Melodies are the heart and soul of songwriting and production, capturing your listeners attention and bringing powerful emotions to the table.
Plus, they help your tracks really stand out, resonate, and stick in the listener’s mind.
As an artist or producer, you’ll need to know all about melodies in order to knock out unforgettable music.
That’s why we’re breaking down everything you need to know, like:
- What is a melody (in western music) ✓
- How melody differs from harmony and rhythm ✓
- Key components of a melody ✓
- Pitch examples ✓
- Intervals & scales ✓
- Rhythm in melody ✓
- Different forms of melodies ✓
- Melody writing techniques of popular music ✓
- Melodic layering examples ✓
- Effects and processing on vocal melodies ✓
- Much more about melodies to enhance your song ✓
After reading this article, you’ll know everything about creating beautiful melodies so your music is always on point and emotionally engaging.
This way, you’ll be able to write captivating melodies and produce hit songs like a true professional 一 you’ll never have to ask the question, “what is a melody?” again.
So, let’s dive in…
Table of Contents
What is a Melody? Breaking it Down

In simplest terms, a melody is a sequence of musical notes that the listener perceives as a single entity.
It’s the tune you sing along to in your favorite song or the catchy part you just can’t get out of your head no matter how hard you try.
In musical composition, a melody combines rhythm and pitch to create a recognizable pattern of musical tones (this is the most important thing to remember).
Unlike harmony, which supports the melody, and rhythm, which gives music its timing, a melody stands out as the main theme of your track.
Think of the “Happy Birthday” song 一 its simple yet memorable melody is what makes it one of the most instantly recognizable songs in the world.
Understanding what is a melody is key for any music producer aiming to create memorable music.
Don’t worry, we’ll be breaking it all down in detail throughout the article.
-
Pro Tip: How Melody Differs from Harmony and Rhythm
A melody consists of a series of single notes played in succession; creating a tune that stands out.
Harmony, on the other hand, involves multiple notes played simultaneously to support the melody, which enhances the overall sound.
For example, while a melody might be a single line of music played by a lead instrument (let’s say a guitar), harmony would be the chords played underneath that melody.
Rhythm provides the timing and beat, giving the melody its tempo and groove.
It’s all about using this trio to add depth to your tracks.
To create a beautiful melody, focus on the melodic line 一 ensuring it flows smoothly and stands out over all the competition.
Key Components of Melody in Music
When it comes to creating an impactful melody, it all boils down to understanding its key components. So, let’s dive into pitch, intervals, scales, and rhythm in melody. It will help you answer the question of what is a melody.
-
Pitch

Pitch refers to how high or low a musical note sounds and is the foundation of a melody, determining the musical tones that make up the tune.
- Higher pitches 一 Can create a sense of excitement or tension.
- Lower pitches 一 Can evoke calmness or sadness.
For example, rising pitches in a chorus can build emotional intensity.
Producers, artists, and other musicians often use pitch to create contrast within a melody, moving between high and low notes to keep the listener hooked.
Side note, in musical notation/sheet music, pitch is represented on a staff with notes placed higher or lower to indicate their pitch.
Remember, mastering pitch manipulation is key for creating a memorable melody.
-
Intervals
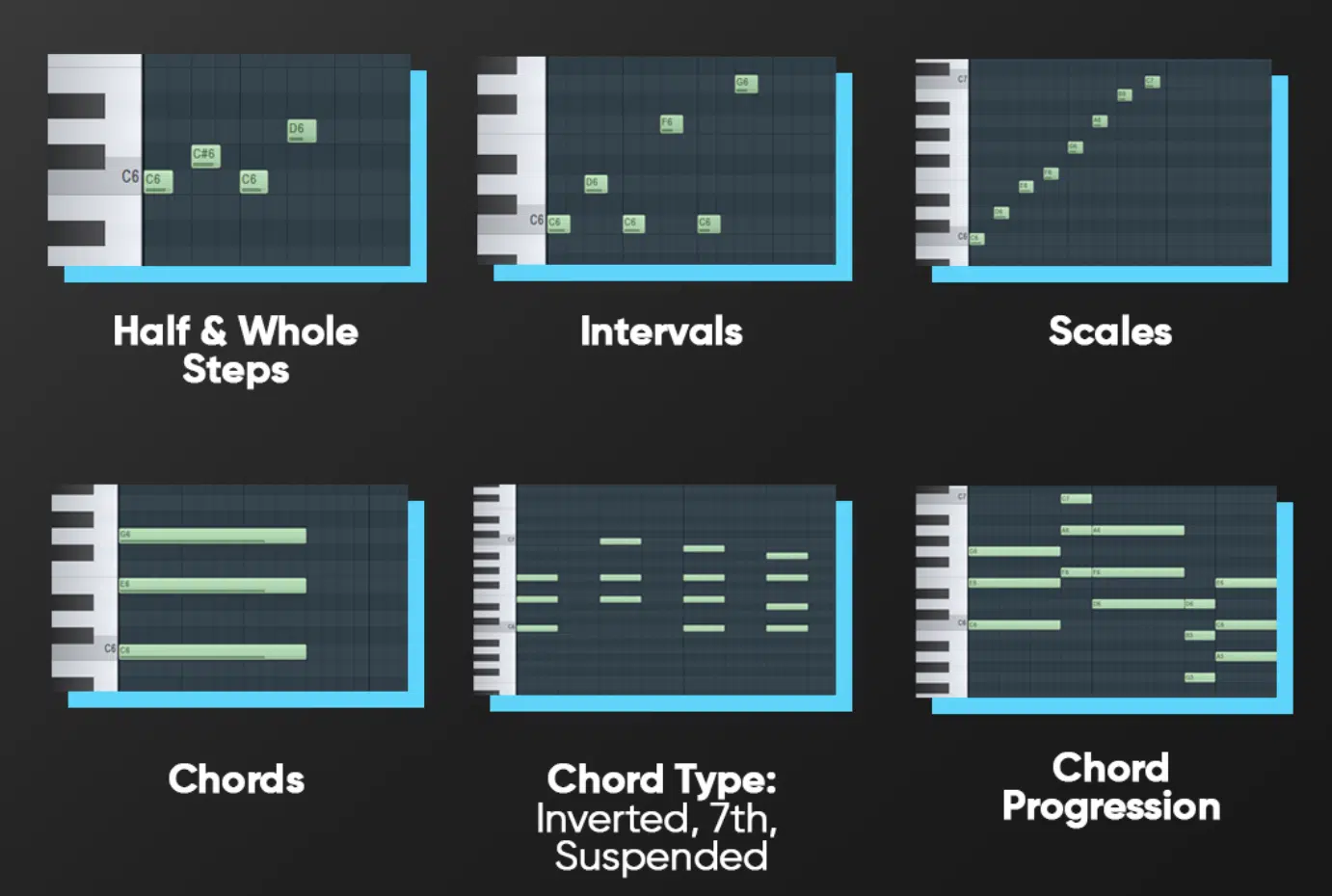
Intervals are the distances between two notes in a melody that define the relationship between notes and contribute to the melody’s overall feel.
Small intervals, like seconds and thirds, create smooth, stepwise motion 一 making melodies easy to sing.
Larger intervals, like fifths and octaves, can add dramatic leaps and interest to a melody, which can enhance it even more.
Understanding intervals helps in laying down both vocal melodies and instrumental lines, allowing for the perfect placement of tension and release.
For example, a series of small intervals might create a calming effect, while larger intervals can add excitement.
Learning to play and recognize different intervals is a powerful songwriting tool.
-
Scales
Scales are ordered sequences of notes that provide the melodic base of whatever vibe you’re going for.
They are essential in classical music, most European music, and more modern/popular music for creating melodies.
Major scales and minor scales are of course the most common 一 each bringing different emotional tones to the table (both of which are super important).
For example, a major scale typically sounds bright and happy, while a minor scale can convey a more melancholic or tense feel.
Many melodies use notes from a specific scale to make sure the song is coherent, fluid, makes sense, and is consistent.
Exploring various scales, including modes and exotic scales, can inspire unique melodic ideas and bring your composition skills to the next level.
Plus, enhance your musical vocabulary in the process, which is always a plus.
Remember, incorporating different scales into your compositions can lead to creating beautiful melodies, so always think outside the box.
-
Rhythm in Melody
Rhythm gives a melody its timing and flow, determining how long notes are held and the placement of each note within a musical phrase.
Syncopation, where notes are played off the regular beat, can make a melody more engaging and dynamic.
Rhythm also influences how a listener perceives the melody’s movement and structure…
For example, a melody with a steady rhythm can create a sense of stability, while the same melody with varying rhythms can add complexity and interest.
In pop music, catchy rhythmic patterns are key for creating memorable melodies.
Combining different rhythmic elements (which you’ll hear melodies do all the time), such as long notes and short, staccato notes, can add variety to your melodic lines.
Understanding rhythm’s role in melody helps in laying down compelling tracks that keep the listener engaged and not bored.
Creating Your Own Melodies
Creating your own melodies involves creativity and technical knowledge. So now let’s dive into some essential techniques/tools to help you write melodies that actually stand out.
-
Melody Writing Techniques
Writing melodies involves experimenting with different musical ideas, so start by playing around with short musical phrases and building on them.
For example, you can create a memorable melody by using repetition and variation by taking a simple musical phrase and repeating it with slight changes in pitch or rhythm.
Another great technique is sequencing, where you repeat a motif at different pitch levels, like moving up or down a scale.
Also, incorporate some stepwise motion (which means moving between adjacent notes in a scale) to create smooth and ‘sing-song’ melodies people just can’t forget.
Contrast stepwise motion with occasional leaps or larger intervals can add interest and excitement as well, so make the decision based on your specific song.
Make sure to practice regularly, and analyze melodies from different genres to understand various melodic structures and apply them to develop your unique style.
Reference tracks are always recommended.
Remember it’s all about playing around with different techniques 一 you never know what you’ll stumble upon.
-
Tools and Software for Melodic Composition
Melodyne
Modern music production gives you everything you need for creating melodies like a professional, even right within your DAW like:
These platforms provide virtual instruments like bass, guitars, drums, etc. and MIDI capabilities to experiment with killer melodic ideas.
Plugins like Serum and Massive offer extensive sound design options for laying down some unique melodies as well.
Plus music notation software (the ultimate sheet music, if you will) can help in visualizing and editing your melodic lines.
Tools like Melodyne will help you with detailed pitch correction and melody manipulation, which is always a great choice.
Remember to combine these tools to fast-track your melodic process and work with the ones you feel most comfortable with.
-
Melodic Layering
Layering is a technique used to add depth and richness to your melodies and by stacking multiple melodic lines, you can create complex and textured tracks.
Which, let’s face it, is always the goal.
Make sure to use different instruments and sounds to differentiate each layer 一 ensuring they complement each other throughout the song.
You don’t want things to sound amateur or cause your listeners to cringe.
Countermelodies (secondary melodies that harmonize with the main melody) can add some additional interest and complexity as well.
Just make sure each layer supports the main melody without overpowering it to maintain a balanced mix.
NOTE: Try experimenting with panning and volume to create space and clarity within your arrangement.
Melodic layering is essential for producing dynamic and engaging music that captivates listeners, so don’t slack in this area if you’re aiming for the top of the charts.
-
Effects and Processing on Vocal Melodies
Effects can completely transform vocal melodies, adding that extra layer of character that people are drawn to.
Reverb and delay can create a sense of space and make melodies sound more expansive.
Modulation effects like chorus and flanger can thicken and enrich vocal tones, giving them a fuller sound that you should be aiming for.
Pitch correction tools, such as Auto-Tune, help in refining intonation and tuning, ensuring the vocal melody in music is pitch perfect. Whether it’s only one note or only two notes, you want to make sure everything is on point.
Creative effects like distortion and filtering can add unique textures and make your vocal melodies stand out.
Automation can dynamically change effects throughout the song, adding interest and variation, so don’t overlook it.
Processing vocal melodies with effects is super important for modern music production 一 allowing you to create professional-sounding tracks like a boss.
Bottom line, it’s all about making your melodies stand out and evoking the desired emotions so your music captivates your audience from start to finish.
-
Integrating Melody with Other Elements
A good melody should flawlessly mesh with your harmony and rhythm, period.
Start by creating a chord progression that complements your melodic line 一 for example, a C-G-Am-F progression can provide a solid foundation for a pop melody.
Just make sure the rhythm of the melody fits with the overall groove of the song.
- A syncopated rhythm can add excitement.
- A straight rhythm can create a sense of stability.
Use harmonization techniques, like adding thirds or sixths to your melody notes, to add depth and richness as we touched upon earlier.
Remember, melodic lines should interact with basslines and other instrumental parts, like having a bassline that moves in contrary motion to the melody to create tension.
Balancing all elements will make sure everything is on point and polished to perfection, like how the melody and chords work together in a well-produced pop song.
Integration is key to making your melodies stand out in a mix 一 ensuring each part enhances the overall musical experience and doesn’t kill the vibe.
Just remember it’s all about the melodic motion.
Bonus: Melodies in Different Genres

Sad pop melody
Different genres employ melodies in unique ways, each with its own styles, so let’s break it down as a quick bonus.
In pop music, catchy and repetitive melodies are essential for commercial success 一 think of the simple yet infectious hooks that dominate the charts.
Electronic Dance Music (EDM) typically uses synthesized melodies with intricate modulation and automation to create evolving soundscapes that captivate the listener.
Hip-hop and trap melodies typically use short, repetitive phrases, often incorporating syncopated rhythms and unique sound textures to complement the beats/lyrics.
Jazz melodies are characterized by complex improvisation and harmonic exploration, featuring blue notes and swing rhythms that add a distinctive flavor to any song.
Classical music features structured and thematic melodic development, where motifs are developed and varied throughout a symphony or concerto.
-
Pro Tip
Studying melodies across genres like pop, EDM, hip-hop, trap, jazz, and classical can expand your toolkit and help you understand the different techniques and styles that make each genre unique. Experimenting with different styles allows you to create versatile and innovative music that can cross genre boundaries and appeal to a wider audience (hybrid genres are super popular right now).
What is a Melody? Final Thoughts
Well, there you have it; everything about what is a melody and how to create show-stopping melodies for your music.
From understanding the key components like pitch, intervals, scales, and rhythm, to exploring melody writing techniques and integrating melodies with other elements.
You now have the tools to lay down memorable and engaging melodies all day.
We also covered how melodies differ across genres such as pop, EDM, hip-hop, trap, jazz, and classical, which will be super helpful in your journey.
Understanding what is a melody and mastering the art of melody writing will elevate your music production skills tenfold.
To make your tracks even catchier and more addicting, check out these show-stopping Free Melody Loops.
These unique, hit WAV melody loops can be instantly plugged and played into your music 一 making them the key to creating tracks that listeners will play on repeat.
Remember, never stop experimenting and playing around with different melodies.
Keep pushing your creative boundaries, and you’ll continue to grow as a music producer every single day (which is what it’s all about).
Until next time…







Leave a Reply
You must belogged in to post a comment.