Polyrhythms are an essential and mesmerizing element in the vast world of music production.
They can transform a simple beat into a complex, captivating rhythm and elevate the listener’s experience.
That’s why, as a music producer, knowing how to recognize, create, and manipulate polyrhythms can help you enhance the depth and appeal of your music.
Mastering polyrhythms opens up a world of rhythmic possibilities, allowing you to infuse your tracks with a unique and sophisticated sound.
In today’s article, we’ll break down:
- What a polyrhythm is ✓
- Their role in modern music ✓
- Practical application in music production ✓
- Technical aspects and notation ✓
- Advanced polyrhythmic techniques ✓
- Incorporating polyrhythms in various instruments ✓
- Recording and mixing strategies for your polyrhythm ✓
- Digital tools for creating polyrhythms ✓
- Much more about the legendary polyrhythm ✓
After reading this article, you’ll be able to identify and use polyrhythms in your music production confidently.
You’ll understand the intricacies of these complex rhythmic patterns and how they can transform your music.
Plus, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge to apply these rhythms creatively, crafting beats and compositions like a professional.
Whether you’re a beginner or a professional, this guide will elevate your understanding and application of polyrhythms.
So, let’s dive in…
Table of Contents
What are Polyrhythms?

Polyrhythms, a cornerstone in the vast world of music, are a delightful challenge for any music producer.
They occur when two or more rhythms are played simultaneously, creating a complex and captivating sound.
This phenomenon is not just a modern invention but has deep roots in various musical traditions, prominently in African music.
Understanding a polyrhythm starts with grasping its basic structure.
Imagine two different rhythmic patterns, say in quarter notes and eighth notes or sixteenth notes, played at the same time.
This combination creates a layered texture of sound, where the interplay between the rhythms results in a rich tapestry of beats.
The beauty of polyrhythms lies in their versatility, ranging from:
- Simple polyrhythms, easily perceivable to the ear.
- To highly complex ones that challenge even professional musicians.
As a digital music producer, recognizing and appreciating the role of polyrhythms in your music is crucial.
They are more than just a technical aspect of music 一 they are an expressive tool that can add depth and character to your beats.
Whether you are working with drums, pianos, or any other instrument, mastering polyrhythms can elevate your music from ordinary to extraordinary.
The Role of Polyrhythms in Modern Music

Polyrhythms are not confined to traditional music settings.
They have found a significant place in modern music genres, including jazz, disco, progressive rock, and other popular music.
This crossover has not only expanded the horizons of these genres but has also introduced a broader audience to the intricacy of rhythmic patterns.
In popular music, polyrhythms often serve as a bridge, connecting listeners to more complex musical ideas without overwhelming them.
Many artists have extensively used polyrhythms to create sounds that stand out, as their African origins can transcend different genres.
In jazz, for example, the legendary lead drummer Elvin Jones has employed complex polyrhythms (polyrhythmic drumming) in almost every album to bring a unique flavor.
And, nobody can argue that Elvin Jones is a true superstar, down to his hand drumming.
Similarly, in progressive rock and other forms of popular music, the use of contrasting rhythms helps define the sound and style of numerous influential albums.
The Talking Heads, for example, have many a song that includes a simultaneous combination of rhythms.
This integration of polyrhythms into various music styles demonstrates their versatility and importance.
As a music producer, understanding this can inspire you to incorporate polyrhythms in your own song, adding a layer of sophistication to your beat, album, or EP.
By doing so, you’re not just following a drumming trend 一 you’re engaging with a rich musical tradition that spans across cultures and genres.
Polyrhythms in Practice
Now that we’ve explored the essence and significance of polyrhythms and their generating principle, let’s dive into how they can be practically applied in music production. From common patterns found in various genres (like Jazz or Progressive Rock) to the creative process of incorporating these rhythms into your beats, the world of polyrhythms offers endless possibilities.
-
Common Polyrhythms in Music
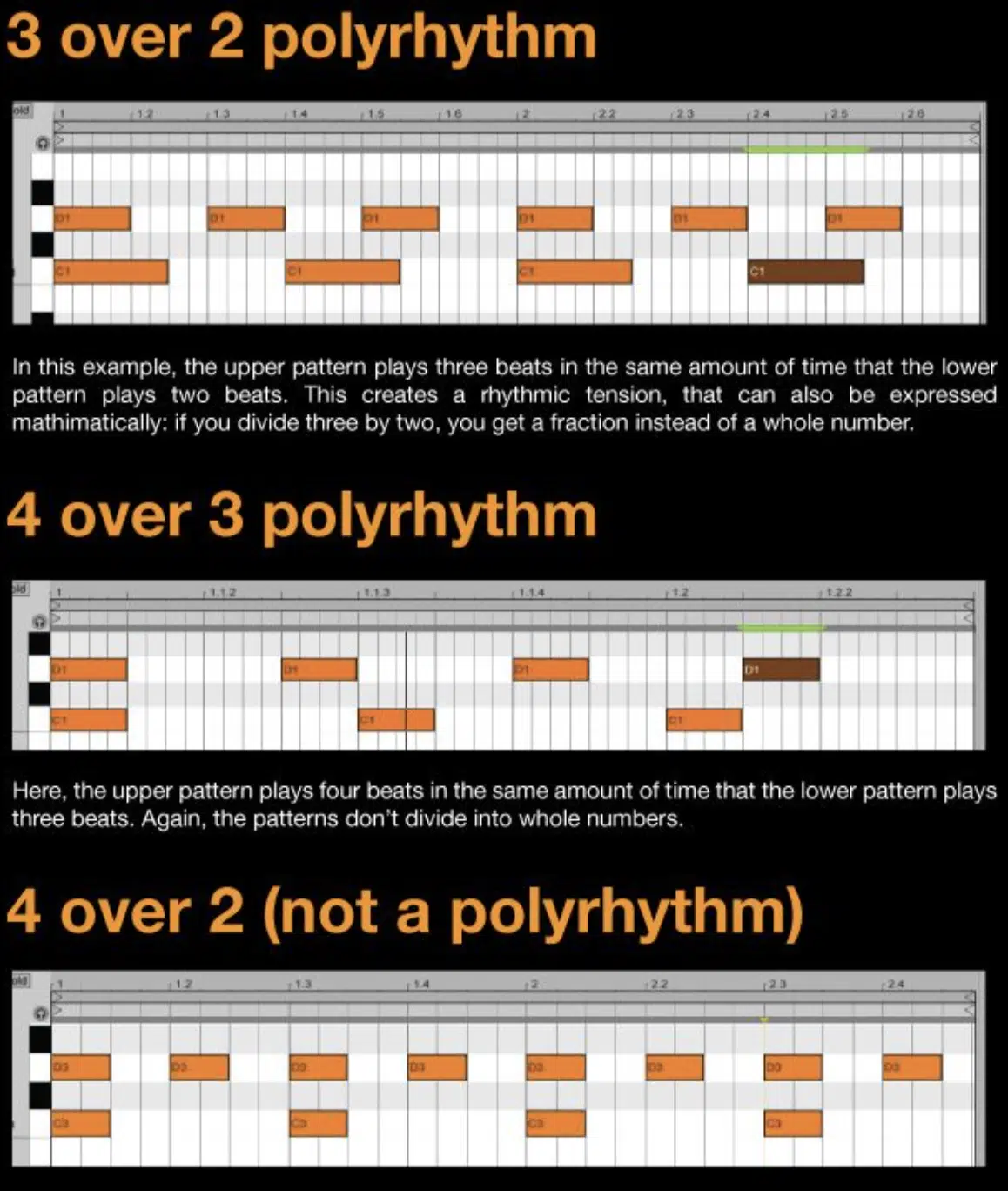
Common polyrhythms found in music often involve simple ratios like 3:2 or 4:3.
These ratios represent the number of beats in each rhythmic pattern within a measure.
For example, a 3:2 polyrhythm would have one rhythm playing three beats per measure, while another plays two.
This results in a syncopated, dynamic rhythm that can add a lively feel to any song.
In African music, such polyrhythms are a fundamental part of the musical landscape, creating a layered, pulsating effect that is both complex and harmonically rich.
These rhythms are not just limited to percussion.
They can be found in the melodic lines and bass patterns 一 providing a holistic rhythmic experience and unique sounds.
In popular music, common polyrhythms are often used to add interest and variety to songs.
They can be subtle polyrhythms, which serve as an undercurrent to the main rhythm, or more pronounced, which take center stage in the composition.
As a producer, experimenting with these common polyrhythms can give your tracks a distinctive edge.
This makes them more engaging, captivating, and memorable.
-
Incorporating Polyrhythms in Your Beats

Incorporating polyrhythms into your beats can seem daunting at first, but with practice, it becomes an exhilarating creative process.
Start by experimenting with different rhythms in your drum patterns.
Playing polyrhythms on drums is a straightforward way to understand how these contrasting rhythms work together.
You can begin with simple polyrhythms and gradually move to more complex combinations.
The simultaneous combination of a beat played by the drummer or digital producer, influenced by various sounds, allows you to hear how each element contributes to the overall polyrhythms.
Another approach is to layer different rhythmic patterns across various instruments.
For instance, your drum line could follow a 3:2 rhythm, while the bass line plays in a contrasting 4:3 rhythm.
This method not only adds depth to your music but also creates a rich tapestry of sound that is both intriguing and harmonically satisfying.
The key to successfully incorporating a polyrhythm in your beat is to maintain a balance so it sounds fluid and appealing.
While it’s tempting to create highly complex polyrhythms, it’s important to remember that simplicity often holds its own charm.
A well-placed simple polyrhythm can be just as effective as a more intricate pattern.
It’s all about how these rhythms serve the overall feel and flow of your song.
NOTE: Experimentation is your best tool here 一 don’t be afraid to try different combinations and see what resonates best with the sound you’re aiming to create.
-
Experimenting with Different Rhythms
Experimentation is at the heart of working with polyrhythms, so make sure to explore the boundaries of rhythmic patterns and how they interact with each other.
Start by playing with common polyrhythms and then gradually introduce more complex rhythms as your song progresses.
Listen to how the different rhythms play off each other to create a unique sonic landscape.
One effective way to experiment is by varying the tempo and seeing how it affects the interplay of rhythms.
- Slower tempos can make complex polyrhythms more discernible.
- Faster tempos can heighten the energy and intensity of the polyrhythmic patterns.
Don’t limit yourself to traditional instruments or sounds when experimenting with polyrhythms in your unique beat.
Digital music production opens up a world of possibilities.
It allows you to create and manipulate rhythms in ways that are not possible with acoustic instruments.
Use software and digital tools to layer, stretch, and morph rhythmic patterns, pushing the boundaries of what can be achieved with polyrhythms in music.
The Technical Aspects of Polyrhythms
Understanding the technical aspects of polyrhythms is crucial for any music producer looking to incorporate them effectively in their work. Let’s break down some key concepts, from the basic notation of rhythms to the more nuanced aspects of polyrhythmic composition.
-
Understanding Quarter Notes and Eighth Notes in Polyrhythms
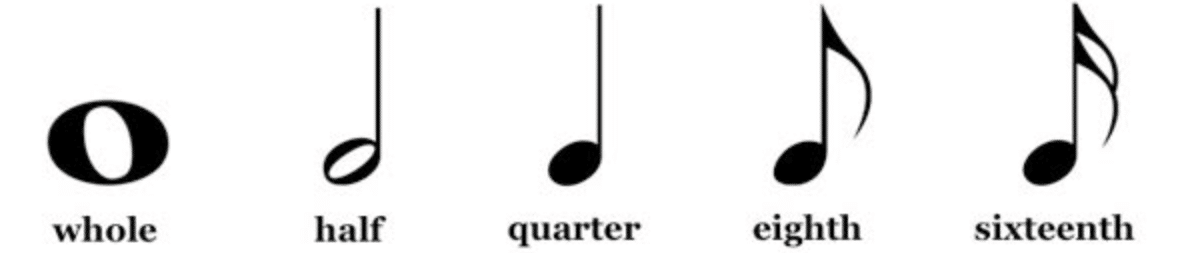
The key to understanding a polyrhythm is grasping the role of basic rhythmic units like quarter notes and eighth notes.
In a polyrhythmic context, these notes can be used to create the foundational layers of contrasting rhythms.
For example, a rhythm in quarter notes played against a rhythm in eighth notes creates a simple yet effective polyrhythms.
NOTE: When you combine dotted quarter notes with syncopations and play them in different metres, you can hear how these elements enrich the rhythmic complexity.
It helps in creating a captivating song/beat that people love.
You’ll instantly hear the intrigue associated with this drumming technique.
The interplay between quarter and eight notes in polyrhythms can be manipulated to create different:
- Sounds
- Textures
- Vibes
- Emotions
By varying the emphasis and dynamics of these notes, you can create rhythms that are subtle or bold, depending on the needs of your music.
It’s essential to understand how these basic rhythmic units work together to form the building blocks of more complex polyrhythmic patterns.
-
Cross Rhythms and Cross Beats
Cross rhythms and cross beats are integral to the fabric of polyrhythms.
Cross rhythm, a term often used interchangeably with polyrhythm, refers to the layering of contrasting rhythmic patterns.
Meanwhile, cross beats are the points where these contrasting rhythms intersect.
These intersections are crucial as they provide the rhythmic tension and release that makes a polyrhythm so captivating.
The significance of cross-rhythms and cross-beats lies in their ability to create rhythmic complexity and interest.
They challenge the listener’s expectations and create a sense of movement and progression within the music.
As a producer, understanding how to effectively utilize cross-rhythms and beats can greatly enhance the dynamism and appeal of your tracks.
Cross rhythms can be used to add a sense of unpredictability and excitement to a piece.
For example, in a 4/4 time signature, introducing a 3:2 cross rhythm can disrupt the predictable flow of the music.
Cross-rhythm techniques like this add an element of surprise that keeps the listener engaged.
This cross-rhythm technique is particularly effective in genres like jazz, trance, house, future bass, and progressive rock, where rhythmic innovation is a hallmark.
-
Complex Polyrhythms vs. Simple Polyrhythms
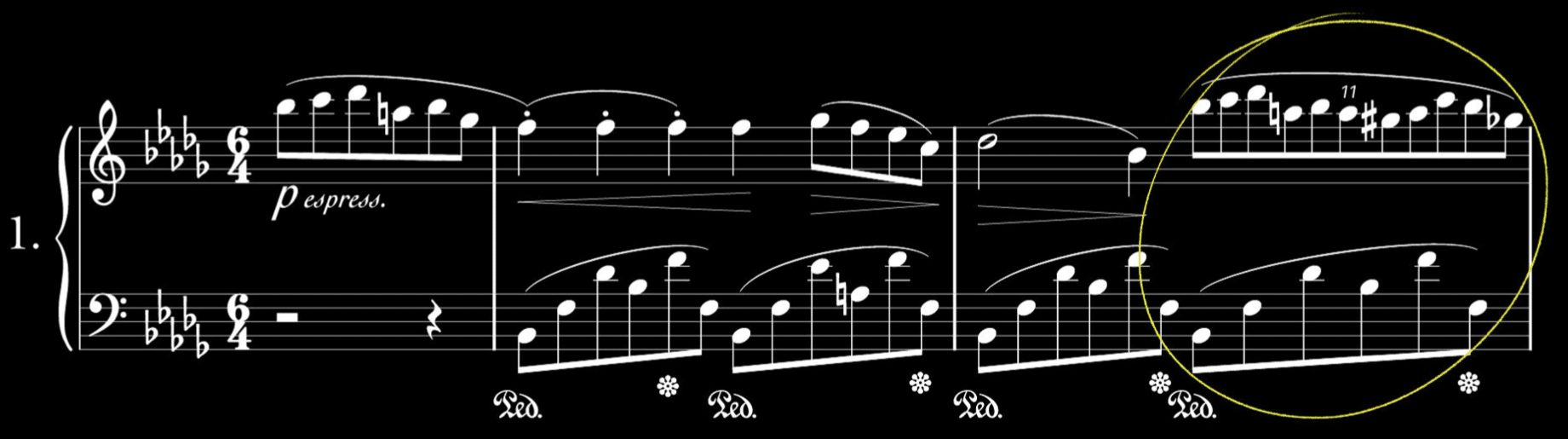

The distinction between complex and simple polyrhythms is crucial for polyrhythmic music producers and audio engineers.
Simple polyrhythms are more straightforward to follow.
They often involve basic ratios like 2:1 or 3:2, making them accessible and enjoyable for a wide range of listeners.
Simple polyrhythms are a great starting point for producers new to this concept, as they provide a foundation for understanding more complex rhythmic structures.
NOTE: By layering multiple rhythmic patterns, a music producer can create a composite rhythm, which is a sophisticated combination of various polyrhythms that work together to produce rich and intricate sounds.
This will help your beat stand out in a major way.
Complex polyrhythms, on the other hand, involve more intricate patterns and ratios.
They can include combinations like 5:4 or 7:3 一 presenting a more challenging listening experience.
These rhythms require a higher level of skill to execute and appreciate, but they offer a richer and more textured soundscape.
It’s important to recognize when to use complex versus simple rhythms in your beats.
While complex polyrhythms can add depth and intricacy to your beat, they can also overwhelm the listener if not used properly.
Balancing the complexity of the rhythms with the overall accessibility of the music is key to creating a harmonious and engaging listening experience.
It’s all about striking the right balance and knowing your audience.
For more mainstream or pop tracks, simpler polyrhythms might play more effectively.
While genres like jazz or experimental polyrhythmic music might lend themselves well to the extensive use of more complex patterns.
Advanced Polyrhythmic Techniques
As we delve deeper into the world of polyrhythm, it’s time to explore some advanced techniques. These approaches can add a unique flavor to your music, distinguishing your work in a crowded music field.
-
Creating Highly Complex Polyrhythms
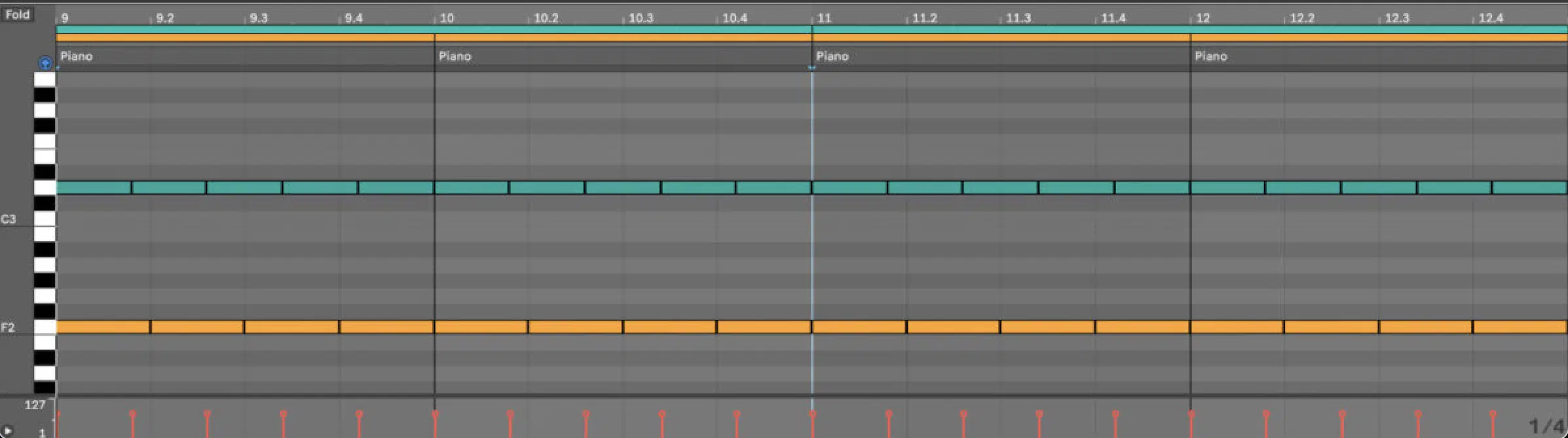
Creating highly complex polyrhythms is an art form that requires a deep understanding of rhythmic music theory and a keen ear for detail.
These polyrhythms often involve layering multiple rhythmic patterns (each with a different meter) to create a dense and intricate rhythmic tapestry.
The key is to maintain a coherent overall structure while allowing each rhythm to express its unique character.
One approach to creating these complex patterns is to start with a basic rhythm and gradually add layers, adjusting each one to complement the others.
This process requires patience and a willingness to experiment with a simultaneous combination.
The use of digital music production tools can be particularly helpful here 一 allowing for precise manipulation and alignment of rhythmic elements.
When highly complex polyrhythms are played, the interaction between different rhythms can create a sense of tension and release.
It’s the dynamic interplay that keeps the music engaging and unpredictable.
These rhythms can be particularly effective in genres that thrive on complexity and innovation, such as progressive rock, avant-garde jazz, and certain forms of electronic music.
-
Unique Instruments and Their Polyrhythmic Patterns

Polyrhythms are not limited to drums; they can be explored on a variety of instruments.
For example, besides drums, the piano can create contrasting rhythms between the left and right hands, producing a rich polyrhythmic effect.
Similarly, stringed instruments like the guitar or the bass can interweave different rhythmic patterns 一 adding complexity to the music.
Incorporating polyrhythms on these instruments (drums, pianos, etc.) can add a unique dimension to your music.
It allows for a broader sonic palette and can help in creating more emotionally resonant and texturally diverse compositions.
As a music producer, exploring polyrhythm techniques on various instruments can open up new avenues for creativity and innovation.
Practical Tips for Music Producers
Having explored the various aspects of polyrhythms, let’s focus on some practical tips that can help music producers effectively incorporate them into their work. Whether you are new to the polyrhythm world or looking to refine your skills, these suggestions will be invaluable.
-
How to Play Polyrhythms on Different Instruments
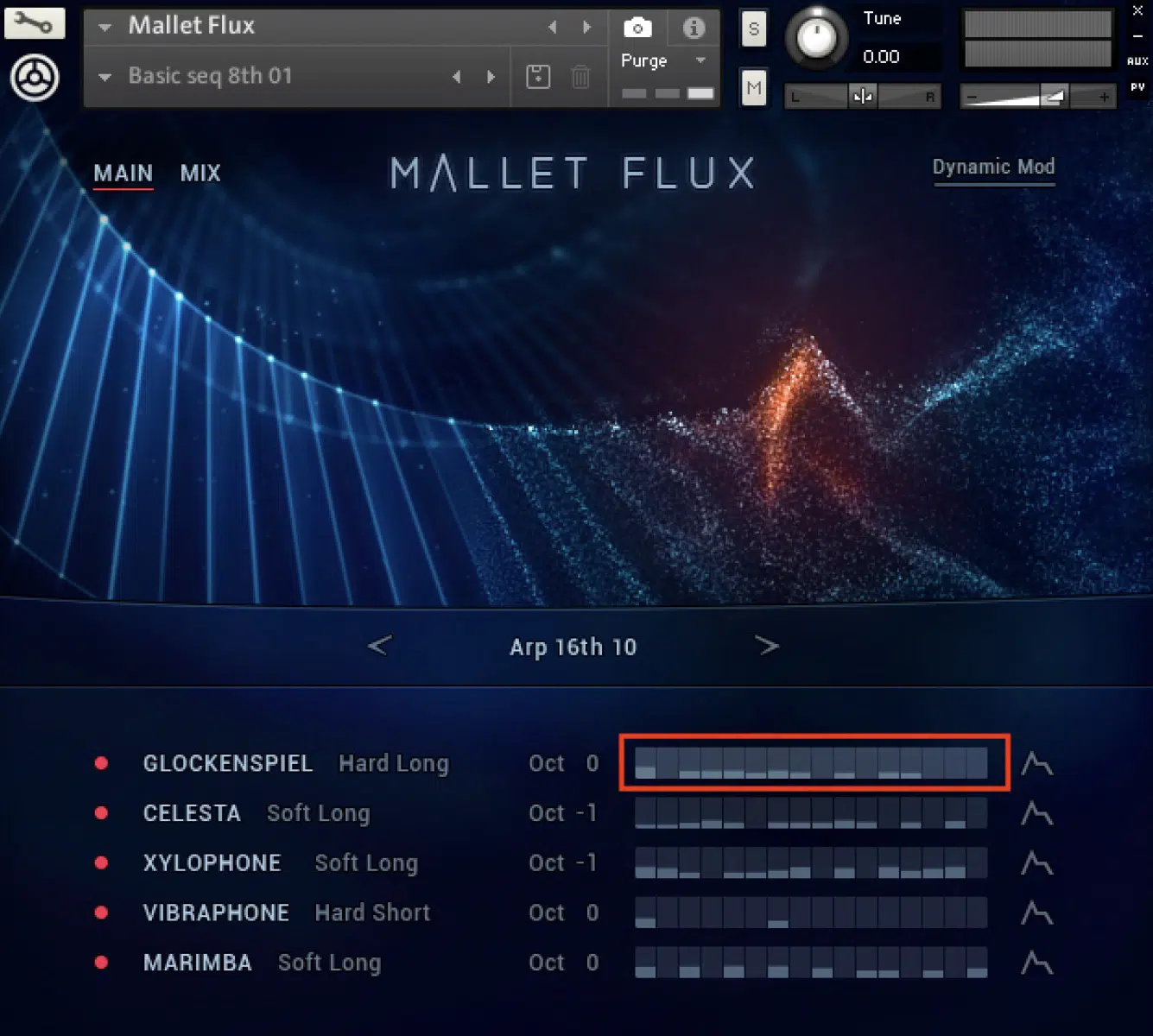
Playing polyrhythms on different instruments requires both technical skill and a good ear for rhythm.
On percussion instruments, such as drums, it involves coordinating different limbs to produce contrasting rhythms simultaneously (simultaneous beats).
This can be challenging at first, but with practice, it becomes more intuitive.
On melodic instruments like the piano or guitar, playing polyrhythms involves using different hands or fingers to create independent rhythmic patterns.
This can add a rich layer of complexity to your music and is particularly effective in solo or small ensemble settings.
It’s important to start slowly, focusing on accuracy and timing, before gradually increasing the complexity and speed of the patterns.
-
Techniques for Recording and Mixing Polyrhythms

Recording and mixing a polyrhythm present unique challenges and opportunities for music producers.
When recording, it’s crucial to ensure that each rhythmic element is captured clearly, maintaining the integrity of the polyrhythmic structure.
This might mean isolating each instrument or rhythm during the recording process to give you more control during mixing.
When mixing your music, balance and clarity are key.
Each rhythmic layer should be discernible, yet harmoniously blended with the others.
To help achieve this balance, pay attention to:
- Equalization
- Panning
- Etc.
For instance, placing contrasting rhythms in different stereo fields can enhance the polyrhythmic effect and make the individual patterns more distinct.
Another technique is to use dynamic processing thoughtfully.
Compression can be used to even out the dynamics of the rhythms 一 ensuring that none overpower the others.
NOTE: It’s important not to overcompress, as this can flatten the dynamic range and reduce the impact of the polyrhythm.
-
Using Digital Tools and Software for Polyrhythm Precision
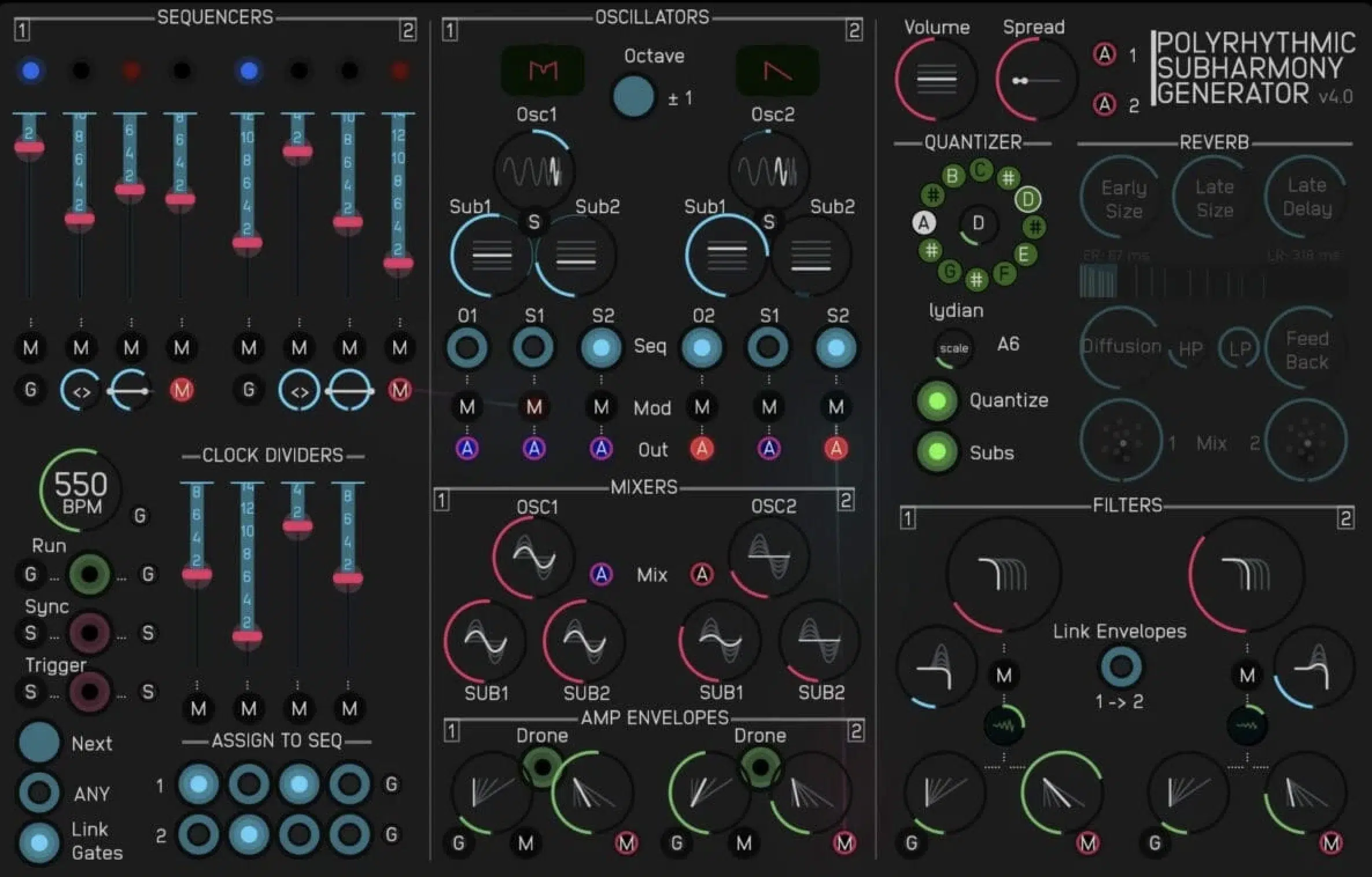
In the realm of digital music production, software and tools have revolutionized the way polyrhythms can be created and manipulated.
Digital audio workstations (DAWs) offer immense flexibility in programming and editing rhythmic patterns.
You can easily experiment with different polyrhythmic structures by adjusting:
- Tempo
- Time signatures
- Rhythm quantization
Many DAWs also offer advanced features such as polyrhythmic loop creation and manipulation, allowing for intricate rhythmic layering and experimentation.
Additionally, MIDI controllers can be invaluable in programming complex polyrhythms, giving you hands-on control and a more intuitive feel for the rhythms.
Using these digital tools, producers can push the boundaries of traditional polyrhythmic concepts, creating novel and innovative rhythmic patterns.
These tools not only make it easier to experiment with a polyrhythm but also open up possibilities for new musical expressions that might be difficult to achieve with acoustic instruments alone.
Final Thoughts
It’s clear that mastering these complex rhythmic patterns is a game-changer for any music producer.
From understanding the basics to exploring advanced techniques, polyrhythms open up a realm of creative possibilities.
They allow you to infuse your tracks with unique textures and rhythms.
To help you put these concepts into practice, you must check out one of the most invaluable resources out there 一 the free Essential MIDI Drum Kits.
This collection is a treasure trove for producers looking to experiment with polyrhythms and enhance their rhythmic arsenal.
The kit includes 5 complete MIDI drum kits, each designed to give you a wide range of rhythmic options.
You’ll find 5 kick MIDI lines, 5 closed hat MIDI lines, 5 open hat MIDI lines, 5 snare/clap MIDI lines, 6 perc MIDI lines, and 2 off-snare MIDI lines.
These meticulously crafted MIDI lines are perfect for experimenting with the polyrhythmic concepts discussed in this article.
Whether you’re layering kicks against off-snares to create contrasting rhythms or blending closed and open hats for a complex rhythmic pattern, these kits provide the ideal starting point.
The versatility of MIDI also means you can tweak and tailor these rhythms to fit perfectly into your musical projects, regardless of the genre.
So go ahead, explore these rhythms, and let your creativity flow.
Until next time…







Leave a Reply
You must belogged in to post a comment.