Chord voicings can transform a simple melody into a rich, harmonious tune and create different emotions in a track.
Plus, they can help add depth and texture to your music.
So, as a music producer, it’s important to know all about chord voicings to effectively communicate your musical ideas.
As well as enhance the emotional impact of your tracks and ensure your music blows the competition out of the water.
In today’s article, we’ll be breaking down:
- The fundamentals of chord voicings ✓
- How notes and octaves form voicings ✓
- The roles of different chord tones (+ chord tone tips) ✓
- Variations in chord voicings and their effects ✓
- The significance of voice leading ✓
- Breaking down chord inversions ✓
- The importance of root notes in your chord voicing ✓
- Major and minor chord structures ✓
- Techniques for extended chords ✓
- Advanced voice leading strategies ✓
- Crafting effective chord progressions ✓
- Utilizing octaves for diverse voicings ✓
By the end of this article, you’ll have a thorough understanding of chord voicings so you can create compelling, professional-sounding chords.
You’ll be equipped to manipulate chord voicings with confidence and creativity.
This way, your tracks will resonate with your audience and stand out in the competitive world of digital music production.
So, let’s dive in…
Table of Contents
- What are Chord Voicings?
- Components of Chord Voicings: Notes and Octaves
- Chord Tones and Their Roles
- Different Chord Voicings and Their Effects
- Voice Leading and Its Significance
- Chord Inversions: Breaking it Down
- The Role of Root Notes in Chord Voicings
- Major Chord Voicings and Their Variations
- Extended Chords and Their Usage
- Advanced Voice Leading Techniques
- Chord Voicings: Final Thoughts
What are Chord Voicings?
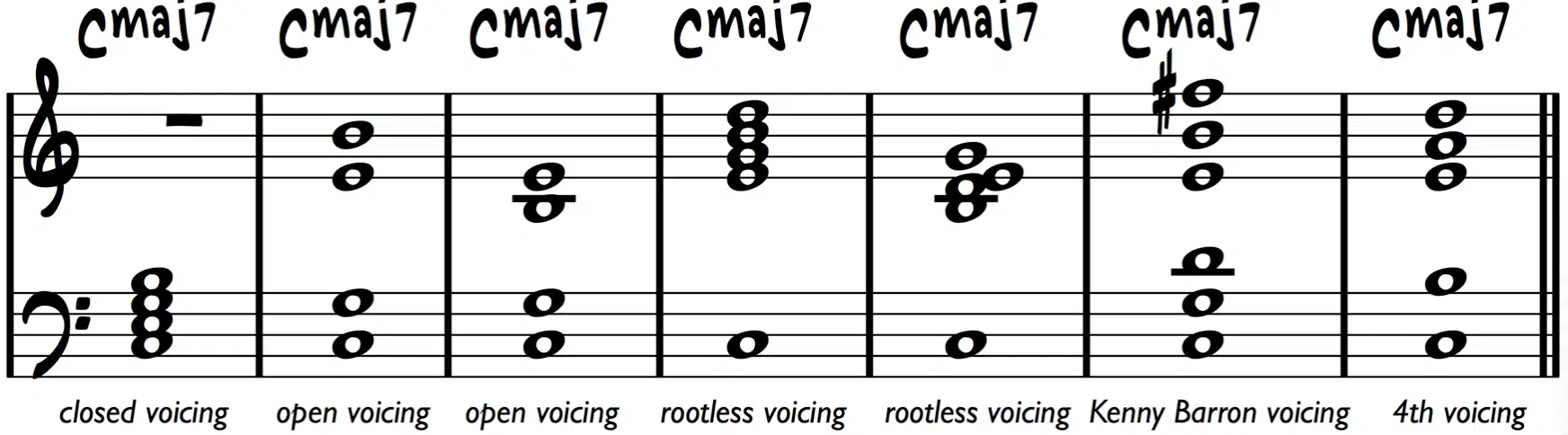
Chord voicings are a fundamental aspect of music production.
At its core, a chord voicing refers to how the notes of a chord are spread out or arranged.
This arrangement significantly affects the sound and mood of the music.
Chord voicings are not just about playing chords and memorizing the notes of a chord 一 they’re about how you choose to express those chords.
When discussing chord voicings, it’s essential to understand that a single chord can be played in multiple ways.
For example, a C major chord, consisting of the notes C, E, and G, can have different chord voicings, like:
- Playing it in an open position 一 Where the notes are spread across multiple octaves.
- Using an inversion where E or G is the lowest note 一 Creating varied harmonic textures.
These voicings impact how the chord blends with other elements of the track and its overall effect on the listener.
The choice of voicing can make the same chord sound entirely different.
So, playing around with different chord voicings can significantly enhance your appeal and ensure your tracks are intriguing.
Components of Chord Voicings: Notes and Octaves
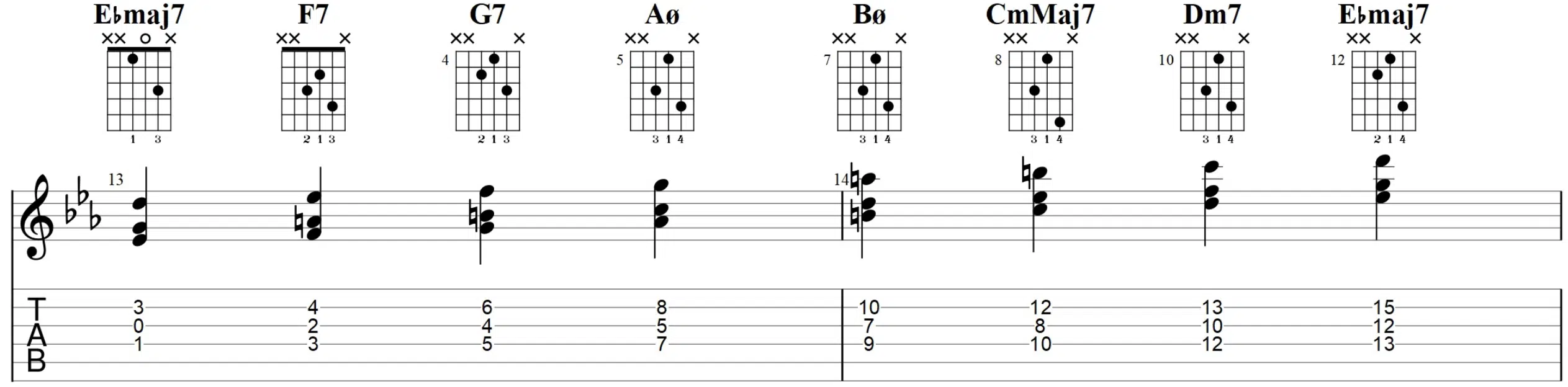
The primary components of chord voicings are the notes that make up the chord and the octaves in which these notes are played.
In digital music production, manipulating these two elements is straightforward yet powerful.
For instance, playing the notes of a C major chord in different octaves can significantly change its:
- Character
- Depth
- Texture
Using different octaves in voicing chords allows you to explore a wider sonic range.
For example, voicing a C major chord with the root note, C, in a lower octave and the other notes, E, and the next note G, in higher octaves creates a sense of depth and space.
This technique is beneficial in genres where the clarity and distinction of each note are paramount.
The choice of octaves in chord voicings can also be used to avoid sonic clashes with other elements of the track, like the bassline or melody.
This is particularly important in digital music production, where the clarity of each element is crucial for a clean mix.
Chord Tones and Their Roles
Chord Spelling
Chord tones are the individual notes that constitute a chord, and each has a unique role.
The root note, often the lowest note in the chord, provides the foundational tone.
Other notes, like the third and fifth in a triad (major/minor triad), add different chord qualities, such as major or minor tonality.
NOTE: In understanding chord voicings, it’s also important to grasp the concept of chord spelling, which is the specific sequence of notes that make up a chord (shown above).
This defines its overall sound and character.
Understanding the role of each chord tone is crucial for effective voicing.
For instance, altering the third of a C major chord from E to Eb turns it into a C minor chord 一 completely changing its emotional impact.
Similarly, adding a seventh or other extension tone can add complexity and richness to the chord.
Chord tones in digital music production can be manipulated to create unique textures.
You can tweak individual chord tones using synthesizers or samples to achieve your desired sound.
This level of control makes chord tones a powerful tool in the hands of a skilled music producer.
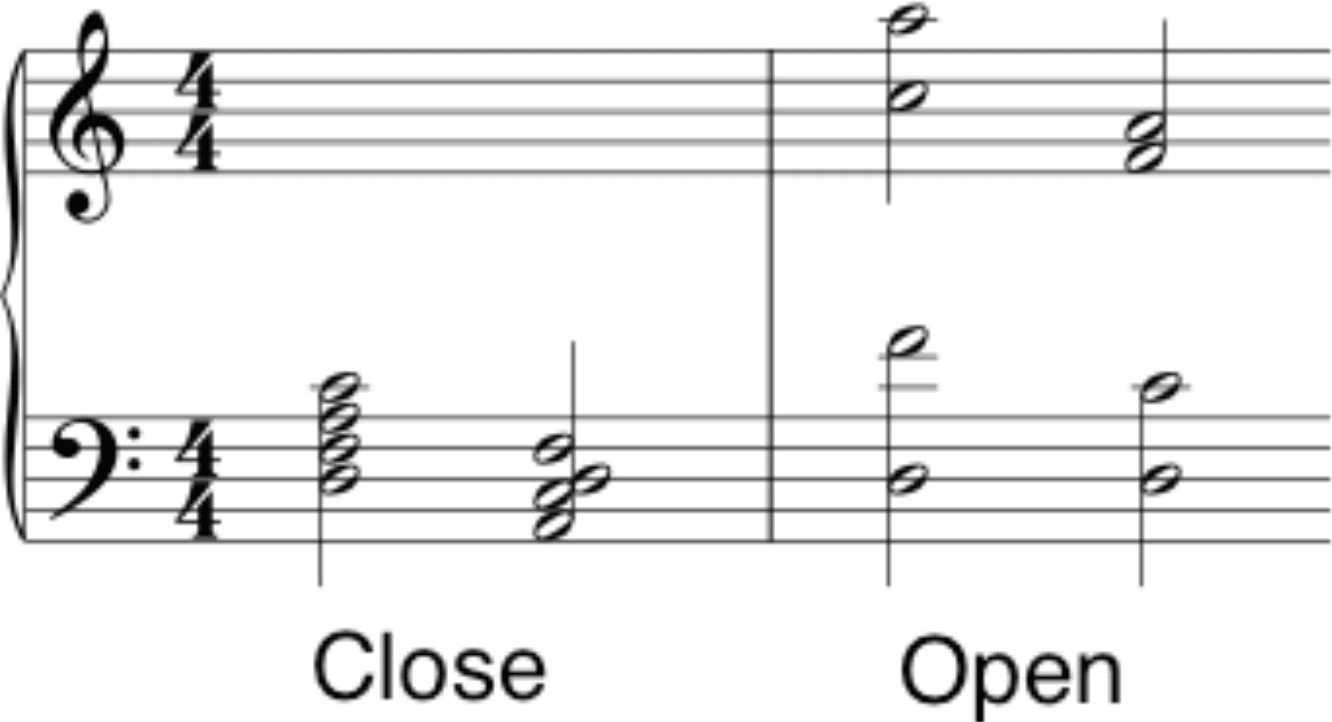
Different Chord Voicings and Their Effects

Different chord voicings can dramatically alter the mood and feel of a piece.
For instance, a standard C major triad sounds clear and direct, while the same chord voiced with an added ninth or eleventh can sound more complex and ethereal.
Voicings also affect the harmonic relationship between chords.
Voice leading, or the movement from one chord to another, can be smooth or disjointed based on the voicings chosen.
This is crucial in producing chord progressions that feel natural and engaging.
Experimenting with different voicings (different positions) is a key part of a digital music producer’s workflow.
For example, using:
- Close position voicings 一 Can create a sense of tension.
- Open position voicings 一 Offer a sense of expansiveness.
The choice depends on the emotional effect that you’re striving to achieve and the specific beat you’re working on.
Voice Leading and Its Significance
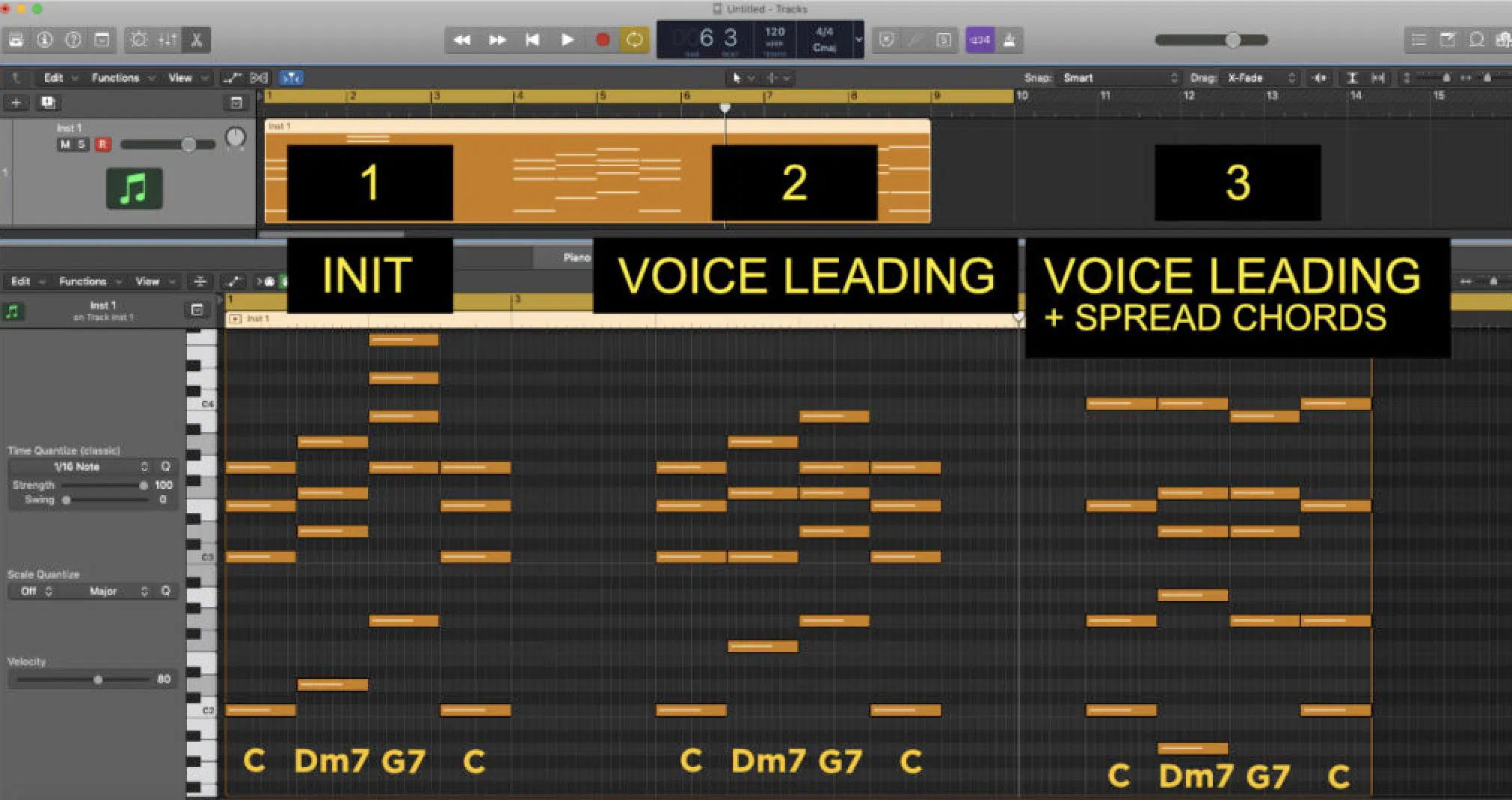
Voice leading is a critical concept in music theory, especially regarding chord voicings.
It refers to the way individual notes (or individual ‘voices’) move from one chord to the next.
In digital music production, effective voice leading ensures that your chord progressions are smooth and harmonically pleasing.
For instance, when transitioning from a C major chord to an A minor chord, the note C can smoothly move to the next note B, while the other notes/other voices shift minimally.
This will create a seamless transition and sound amazing.
The significance of voice leading in chord voicings cannot be overstated 一 it’s not just about the basic chords themselves, but how they connect and flow in a song or piece of music.
Good voice leading can make even simple chord progressions sound more professional and musically coherent.
For example, by paying attention to the movement of individual notes when you play chords, you can avoid jarring jumps between chords.
This will make your music more pleasing to the ear and easier for other musicians, like a bass player or guitar player, to follow.
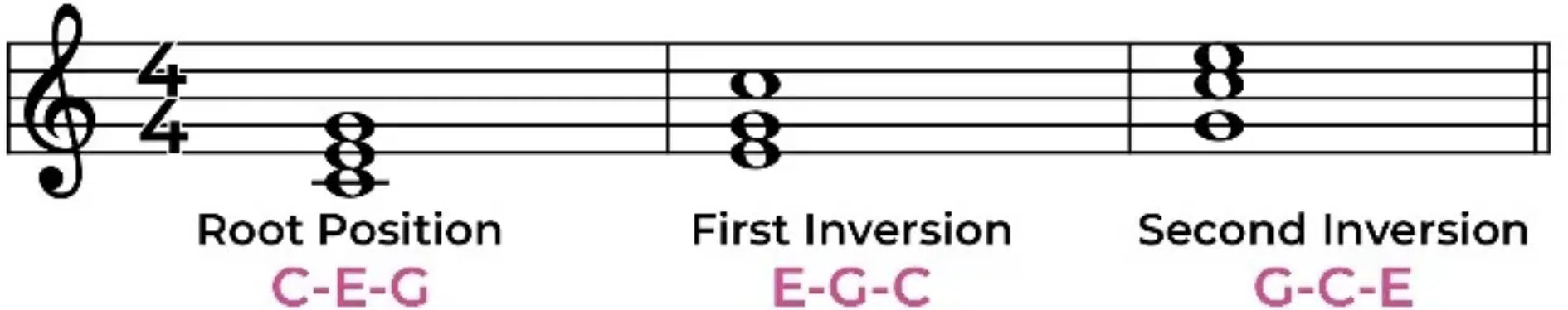
Chord Inversions: Breaking it Down
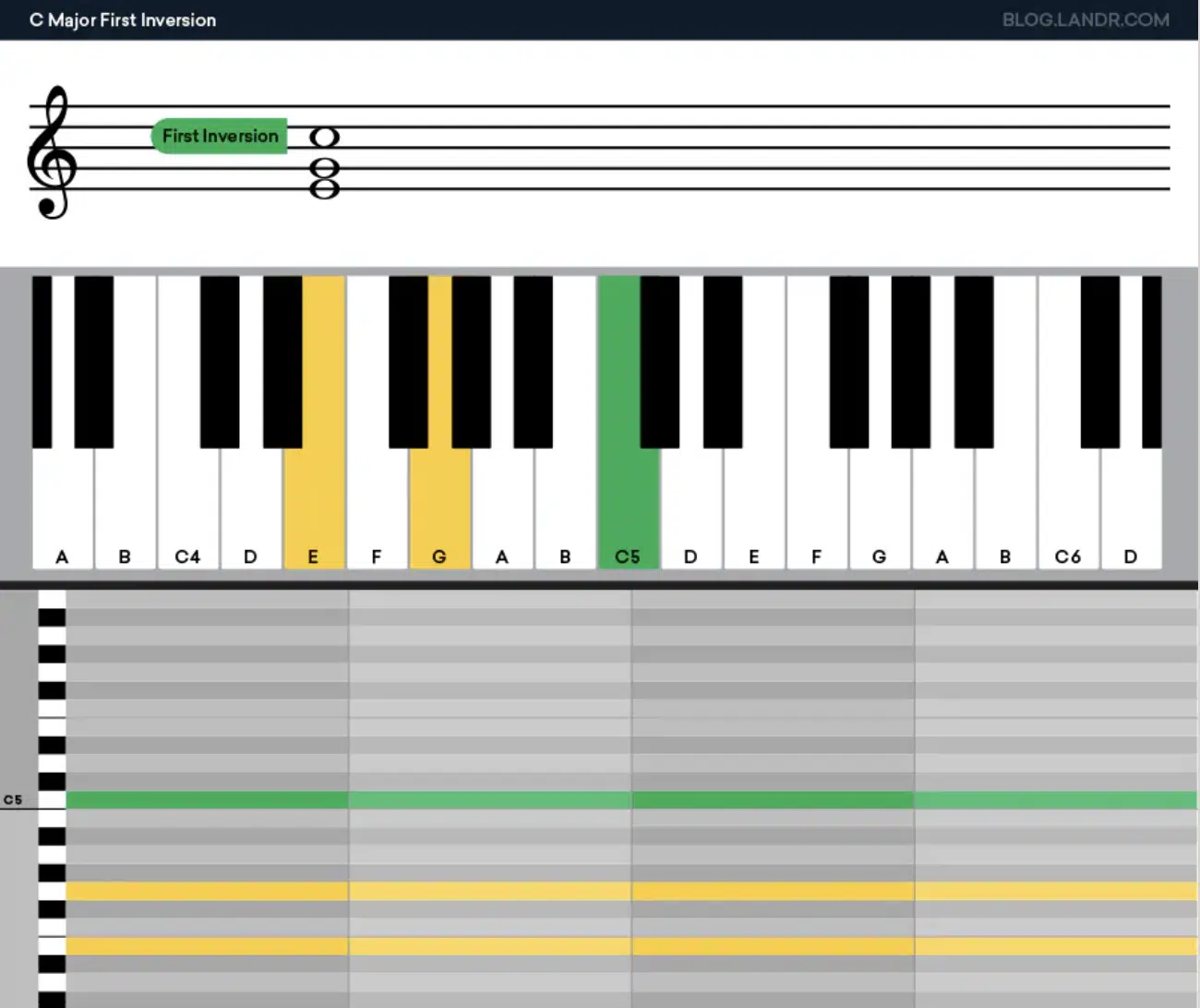
Chord inversions are an essential tool in the arsenal of chord voicings.
A chord inversion (like the third inversion) occurs when you change the order of the notes in a chord so that a different note becomes the lowest note, or bass note.
For example, in a C major chord (C-E-G), if E or G is played as the lowest note, it’s an inversion of the original chord.
Inversions are key in voice leading, as they often allow for smoother transitions between the individual chords in a progression.
Understanding and using chord inversions can add a new dimension to your music.
They offer a way to play the same chord progression while making it sound different.
For instance, let’s imagine playing a chord progression in root position (where the low root note is the lowest note)…
Then, after you play that chord progression in root position, playing the same progression using first inversion or second inversion chords can give the progression a totally different feel.
It adds variety and interest to your music; don’t feel obligated to root position.
The Role of Root Notes in Chord Voicings
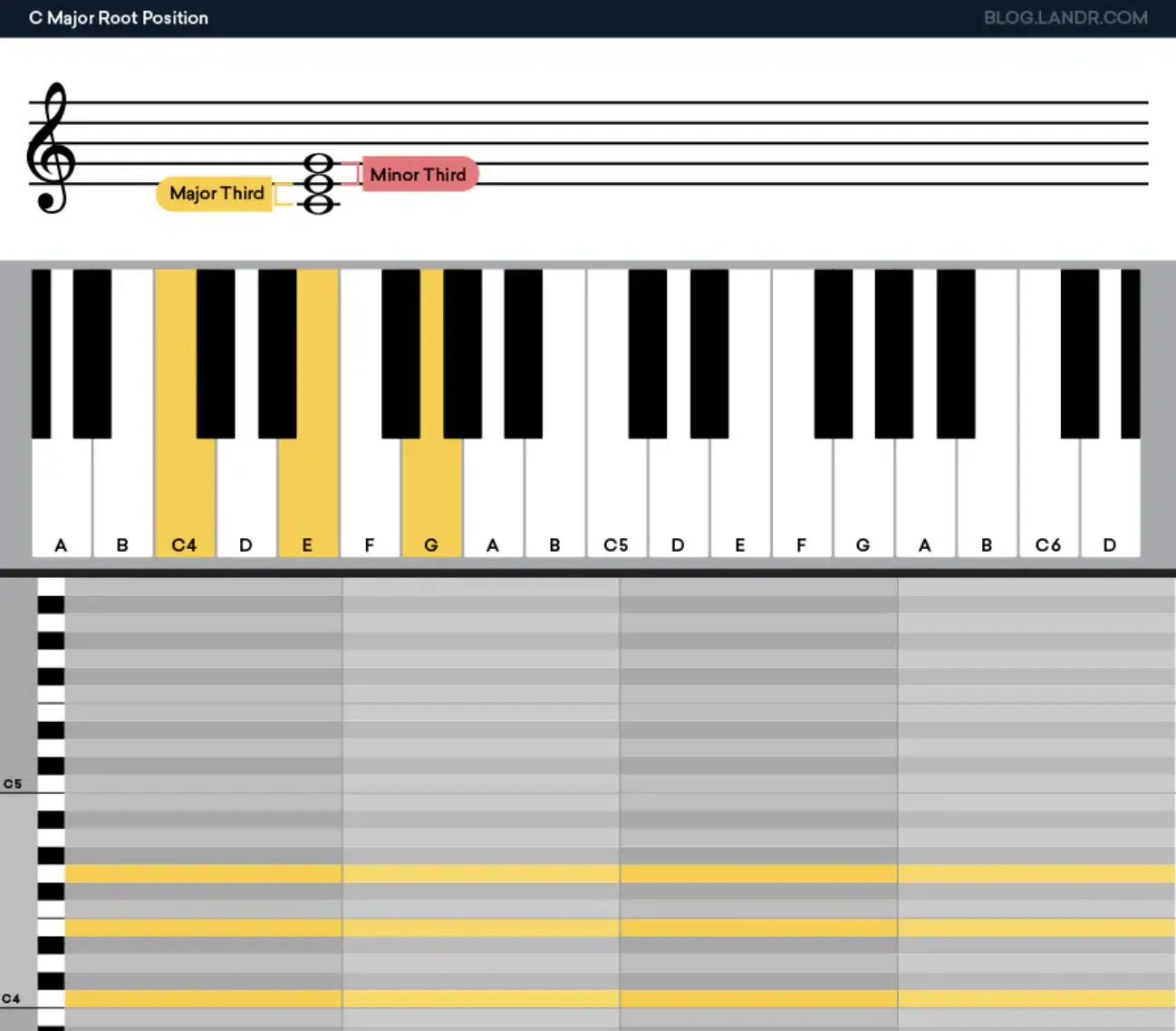
Identifying the root note of a chord is essential for understanding its structure and function within a chord progression.
The root note is typically the lowest note in a chord and gives the chord its name (for example, in a C major chord, the root is C).
This note sets the tonal foundation for the rest of the chord and often determines the overall sonic quality of the chord voicing.
In digital music production, identifying the root note is crucial for:
- Layering sounds
- Creating harmonious mixes
If the root note clashes with other elements, like the bassline or a melody in a different key, it can create dissonance.
Understanding the root note of each chord in your progression allows you to make informed decisions about other elements in your track.
This will ensure a coherent and pleasant sound.
Manipulating root notes can significantly alter the feel and direction of your music.
For instance, shifting the root note of a chord to a different octave can add depth or brightness to the chord voicing.
In a C major chord, playing the root note C in a lower octave adds richness and depth 一 while playing it in a higher octave can make the chord sound lighter and more ethereal.
Major Chord Voicings and Their Variations
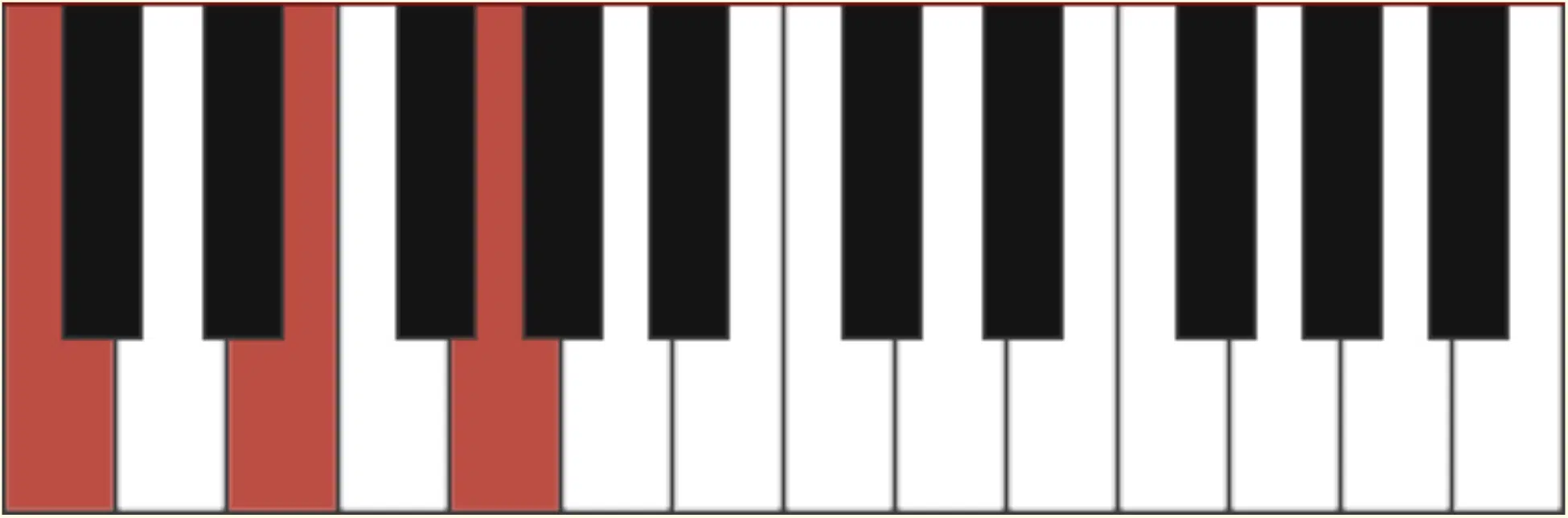
Major chord voicings (major chord progressions) are known for their bright and uplifting sound.
A basic major chord comprises:
- The root note
- A major third
- A perfect fifth
For example, a C major chord consists of C-E-G: C (root), E (major third), and G (perfect fifth).
These basic major chords are the building blocks of many musical genres and are essential in creating a positive and energetic mood in your tracks.
Variations of major chords can add color and interest.
For example, adding a seventh (major or dominant) to a C major chord creates a C major seventh or C dominant seventh chord.
These extended chords offer a more complex sound, often used in jazz and advanced pop music to create depth and sophistication.
Another variation is to play major chords in different voicings.
For instance, playing a C major chord in an open position, where all the notes are spread out over multiple octaves, can give a more expansive and resonant sound.
Experimenting with these variations will help you find that perfect sound.
-
Minor Chord Voicings and Their Impact
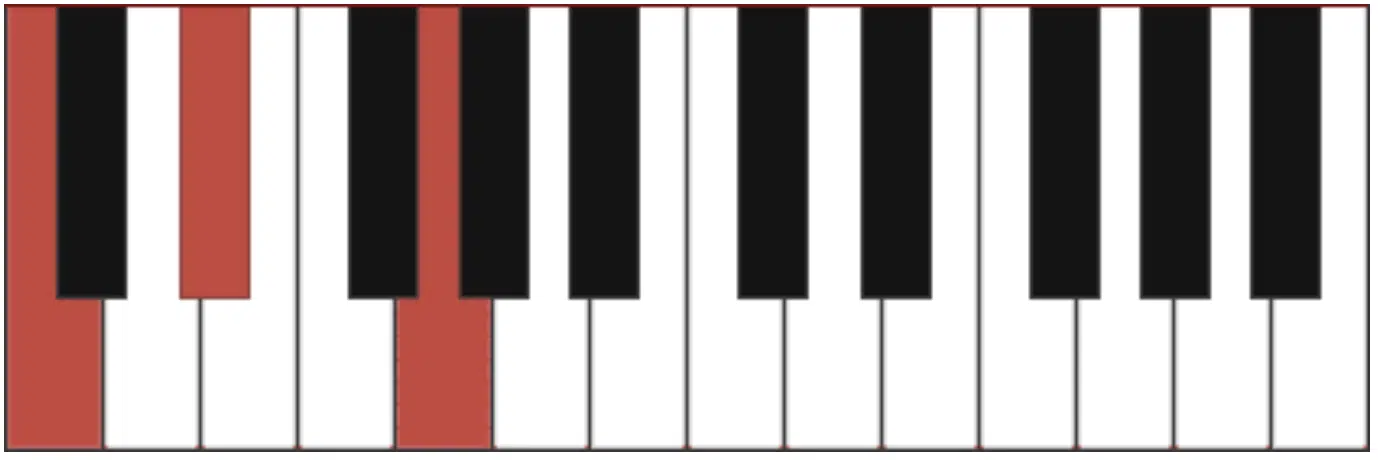
Minor chord voicings (minor chord progressions), comprising the root, a minor third, and a perfect fifth, bring a sense of melancholy or introspection to music.
For example, a C minor chord is formed with:
- C (root)
- E♭ (minor third)
- G (perfect fifth)
This chord voicing has a distinctly different emotional quality compared to its major counterpart, often used to evoke more somber or reflective moods.
Altering a minor chord voicing by adding notes, such as a seventh or a ninth, can further influence their emotional impact.
These additions can add complexity and a sense of tension (just ask any bass player).
It’s a testament to the versatility and expressive power of chord voicings in music production and sound design.
Extended Chords and Their Usage
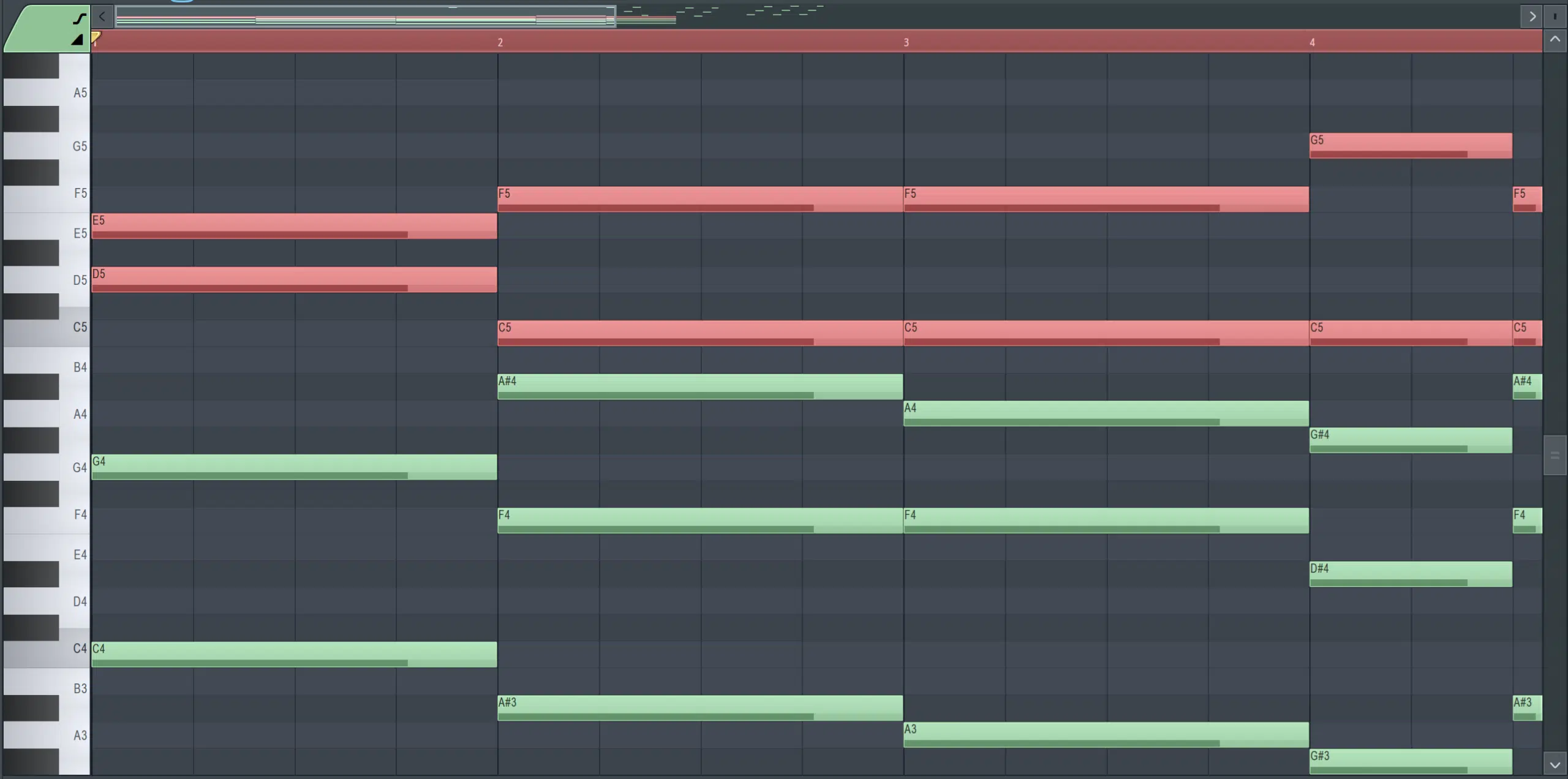
Extended chords (such as ninth, eleventh, and thirteenth chords) are fundamental in advanced chord voicings.
These individual chords add additional notes beyond the basic triad, creating a richer and more complex sound.
For example, a C major ninth chord adds a D (ninth) to the basic C major triad; providing a more jazzy, sophisticated flavor.
In digital music production, extended chords can be used to create a sense of depth and innovation in your tracks.
They work well in genres that thrive on complexity and nuance, like:
- Jazz
- Progressive rock
- Even certain forms of hip-hop & electronic music
Using extended chords carefully can elevate your music 一 giving it a professional and polished feel.
As always, experimentation is key, so make sure to play around with your voicing variations like extended chords.
Advanced Voice Leading Techniques
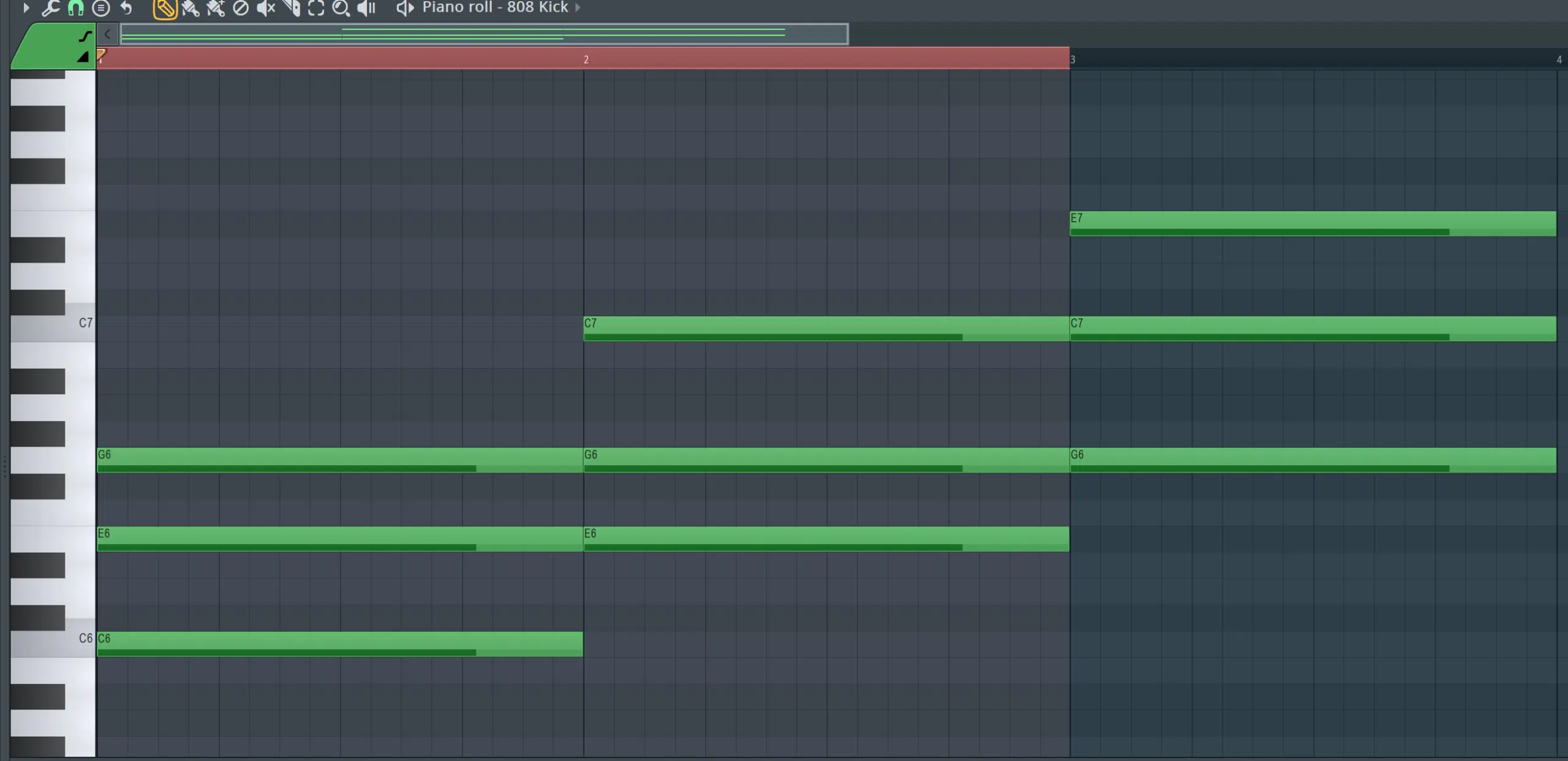
Chord Inversion
Advanced voice leading techniques are crucial for creating smooth, sophisticated chord progressions.
This includes techniques like:
- Chord inversions
- Voice exchanges
- Smoothly transitioning between different chord voicings
Mastering these methods will help you not only expand your production skills but push boundaries and make your music shine.
Chord inversions, which involve changing the bass note (or the lowest note) of a chord, are a great starting point.
For example, in a C major chord (C-E-G), if E or G is played as the lowest note instead of C, the chord is said to be in first or second inversion.
This production technique allows for smoother transitions between voice chords, as it often requires smaller movements between the notes.
Therefore, making the progression sound more cohesive and fluid.
Voice exchanges, another important technique, is where two individual voices (or notes) in adjacent chords swap places.
For instance, in a progression from a C major chord to an F major chord, the C note in the C major chord (played by the right hand) could move down to the A note in the F major chord.
While the A note in the C major chord (played by the left hand) moves up to the C note in the F major chord.
NOTE: if you play guitar, remember that the position of your left and right hands are very important, especially when it comes to a top note or bottom note.
This creates a melodically interesting and harmonically smooth transition between the voice chords.
Smoothly transitioning between different chord voicings is another superb technique.
It can be achieved by using inversions that keep common tones in the same place and move other notes by step.
-
Creating Chord Progressions with Effective Voicings

Creating new chord progressions with effective voicings is an art that combines musical theory with creative intuition.
The choice of voicings can significantly affect the mood and direction of a progression.
- Using open position chords 一 Can give a sense of openness and airiness.
- Close position chords 一 Can create a feeling of tension and release.
A well-crafted chord progression should not only follow music theory but also complement the other elements of the track.
A professional new chord progression should support the melody, rhythm, and overall structure of the song.
Experimenting with different chord voicings and observing their effects on the overall sound is key to becoming a chord voicing master.
-
Utilizing Different Octaves in Chord Voicings

Utilizing different octaves (octave position) in chord voicings is a powerful technique in music production.
It involves playing all the notes of a chord in various octaves to create different textures and sounds.
For instance, a C major chord can be voiced with the root note C in:
- A lower octave 一 To add depth.
- A higher octave 一 To create a brighter sound.
This ‘root of the chord technique is particularly useful in digital music production, where you can easily manipulate the octave placement of each note/voicing.
It allows for a greater range of expression and can help in creating a more dynamic and interesting chord voicing.
By carefully choosing the octave placement for each note, you can ensure that the chord voicing complements the other elements and enhances your track as a whole.
Chord Voicings: Final Thoughts
Chord voicings are not just a series of notes; they are the essence of emotional expression in music.
They have the power to transform a simple melody into a rich tapestry of sound, bringing depth and complexity to your tracks.
As a digital music producer, mastering chord voicings is paramount to crafting unique and captivating music.
To further explore this fascinating world, consider the free Essential Advanced MIDI Chord Progressions pack.
This resource offers a collection of 24 unique, impressive MIDI chord progressions 一 providing a hands-on experience in advanced chord voicings.
It’s a perfect tool for those looking to apply their knowledge of chord voicings in a practical, creative way.
With these MIDI chord progressions, you can instantly infuse your music with professionally crafted chords, elevating your tracks to new heights.
Embrace these tools and let your music stand out with the power of sophisticated chord voicings.
Until next time…







Leave a Reply
You must belogged in to post a comment.