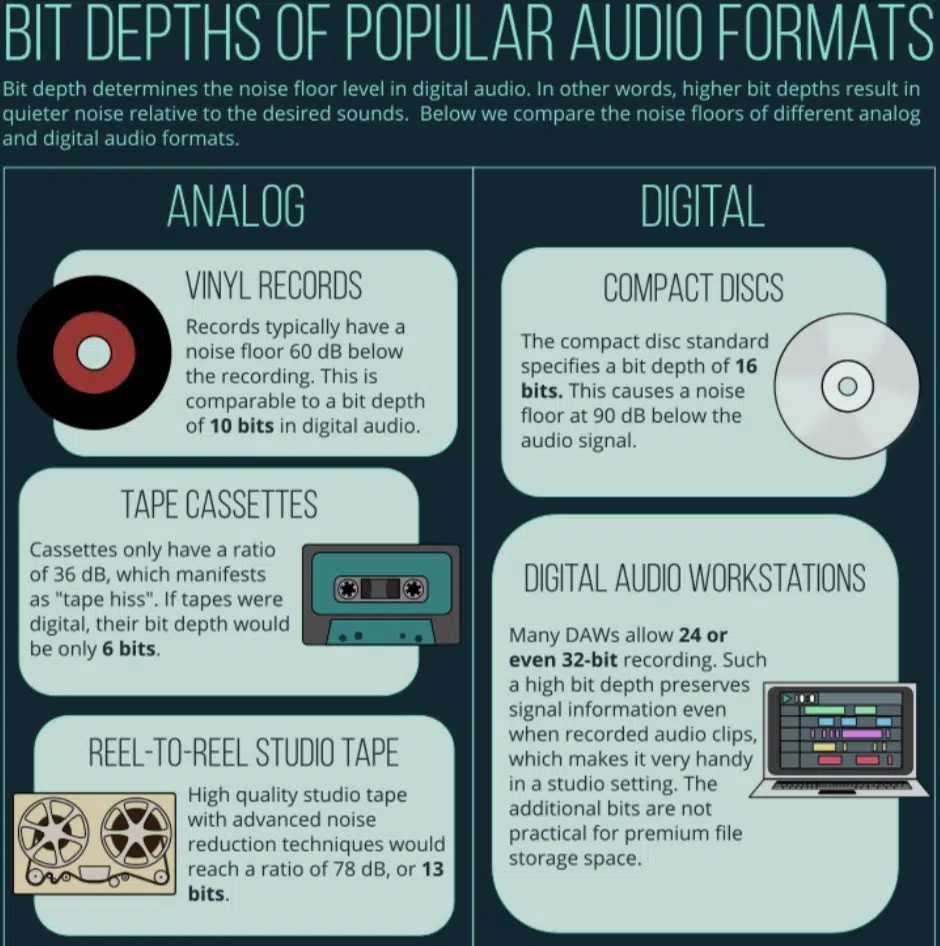
- 16-bit
- 24-bit
CDs use 16-bit audio, which offers a dynamic range of 96dB. This is sufficient for most consumer audio applications and provides good quality of sound.
However, many professional music producers prefer working with 24-bit audio, which offers a dynamic range of 144dB.
The increased dynamic range provided by 24-bit audio allows for more accurate audio capture, and produces cleaner recordings with less noise.
Additionally, working at 24-bit can provide more headroom during the mixing and mastering process, giving you greater flexibility to manipulate audio levels without introducing noise or distortion.
Sample Rates vs. Bit Depth
While both sample rate and bit depth play crucial roles in digital audio, they serve very different functions.
- Sample Rate 一 Determines the number of samples captured per second, affecting the frequency range and overall fidelity of the digital representation of the original sound wave.
- Bit Depth 一 Determines the accuracy of the amplitude values for each audio sample, impacting the dynamic range and noise levels of the digital audio signal.
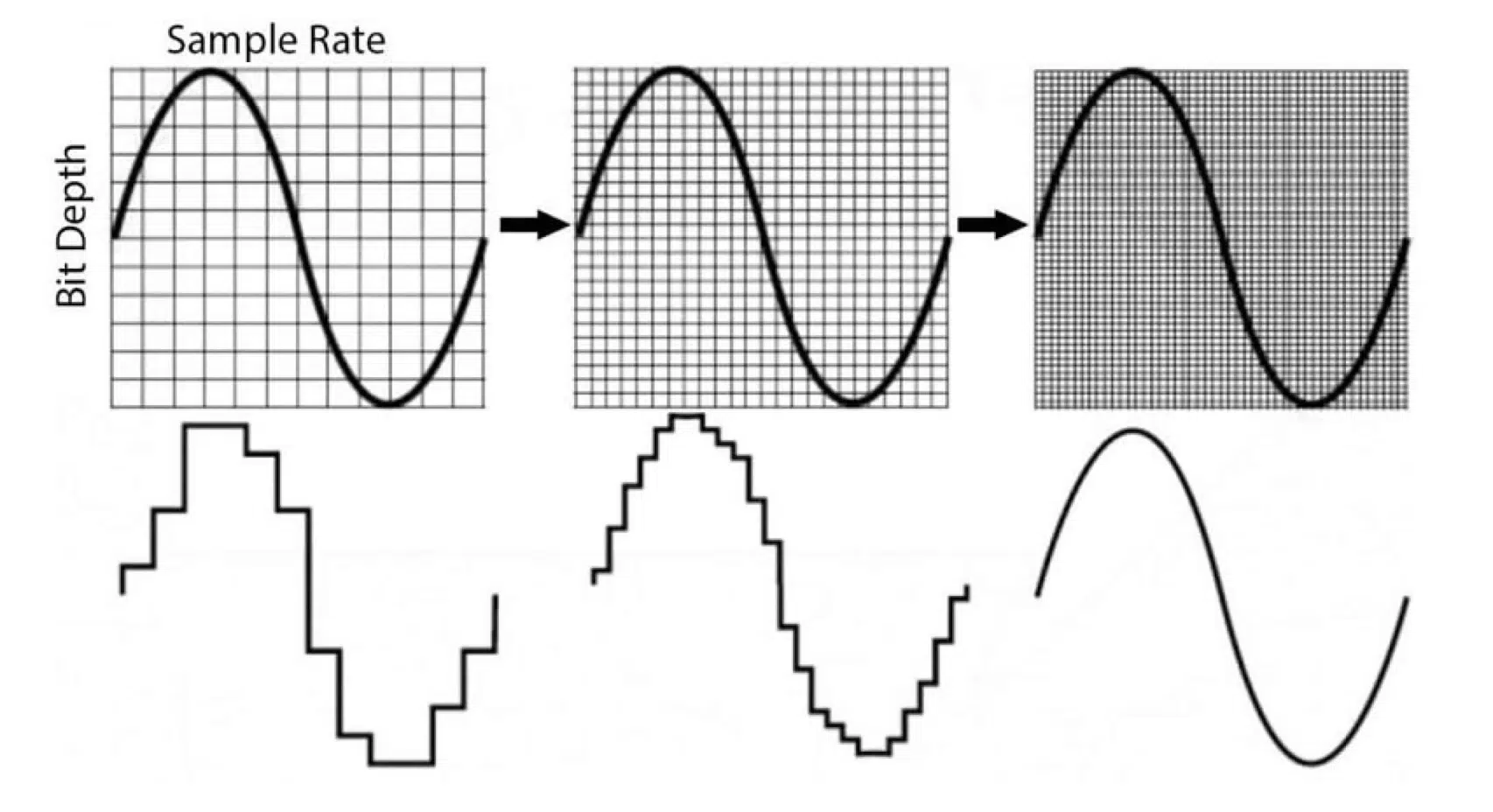
Selecting the optimal combination of sample rate and bit depth for your unique projects depends on several factors, such as:
- The desired sound quality
- Available storage space
- Processing power
- End-use compatibility
Oftentimes, working with a sample rate of 44.1 kHz or 48 kHz and a bit depth of 24 bits will provide a good balance between quality and practical considerations.
However, it’s essential to experiment with different sample rates and bit depths to determine which combination best suits your specific needs and workflow.
Producer Tips on Sample Rates & Bit Depth
1. When starting a new project, establish a consistent sample rate and bit depth to ensure compatibility and seamless file sharing with collaborators.
2. If your project requires significant processing, such as time-stretching or pitch-shifting, working at a higher sample rate may provide better audio quality and reduced artifacts.
3. When exporting your final mix or master, consider the intended end-use and format requirements, such as streaming services, CD quality audio, or vinyl, to ensure compatibility.
4. Always backup your project files and regularly save multiple versions, especially when working with large file sizes or high sample rates and bit depths.
The Human Hearing Range and Sample Rate
Human hearing typically ranges from 20Hz to 20kHz, with the upper limit decreasing as we age.
When selecting a rate for your music production projects, it’s important to consider the capabilities of the human auditory system.
This way, you can ensure that your files provide an accurate and enjoyable listening experience.
The Nyquist Frequency

The Nyquist Frequency is a fundamental concept in digital audio that states: the highest frequency that can be accurately represented in a digital signal is half the sample rate.
For example, a 44.1kHz sample rate can accurately represent frequencies up to 22.05kHz (half of 44.1kHz).
This is important because it helps determine the optimal sample rate for capturing the full range of human hearing while minimizing aliasing and other digital artifacts.
Choosing an Optimal Sample Rate Based on Human Hearing
Considering the limits of human hearing and the Nyquist Frequency, a rate of 44.1kHz or 48kHz is generally sufficient for capturing the full frequency spectrum.
Higher sample rates 一 such as 88.2kHz, 96kHz, or 192kHz 一 may provide additional benefits in specific situations, such as when processing audio or working on high-resolution projects.
However, for most music production applications, the increased file size and processing requirements of these higher sample rates often outweigh the perceived improvements in sound.
Advanced Topics in Sample Rates
Now that you have a firm understanding of Samples Rates, let’s dive into some more advanced topics.
Your audio interface plays a crucial role in determining the quality of your digital audio recordings.
High-quality audio interfaces will provide better digital conversion, ensuring that the analog signal is accurately captured and represented in the digital domain.
When choosing an audio interface, be sure to consider its supported sample rates and bit depths, as well as the quality of its analog-to-digital (A/D) and digital-to-analog (D/A) converters.
This will help ensure that your interface is capable of delivering the quality you need, otherwise you could run into some frustrating circumstances.
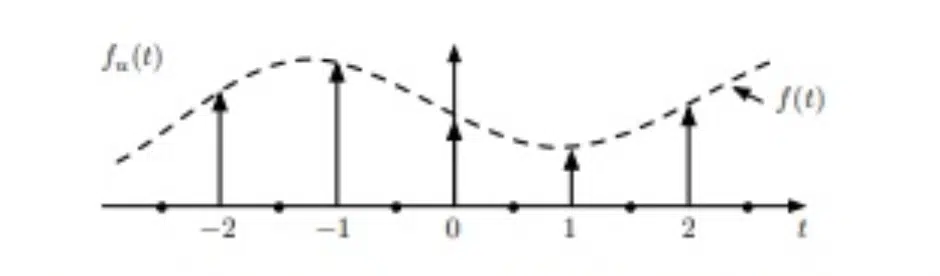
Upsampling & Downsampling
Upsampling and downsampling are processes used to convert audio files between different sample rates.
- Upsampling 一 Involves increasing the sample rate.
- Downsampling 一 Reduces the sample rate.
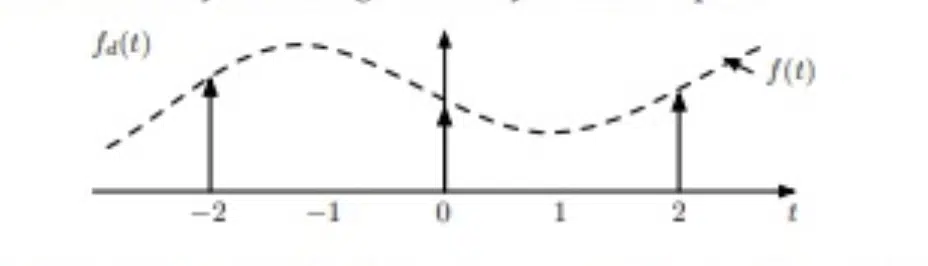
These processes can be useful for various purposes, such as preparing files for different formats or working with files recorded at different sample rates.
However, it’s essential to be aware that upsampling and downsampling can introduce artifacts and degrade audio quality if not performed correctly.
To minimize potential issues always use a high-quality software or hardware tools for sample rate conversion and avoid unnecessary up- or down-sampling whenever possible.
Dithering
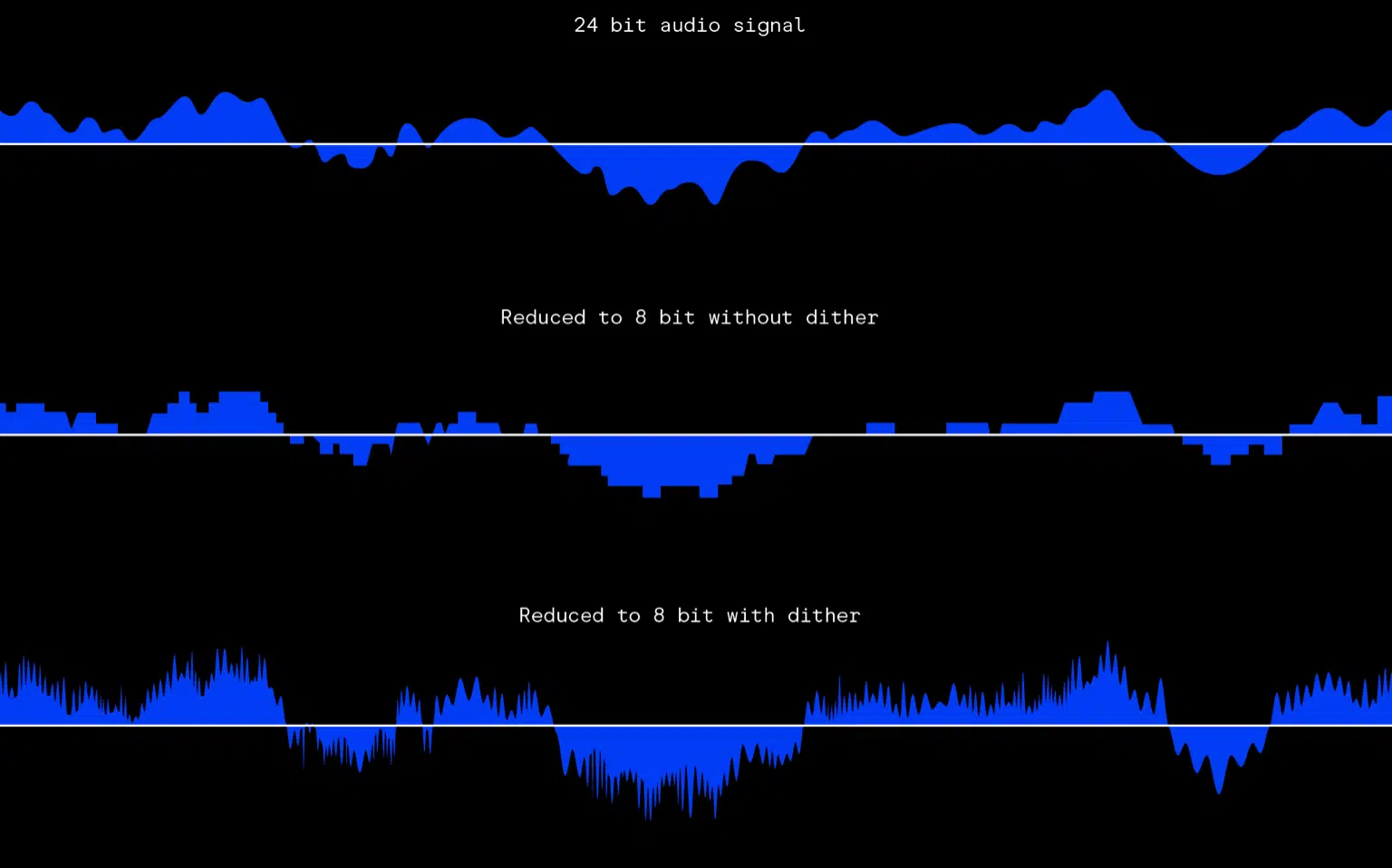
Dithering is a technique used when reducing the bit depth of an audio file, typically during the final stages of mastering.
By adding a small amount of noise to the signal, dithering helps mask quantization errors and reduce distortion caused by truncating the least significant bits of the audio data.
Although dithering might seem counterintuitive, it actually improves the perceived quality of sound by making the transition between different amplitude values smoother and more natural-sounding.
When working with high-resolution audio, such as 24-bit files, dithering is an important step to consider before exporting your final mix or master at a lower bit depth.
5 Pro Tips for Working with Sample Rates
- Establish a consistent sample rate and bit depth for your projects to ensure compatibility with collaborators and audio equipment.
- Experiment with different sample rates and bit depths to find the best combination for your specific needs and workflow.
- Consider the intended end-use and format requirements for your files when choosing a sample rate and bit depth.
- When processing audio, be aware that certain processes, such as time-stretching and pitch-shifting, may benefit from working at higher sample rates.
- Backup your project files regularly and save multiple versions, especially when working with large file sizes or high sample rates and bit depths.
Sampling Rate & Frequency Content
The term “sampling rate” refers to the number of audio samples captured per second during the digital audio conversion process…
But how does this relate to the frequency content of the audio signal?
The answer lies in the Nyquist-Shannon Sampling Theorem, which states that a signal must be sampled at a rate that is at least twice the highest frequency component to be accurately represented in the digital domain.
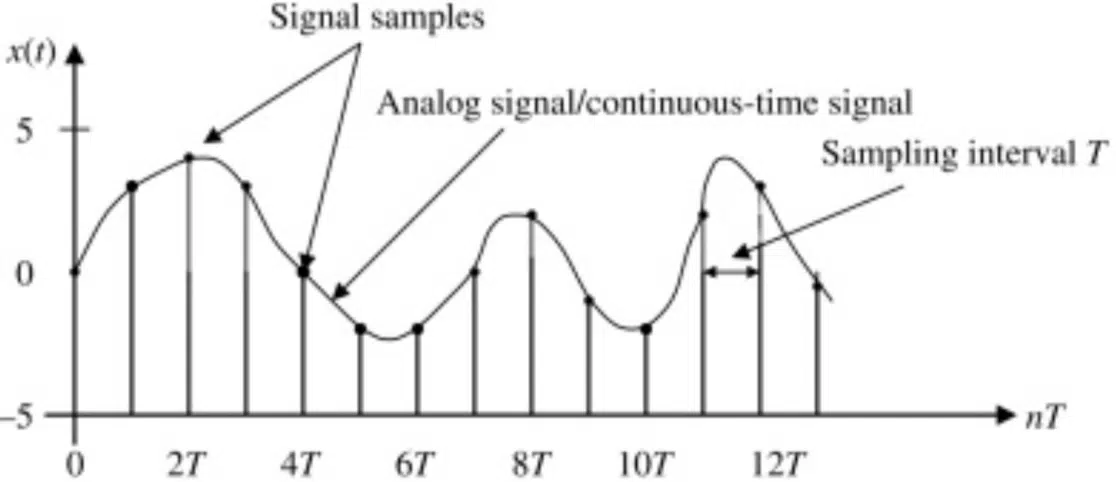
This means that the higher the sampling rate, the greater the frequency range that can be captured and reproduced.
Optimal Sampling Rate for Various Applications
When it comes to choosing an optimal sampling rate for your projects, it’s essential to consider your specific needs and the intended end-use of your files.
For example, CD audio uses a sampling rate of 44.1kHz, while most video and film productions use a sampling rate of 48kHz.
If you’re working on a project intended for high-resolution audio formats, you may want to consider using a higher sampling rate, such as 96kHz or 192kHz, to capture and preserve the most detail and sampling frequency content.
The Trade-Offs of Higher Sampling Rates
While higher sampling rates can provide increased audio resolution and frequency range, it’s important to be aware of the trade-offs involved.
Higher sampling rates result in larger file sizes and increased demands on processing power. This can potentially slow down your workflow and put more strain on your computer’s resources.
Therefore, it’s essential to balance the benefits of a higher sampling rate with the practical considerations of your production environment and available resources.
The Importance of a Consistent Sampling Rate in Your Projects
Maintaining a consistent sampling rate throughout your tracks is crucial to avoid potential compatibility issues with other audio equipment, software, and collaborators.
By establishing a standard sampling rate for your projects, you’ll ensure that your files can be easily shared and played back across various platforms and devices.
Additionally, working with a consistent sampling rate can help minimize the need for upsampling or downsampling, which can sometimes introduce artifacts and degrade audio quality if not performed correctly.
Working With Higher Sample Rates
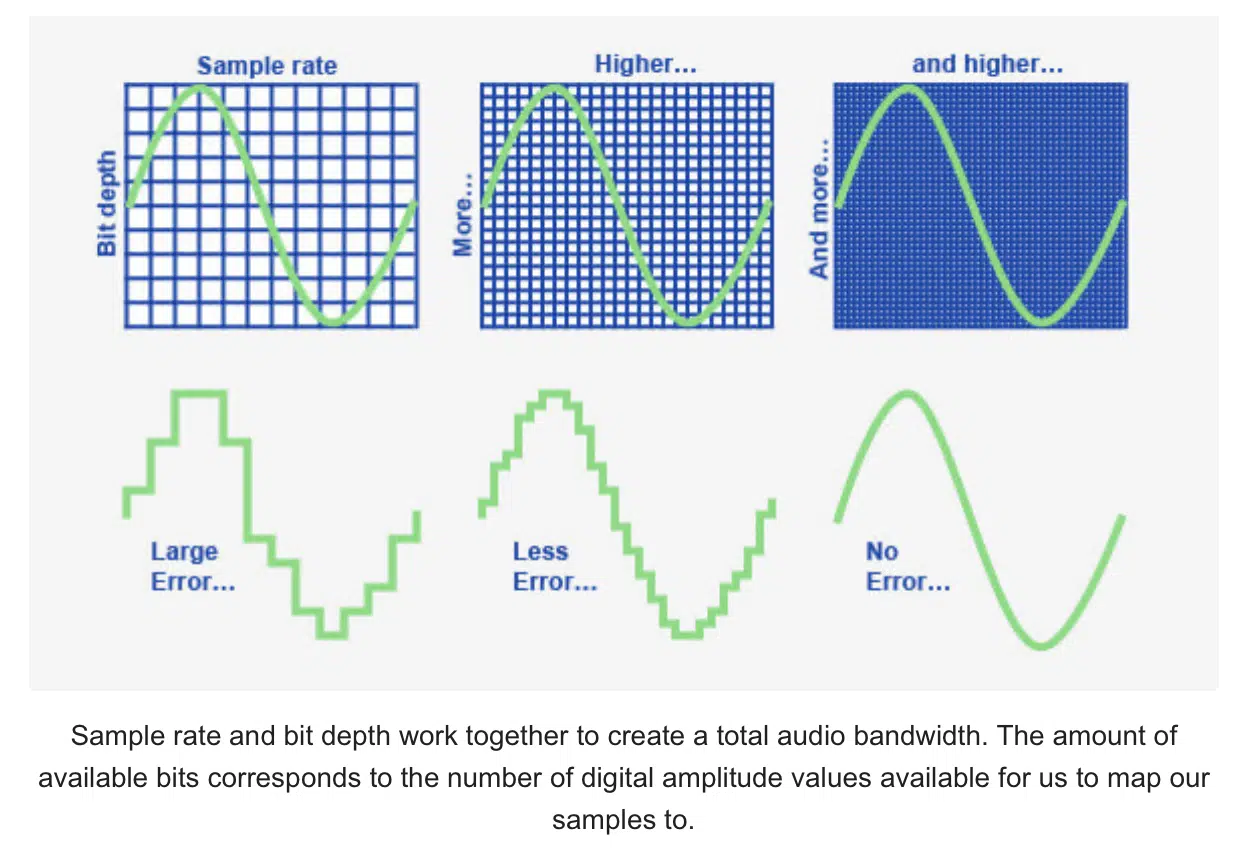
Working with higher sample rates can open up a new world of creative possibilities in sound design and audio effects processing.
The increased frequency range and audio resolution provided by higher sample rates can lead to more detailed and nuanced soundscapes.
This will allow you to push the boundaries of your productions.
-
Time-Stretching & Pitch-Shifting
As mentioned earlier, time-stretching and pitch-shifting can benefit from higher sample rates.
When working at a higher sample rate, the additional frequency content can help maintain the quality of the audio signal even when subjected to extreme time-stretching or pitch-shifting.
This can result in cleaner, more natural-sounding effects and provide you with more creative flexibility in your productions.
-
Granular Synthesis and Other Experimental Techniques
Higher sample rates can also be beneficial when working with experimental audio techniques such as granular synthesis.
Granular Synthesis involves breaking an audio signal into small ‘grains’ that can be manipulated individually.
The increased audio resolution offered by higher sample rates can provide a greater level of detail and control in the granular synthesis process.
This helps produce more intricate and complex sound textures.
3 Things To Remember When Working With Higher Sample Rates
- Don’t be afraid to experiment with higher sample rates in your sound design and audio effects processing, as it can lead to new creative possibilities and unique sounds.
- Be mindful of the increased processing power and file size requirements when working at higher sample rates and balance these factors with your desired sound quality and creative goals.
- Explore various audio effects and synthesis techniques to discover new ways to manipulate and process your audio at different sample rates.
Sample Rate Cheat Sheet

The Future of Sample Rates & Audio Technology
As digital audio technology continues to advance, we can expect to see new developments and improvements in sample rates, bit depth, and audio processing capabilities.
These advancements may lead to:
- Even higher sample rates
- Greater audio resolution
- More efficient processing algorithms
Ultimately, it can help expand the potential for music production greatness across the board.
The Role of AI and Machine-Learning
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are already playing a significant role in the music production landscape.
There are already advancements in algorithms that assist in tasks such as audio mixing, mastering, and sound design.
As these technologies continue to advance, we may see AI-driven tools that can automatically optimize sample rates and bit depths for specific applications.
Tips For Staying Ahead in an Evolving World
- Stay informed about advancements in digital audio technology, as new developments may impact the way you work with sample rates and audio processing.
- Embrace new tools and technologies that can enhance your music production capabilities, such as artificial intelligence-driven audio tools and immersive audio formats.
- Keep experimenting and pushing the boundaries of your audio production, as the constant evolution of audio technology offers endless opportunities for growth and creativity.
Conclusion
Understanding “sample rate” is an essential aspect of music production that directly impacts the sound quality of your digital audio recording.
By familiarizing yourself with the fundamentals of sample rate and its relationship with bit depth, you’ll be better equipped to make informed decisions that lead to better-sounding music.
Armed with this knowledge, you’ll be well on your way to producing high-quality music that stands out in today’s competitive industry.
If you want to skip this process altogether, you’ll need already pristine sounds, and luckily, we’ve got you covered.
Within our Unison Famous Beatmaker Drum Essentials you’ll find 19 professionally crafted, proven to work drum samples from the following hits:
- 21 Savage – Bank Account
- A$AP Rocky – Babushka Boi
- Big Sean, Post Malone – Wolves
- Kanye West – Father Stretch My Hands Pt. 1
- XXXTENTACION – SAD!
With these samples, created by world class sound designers, who certainly know about sample rates and bit depth, you’ll be able to make hits easier than you could ever imagine.
You’ll impress anybody who hears your tracks created with these sounds, and the best part is, it’s absolutely free! I know, mind-blowing, right?
Until next time…







Leave a Reply
You must belogged in to post a comment.