Harmonics are a fundamental aspect of music production.
They often act as the building blocks that give your music depth, texture, and a distinctive character.
Understanding how they work and how to manipulate them can significantly elevate the quality and uniqueness of your tracks.
As a music producer, getting a grip on harmonics is key to standing out and developing your signature sound.
Luckily, we’re breaking it all down for you today, including:
- What are harmonics? ✓
- Fundamental frequencies ✓
- The role of overtones ✓
- The harmonic series ✓
- Harmonics & pitch: a closer look ✓
- The significance of Hz in production ✓
- Creating unique sounds & timbre ✓
- Instrumental harmonic creation ✓
- Wavelength & signal manipulation for texture ✓
- Much more ✓
By the end of this guide, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of what harmonics are and how they contribute to the sound you produce.
This way, you can successfully craft your signature sound, create legendary songs, and elevate your production game.
So, let’s dive in…
Table of Contents
Harmonics: The Basics, Broken Down
Harmonics are the building blocks of every sound you’ve ever heard (except a pure sine wave, of course).
Understanding them is the key to crafting everything from the perfect synth sound to a crystal clear mix, so let’s break it down.
-
What Are Harmonics & Why Are They So Important?
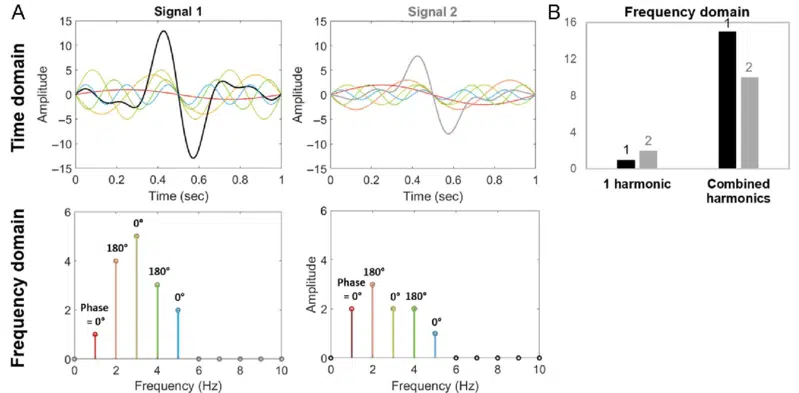
Harmonics are integral components of a sound wave that exist at integer multiples of the fundamental frequency.
They add character and richness to the sound; defining the timbre that distinguishes one musical instrument from another.
For us digital music producers, harmonics are crucial.
They allow us to successfully:
- Manipulate sounds
- Create unique textures
- Briing that extra flair to our tracks
Playing with harmonics is like taking a block of ice and chipping away at it until it creates a beautiful, pristine sculpture.
A practical example is when a guitar string is plucked.
The string vibrates at the fundamental frequency 一 producing the basic pitch.
But there are also various harmonics (overtones) vibrating at integer multiples of this fundamental which adds additional complexity and richness to the sound.
Throw a guitar pedal on it and the distortion takes those multiples and then adds multiples of that, which is legendary.
Don’t worry, after this article you’ll never have to ask yourself “what are harmonics?” again.
-
Defining The Fundamental Frequency
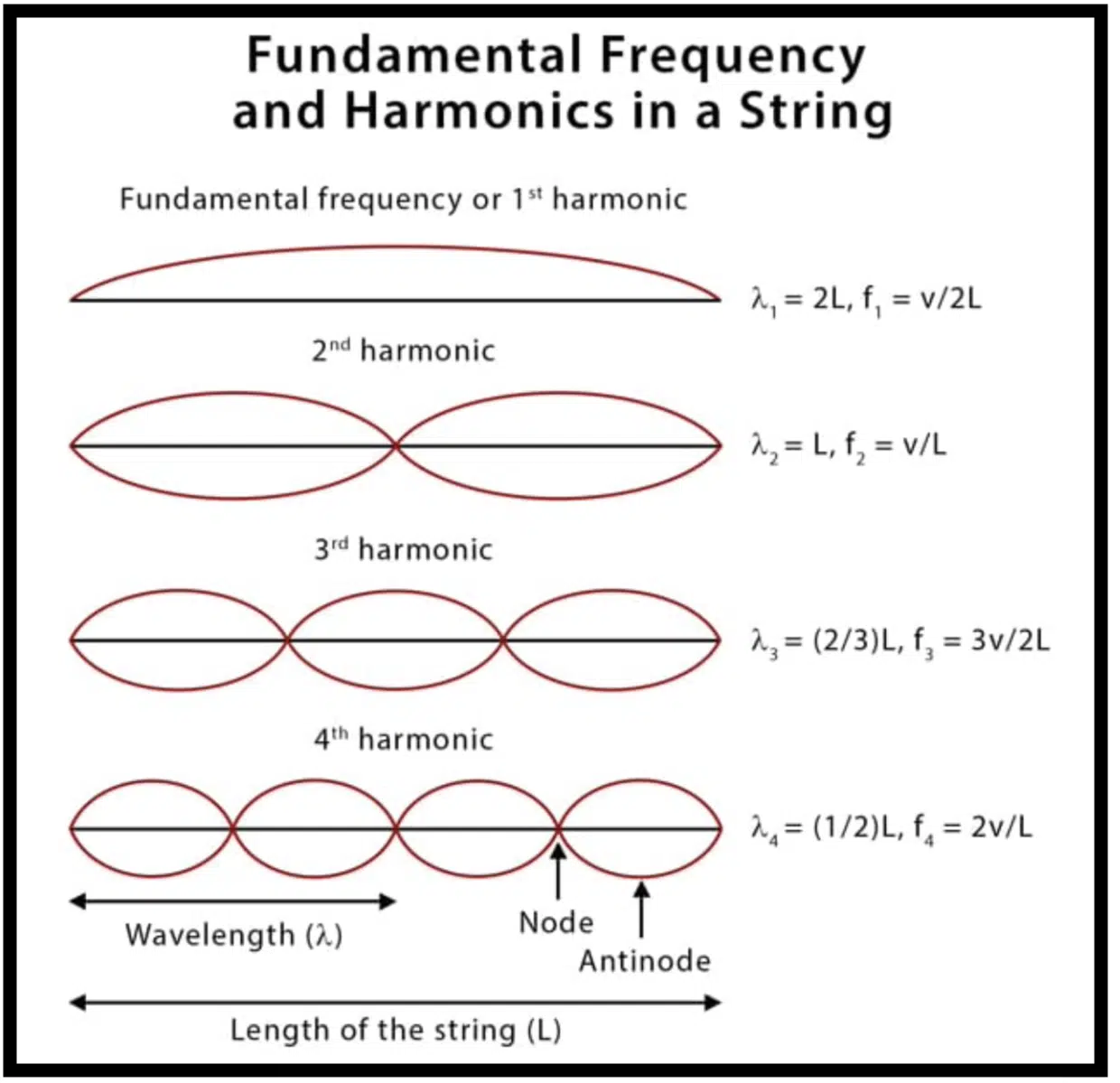
The fundamental frequency is the backbone, the first harmonic of any sound.
It’s the lowest harmonic frequency of a periodic waveform and determines the pitch of the musical note.
But it’s the harmonic frequencies (the higher harmonics, to be exact) that can add additional color and vibe your tracks.
The fundamental frequency is the true heartbeat of a sound.
It’s measured in Hz and is essential for determining the musical note and pitch.
NOTE: When you pluck a guitar string, the fundamental frequency is the first sound you hear, the first harmonic.
In music production, manipulating the fundamental frequency (fundamental note) can alter the pitch and pure tone of the sound.
For instance, if you’re producing a trap beat and you tweak the fundamental frequency of a sample, you’re essentially shaping the character of your track.
Instruments, both string instruments and wind instruments, have unique fundamental frequencies.
The vibrations of a guitar string or the air inside a flute create distinct fundamental frequencies 一 which dictate the pitch of the note played.
Understanding and manipulating fundamental frequency relationships allow you to explore creative avenues of production.
Whether you’re looking to mimic the raw energy of open strings, the smooth flow of wind instruments, or even the human voice itself (think air column), it all starts with the fundamental frequency.
-
Role of Overtones in Music
Overtones are all the harmonics except the fundamental frequency.
They’re the additional frequencies that vibrate along with the fundamental, adding depth and dimension to the sound.
In the realm of digital music, an overtone can be your best friend.
They allow you to shape and mold the sound, to create textures that make your beats stand out.
Imagine tweaking the overtones of a synth to craft a unique trap lead; that’s the power of understanding overtones!
NOTE: Subtractive synthesis and additive synthesis are essentially just two different ways to manipulate harmonics and overtones.
Different instruments produce different overtones.
The overtones of a guitar string vibrating are distinct from those of a blowing trumpet.
Recognizing these differences enables you to replicate instrument sounds digitally, giving authenticity to your tracks.
It’s the series of overtones each unique sound or stringed instrument contains that defines it (other than the pitch, that is).
Experimenting with overtones can lead to discovering new soundscapes.
For instance, manipulating the overtones of a square wave can yield interesting results 一 opening doors to innovative beats and textures in hip-hop production.
This is because a square wave is simply a fundamental frequency (sine wave) and odd harmonics of that particular fundamental.
You can use a low-pass filter to reduce or silence harmonics in the upper range.
This will enable you to create something much softer, less harsh than a square wave, plus so much more.
-
The Harmonic Series: Broken Down
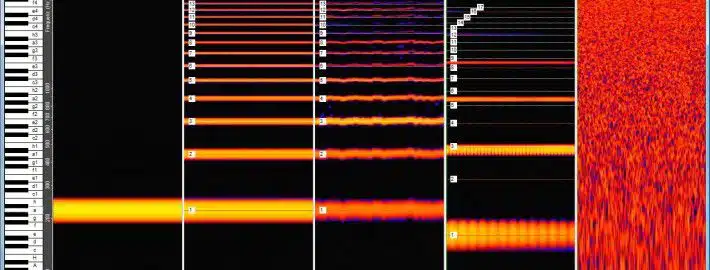
The harmonic series is a musical theory fundamental, showcasing the relationship between the fundamental frequency and its harmonics.
It’s a sequence of frequencies that occur naturally in the vibration of any given sound.
For example, when an open string is plucked, the harmonic series is produced; compromising the fundamental and various harmonics.
These harmonics, at integer multiples of the fundamental, create the complexity and richness we hear in a musical note.
Exploring the harmonic series unlocks the door to sound manipulation.
By understanding how harmonic frequencies relate to the fundamental, you gain the ability to shape and mold sounds in our digital music production journey.
This is especially true when it comes to creating synths/instruments in any popular genre.
In fact, sometimes the sound that fits a given genre is actually defined by its harmonic series, so it’s very important that you know about them.
The harmonic series is not just theory 一 it’s a practical tool.
It’s all about:
- Experimenting with sounds
- Discovering new textures
- Creating music that truly resonates
Whether it’s tweaking the second harmonic, third harmonic or fourth harmonic for a punchy snare or manipulating the harmonic series for a lush pad, the possibilities are endless.
So, make sure that you really get acquainted with harmonic series, as they can help make your music stand out in a major way.
Unpacking the Octave & Musical Notes
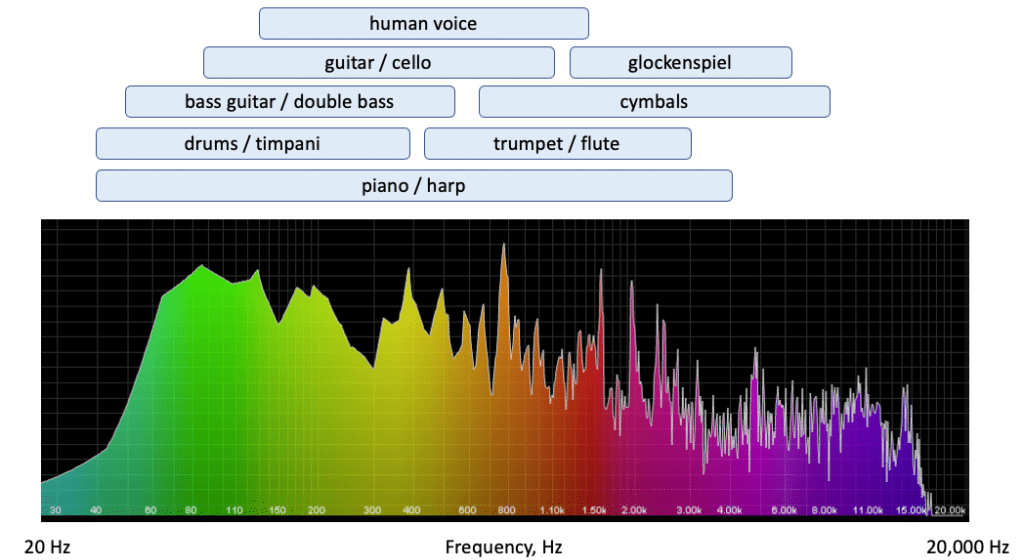
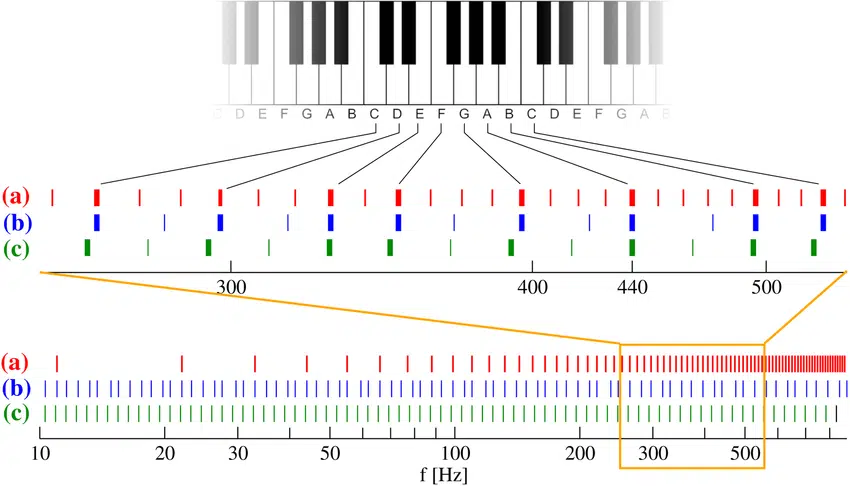
An octave in music is a natural frequency interval, where the higher note is twice the frequency of the lower note; connecting musical notes and harmonics.
It’s somewhat simple math, as you just keep doubling the harmonic frequency per octave (it’s not three times the frequency, it’s double).
For instance, the ‘A’ above middle C resides at 440Hz; therefore, the octave above that would be 880 Hz.
When you play two musical notes an octave apart, they are the same note, just in a different pitch.
This is due to the harmonic relationship between the frequencies 一 the higher note is double the frequency (Hz) of the lower note, not one half.
For us producers, understanding octaves is crucial.
It allows you to:
- Create harmony and balance in your tracks
- Layer sounds effectively
- Construct melodies that resonate
Whether it’s layering basslines in trap or harmonizing melodies in hip-hop, octaves are most certainly key.
The relationship between octaves and musical notes is not just theoretical 一 it’s a practical tool for music creation.
By manipulating octaves, you can alter the feel and vibe of your tracks, creating music that is both innovative and harmonious.
NOTE: It’s also key when it comes to mixing and mastering EQ, as you’ll know exactly where and when a given cut/boost should be implemented.
So, needless to say, it’s very beneficial to know.
The Significance of Hz in Music Production
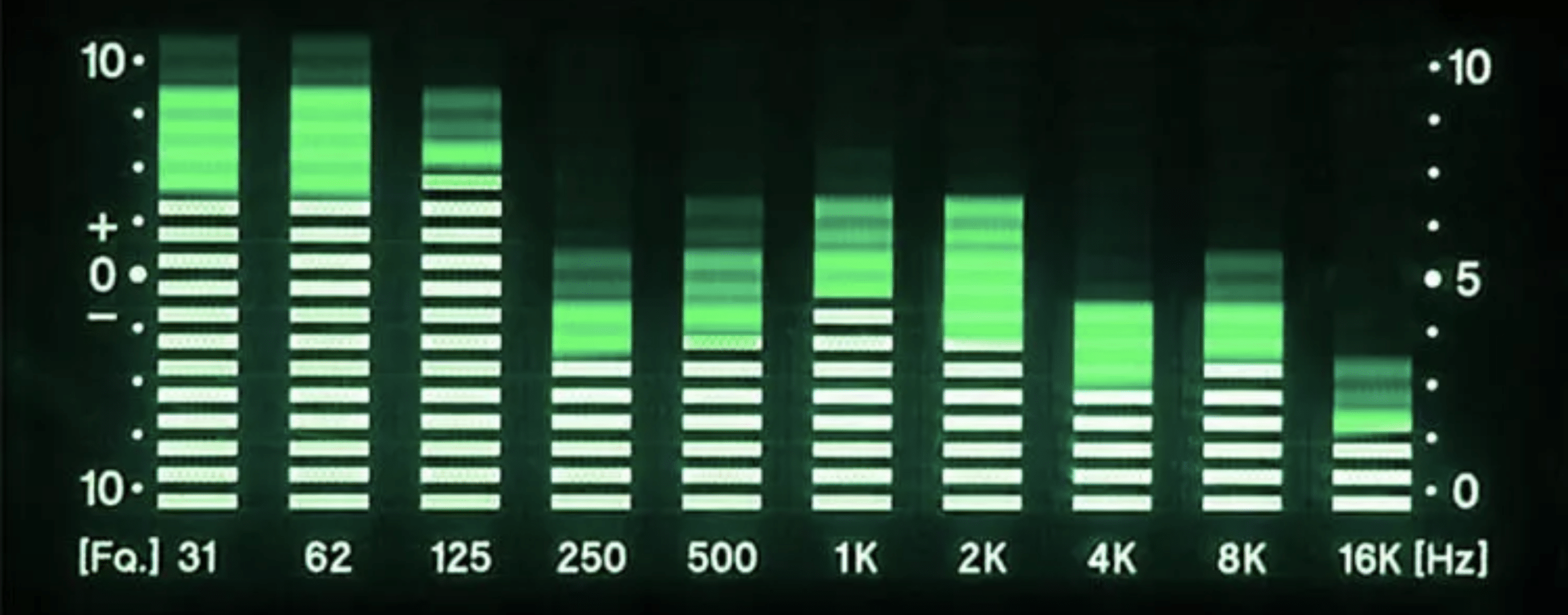
Hz, or Hertz, is the unit of measurement that represents the number of cycles per second; corresponding to the pitch of any given audio signal.
As a music producer, understanding Hz is super important as it directly relates to the same pitch of the musical note.
Every single musical note out there corresponds to a specific frequency in Hz.
For instance, the note A4 corresponds to 440 Hz…
When we manipulate this frequency in our digital audio workstation, we are essentially altering the pitch of the note; creating variations in our music.
You do this through mathematical equations, as the key to music and sound are vibrations, and the overtones you create can be figured out with some simple math (as touched upon above).
The world of digital music production offers endless possibilities for manipulating Hz.
Understanding the significance of Hz is the very first step in successfully mastering sound design, whether it’s:
- Producing bass-heavy trap beats
- Creating high-pitched leads in a hip-hop track
- Or anything in between
Remember, Hz is not just a number 一 it’s a representation of sound.
It’s about feeling the vibe, understanding the mood, and creating music that leaves a lasting impression in your listeners heads and hearts.
Whether you’re aiming for a chill vibe or an energetic beat, Hz is the key to discovering a soundscape that occupies the entire spectrum in a very specific (and desirable) way.
-
How Various Harmonics Affect Pitch
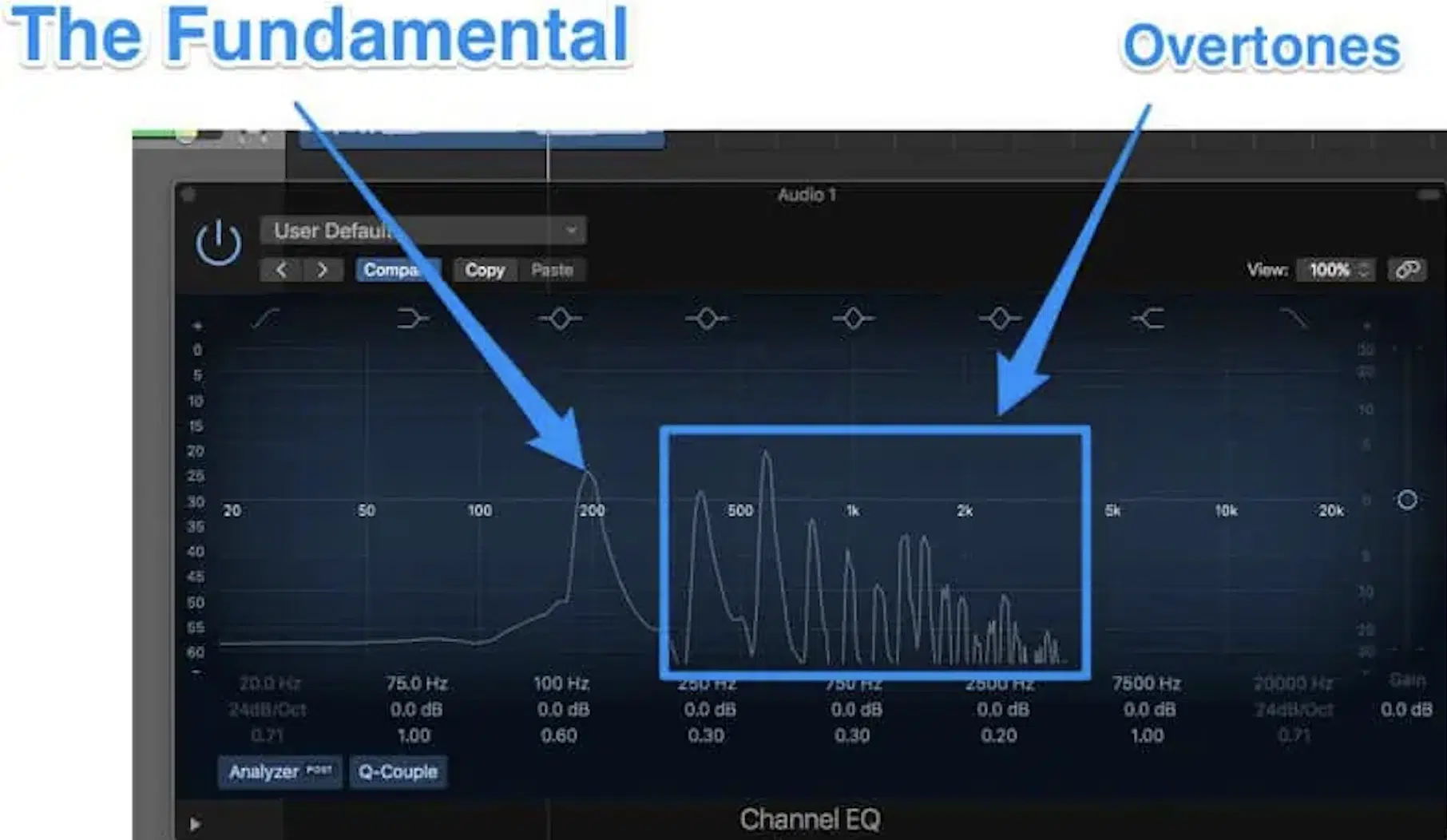
Delving into the nuances, different harmonics interact with the fundamental frequency to influence pitch.
Each harmonic (again, being an integer multiple of the fundamental frequency) contributes to the overall perception of pitch and tonality in a piece of music.
For example, in the production of a hip-hop beat, the interaction between the fundamental frequency and the higher harmonics can either:
- Sharpen the perceived pitch.
- Flatten the perceived pitch.
This subtle manipulation of harmonics is instrumental in crafting the distinct soundscapes that encompass every genre you can think of (like lofi, hip-hop, R&B, etc.).
Instruments naturally produce harmonics that shape their distinctive sounds.
A violin, for instance, generates a combination of both even and odd harmonics that create a sharp, bright sound.
On the other hand, a tuba’s harmonics are predominantly odd (think square waves) 一 resulting in a deeper, richer tone.
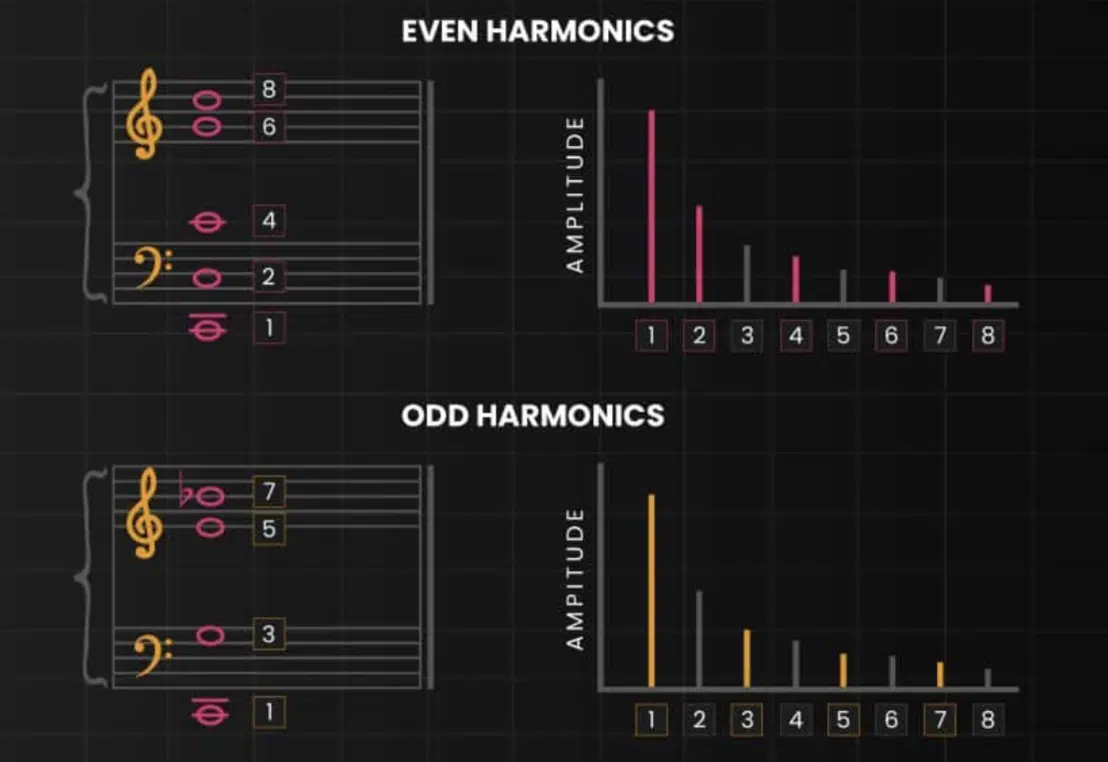
By understanding this, you can manipulate harmonics to emulate these instrumental tones and textures.
The manipulation of harmonics opens up a playground of creative possibilities.
By tweaking various harmonics, you can explore a vast spectrum of pitches; producing unique and diverse sounds that define their musical style and identity.
-
The Role of Musical Instruments in Harmonic Creation
With a foundational understanding of harmonics and pitch, we now venture into the realm of timbre and texture, exploring how they craft the unique sounds that distinguish one musical piece from another.
Every single instrument you can think of is a unique creator of harmonics.
The way a piano string vibrates (yes, piano is a string instrument!) produces a very different set of harmonics compared to the oscillations of a drum head.
This distinction results in intriguing musical textures and timbres.
If you’d like to learn everything about different timbres, we break it all down for you, right here.
As digital music producers, we often sample live instruments in order to capture their unique harmonic signatures.
For example, sampling a saxophone (or other instruments that are similar) can bring a jazz vibe to a hip-hop track, thanks to the characteristic harmonics of the instrument.
NOTE: In genres like hip-hop and trap, it’s very common to twist and bend the timbre, usually through some sort of formant shifter.
But it’s not just about replication 一 it’s about innovation.
By understanding the harmonic creation of instruments, you can synthesize new sounds and blend the organic with the electronic to forge new musical masterpieces.
In essence, musical instruments are harmonic laboratories, or harmonic experiments.
Exploring their sonic possibilities helps you delve deeper into sound design, crafting textures and timbres that are as diverse as they are unique.
-
Manipulating Wavelength & Signal for Texture
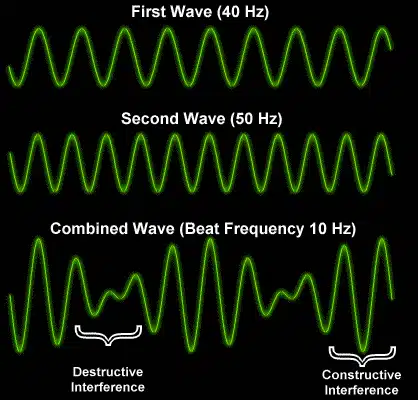
In the digital soundscape, manipulating the wavelength and signal of a sound source (sound wave) is pivotal in creating texture.
Now, we’re not talking about hardware, so we’re not going to be discussing electronic power transmission to the nth harmonic; so stay in the digital mindspace.
By altering these elements, you can mold the harmonic content and craft sounds that are rich, diverse, and distinctive.
For instance, adjusting the wavelength of a sound can influence its frequency and subsequently, its pitch.
In reality, saying we’re effecting an instruments’ wavelength is just a complicated way of saying we’re shifting it’s pitch (the distance of space between a wave’s oscillation).
Stacking these nearly identical signals and manipulating it at different pitches can lead to the creation of:
- Lush pads
- Gritty basslines
- Sharp leads
These are, of course, essential elements in genres like hip-hop and trap.
NOTE: Offsetting identical signals by just a handful of Hz (a fraction of a semitone) is the way to create unison and produce the Chorus effect.
Additional signal manipulation, on the other hand, allows for the alteration of the sound’s amplitude and phase.
This can result in the development of dynamic soundscapes.
This is because the interplay between loudness and silence, and the interaction of different sound waves, contribute to the texture of the track.
It’s also key to mastering the all-too-mystifying phase issues in a mix.
Ultimately, the art of manipulating the wavelength (pitch) amplitude and phase of any given sound, as well as individual harmonics, is a journey of discovery.
It enables you to experiment, innovate, and push the boundaries of what is sonically possible.
Which, in turn, can contribute to the evolution of music production and inspire you to create sounds the world has never heard before.
What Are Harmonics: Final Thoughts
Harmonics, as you now know, are the sonic building blocks that add depth, character, and texture to your music.
They’re integral to shaping the ambiance of a track and can help you craft unique and memorable soundscapes.
When you dive into the world of harmonics, it becomes evident just how transformative they can be.
And now, with this guide, you can navigate the complex landscape of harmonics like a professional 一 ensuring your music stands out in a major way.
But understanding “what are harmonics” in theory is one thing….
Implementing them practically, using advanced tools, takes your production game to a whole new level.
This is where these free Serum Essentials comes into play.
This preset pack contains the most clean, polished, and professional Serum presets tailored for each genre.
Leveraging Serum’s Additive Harmonic Editor, you can manipulate the pitch, phase, and amplitude of any wavelength of your choice.
As you explore “what are harmonics” further, the ability to adjust these harmonics in real-time to create your very own waveforms becomes an invaluable skill.
This feature not only aids in your comprehension of harmonics but also provides hands-on experience that can help you become a harmonics expert in no time.
The answer to “what are harmonics” lies not just in understanding their theory but in harnessing their power in real-time music production.
And, with the insights from this guide, you’re well on your way to mastering the art and science of harmonics in your tracks.
So, go experiment, create, and dominate the production world with your legendary music.
Until next time…







Leave a Reply
You must belogged in to post a comment.