A bass synth is a complex and multifaceted instrument that is used to give your tracks the depth, power, and rhythm that instantly draws people in.
It ranges from mimicking the natural warmth of an acoustic bass to producing electrifying synthetic textures.
As well as laying down the foundational groove that drives your song forward.
So, as a music producer, it’s important to know all about bass synthesizers so you can use them like a pro and elevate your music production skills.
Whether you’re creating a dubstep track or just want to mess around with sound design, understanding the ins and outs of bass synths is key.
It will help you create more impactful and emotionally powerful music.
In today’s article, we’ll break down:
- The basics of what a bass synth is ✓
- How oscillators shape sound ✓
- The role of low-pass filters ✓
- The importance of modulation ✓
- Advanced techniques for creating complex sounds ✓
- Digital vs analog synths ✓
- Tips to make your bass lines stand out in the mix ✓
- How to produce unforgettable basslines ✓
- So much more ✓
You’ll know everything about bass synths so you can start to create those show-stopping beats that make people stop in amazement.
After all, if you learn how to manipulate bass sounds the right way, there’s no limit to what you can achieve.
So, if you want to enhance your skills and create powerful, dynamic basslines, let’s go…
Table of Contents
- What is a Bass Synth? Breaking it Down
- Oscillators and How They Shape Sound
- Understanding Filters and Their Role
- Basic Parameters and Controls
- Analog Synthesizers vs Digital Bass Synths
- How to Make Your Basslines Stand Out in the Mix
- Bonus: Bass Dragon (The #1 Bassline Generator Ever)
- Bass Synth: Final Thoughts
What is a Bass Synth? Breaking it Down

A bass synth is the powerhouse behind the deep, rumbling sounds that give music its richness and depth.
It’s an essential tool that helps you to dial in those perfect low-end tones (low-frequency sounds) that can make a track become unforgettable.
Whether you’re creating a heart-stopping dubstep bassline or adding that subtle, warm hum beneath a soulful melody, the bass synth is incredibly versatile.
It can mimic the natural resonance of an acoustic bass guitar, produce electrifying synthetic pulses, and anything in between.
Understanding a bass synth well enough to manipulate it like a professional involves knowing about its core components:
- Oscillators 一 For generating raw sounds
- Filters 一 For shaping/refining the timbre
- Modulation options 一 For adding texture and movement
You can manipulate them through different knobs and controls to fine-tune your bass sounds with precision and confidence.
Don’t worry, we’ll break everything down for you about synthesizer parameters in detail in the following sections.
Oscillators and How They Shape Sound
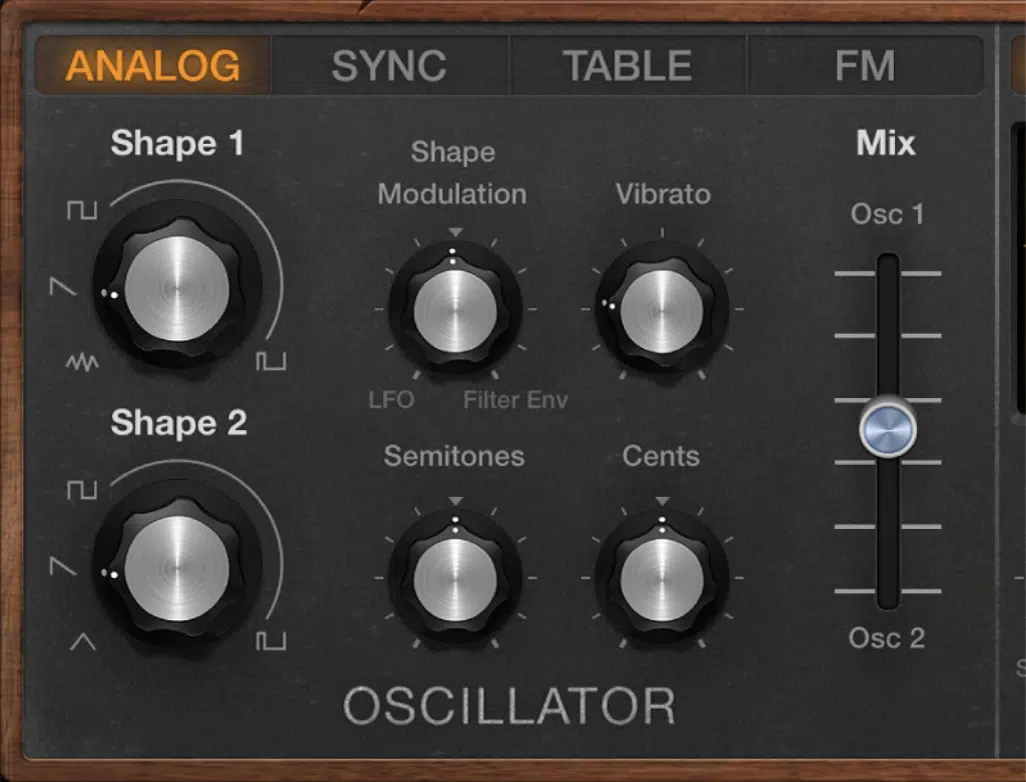
Oscillators are the secret sauce of any synth, bass synths included.
They generate the initial sound waves that are the raw material for everything you hear in a synth bass.
Different oscillators produce different types of waves with their own characteristic sound, such as:
- Sine
- Square
- Sawtooth
- Triangle waves
For bass sounds, sine waves offer that deep, pure tone perfect for sub-bass (and sub-bass manipulation).
Sawtooth waves, on the other hand, have a richer harmonic content 一 making them ideal for playing around with punchier, more present bass lines.
But it’s not just about selecting a wave type.
Oscillators in bass synths can be tweaked and tuned to create mind-blowing bass tones that people love to listen to.
Side note, if you want to learn everything about different tones in music, we’ve got you covered.
You can adjust the pitch, blend multiple oscillators together, or even detune them slightly for a thicker, more complex sound
This versatility is why understanding oscillators is non-negotiable for anyone looking to master bass synth programming.
And, in turn, enhance your production skills and create sounds that will get people hooked.
-
Creating Depth with Sub-Oscillators

A sub-oscillator adds an additional layer of depth by generating a tone one or two octaves below the primary oscillator.
This technique is a secret weapon for achieving those earth-shaking bass sounds that fill the room.
For instance, pairing a sawtooth wave with a sub-oscillator tuned two octaves down can produce a bass sound with insane body and warmth.
It’s perfect for genres like Techno, Dubstep, and House.
-
The Power of Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)
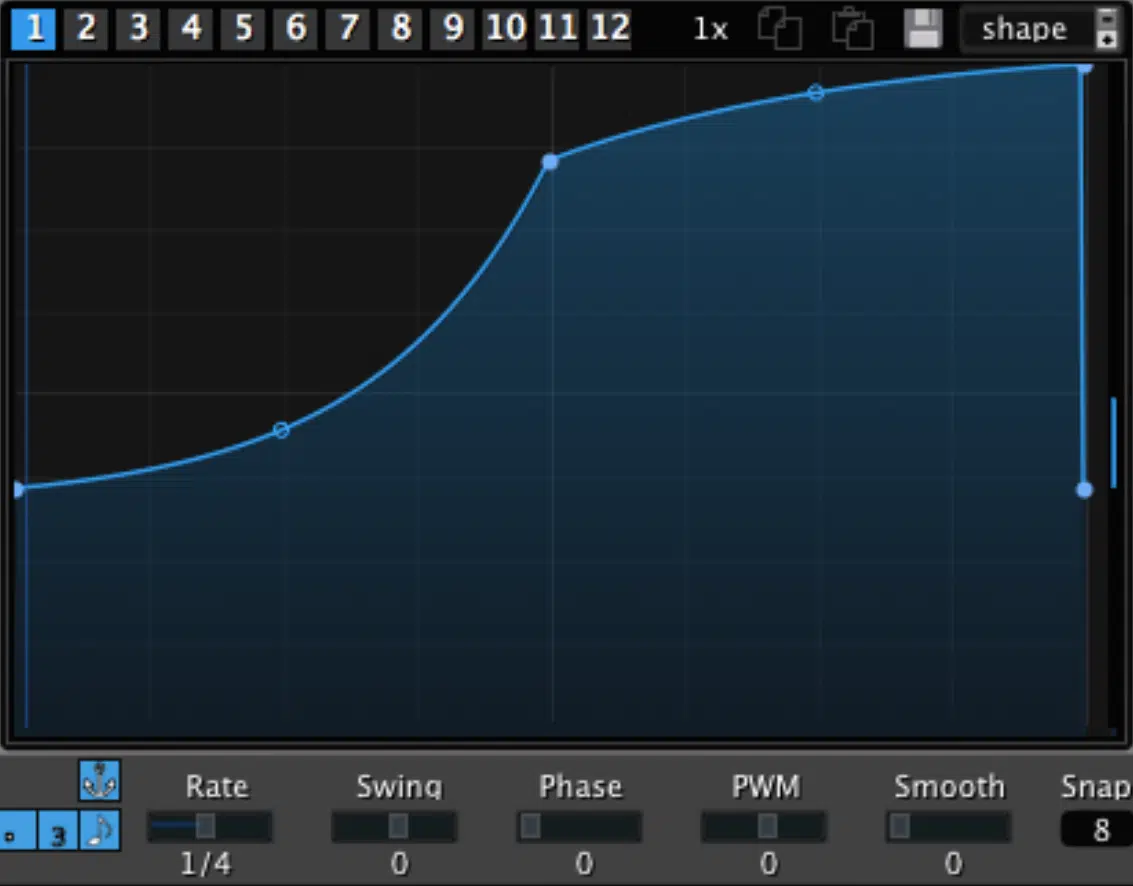
PWM is a method of creating movement and life in your bass sounds with your synth bass.
By modulating the width of a square wave, you can create a sound that pulses and evolves over time.
This is particularly useful for creating dynamic bass lines that stand out in a mix without overwhelming other elements.
Understanding Filters and Their Role
When it comes to bass synths, filters are your sculpting tools, shaping the raw sounds produced by oscillators into the polished bass tones that define your track.
The low-pass filter, in particular, is a staple in synth bass synthesis.
It works by allowing low frequencies (low-frequency sounds) to pass through while attenuating the higher frequencies.
This is super important for ensuring your bass sounds are powerful without stepping over the clarity of other elements in the mix.
When you play around with the cutoff frequency of a low-pass filter, it can dramatically change your synth bass sound.
- Lowering the cutoff 一 Produces a deeper, more subdued bass.
- Increasing it 一 Allows more of the harmonics to shine through, creating a brighter tone.
This is especially useful in genres where the bass needs to cut through dense arrangements, such as in electronic music or hip-hop.
But filters aren’t just about cutting frequencies…
The resonance parameter adds a peak around the cutoff point, which emphasizes certain key harmonics.
This can be used to create more pronounced bass tones or to add a distinctive groove/character to your basslines.
For example, cranking up the resonance on a bass patch might give you that squelchy sound heard in acid house beats.
Note
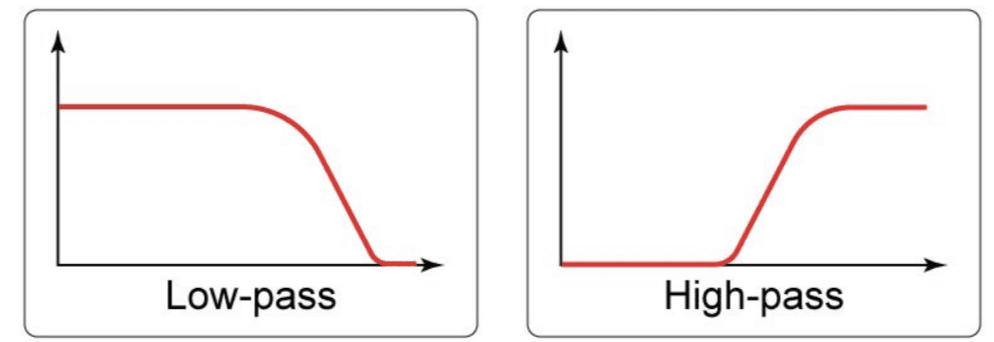
Beyond the basic low-pass filter, experimenting with high-pass and band-pass filters can unlock new bass textures.
A high-pass filter might seem counterintuitive for bass sounds, but it can be useful for layering bass lines or creating bass sounds that sit higher in the mix.
It complements the main bass in the best way.
Band-pass filters, meanwhile, can help in isolating a specific frequency range 一 making your bass sound more focused and unique.
This technique is often used in dubstep and drum and bass for its ability to create tight, punchy bass sounds that still have a lot of character.
Basic Parameters and Controls

Getting to grips with the basic parameters and controls of your bass synthesizer (and bass synth sounds) is key to creating that perfect bass sound for your track.
These controls give you the power to shape and fine-tune your sound, making it fit perfectly within your track.
From oscillators and filters to envelopes and LFOs, each component plays a super important role in the final sound.
The envelope generator, with its attack, decay, sustain, and release (ADSR) controls, shapes the dynamic contour of your bass sound.
- A short attack and decay 一 Great for punchy, attacking bass sounds that jump out of the speakers.
- A longer attack and release 一 Great for a smoother, more evolving bass sound.
Pitch and glide controls add yet another layer of expressiveness to your bass lines, so always make sure to play around.
The pitch control allows you to set the initial pitch of your sound, essential for tuning your bass correctly with the rest of your track.
Glide, or portamento, introduces a sliding effect between notes.
This is perfect for creating legato bass lines that smoothly transition from one note to the next.
It can be particularly effective in genres like techno or ambient, where the fluidity of the bass line contributes to the overall atmosphere of the track.
-
Pro Tip: Reese Bass

The Reese Bass is a sound beloved by bass music producers and beat-makers, known for its thick, detuned texture.
Originating from Kevin Saunderson’s project Reese, it has become a staple in distortion genres like drum and bass and dubstep.
Creating a Reese Bass involves:
- Layering two or more sawtooth oscillators
- Detuning them slightly from each other
- Applying a low-pass filter to blend them smoothly
This technique results in a rich, moving synth bass sound that can add depth and intensity to your beats.
For added movement, modulating the filter cutoff with an LFO can introduce a rhythmic pulsation to the Reese Bass, which makes it even more captivating.
Analog Synthesizers vs Digital Bass Synths
Both analog synthesizers and digital bass synths bring their unique flavor and capabilities to the table. Let’s break it down, so you’ll get a further understanding of analog bass synths and digital bass synths and what makes them so versatile and flexible.
-
Analog Synths
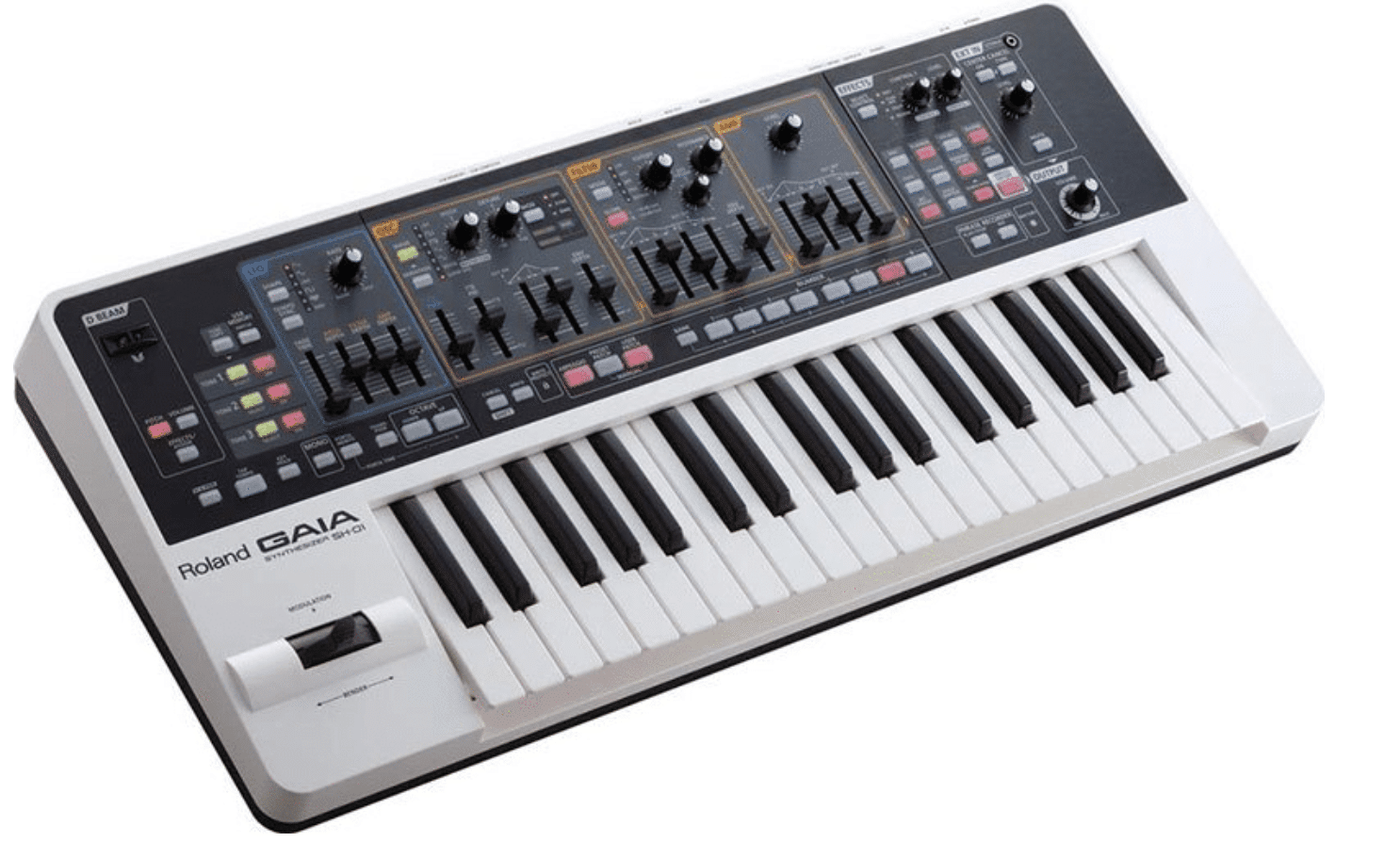

Analog synths are celebrated for their warm, organic sounds that emanate from their physical circuitry.
These instruments generate sound through analog oscillators, filters, and modulation sources.
It gives you beautifully rich, dynamic tones that many argue have a certain depth and presence hard to replicate digitally.
For example, the Moog Sub 37 has a ladder filter that offers a distinctive warmth and resonance that would be hard to emulate.
It produces bass sounds with finesse and unparalleled richness.
If you want your tracks to be heard/felt and have a unique texture, there’s nothing more valuable than an analog synth.
Plus, the physical touch of different slides, knobs, etc. is always an exciting experience.
-
Digital Bass Synths

Digital bass synths, on the other hand, offer a level of precision and versatility that analog units can struggle to match.
From emulations of classic analog warmth to entirely new, digitally-enhanced textures, they can achieve it all.
The advantage of digital synths lies in their versatility and the convenience of presets and programming, which allows for rapid experimentation and creativity.
Digital bass synths often offer features like:
- FM synthesis
- Granular synthesis
- Extensive modulation capabilities
It helps you mess around with complex sound design, like FM bass, with a level of control that’s both intricate and addictive.
Basically, the analog synths can’t be beat when it comes to organic sound, warmth, and depth (and physical touch).
And, conversely, digital bass synths can’t be touched when it comes to advanced sound design possibilities, groove, and convenience.
NOTE: Try experimenting with different variations like incorporating a deep sub-bass with FM synthesis, applying a touch of reverb for spatial depth, and using a Roland-inspired vibrato effect.
It will help transform a simple bassline into a sonic masterpiece.
If you want to elevate your production game and learn all about FM synthesis, you’ll be pleasantly surprised by the options it unleases (sound-design-wise).
-
Pro Tip: Two Analog Powerhouses
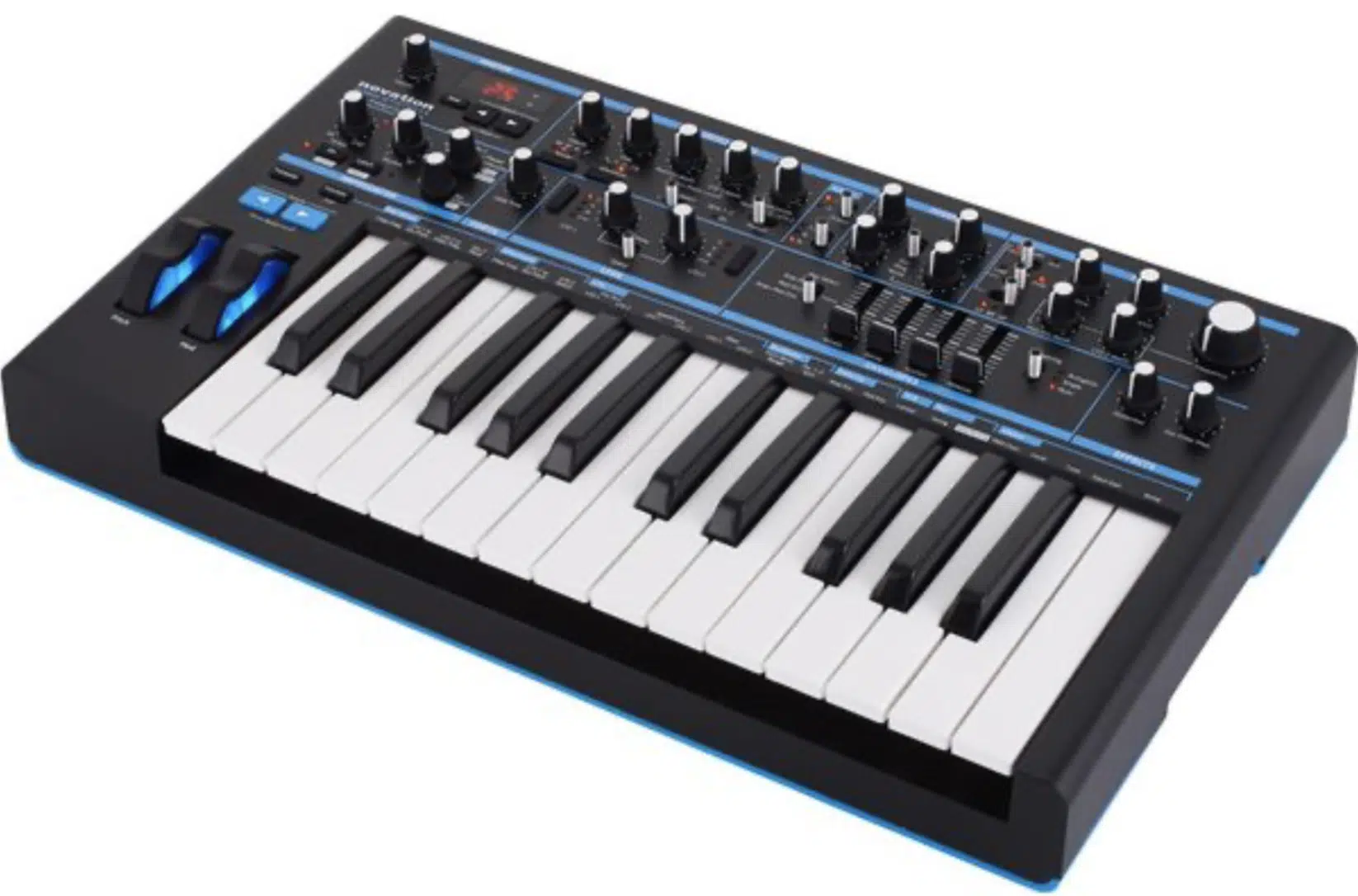

The Novation Bass Station II redefines what a modern analog synth can do, combining classic design with contemporary functionality.
Its dual oscillators, supplemented by a sub-oscillator, deliver endless sounds from deep, warm lows to screaming leads.
This helps to crown this synthesizer incredibly versatile.
Its analog signal path, including a filter section that pays respect to the original Bass Station synthesizer, is on point.
Beyond its sound generation capabilities, the Bass Station II excels in its hands-on control layout.
With dedicated knobs and sliders for nearly every function, playing around with signature sound-shaping is super easy (and fun).
Meaning, with Bass Station II, you can fine-tune your bass sounds with precision and ease.
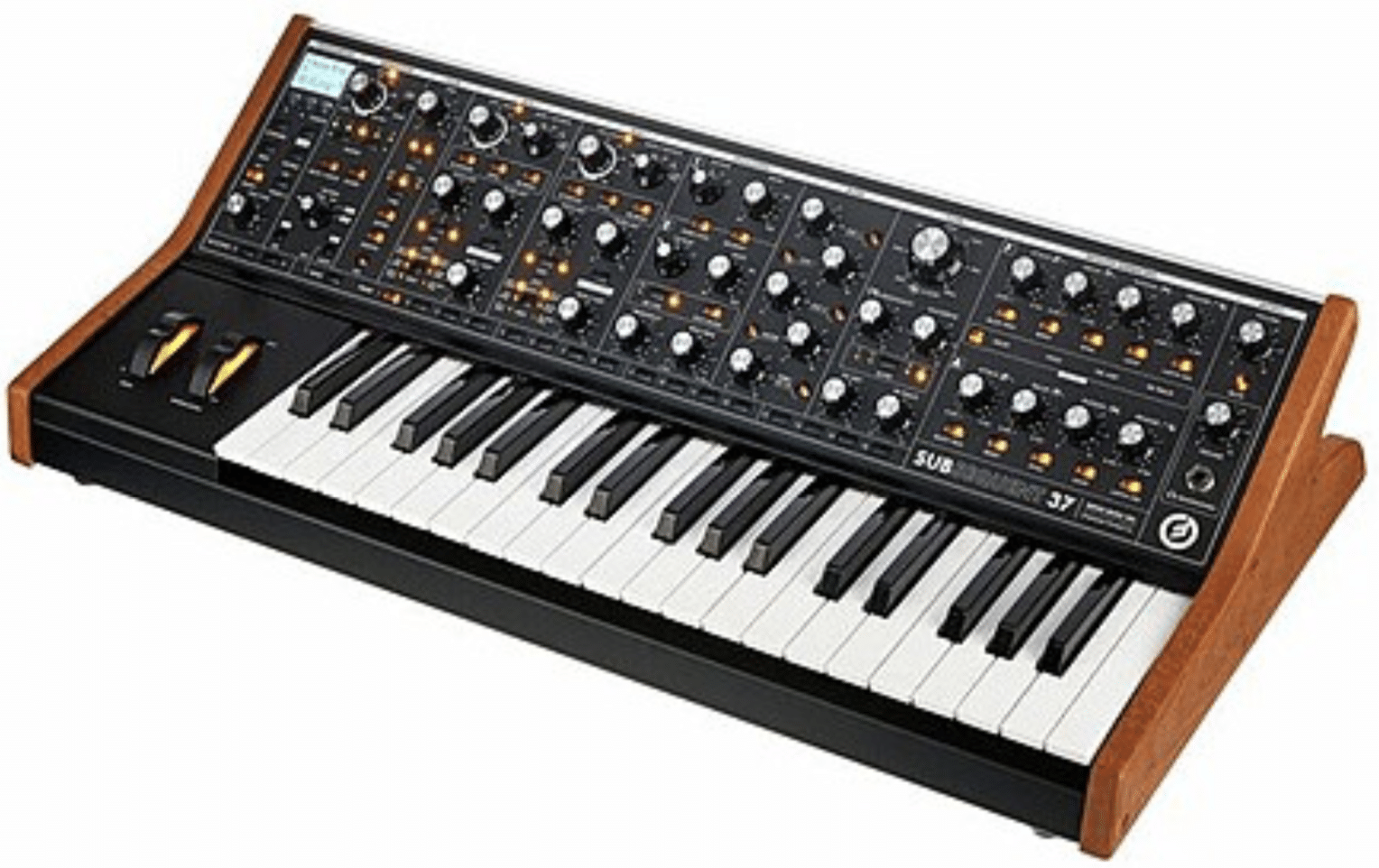

The Moog Sub 37 takes the legacy of Moog’s analog synthesis to new heights 一 offering a paraphonic analog synthesizer that’s both powerful and accessible.
With its rich oscillators and Moog’s legendary ladder filter, it produces synth bass sounds of unparalleled warmth and depth when you listen.
Its extensive modulation matrix and sequencer push the boundaries of traditional bass synthesizer capabilities for complex soundscapes and sequences.
One of the standout features of the Moog Sub 37 is its ability to seamlessly integrate into both analog and digital workflows, courtesy of its MIDI and CV connectivity.
It’s a perfect synthesizer choice for producers looking to combine the warmth of analog synthesis with the precision and flexibility heard in digital music production.
How to Make Your Basslines Stand Out in the Mix
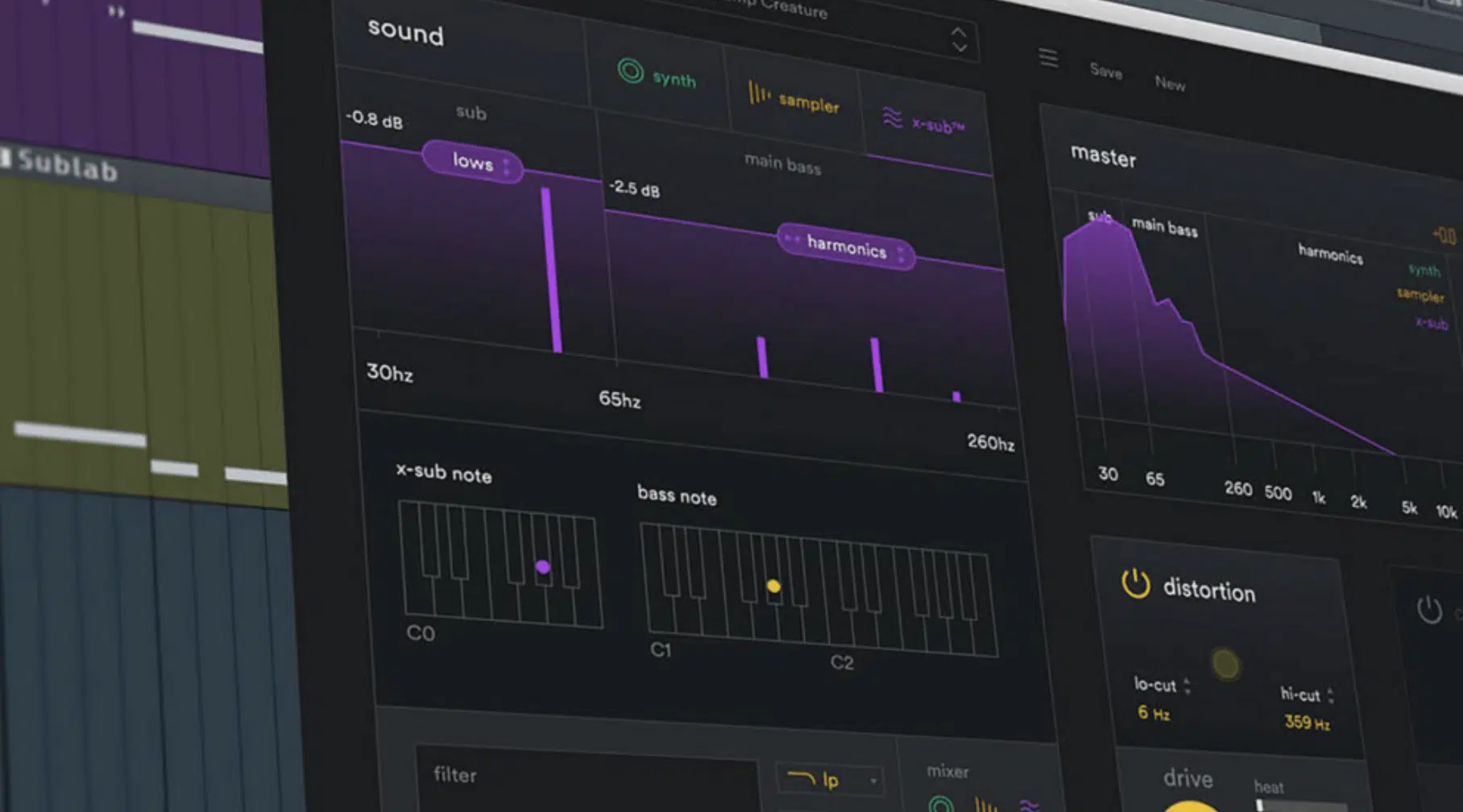
Making your basslines stand out in the mix is key, especially in genres where the bass drives the rhythm and mood, like techno, hip-hop, and dubstep.
Utilizing sidechain compression is a standout technique, allowing the bass to rhythmically duck in volume with each kick drum hit.
It enhances groove and ensures clarity between all the foundational elements.
This method not only creates a dynamic back-and-forth between the bass and kick but also helps prevent the mix from becoming muddy.
Enhancing the presence of your bass in the mix can also be achieved through strategic EQ and saturation (and distortion).
With EQ you can apply slight boosts in the mid to high frequencies to make the bass more perceptible on smaller speakers, which ensures it maintains impact.
Saturation, on the other hand, adds warmth and enriches the bass with harmonics, which makes it fuller and more noticeable.
Layering different textures (think step sequencer) of bass sounds can further define your bassline 一 providing depth and complexity that cuts through the mix.
It will help impress your listeners on any playback system.
Bonus: Bass Dragon (The #1 Bassline Generator Ever)
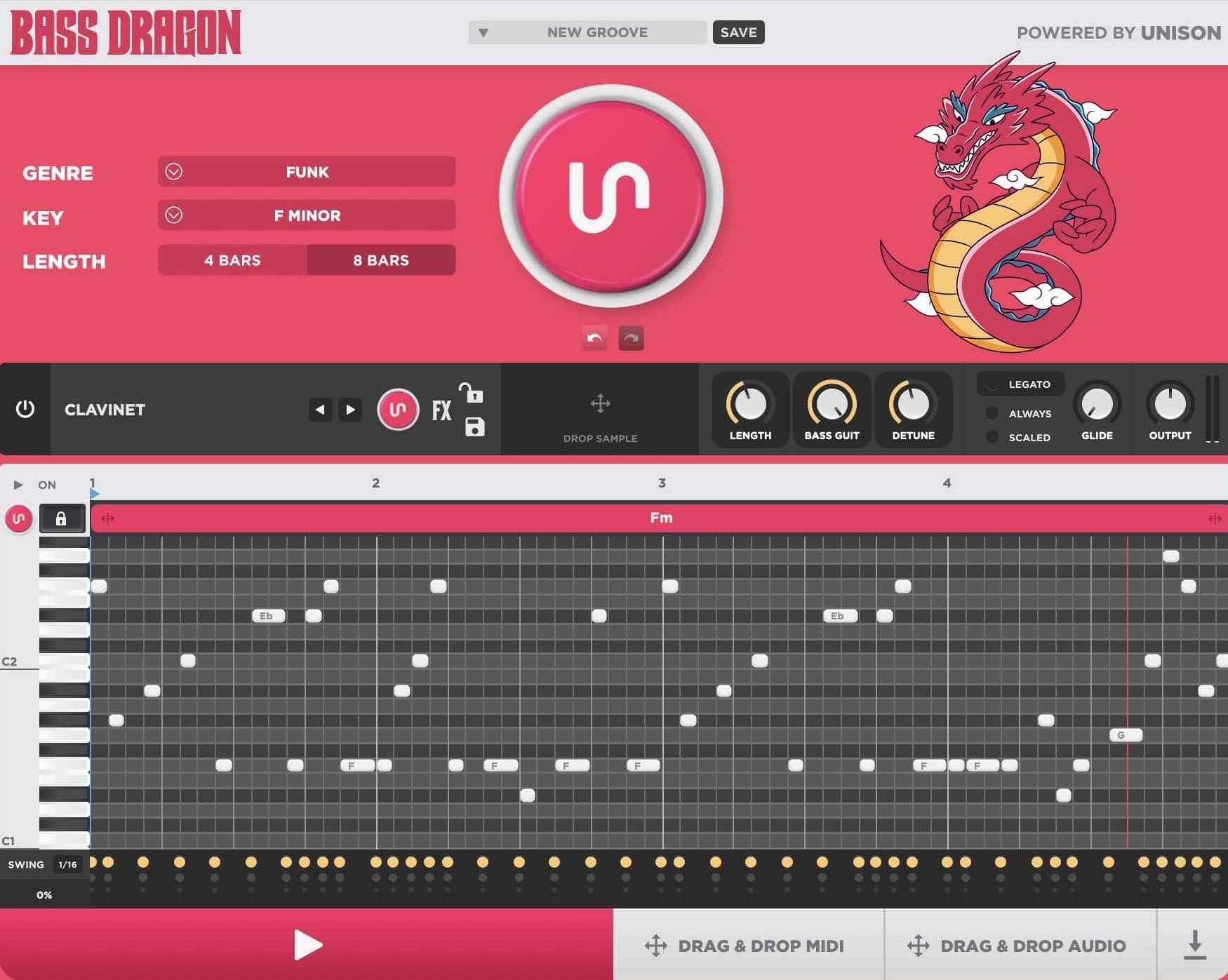
Bass Dragon stands out as the world’s first AI Bassline Generator, a game-changer for producing unlimited, fire basslines and 808s tailored to 30 genres of music.
This cutting-edge bassline beast will help you create the most show-stopping synth bass sounds on the planet.
Bass Dragon will also help you destroy beatblock and give you instant inspiration.
Plus, you’ll be able to push your music beyond traditional boundaries, by creating basslines that are:
- Simple
- Complex
- Insanely advanced
- Unique & captivating
All you have to do is: select a genre, press a button for an instant bassline or 808 pattern, and drag & drop directly into your project.
Its AI seamlessly matches basslines with your chord progressions, ensuring flawless integration.
-
Built-in Synth, Sampler & 200+ Factory Presets
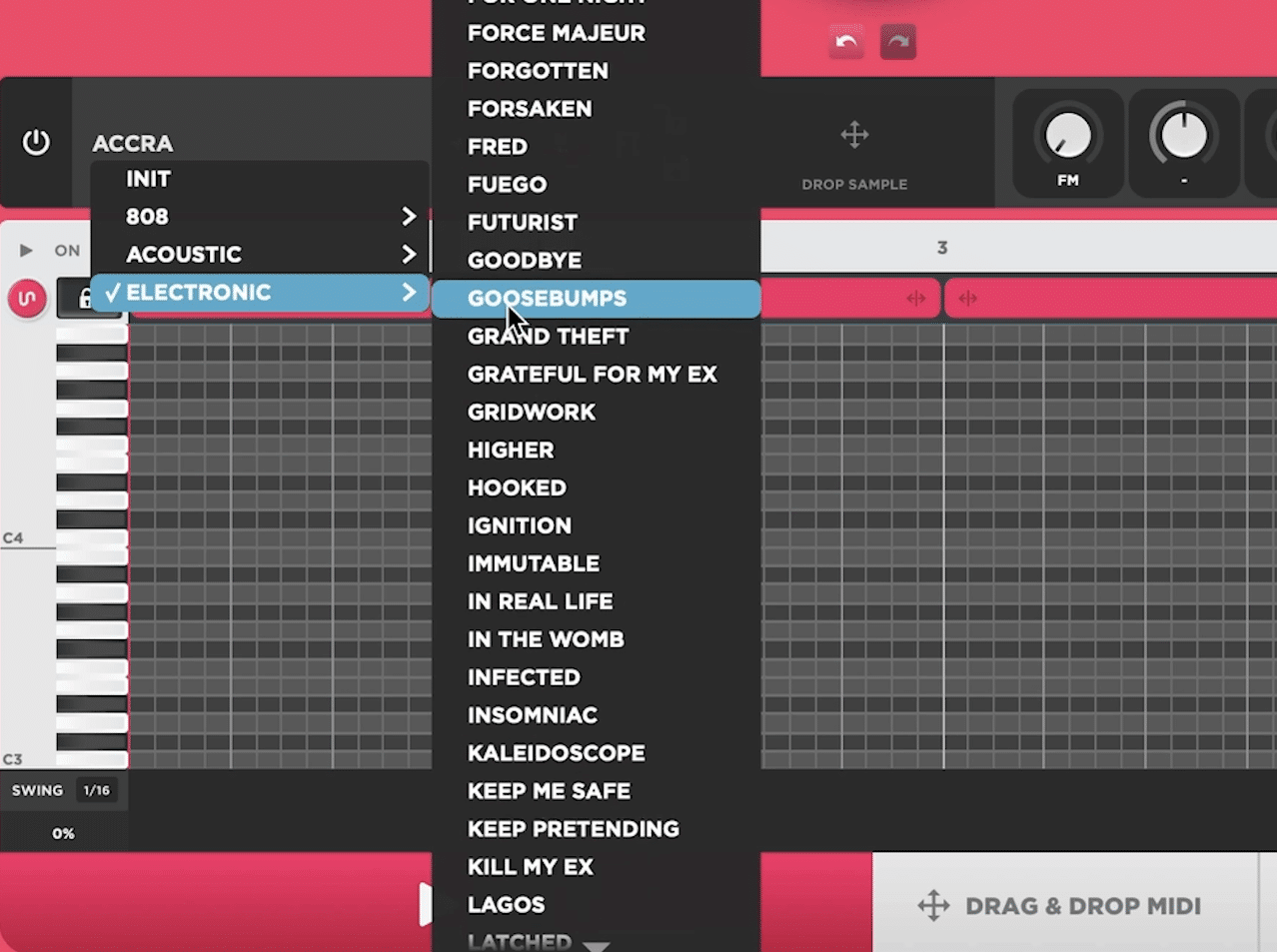
The built-in synthesizer and sampler, alongside 200+ factory presets equipped with macros for easy tweaking, offer endless sonic possibilities.
This allows for precise sound shaping and experimentation with different presets to perfectly suit your track.
Bass Dragon’s sampler also invites you to incorporate your favorite one-shots or 808s, further customizing your sound.
You’ll be able to completely enhance your music production skills in just minutes.
Bass Synth: Final Thoughts
Mastering different bass synth techniques is a game-changer in music production.
Knowing how to manipulate its electrifying sounds can really help your tracks stand out and put the competition to shame.
Plus, by combining traditional synthesis techniques with cutting-edge digital innovations, you can push the boundaries of what’s sonically possible.
Whether it’s producing the perfect sub-bass, spicing up your soundscapes with FM synthesis, or adding depth with reverb and vibrato, the possibilities are endless.
So, go use what you’ve learned today and embrace the power of bass synths.
Let them help elevate your music to new heights and sure your tracks not only sound professional but irresistible.
Until next time…







 40 Chord
Progressions
40 Chord
Progressions

Leave a Reply
You must belogged in to post a comment.