Time signatures can shape the groove, set the pace, and guide the overall feel/vibe of your music.
They help you structure your beats per measure (BPM) and decide which note values to use for each beat.
As a producer, knowing all about different time signatures will seriously up your game by giving you more control over the rhythm and flow of your tracks.
As well as helping you experiment with unconventional rhythms, time signatures are key to creating unique and engaging music.
That’s why we’re breaking down everything you need to know about what are time signatures in music, like:
- What time signatures consist of ✓
- Beats per measure and note values ✓
- Common time signatures in music production ✓
- Advanced time signatures for complex rhythms ✓
- How to switch time signatures in your DAW ✓
- Layering tracks with different time signatures ✓
- Syncing multiple time signatures ✓
- The most common time signatures ✓
- Creative uses for unconventional time signatures ✓
- Tips for choosing the right time signature ✓
- The impact of time signatures on groove & feel ✓
- Real-world examples of different time signatures ✓
- More to help you answer, ‘what are time signatures in music ✓’
After this article, you’ll know everything about time signatures, so you can confidently lay down tracks that groove and flow exactly how you want.
Plus, you’ll be able to experiment with more unconventional rhythms and push your creativity further, which is always a plus.
This way, your tracks will stand out from the competition, and you’ll be able to create music that’s both innovative and impactful.
So, let’s dive in…
Table of Contents
What are Time Signatures in Music? Breaking it Down
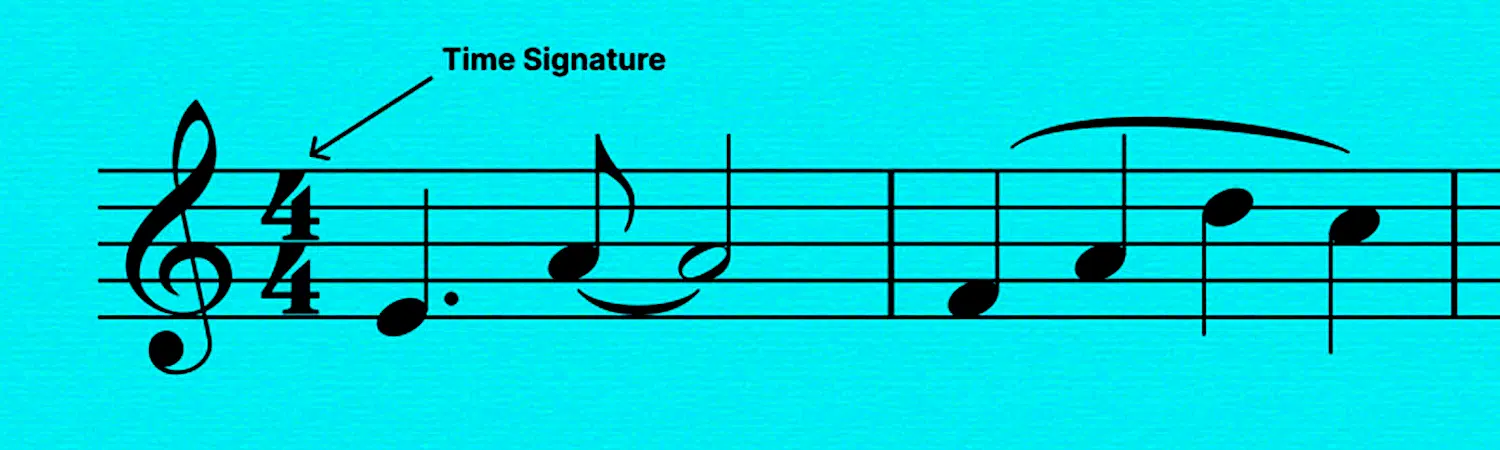
When diving into music production, understanding time signatures is key.
But what are time signatures in music, exactly?… Well, time signatures tell you how many beats are in each measure and which note value represents one beat.
In most Western music notation (sheet music), you’ll see time signatures at the beginning of a piece of written music, right after the key signature.
These meter signatures are like the foundation for your track 一 setting the framework for the rhythm.
Knowing what time signatures in music are and how they work helps you create tracks that groove, move, and connect with listeners on a deeper level.
Don’t worry, we’ll be breaking down everything in detail throughout the article, especially pertaining to digital music production.
The Components of a Time Signature
To really understand time signatures in sheet music and digital production, you need to break them down into their main components: beats per measure and note values. These two elements work together to define the rhythmic structure of your music. So let’s get into it.
-
Beats Per Measure
The first number in a time signature tells you how many beats per measure there are.
For example, in a 4/4 time signature, the “4” on top indicates that there are four beats per measure (shown above).
Again, understanding the beats per measure is key because it sets the foundation for the rhythm of your track.
Whether you’re working with three beats per measure, five beats per measure, or the standard four beats per measure, this number defines the basic pulse that listeners feel.
In genres like electronic dance music, having a steady four beats per measure is common because it provides a consistent and danceable rhythm.
However, if you’re looking to experiment, you can explore time signatures with different beats per measure, like seven or even eleven.
The number of beats per measure influences how your music flows and can add a unique twist to your tracks.
Knowing how to manipulate the beats per measure in your tracks gives you more creative control over the rhythmic structure.
Whether you stick to the common four beats per measure or venture into more complex rhythms, mastering this concept is key to becoming a skilled music producer.
-
Note Values
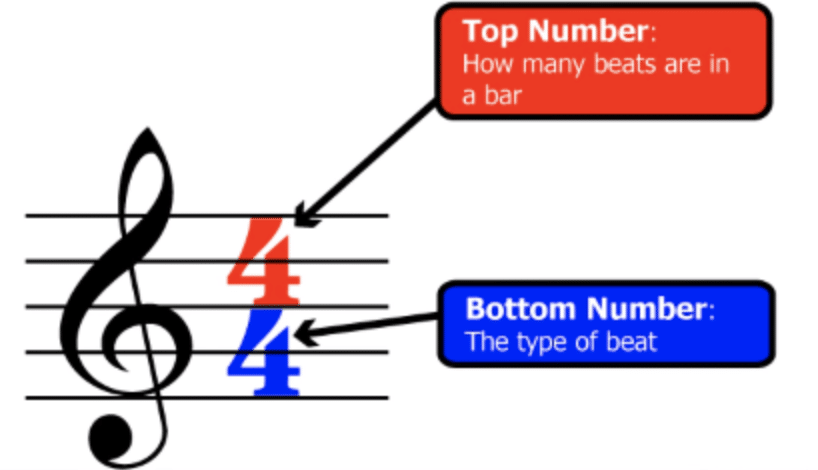
The bottom number in a time signature represents the note value that equals one beat, for example, in a 4/4 time signature, the “4” on the bottom tells us that each beat is a quarter note.
Understanding note values is just as important as beats per minute because they determine the rhythm’s pacing and how the beats per measure are divided.
If the bottom number is “8,” it means each beat is an eighth note, which changes the feel of the rhythm compared to a quarter note.
When it comes to more complex time signatures, you might encounter a sixteenth note as the basic unit 一 providing an even faster rhythmic pulse.
For producers, playing around with note values can lead to some seriously interesting rhythmic textures and outcomes.
For instance, using eighth notes or even sixteenth notes within a 4/4 time signature can give your track a faster, more energetic feel.
On the flip side, quarter notes can create a more laid-back, steady groove.
Experimenting with different note values in your tracks will help you discover how they impact the overall feel and timing, which is a powerful tool in music production.
Whether you’re working with quarter notes, eighth notes, or more complex note values, mastering how they interact with the beats per measure will up your game all day.
Common Time Signatures in Music Production
In music production, some time signatures are more commonly used than others, of course. These are the ones you’ll likely encounter most frequently, especially in genres like electronic dance music, pop songs, and hip-hop.
-
4/4 Time
4/4 time is known as “common time” for a reason… It’s by far the most used time signature in modern music production.
With four beats per measure and the quarter note representing each beat, 4/4 time is straightforward yet versatile.
It’s the go-to time signature for:
- Electronic dance music
- Pop songs
- Countless other genres
This is because it provides a steady, easy-to-follow rhythm.
You can use 4/4 time when you want to create tracks with a strong, predictable groove, but remember you can always switch things up.
The simplicity of four quarter notes in each measure makes it easier to build layers of sound and keep everything in sync.
Whether you’re making a club banger or a more chilled-out track, 4/4 time offers a familiar outline that listeners will instantly recognize (and vibe to).
Understanding how to work within this common time signature is essential for any music producer looking to create great music that connects with audiences.
Which, let’s face it, is what production is all about.
-
3/4 (Triple Time)
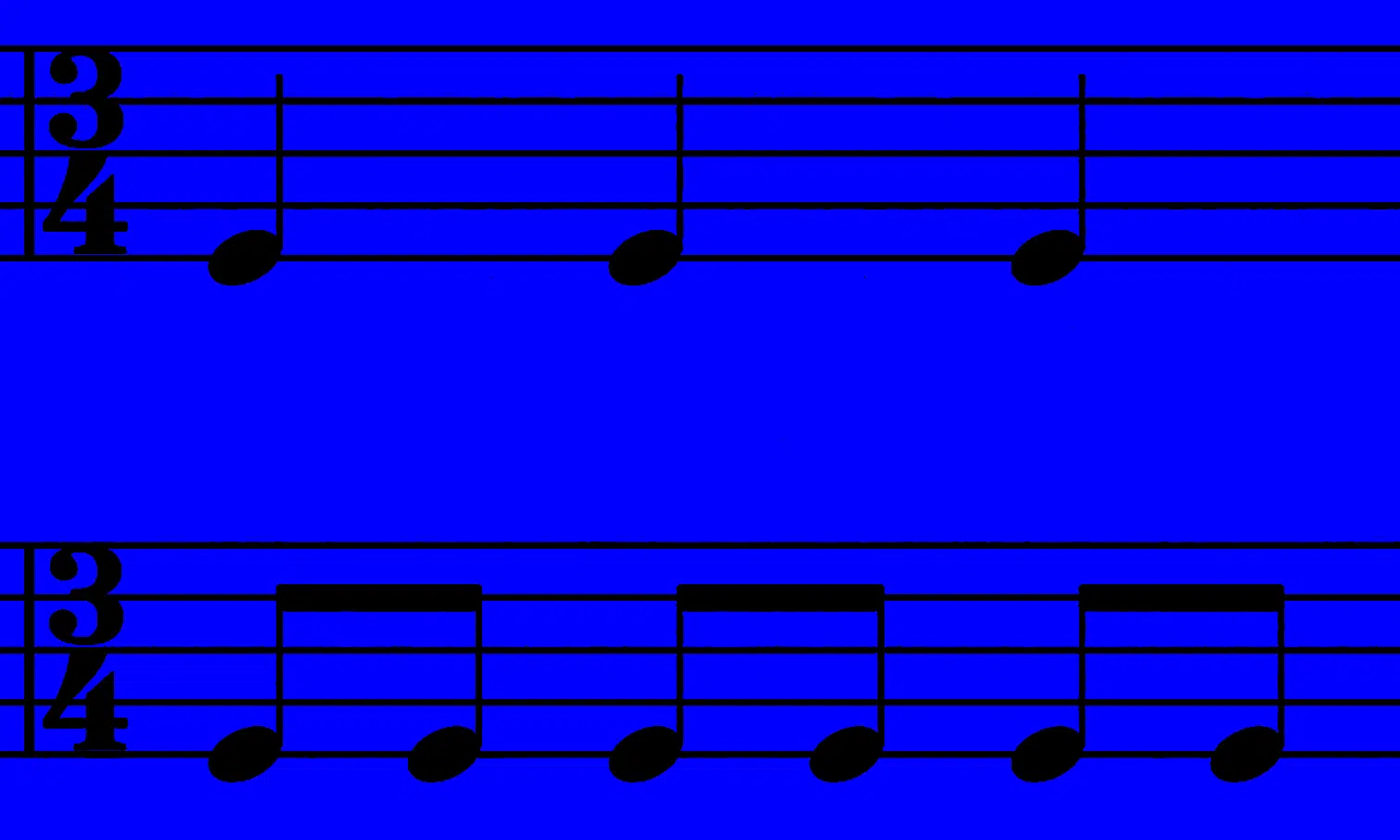

3/4 time (triple time) gives your music a distinct feel with three beats per measure.
Unlike the steady pulse of 4/4, 3/4 time creates a lilting, circular rhythm that’s perfect for slower, more melodic tracks.
Each measure in 3/4 time is divided into three quarter notes, which gives the rhythm a rolling motion.
This time signature isn’t as common in electronic dance music, but it’s popular in genres that require a more flowing, elegant feel(think “When The Party’s Over” by Billie Eilish).
If you want to add a unique twist to your productions, try experimenting with 3/4 time, it really couldn’t hurt.
The three beats per measure can lead to some interesting rhythmic patterns that stand out from the typical 4/4 time.
Whether you’re producing a slow jam with some depth or just looking to break away from the norm, 3/4 time provides a fresh alternative that can set your music apart.
-
6/8 Time: Common Compound Time Signatures
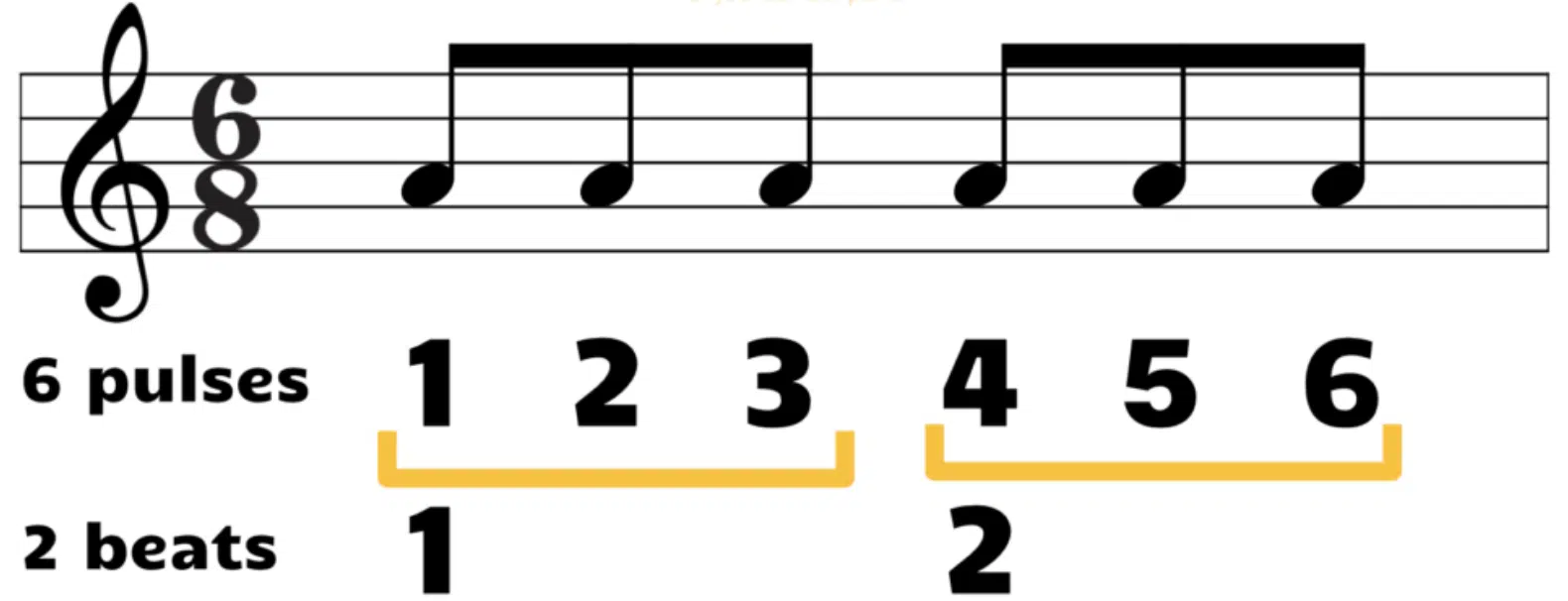
6/8 time is a compound time signature, which means it combines the feel of both simple and compound meters.
In 6/8 time, there are six beats per measure, but these beats are grouped into two sets of three eighth notes each…
This grouping creates a rhythmic feel that’s different from simple time signatures like 4/4 or 3/4.
You’ll often find 6/8 time in genres that need a flowing, yet driving rhythm, such as blues, rock ballads, R&B, or even some electronic dance music believe it or not.
Actually the biggest one I can think of off the top of my head is Adele’s ‘Someone Like You’ which, love it or hate it, was super popular.
The compound time signatures like 6/8 time allows for a smooth, swinging feel that can add a lot of emotional depth to your tracks.
When producing in 6/8 time, you might notice that it lends itself well to triplet-based rhythms 一 giving your music a unique groove.
Understanding how common compound time signatures like 6/8 work can open up some new possibilities for your music.
Whether you’re aiming for a soulful R&B record or a more emo vibe, 6/8 time offers a versatile foundation that can enhance your productions in general.
Advanced Concepts in Time Signatures
Beyond the common time signatures, there are more complex and irregular time signatures that can add a unique character to your music. Exploring these advanced concepts can help you push the boundaries of traditional music production, whether it’s your first beat or 100th.
-
Complex Time Signatures
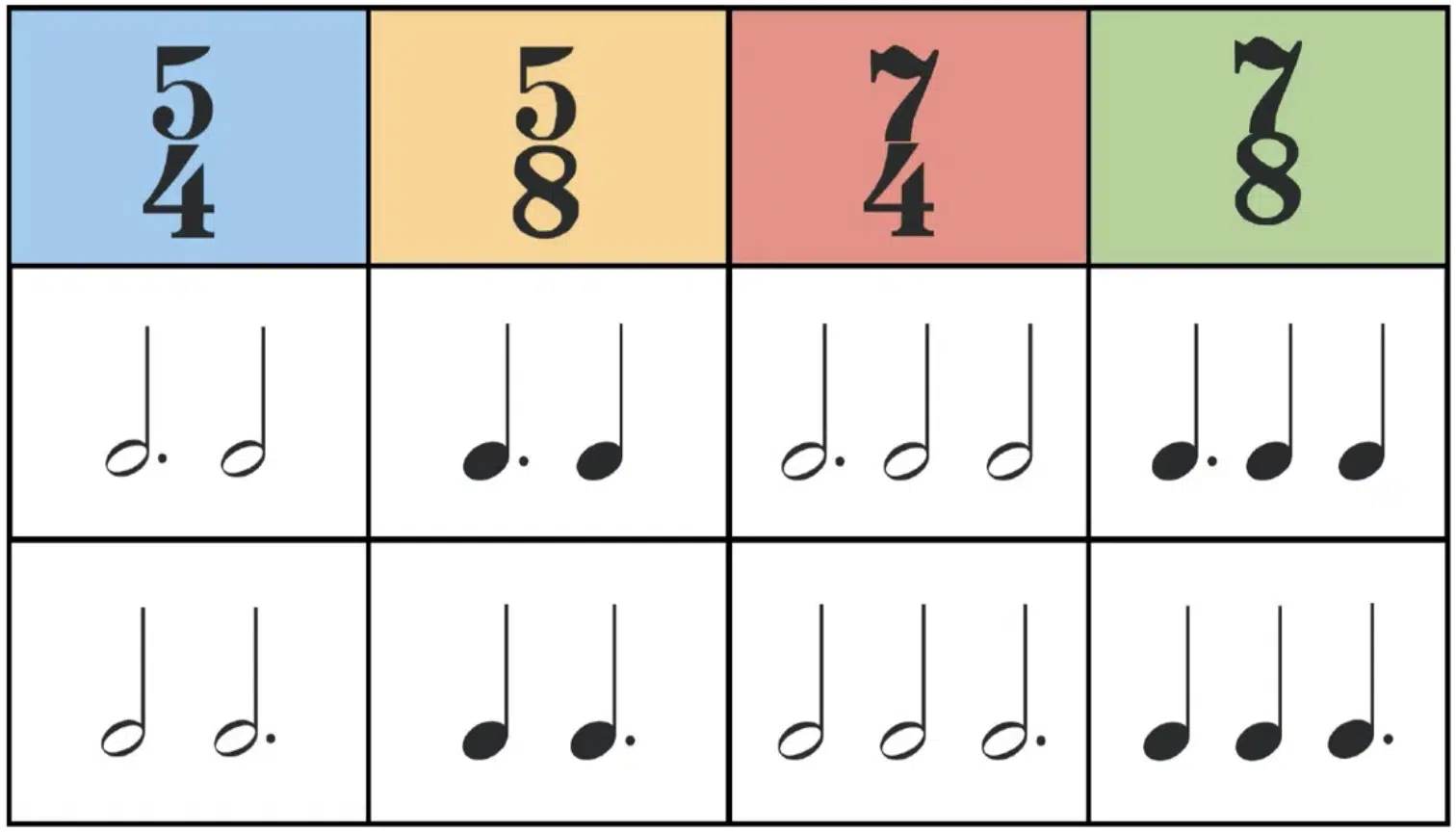
Complex time signatures, like 5/4 or 7/8, break away from the conventional patterns you find in common time.
These time signatures have an odd number of beats per measure, which creates a more unpredictable, off-kilter rhythm.
For example, 5/4 time signature consists of five beats per measure, with each beat typically being a quarter note.
This uneven number of beats in each measure makes complex time signatures perfect for genres that thrive on unusual rhythms, like progressive rock or jazz fusion.
Remember, hybrid genres are taking over right now for real.
If you’re looking to create music that stands out, experimenting with complex time signatures is a great way to do it.
These complex time signatures challenge both the producer and the listener 一 making your tracks more engaging and memorable.
Pro Tip

Working with complex time signatures requires a solid understanding of music theory, as it can be a little tricky to keep everything in sync.
But once you get the hang of it, using these time signatures can add a new layer of sophistication and creativity to your music production.
If you want a refresher course on music theory, we’ve got you covered.
-
Irregular and Mixed Time Signatures
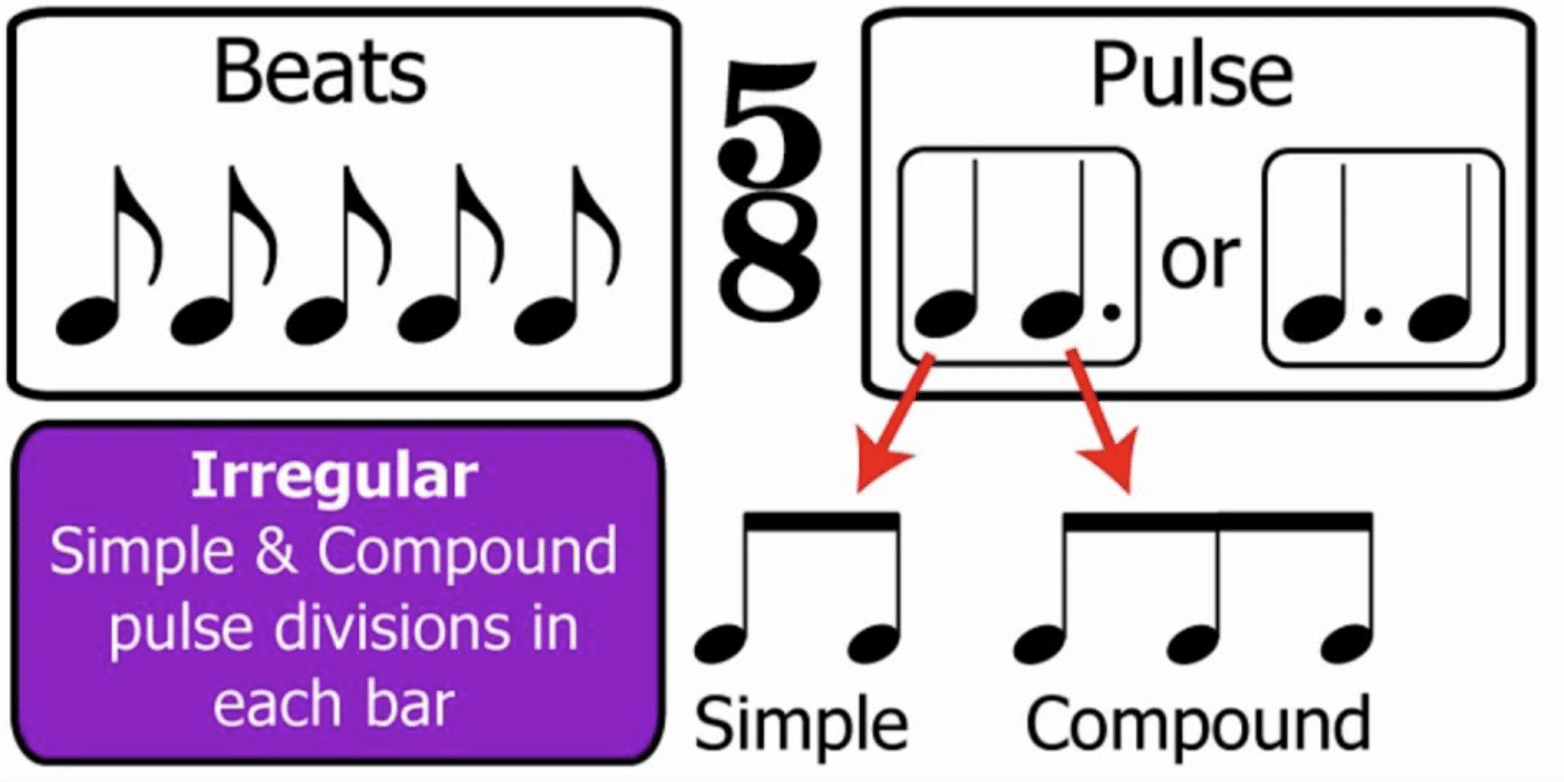
Irregular time signatures are those that don’t follow the typical patterns of 2, 3, or 4 beats per measure.
Instead, they might have 7, 11, or even 13 beats per measure 一 leading to very unconventional rhythms that catch people by surprise (categorized as simple or compound).
Mixed time signatures, on the other hand, involve alternating between different time signatures within the same piece of music.
For instance, a song might switch between 4/4 and 3/4 time, which creates a dynamic and unpredictable rhythmic structure.
Such time signatures are often found in genres that really go hard when it comes to experimentation, like progressive metal or avant-garde music.
If you want to challenge yourself as a producer, try incorporating irregular or mixed time signatures into your tracks.
These time signatures can add a level of complexity and originality that’s hard to achieve with standard meters (which is great).
While they might be tricky to master, the results can be incredibly rewarding, giving your music a distinctive edge.
-
Polyrhythms and Time Signatures
Polyrhythms involve layering different rhythms on top of each other, often in different time signatures, for a super interesting sound.
For example, you might have a drum pattern in 4/4 time playing alongside a melody in 3/4 time, creating a complex interplay of rhythms.
Polyrhythms are common in genres like African music, jazz, and progressive rock, where the rhythmic complexity adds some extra intrigue to the music.
Incorporating polyrhythms into your process can make your tracks more rhythmically awesome and engaging.
Pro Tip
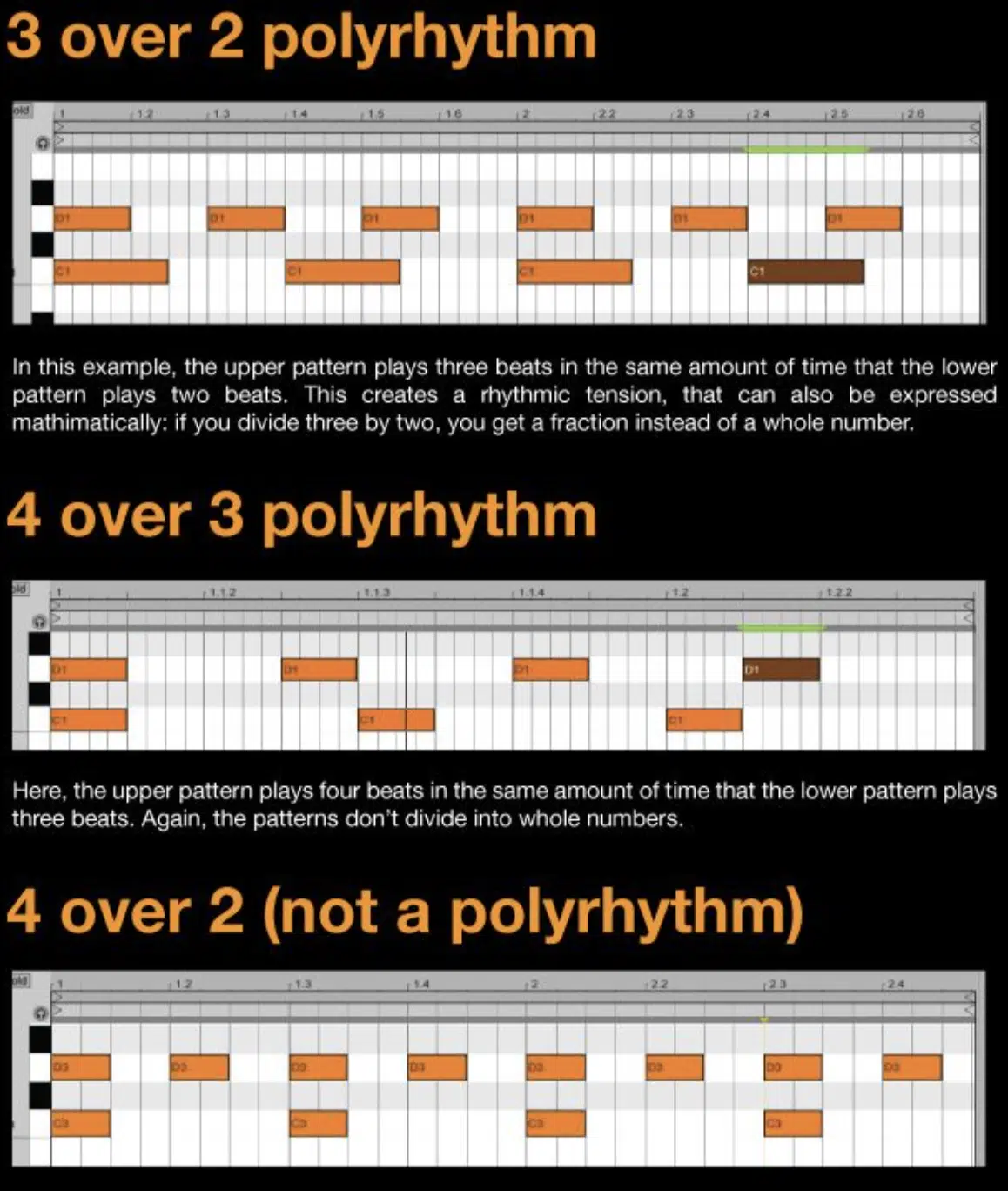
Working with polyrhythms requires careful attention to how the different time signatures interact…
The key being to ensure that the different layers of rhythm complement each other rather than clash, because nobody wants that.
By mastering polyrhythms, you can add a new level of professionalism to your music, making it stand out in a crowded market, which is pretty hard nowadays.
Music Production Musts: Time Signature Edition
When producing, understanding what are time signatures in music is just the beginning. Knowing how to apply them correctly in your tracks can elevate your production skills and give your music a professional edge.
-
Understanding Impact on Groove and Feel
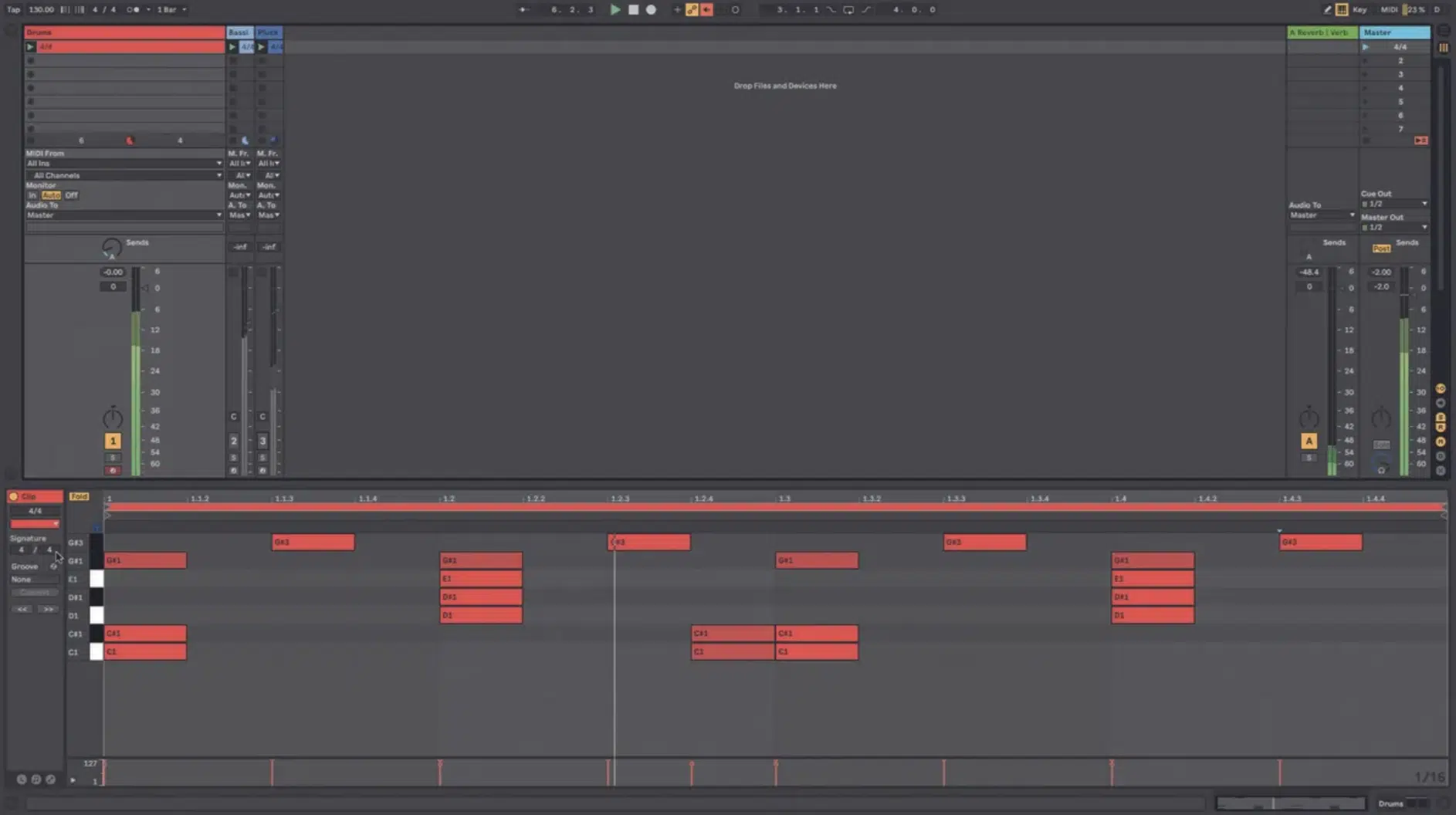
The time signature you choose directly impacts the groove and feel of your track.
For example:
- A 4/4 simple time signature offers a steady, driving rhythm perfect for upbeat tracks.
- A 3/4 or 6/8 time signature can give your music a more flowing vibe.
If you’re producing a track with a strong beat, like in electronic dance music, sticking to common time signatures will make it easier to create a groove that listeners love.
On the other hand, if you want to experiment with unusual time signatures, like 7/8 or 9/8, you can create a more off-kilter, intriguing feel that sets your music apart.
Just be mindful of how the time signature influences the overall vibe, as it’s a powerful tool in shaping the listener’s experience.
-
How to Change Time Signatures in Your DAW
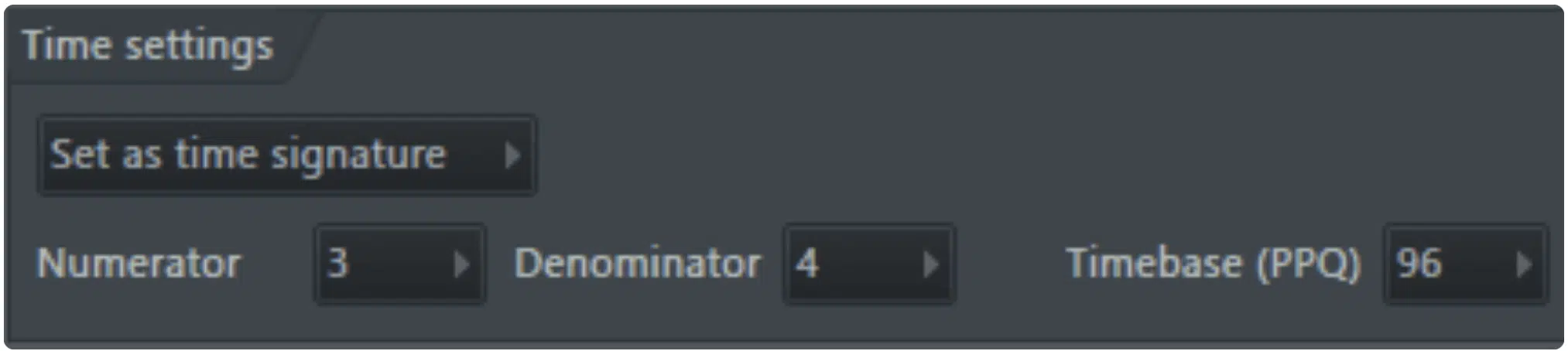
FL Studio Time Settings
Changing time signatures in your DAW (Digital Audio Workstation) is a straightforward process, but it varies slightly depending on the software you’re using.
In FL Studio, you can change the time signature by adjusting the beats per measure (numerator) and note value (denominator) in the settings menu, which will apply the new time signature to your project.
In Ableton Live, the time signature is located in the top left corner of the interface, where you can easily switch between different time signatures as you experiment with your track’s rhythm.
Logic Pro X also makes it simple to change the time signature 一 you can do this by accessing the “Signature List” in the Global Tracks area.
Remember, when you change the time signature, it will affect how your beats per measure are counted and how note values are represented in your project.
This change can alter the feel and flow of your track in a major way, so it’s very important to choose a time signature that matches with your creative vision.
Whether you’re working with a common time signature or something more complex, mastering how to change time signatures in your DAW will give you greater control.
-
Layering and Syncing Tracks with Different Time Signatures
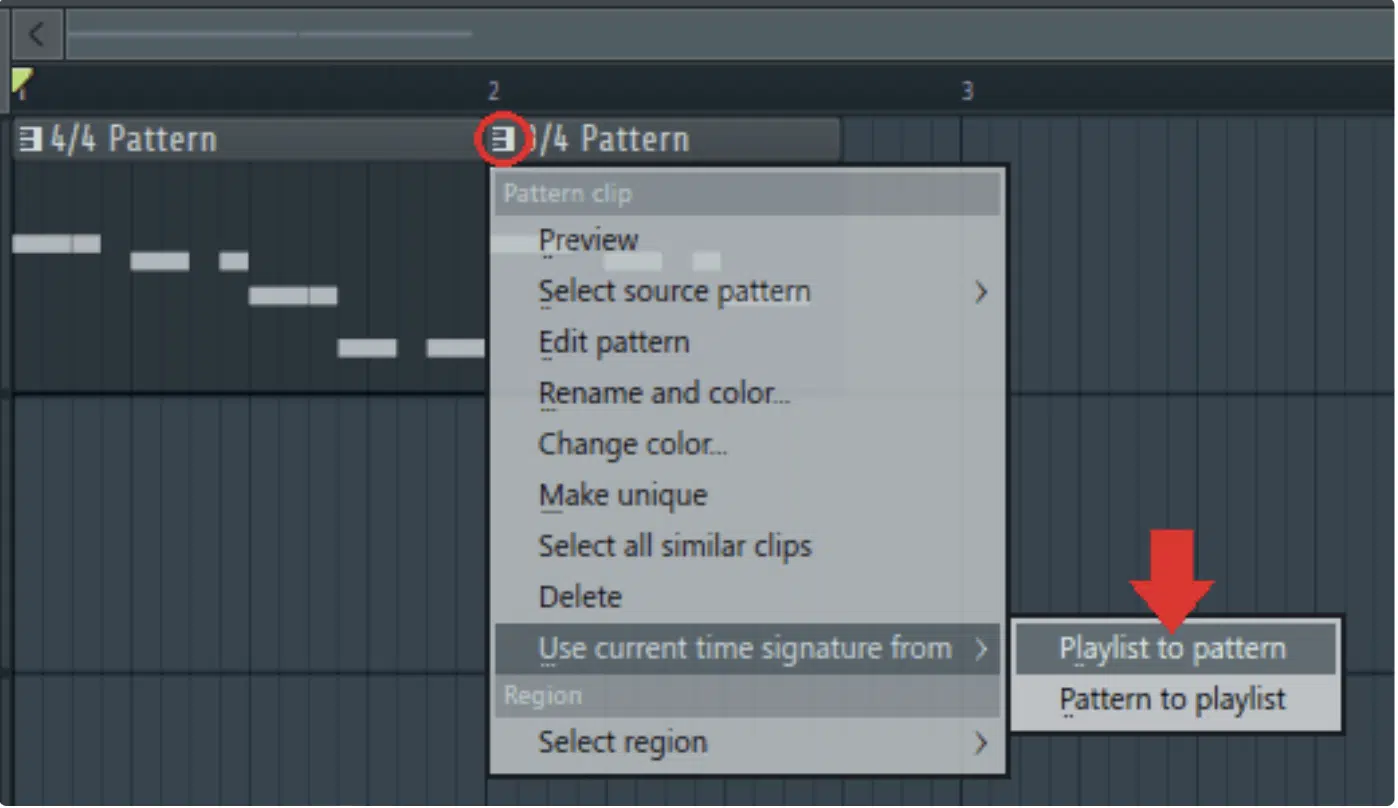
FL Studio
Layering and syncing tracks with different time signatures can add a unique dimension to your music, but it requires careful planning, so don’t slack here.
For instance, if you’re layering a 4/4 time signature track with a 3/4 time signature track, you need to make sure that the beats per measure align in a way that makes sense.
Rhythmically speaking, that is.
One way to approach this is by finding a common note value, like an eighth note, and using it as a reference point to sync the tracks.
Another method is to adjust the tempo of one track so that the beats per measure match up more naturally.
Pro Tip
When done correctly, layering different time signatures can create a sick, polyrhythmic texture that adds extra complexity and interest to your music.
However, if not synced properly, it can result in a disjointed and confusing rhythm that throws off the listener, which you certainly don’t want.
As a producer, it’s important to experiment with different combinations and find the sweet spot where the time signatures complement each other rather than clash.
-
Working with Multiple Time Signatures
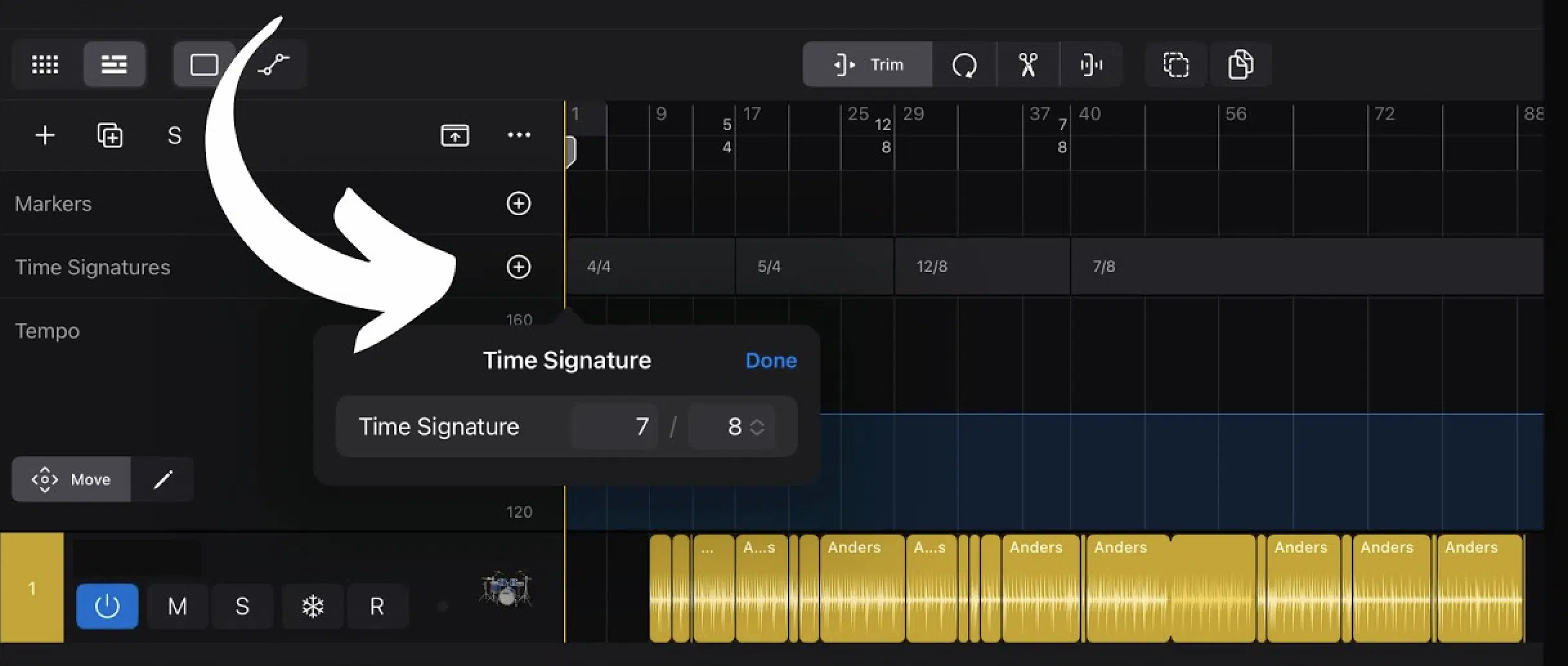
Working with multiple time signatures in a single track can be a powerful way to create dynamic and evolving music.
For example, you might start your track in a 4/4 time signature and then switch to 7/8 or 5/4 in a different section to create a contrasting feel.
This technique is used a lot in genres like progressive rock, jazz, and electronic music to keep the listener hooked with unexpected rhythmic changes.
To make these transitions smooth, try using a transitional section where the beats per measure gradually change 一 easing the listener into the new time signature.
Because remember, if I said it once I’ve said it a thousand times, music production is all about tension and release.
Pro Tip
Another tip is to keep a consistent note value, like quarter notes or eighth notes, between the different time signatures to maintain a sense of continuity.
By mastering the use of multiple time signatures, you can add a new level of complexity and creativity to your music.
It makes it more engaging and memorable for your audience.
-
Syncing Tracks in Different Signatures
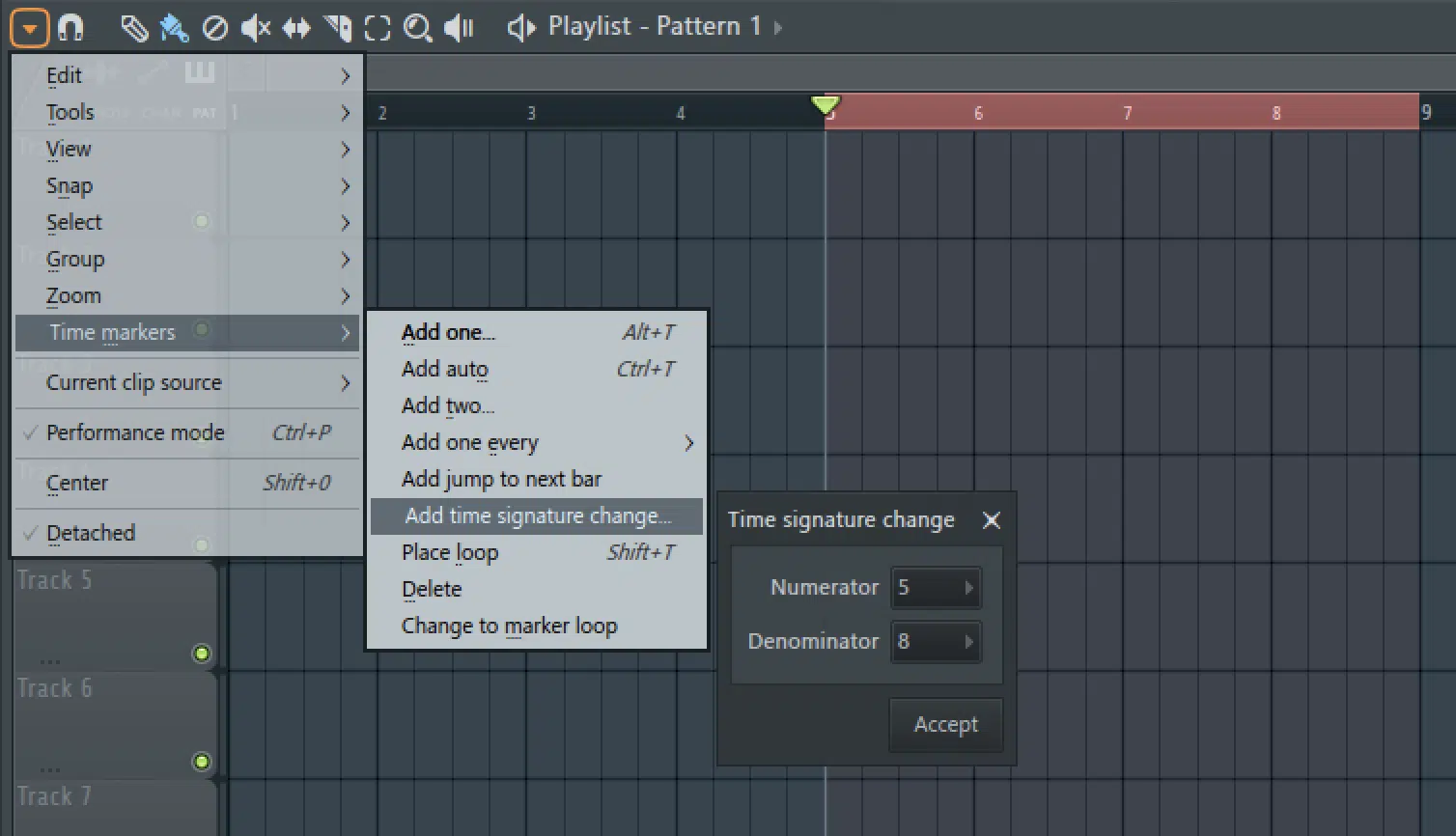
Syncing tracks with different time signatures requires a keen understanding of rhythm and timing.
One helpful tip is to use a click track or metronome set to a common note value to keep everything in synth, like:
- Quarter notes
- Eighth notes
- Sixteenth notes
Another approach is to create a “guide track” that combines elements from both time signatures 一 acting as a bridge between the different sections of your song.
This guide track can help you maintain a consistent tempo while allowing the different time signatures to coexist harmoniously.
If you’re working in a DAW, you can also use automation to gradually transition between time signatures for a smoother, more natural switch up.
Pro Tip
You can also use markers or labels within your DAW to clearly define where each time signature starts and ends to help you stay organized as you work.
By following these tips, you can successfully sync tracks in different time signatures, adding complexity and interest to your music without losing the overall groove.
Bonus: Creative Applications
Time signatures are more than just a way to organize beats 一 they can be a powerful tool for innovative, immersive music production.
-
Additive Time Signatures
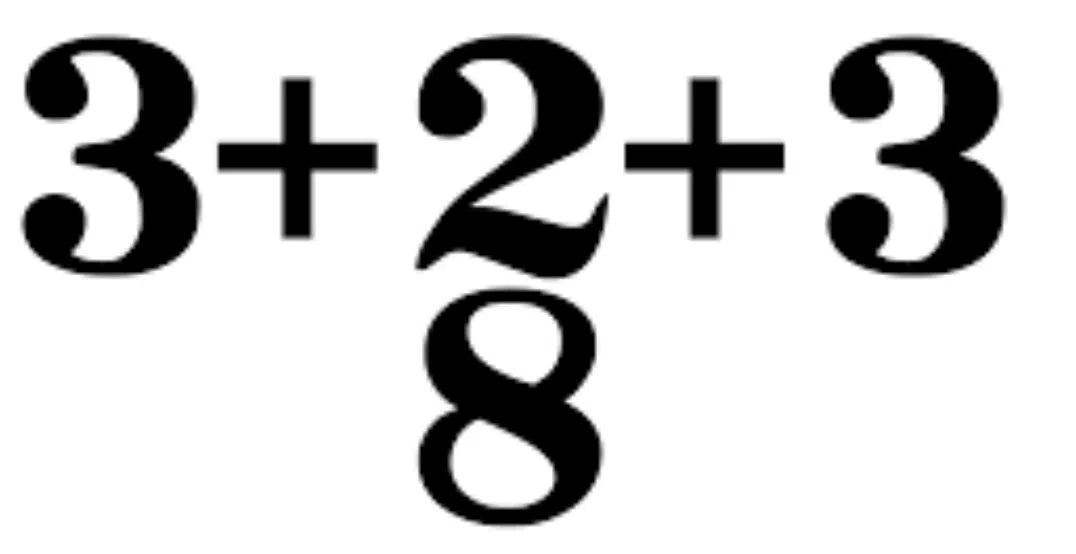
One advanced technique is to use additive time signatures, where you combine different lengths of beats within a single track. For instance, you could create a pattern where a measure starts with a whole note followed by a quarter note and ends with a half note. It produces a sick rhythm.
-
Metric Modulation
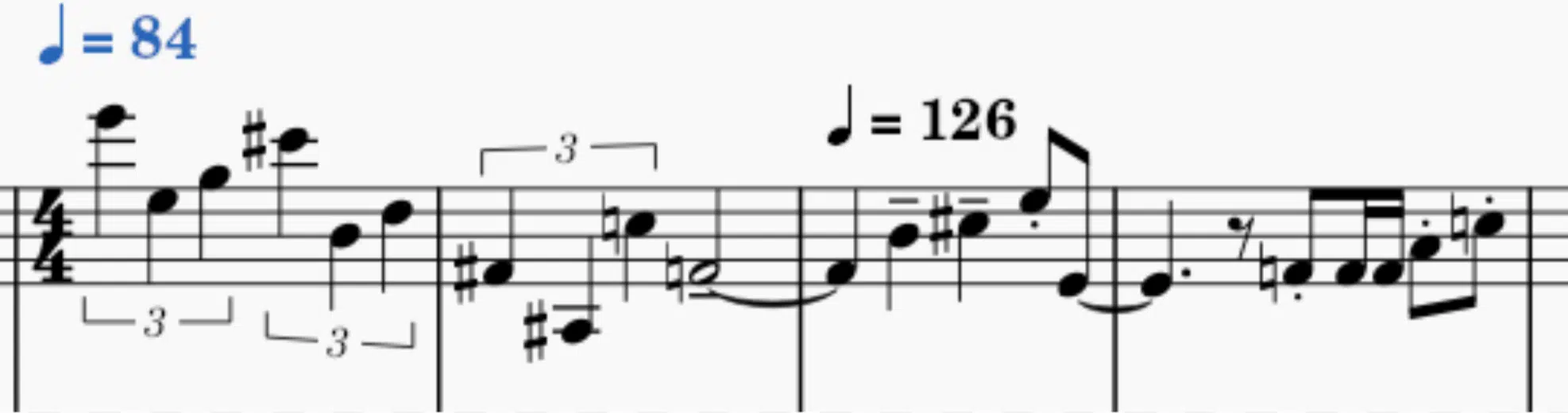

You can also experiment with metric modulation, where you change the perceived pulse of the track by shifting from an eighth note-based rhythm to a half note-based rhythm. This alters the groove without changing the time signature itself.
-
Explore Odd Time Signatures
If you’re exploring odd time signatures, consider using a structure where a measure contains two beats followed by a whole note. It will give your music an off-kilter, intriguing rhythm.
-
Displaced Time Signature

Another creative approach is displaced time signatures, where you intentionally move the downbeat. Start with a phrase with one half note instead of a quarter note, for example, to create a sense of rhythmic displacement. This technique is super effective in genres that embrace unconventional rhythms (which most do).
-
Include All The Notes, Baby!

Finally, you could challenge the listener by laying down a rhythm that includes all the notes from a half note to an eighth note, ending with two half notes in the same measure. This creates a complex and engaging song structure. By creatively using time signatures in these ways, your tracks will have a distinctive edge 一 making them stand out in any playlist.
What are Time Signatures in Music: Final Thoughts
Time signatures are the foundation of rhythm in music, as you now know, helping you to shape the groove, dictate the pace, and provide structure to your tracks.
Plus, they can help you experiment with different rhythmic feels and explore unconventional patterns that set your music apart.
And, if you get super creative, you can blend different time signatures and rhythms, which will really make your productions stand out.
If you want to dive even deeper into music theory and master every aspect, the highly-renowned Songwriting Secrets course is a perfect fit.
This legendary (and super popular) course will help you understand everything from key signatures and what are time signatures in music, to arrangement and structure.
Plus, it will help you lay down better melodies, polish your songs more effectively, and be able to use time signatures like a professional.
This way, you’ll never have to worry about getting stuck in a rhythmic slump or making your tracks sound repetitive ever again.
It’s a surefire way to enhance your songwriting and production skills altogether.
So, whether you’re just starting out or looking to refine your skills, understanding what are time signatures in music will give you the tools needed for professional tracks.
So, keep experimenting, stay creative, and let your music make a lasting impact.
Until next time…







Leave a Reply
You must belogged in to post a comment.