Music production is an incredible, rewarding journey of sound and creativity.
It can elevate your artistry, opening up a whole new world of possibilities for your musical ideas.
However, you can get lost in the shuffle if you’re using the same old tricks and techniques rather than getting creative.
The music industry is saturated with talent 一 you have to stand out to make an impact.
That’s why we’ll be breaking down exactly how to do so.
In today’s article, we’ll be covering:
- Setting Up Your Space ✓
- Choosing a DAW ✓
- Music Theory ✓
- Crafting Your Own Sound ✓
- Sampling & Sound Design ✓
- Dynamic Range ✓
- The Production Process ✓
- Improving Skills ✓
- Advanced Tips & Tricks ✓
After diving into this extensive guide, you’ll be armed with some of the game’s most beneficial music production tips, tricks, and techniques.
Your tracks will truly shine from start to finish.
So, let’s dive in…
Table of Contents
- Getting Started: Setting Up Your Space
- Digital Audio Workstations (DAWs)
- Understanding Music Theory
- Crafting Your Own Sound
- Sampling & Creative Sound Design
- Creating a Dynamic Track
- The Music Production Process
- Improving Your Production Skills: Music Production Tips
- Music Production Tips: How to Become a Better Music Producer
- Music Production Tips: Final Thoughts
Getting Started: Setting Up Your Space
Before diving into the complexities of music production, you should be aware that your environment and gear matter.
Therefore, we will give you all the tips needed to excel.
-
The Importance of Studio Monitors

Starting your journey as a music producer means investing in essential gear.
High up on that list? Studio monitors.
Studio monitors offer an uncolored, honest representation of your music, unlike regular speakers.
They are pivotal in ensuring what you produce sounds ideal across different sound systems.
Have you ever noticed how different your track sounds when playing on your friend’s sound system or in a car?
That’s due to the colored sound many commercial speakers offer.
Studio monitors reduce those deceptive embellishments.
Studio monitors, by providing a neutral ground, help you understand the intricacies of your mix.
When the mix sounds great on these, it’s more likely to translate well elsewhere.
-
Choosing an Audio Interface

Think of an audio interface as the gateway between the outside world and your computer.
It’s the device that lets you connect instruments, microphones, speakers, and other audio equipment to your digital workspace.
If you’re just starting out, it’s fairly easy to become overwhelmed with the many options available.
When choosing an audio interface, consider the:
- Number of inputs and outputs you’ll need
- Type of connections (USB, FireWire, Thunderbolt)
- Quality of the preamps
Another key factor of choosing an audio interface is compatibility with your DAW and computer.
Look for interfaces that are known to work seamlessly with your specific DAW 一 ensuring the most straightforward music production process.
-
Acoustic Treatment Tips

Optimizing your room is the next step after investing in good monitors and a reliable audio interface.
Enter the world of acoustic treatment.
It’s not just about soundproofing (which prevents sound from escaping or entering the room) but ensuring sound waves within the room don’t distort your perception.
The three main tools for treating a room are:
- Acoustic panels 一 Absorb sound waves, preventing them from bouncing around uncontrollably.
- Bass traps 一 Deal with low frequencies, which are notorious for creating muddy sounds (especially in corners).
- Diffusers 一 Scatter sound waves, eliminate specific frequency build-ups, and ensure an even sound landscape.
With the right acoustic treatment, you can significantly enhance the accuracy of what you’re hearing.
These music production tips can help you pave the way for hotter tracks.
Digital Audio Workstations (DAWs)
DAWs are the heart and soul of digital music production.
Your choice here sets the tone (pun intended) for your music production journey.
-
Industry Standards

While there’s no shortage of DAWs in the market, a few names consistently rise to the top.
Some of the biggest players in the game right now are:
- Ableton Live
- FL Studio
- Logic Pro X
- Pro Tools
These DAWs are popular for a reason.
They offer robust features, an extensive array of plugins, and have large communities.
This community aspect means tons of tutorials, free resources, and third-party plugins are available.
But remember, the best DAW is the one you’re most comfortable with.
It’s like choosing between guitars 一 what works for one artist might not work for another.
NOTE: Feel free to try the demos or lite versions before choosing.
This lets you see if that particular software blends with your unique workflow.
-
Key Factors To Look For
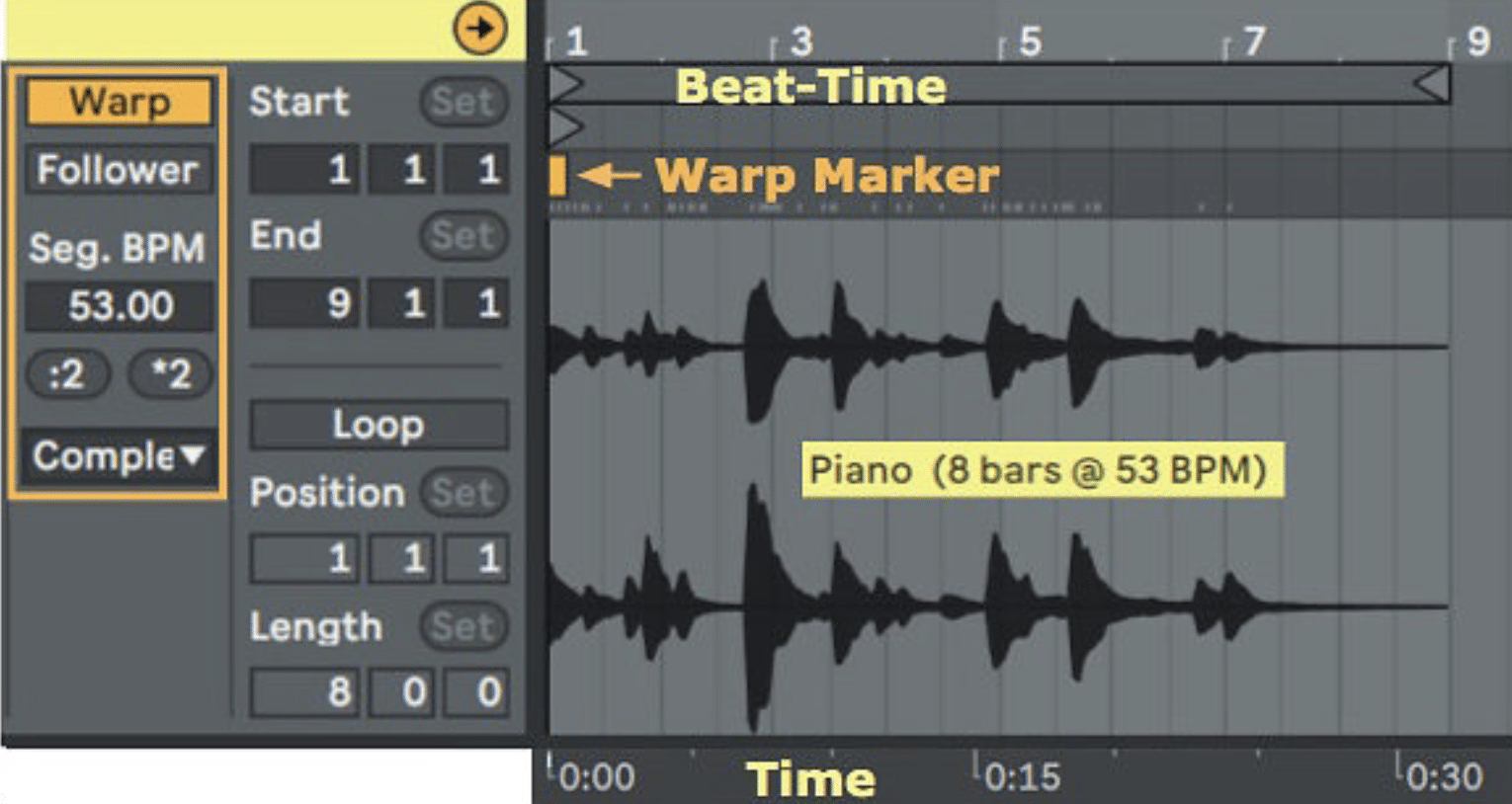
Once you’ve narrowed down your options, there are some crucial aspects to consider in your DAW of choice.
One of the key elements is the workflow.
Does the DAW fit into your way of making music and production style, or is it a constant battle to perform even simple tasks?
Another key aspect is the flexibility of the DAW.
Does it allow you to customize your workspace, or are you stuck with a default configuration?
A customizable DAW will enable you to streamline your music production process 一 making things much easier in regards to your own music.
Also, consider how well the DAW integrates with the rest of your audio equipment.
Ask yourself:
- Does it work well with your audio interface?
- Can you easily map your MIDI controller?
These aspects can make or break your production studio setup.
-
Advanced DAW Considerations

For more experienced producers, the ability to perform advanced routing or the quality of native plugins and virtual instruments might be deal-breakers.
Some DAWs excel in MIDI capabilities, while others shine in audio recording and manipulation.
Also, consider the kind of music you’re looking to produce…
For electronic music producers, Ableton Live or FL Studio offers a wealth of built-in sounds and sampling capabilities.
If you’re into recording live instruments, perhaps a DAW like Pro Tools would suit you better.
Scalability is another factor, as you want a DAW to grow with you.
Check whether you can add more plugins or if the DAW comes with advanced features, you can explore as you become a better music producer.
Understanding Music Theory
Okay, let’s switch gears a little…
Knowing your way around a DAW is great, but understanding music theory gives you a more profound creative edge.
-
The Basics
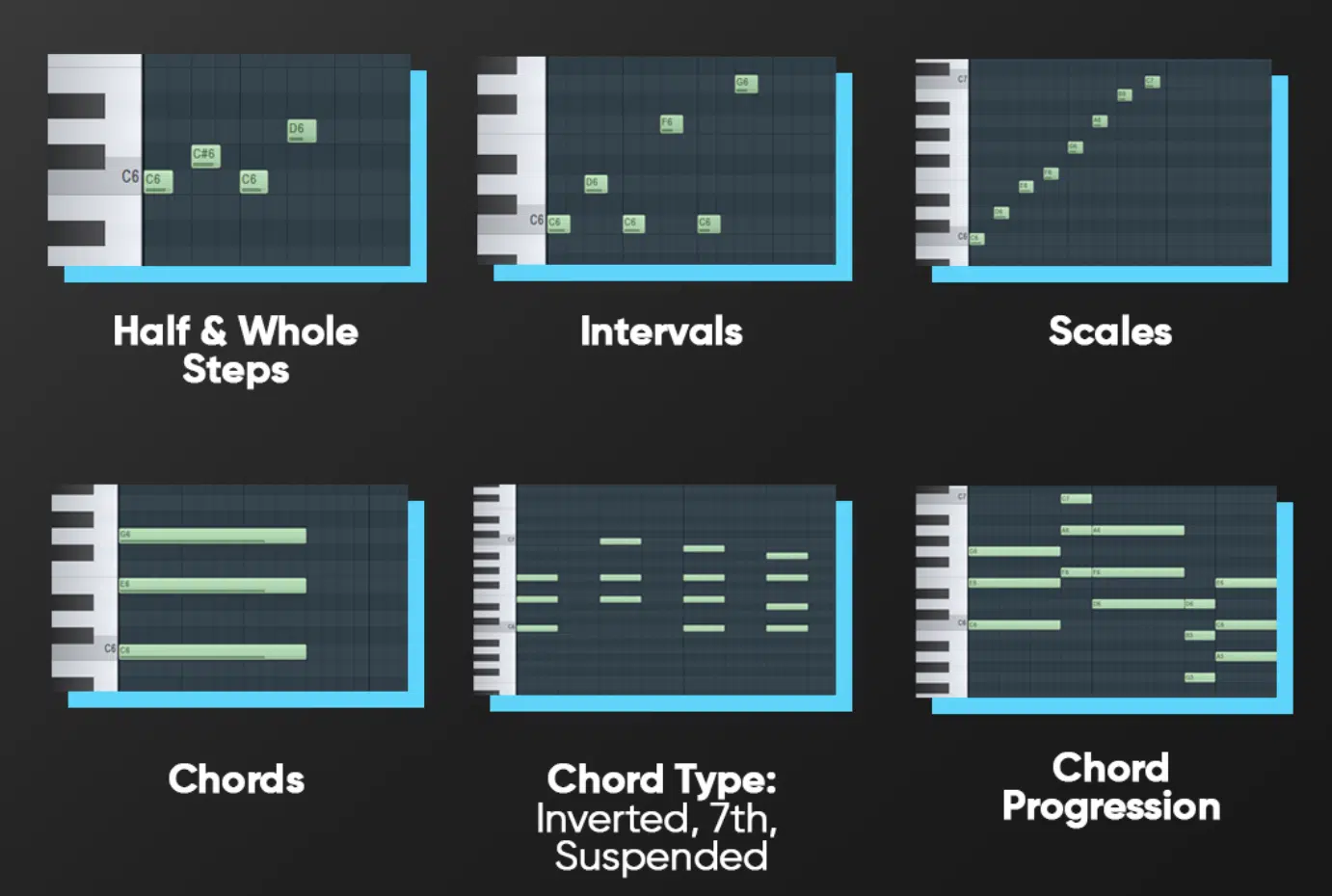
So, you may be asking, “Do I really need to learn Music Theory?”
Let me put it this way 一 knowing the rules of music theory helps you break them more effectively.
Understanding scales, chords, and progressions gives you a robust foundation to produce music that sounds good.
Learning music theory doesn’t mean you need to become a classically trained musician.
Basic guidelines can make a world of difference, like:
- Understanding a minor from a major scale
- Knowing what a seventh or ninth chord is
- Being familiar with the Circle of Fifths
With YouTube tutorials and online courses, learning music theory has become easier than ever.
Spend a few hours each week, and you’ll soon grasp the concepts to help you become a better music producer.
-
Breaking The Rules
Now, music theory is not set in stone… It’s a framework, not a rulebook.
Many music producers (especially in genres like hip-hop, lo-fi, pop, and electronic music) often bend or break traditional theory rules to create something fresh and unique.
Certain things can add a unique touch to your tracks, like:
- Dissonant chords
- Unusual time signatures
- A crazy synth lead that defies conventional scales
Just be aware of these decisions’ emotional and psychological effects on the listener.
Being deliberately unconventional requires you to fully understand what you’re deviating from.
Hence, you’ll still need to understand the basic rules before smashing them creatively.
Crafting Your Own Sound
The magic in music production often comes when you find your own unique style.
Let’s dive into crafting your own sound.
-
How To Find Your Signature Sound

One of the biggest challenges for music producers making music, especially new ones, is finding their own sound.
We all start by emulating our favorite artists, but the real magic starts when you diverge and carve out your own niche.
One of my favorite music production tips for finding your sound is blending elements from different genres.
Let’s say you’re into both techno and jazz…
Why not incorporate jazzy chords or instruments into your techno track?
It could result in something that is distinctly you.
Consider the unique instruments or VST plugins you gravitate towards when working on your music production process.
Your choice of instruments has a huge role in shaping your sound.
Maybe you’re all about that analog warmth from vintage synths, or perhaps you’re drawn to futuristic digital sounds in your own music; embrace it.
Your go-to plugins and effects are another identifier.
If you find yourself consistently using tape saturation, or a specific reverb plugin 一 that’s all part of developing your own signature sound.
-
The Role of Sound Design
Sound design is often the unsung hero in the music production world.
It isn’t just for those complex synth patches or cinematic soundscapes 一 sound design is applicable across the board.
Even something simple can help you create a unique drum sound that stands out, like:
- Layering two snares together
- Tweaking the pitch
- Adding a subtle flanger
Or, consider using field recordings to add an organic touch to your electronic tracks.
The right sound design can breathe life into stale or repetitive tracks.
Spend time getting to know your plugins, especially synthesizers and effects units.
You should be able to create your own patches rather than relying solely on presets.
Once you understand the basics of sound design, you can dive into advanced techniques like granular synthesis, modular synthesis, or FM synthesis.
The deeper you go, the more you can differentiate your music from others.
-
New Techniques for Unique Sounds
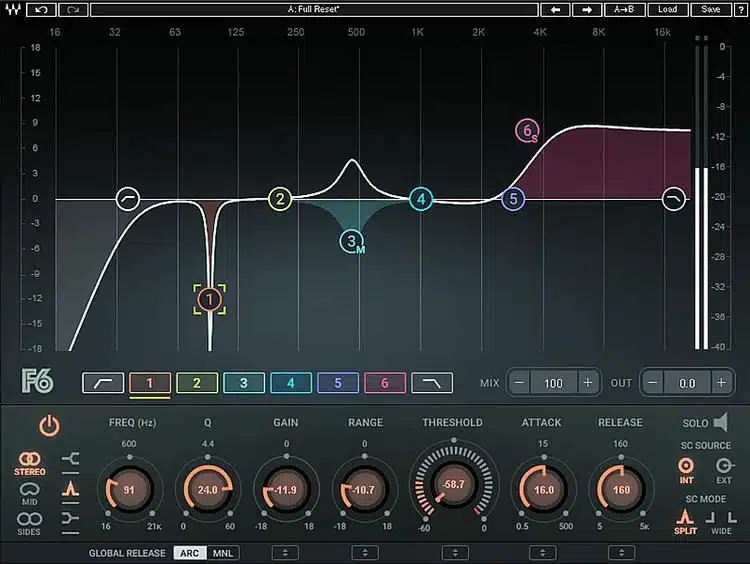
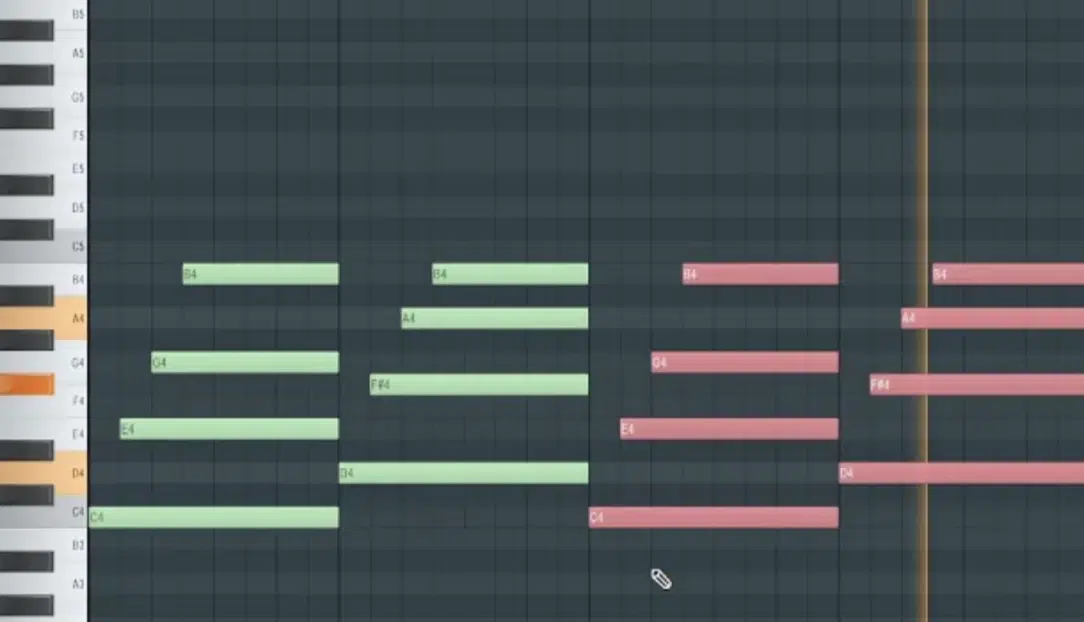
Once you’ve gotten comfortable with the basics, it’s time to experiment with new techniques and music production tips.
Things like sidechain compression or polyrhythms can offer fresh avenues to explore.
Play around with unconventional scales or time signatures.
If you’re an electronic music producer who’s always working in 4/4, what happens if you try a 5/4 time signature? (shown above).
This sort of experimentation can spark inspiration for unique tracks.
Also, don’t overlook the power of automation.
Automating certain parameters can create dynamic movements within your tracks, like:
It’s like your song is alive, constantly evolving as it plays.
Another advanced tip: resampling.
Try taking a finished section of your track and re-importing it into your DAW as a new audio file.
You can chop it up, pitch it down, and layer effects from here to create something entirely new.
This technique often leads to happy accidents that can become the defining feature of a track.
Sampling & Creative Sound Design
Let’s get into the nitty-gritty of sampling and sound design by switching gears a bit.
-
Using Sample Packs Effectively

Sample packs can be a godsend, especially when you’re battling the dreaded writer’s block.
But how do you ensure your music doesn’t sound like everyone else’s?…
First off, don’t just drag and drop samples from a sample pack into your project and call it a day.
Instead, try:
- Chopping them up
- Pitching them differently
- Running them through various effects
There’s a lot you can do to customize samples.
For example, reversing a cymbal or snare sample can create an interesting riser or transitional element in your track.
Try combining samples from different sample packs or even layer a synthetic sound with an acoustic sample.
You might be surprised by the rich and unique textures you can create.
-
Crafting Synth Patches

Synthesizers offer a near-infinite palette for sound design.
Whether you’re creating a lead sound, a thick pad, or a rumbling bass, synthesizers give you the tools to make it happen.
But crafting your own synth patches can be intimidating at first, especially with all the knobs, buttons, and sliders staring back at you.
My best advice? Start simple.
Take a preset you like and start tweaking it, like:
- Change the waveforms
- Mess with the filters
- Add some modulation
Also, you’ll learn a lot by deconstructing other people’s patches.
Modular synthesizers have also become more accessible, thanks to VSTs like Native Instruments’ Reaktor and Softube Modular.
These allow you to create your own signal path 一 combining oscillators, filters, and effects in a nearly endless array of configurations.
It’s a deep dive but well worth the time invested for the sheer range of unique sounds you can create.
NOTE: Keeping the larger context in mind is also beneficial when crafting a synth patch.
An impressive sound in isolation may not necessarily fit well in a mix.
Always consider how the patch will interact with other elements in your track.
For music producers, this holistic approach to sound design will lead to more cohesive and impactful tracks.
-
The Art of Sub-Bass & Frequency Range

The sub-bass range, generally considered to be frequencies below about 60 Hz, is an often misunderstood element in music production.
Many producers tend to either overuse or completely neglect this range.
A powerful sub-bass can make or break a track in genres like hip-hop and electronic music.
However, achieving the right balance is key to ensuring your music sounds professional.
- Too much sub-bass 一 Can muddy your mix.
- Too little 一 Can leave it feeling empty.
To master the art of sub-bass, you’ll need to understand your tools.
Subtractive synthesizers, such as Moog’s Minimoog or software emulations like Arturia’s Mini V, can produce warm and fat sub-basses.
Additionally, using dedicated sub-bass plugins like Waves’ R-Bass can help you further shape this crucial frequency range.
Lastly, proper monitoring is crucial for sub-bass mixing.
Studio monitors with a good low-frequency response or a dedicated subwoofer are essential.
Without them, it’s hard to gauge how your sub-bass will sound on different systems.
Creating a Dynamic Track
As we pivot toward the structural elements of your tracks, let’s delve into the components that give them life and movement.
-
The Role of Dynamic Range
Dynamic range, the difference between a track’s softest and loudest parts, is essential for conveying emotion and energy.
In the world of digital music production, where it’s tempting to make everything loud, understanding and preserving dynamic range is a must.
One common technique to manage dynamic range is using compression.
While it’s a useful tool for evening out levels, excessive compression can suck the life out of your track, so use it sparingly and purposefully.
Automation is another powerful tool for creating dynamics.
Automating volume levels or filter cutoffs during different sections can create a more engaging listening experience.
Don’t underestimate the role of arrangement in dynamic range.
Simple things like dropping out the drums for a section or introducing a new instrument can create dynamics in a very organic way.
-
Music Production Tips: Fine-Tuning Your Sound
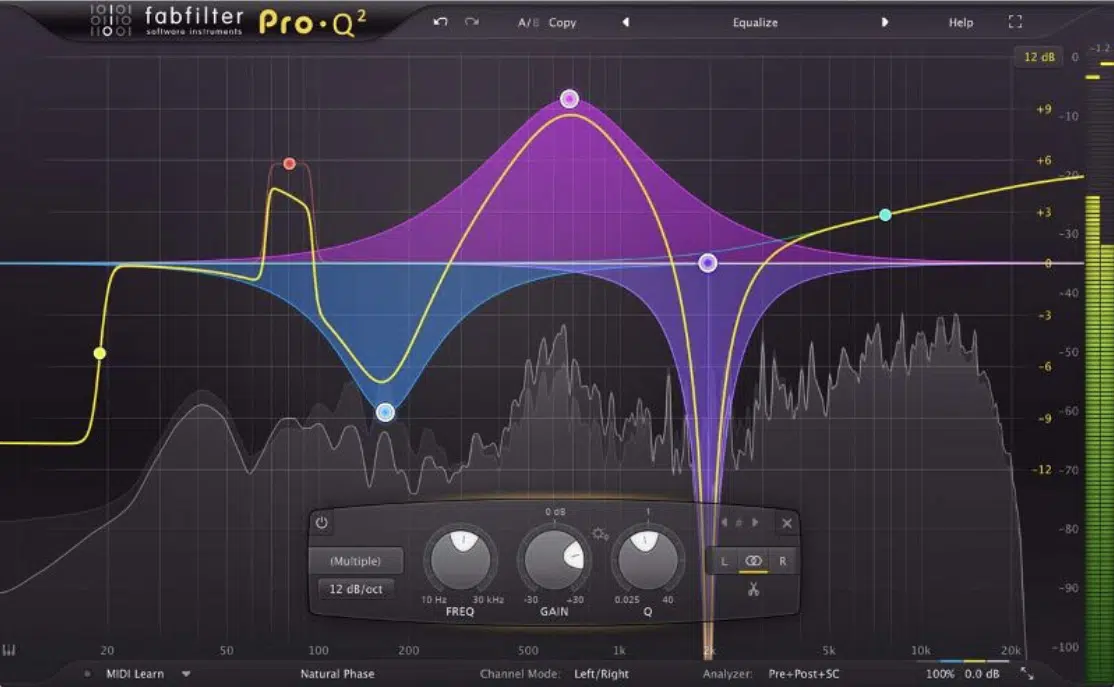
After you’ve got a solid grasp of dynamic range, the next step in the music production process is fine-tuning your sound.
This is where attention to detail really pays off.
Whether you’re sculpting the EQ on a synth or finessing a vocal take, small adjustments can make a big difference.
One essential tool for fine-tuning your sound is a good parametric EQ.
Understanding how to cut and boost frequencies can make your mix sound:
- Clearer
- More balanced
- Super professional
For example, a common mistake is overloading the bass frequencies, which can muddy up the mix.
A simple low-cut can create room for other elements 一 especially in electronic music where sub-bass elements are critical.
A/B comparisons are your best friend here.
This technique involves flipping back and forth between your mix and another production (usually a professional track you admire) to check how your sounds stack up.
It’s a priceless strategy for fine-tuning your mix to ensure it stands up to the competition.
Also, don’t underestimate the power of incremental adjustments.
Small tweaks to things like reverb tails, compressor settings, or even the velocity of your MIDI notes can transform a good track into a great one.
-
Utilizing Stereo Width
Stereo width is one of those aspects of music production that’s often overlooked, but it’s crucial for creating an expansive and engaging mix.
Certain things can make a track come to life, like:
- Proper use of panning
- Stereo imaging plugins
- Even some mid/side EQ
When you’re starting out, it’s easy to pan everything dead center 一 but doing so misses the opportunity to fill up the stereo field.
Try panning different elements to different areas in the mix.
For example, backing vocals or secondary melody lines can be panned slightly off-center to provide a sense of space and depth.
Another advanced technique to utilize stereo width effectively is to employ mid/side processing.
This allows you to independently EQ the center and sides of your stereo field.
For example, you might decide to boost the high frequencies on the sides while keeping the center focused on the low-mid frequencies.
This technique effectively ensures your mix will sound good in mono and stereo settings.
NOTE: Always check your mix in mono to ensure it translates well across all listening environments.
The Music Production Process
As we transition from the nuances of crafting sound to the larger structure of learning music production, let’s consider the key steps involved in taking a song from concept to completion.
-
Laying Down Musical Ideas

The first step in the music production process often begins most humbly: with an idea.
This could be:
- A melody you hum
- A drum pattern you tap out on a table
- Even a chord progression you stumble upon
Sketching these ideas out in a Digital Audio Workstation (DAW) is crucial.
Many producers prefer to start with the drum groove to set the tempo and feel of the track 一 while others may start with a melodic idea or a harmonic progression.
Modern DAWs like Ableton Live, FL Studio, and Pro Tools offer various tools for quickly laying down ideas.
From MIDI sequencing to live recording options, these platforms are designed to adapt to your workflow.
Keep in mind: the goal at this stage isn’t to produce a polished track but to get your ideas out of your head and into a form where they can be developed and arranged.
Spontaneity is key, and overthinking can be the enemy of creativity.
-
Producing Music: Mixing & Mastering

Once your ideas are laid down, mixing and mastering are the next steps.
While often lumped together, these are distinct phases.
- Mixing 一 Involves balancing levels, panning, EQ, and other aspects to ensure every element sits well in the track.
- Mastering 一 Is the final step to prepare your track for distribution.
This involves tasks like volume leveling, adding polish through subtle EQ adjustments, and ensuring the track sounds good on various playback systems.
You can choose to hire a mastering engineer, but if you’d like to do it yourself, we’ve got all the tips.
Tools for these tasks range from traditional studio hardware to many VST plugins.
Remember that while plugins and gear can help, your ears are the most important element in mixing and mastering.
Training your ears to pick up on subtle nuances takes time and practice in audio production, so always keep listening and learning.
-
Audio Effects: Breaking It Down
Audio effects are the spices in the recipe of your music production.
From basic elements like reverb and delay to specialized effects like bit-crushers and vocoders, these tools can dramatically alter the character of your sound.
However, it’s essential to understand how and when to use each effect.
For example, while reverb can add depth and space, too much can drown out your mix 一 making it sound muddy.
Similarly, distortion and saturation can add warmth and character but can also introduce unwanted noise and artifacts if not used carefully.
Various plugins offer innovative approaches to these traditional effects.
NOTE: Valhalla’s VintageVerb offers a modern take on classic reverb sounds, and Soundtoys’ Decapitator is excellent for adding harmonic complexity to your sounds.
Understanding the nuances and applications of different audio effects will improve the quality of your music and enhance your creative options.
Always remember, effects are tools, not crutches.
Use them to enhance your beats, not to mask problems in your mix.
Improving Your Production Skills: Music Production Tips
Now that we’ve dived deep into the nitty-gritty of music production tips and processes, let’s focus on some habits and techniques that can elevate you from a good producer to a great one.
-
The Use of Reference Tracks
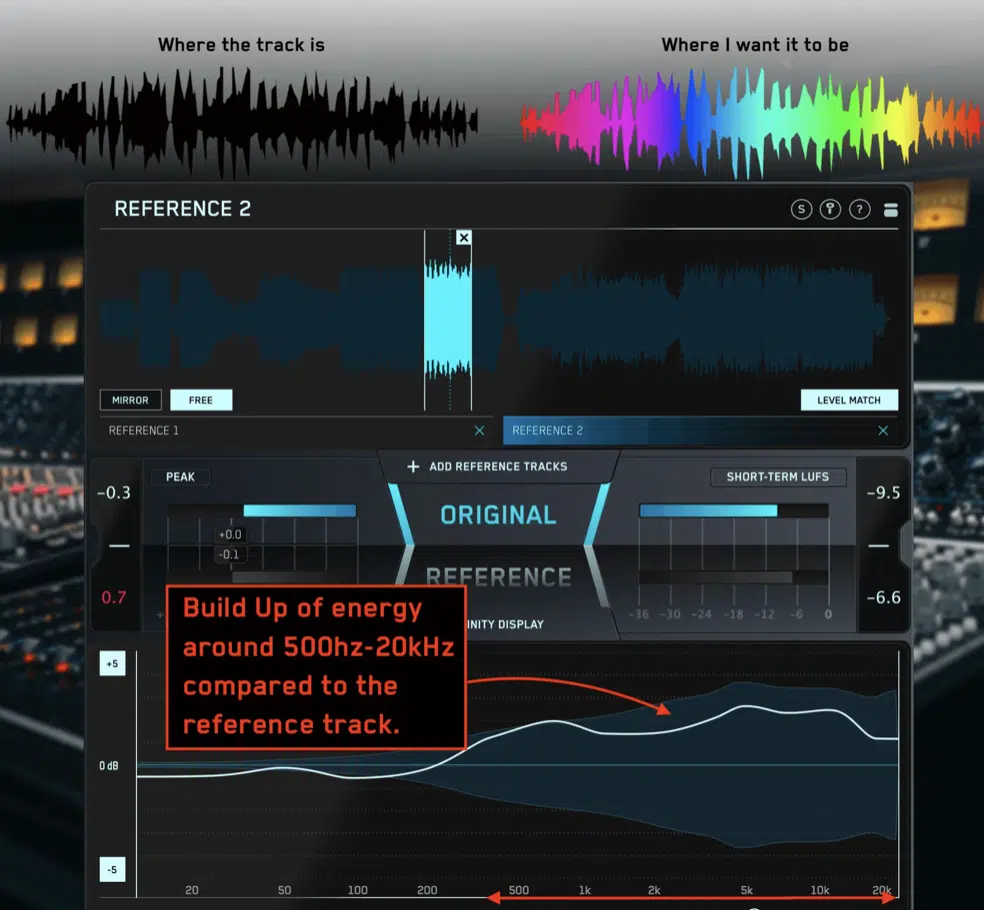
When you’re engrossed in a project, it’s easy to lose perspective, and that’s where reference tracks come in handy.
These are professionally mixed and mastered tracks that you admire and aim to emulate in terms of sound quality and mix balance.
By frequently A/B testing your mix against a reference track (other people’s music), you can quickly pinpoint areas where your song might need improvement.
There are various plugins designed to make A/B testing easier.
Picking a good reference track is essential.
It should ideally:
- Be in the same genre
- Have similar instrumentation
- Represent the level of production quality you’re aiming for
Remember, the idea is not to copy but to use these tracks as a guideline.
Even experienced music producers use reference tracks as a sort of ‘reality check’ to ensure they are on the right path.
-
Battling Ear Fatigue
Ah, the dreaded ear fatigue…
It’s a real issue when you’re producing music and finalizing beats, especially during those marathon mixing sessions.
Over time, your ears can become less sensitive to certain frequencies 一 making it difficult to make accurate decisions.
One effective tip to battle ear fatigue is to take regular breaks.
- Step away from the computer
- Take a walk
- Even listen to some other types of music
Anything to give your ears a ‘palette cleanser,’ so to speak, is a great music production tip.
Also, consider the volume at which you’re working; constantly blasting your studio monitors can accelerate ear fatigue.
A good rule of thumb is to mix at low to moderate volumes and only turn up the volume for short periods to make specific checks.
Music Production Tips: How to Become a Better Music Producer

Becoming a better music producer isn’t just about mastering your DAW or learning new techniques in sound design.
It’s also about:
- Developing good habits
- Being organized
- Constantly seeking to learn
One way to improve is by collaborating with other producers, which can provide fresh insights into your production process.
As well as expose you to new techniques and approaches you might not have considered.
One of the more elementary music production tips is to never underestimate the power of finishing music (aka, experience).
The more tracks you complete, the better you’ll become 一 a finished track, even if it’s not perfect, is better than a dozen unfinished ideas.
The practice of completing your tracks also teaches you valuable skills in arrangement, mixing, and mastering.
Finally, continuous learning is crucial.
Whether it’s through YouTube channels/tutorials, courses, or feedback from experienced producers, always be on the lookout for ways to improve your skills.
Music Production Tips: Final Thoughts
So you’ve soaked up a ton of music production tips.
Including setting up your space with advanced techniques that’ll make you a better music producer.
Now what?…
As you know, real learning happens when you apply these music production tips to your very own music.
That’s where the Beatmaker Blueprint (Free Teaser Pack) comes into play.
This Free Teaser Pack is a treasure trove for any digital music producer.
It includes 449 samples, loops, and MIDIs to infuse your tracks with new life.
And the best part is it’s 100% royalty-free.
Meaning, you can freely incorporate these sounds into your projects 一 perfect for practicing the music production tips and tricks you’ve just learned.
Remember, practice doesn’t make perfect; it makes progress.
So go ahead and let your creativity flow, and your tracks will get a serious upgrade (from start to finish)
Until next time…







Leave a Reply
You must belogged in to post a comment.