MIDI stands for Musical Instrument Digital Interface, and it’s key in mastering your music production workflow.
It can streamline your creative process, help you control and manipulate a wide range of sounds, and enhance the way you interact with your music production software.
As a producer, it’s important to know all about what a solid MIDI setup consists of.
This way, you’ll be able to fully utilize its capabilities, maximize your workflow efficiency, and bring your musical ideas to life with precision and creativity.
In today’s article, we’ll break down;
- How MIDI works ✓
- The basics of MIDI controllers & MIDI keyboards ✓
- Understanding MIDI data ✓
- MIDI messages and their uses ✓
- Connecting MIDI devices ✓
- Navigating MIDI interfaces ✓
- What is a MIDI setup ✓
- Advanced MIDI functionalities ✓
- MIDI and virtual instruments ✓
- Pro Tips about using MIDI ✓
- Much more about MIDI & its invaluable process ✓
After reading this article, you’ll have a solid understanding of MIDI and MIDI setups, which will help you master various MIDI components and configurations like a pro.
This knowledge will empower you to create your music with greater control, flexibility, and creative freedom.
So, let’s dive in…
Table of Contents
- How Does MIDI Work? Understanding the Basics
- MIDI Controllers: Breaking it Down
- Pro Tip: MIDI Controllers vs. MIDI Keyboards
- Exploring MIDI Data and MIDI Messages
- MIDI Connectivity and Your MIDI Setup
- MIDI Wizard 2.0: The Ultimate MIDI Software
- Advanced MIDI Features
- Exploring MIDI 2.0 and Its Advancements
- Building Your MIDI Setup: Essential Components
- What is a MIDI Setup? Final Thoughts
How Does MIDI Work? Understanding the Basics
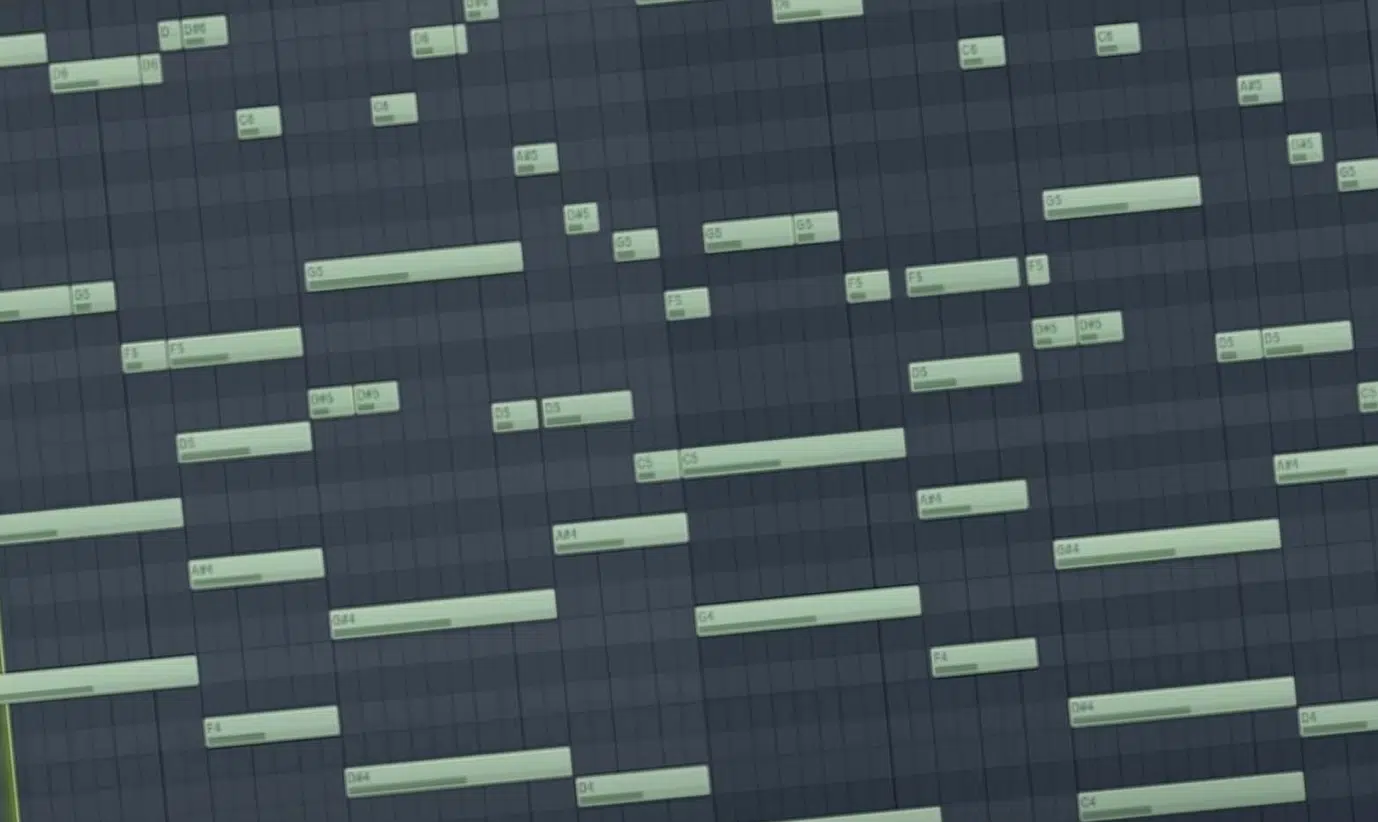

MIDI, or Musical Instrument Digital Interface, is a vital component in the world of digital music production and creation.
It’s a standard that allows musical instruments, computers, and other hardware to communicate.
At its core, MIDI transmits messages about:
- Pitch
- Intensity
- Duration
- Rhythm
- Etc.
This language enables a MIDI keyboard or MIDI controller to interact seamlessly with software instruments and recording software.
This technology revolutionized the music industry 一 allowing for endless creativity and control in the music creation process.
Understanding MIDI is essential for any digital music producer, period.
Unlike audio files, which capture the actual sound, MIDI data comprises digital instructions that can trigger sounds from virtual instruments or synthesizers.
This format gives you immense flexibility, as MIDI information can be edited and manipulated post-recording (something not possible with traditional audio recordings).
It’s the backbone of modern music production, really, as it supports complex arrangements and sound design with ease.
NOTE: The birth of MIDI in the early 1980s, spearheaded by pioneers like Dave Smith and Ikutaro Kakehashi, marked a significant leap in electronic music/electronic instruments.
It facilitated the control of multiple devices from a single controller, streamlining the music production process and MIDI tasks.
MIDI’s versatility extends to its ability to work with various MIDI devices, from drum machines to hardware synthesizers.
This makes it an invaluable universal language in the digital music realm.
MIDI Controllers: Breaking it Down
As we delve deeper into the world of MIDI, let’s focus on MIDI controllers, the physical interface that lets us interact with MIDI data. These devices range from keyboards to drum pads, each serving a unique role in manipulating and creating MIDI information.
-
Understanding Different Types of MIDI Controllers
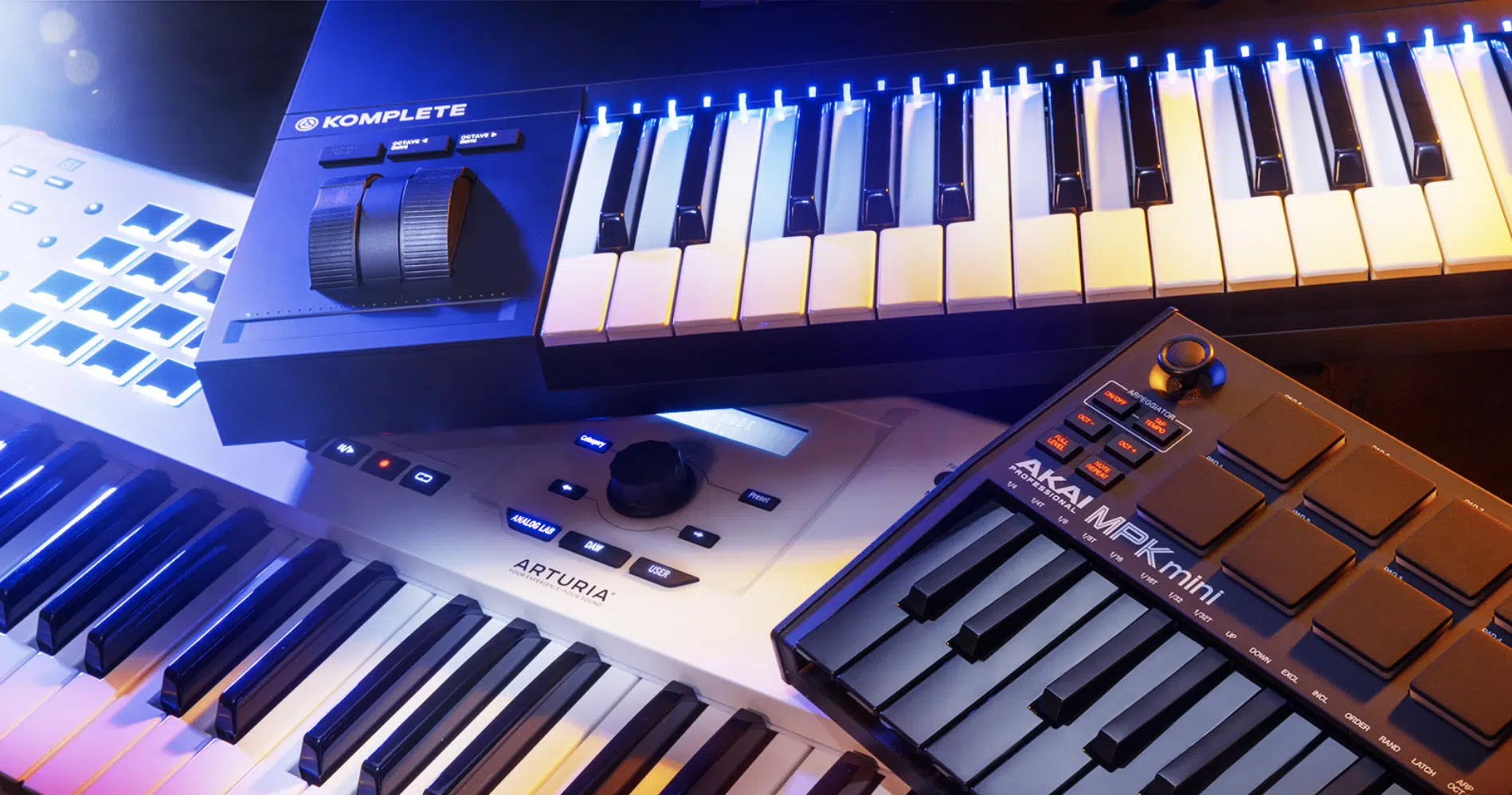

MIDI controllers come in various forms, each catering to specific needs and aspects of music production.
A MIDI keyboard is a super popular option, resembling traditional keyboards but designed to send MIDI data to a connected device.
MIDI keyboards are fundamental for creating melodies and chord progressions 一 offering a familiar interface for pianists and new musicians alike.
Pad controllers are, like MIDI keyboards, prevalent in MIDI setups as well.
These devices feature pads sensitive to velocity and pressure; ideal for programming drum sounds and triggering samples.
They offer a tactile and expressive way to input MIDI data, especially for beat-making and live performances.
MIDI drum controllers, specifically designed for percussionists, mimic the layout of a drum kit, translating physical beats into MIDI messages.
For those seeking extensive control, MIDI control surfaces offer:
- Knobs
- Faders
- Switches
These are indispensable for tweaking synth parameters, mixing tracks, or live performances, allowing for real-time control over multiple aspects of your software.
MIDI wind controllers cater to wind instrument players.
They capture breath and finger movements to control MIDI data, bringing a natural and expressive feel to digital wind instruments.
Stringed instrument MIDI controllers exist for guitarists and bassists.
These instruments convert string vibrations into MIDI messages 一 opening up a new realm of sound possibilities for string musicians.
This variety in other MIDI controllers showcase the versatility of MIDI when it comes to diverse MIDI musical instrument digital interface needs.
From electronic music production to more traditional musical approaches, MIDI controllers are super beneficial.
-
Key Features of MIDI Keyboards

MIDI keyboards are central to many music producers’ MIDI setups.
The key feature of a MIDI keyboard is its keys (which typically range from 25 to 88), mirroring the range of a traditional piano.
Weighted keys offer a piano-like feel, while synth-action keys provide a lighter touch, ideal for fast synth leads or organ parts.
Another significant aspect of MIDI keyboards is the inclusion of additional controls/MIDI events like knobs, faders, and pitch bend wheels.
These elements allow for real-time manipulation of MIDI data 一 enabling dynamic control over virtual instruments.
For instance, a pitch bend wheel can add expressiveness to piano sounds or lead synths, which reflects the bending of notes on a stringed instrument.
MIDI keyboards also often feature a USB port for easy connection to computers and other MIDI-compatible devices.
This simplicity in connectivity streamlines the music production process, allowing for a quick setup and integration into your existing workflow.
Some MIDI keyboards offer MIDI ports for traditional MIDI cables, which ensure compatibility with older hardware synths and drum machines.
A crucial feature of MIDI keyboards is their ability to work with software instruments and digital audio workstations (DAWs).
Through the piano roll in a DAW, MIDI notes played on the keyboard can be:
- Recorded
- Edited
- Played back
It offers, in turn, immense control over the composition process.
This interaction between MIDI keyboards and software is a testament to the power and flexibility of MIDI in modern music production.
NOTE
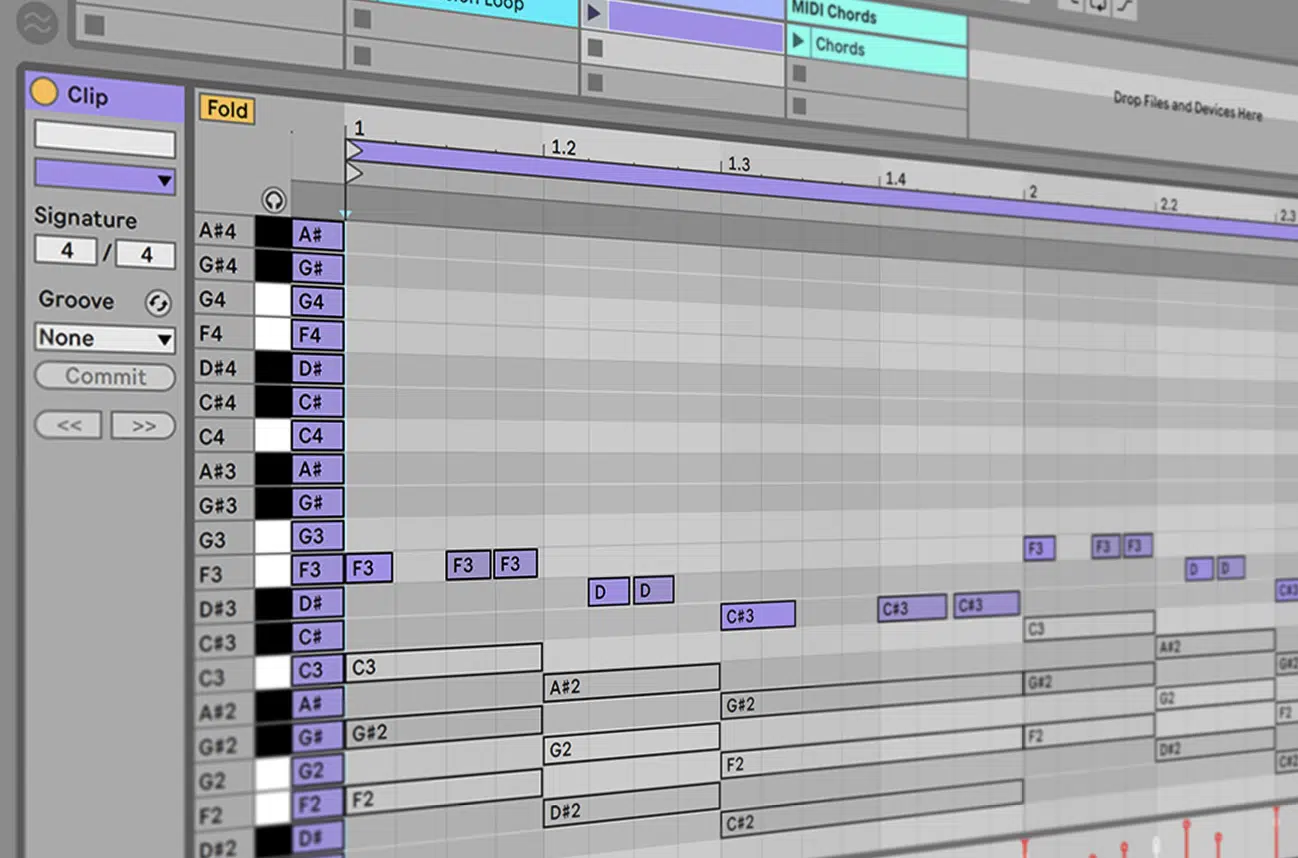
Utilizing the piano roll in a DAW, producers can input and edit MIDI notes with precision, creating the foundation of their tracks.
The piano roll visualizes MIDI data, making it easy to adjust note lengths, velocities, and timings 一 ensuring every element is perfectly in place.
Pro Tip: MIDI Controllers vs. MIDI Keyboards

While the terms MIDI controllers and MIDI keyboards are often used interchangeably, there are just a few distinctions worth noting…
MIDI Controller
A MIDI controller is a broad term that encompasses any device capable of generating and sending MIDI data to other MIDI-compatible devices.
This includes not only keyboards but also drum pads, control surfaces, and even wind controllers.
Essentially, a MIDI controller can be any hardware that facilitates the input of MIDI information into your music production workflow.
MIDI Keyboard
A MIDI keyboard specifically refers to a keyboard-style controller designed primarily for playing MIDI notes.
While many MIDI keyboards include additional features like knobs and faders, as we talked about, their primary function is to emulate a piano keyboard.
It provides an intuitive and familiar layout for playing and creating music.
MIDI keyboards are particularly favored by producers who have a background in piano or want a more traditional approach to creating melodies and harmonies.
-
Key Difference
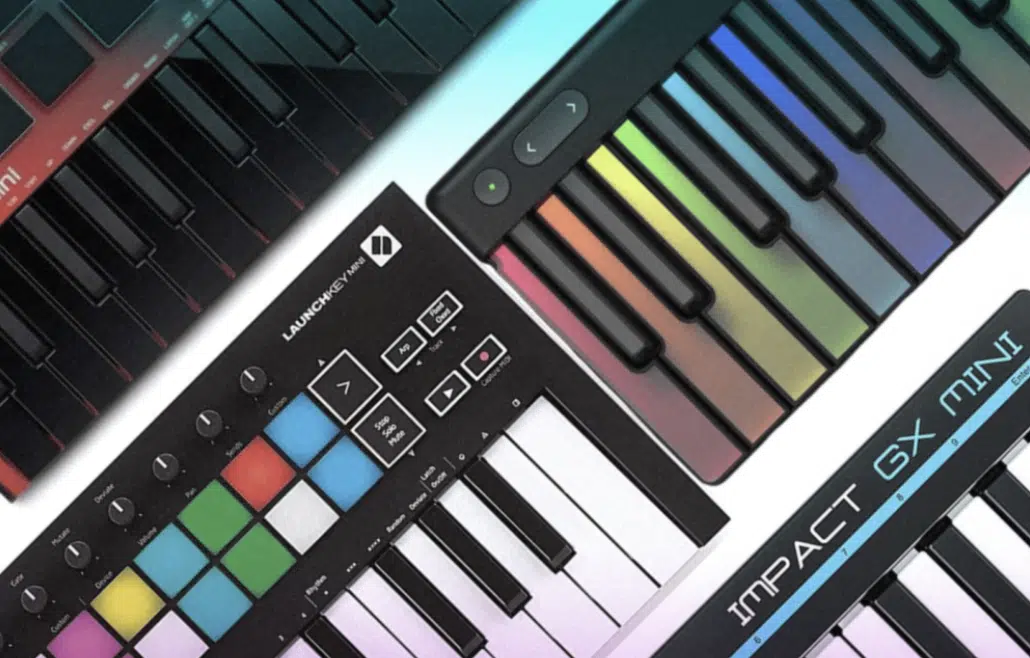

The key difference simply lies in their intended use.
MIDI controllers are more versatile and can be tailored to various aspects of music production, from beat-making to live performance control.
MIDI keyboards, while also versatile, are specifically geared towards the playing and composition of musical notes.
Understanding this distinction helps in choosing the right tool for your specific needs in your MIDI setup, but yes, you can get away with either one.
Exploring MIDI Data and MIDI Messages
MIDI’s true power lies in its ability to transmit a wide range of data and messages. Let’s explore the intricacies of MIDI data and messages, fundamental elements in how MIDI communicates musical information.
-
Understanding MIDI Data
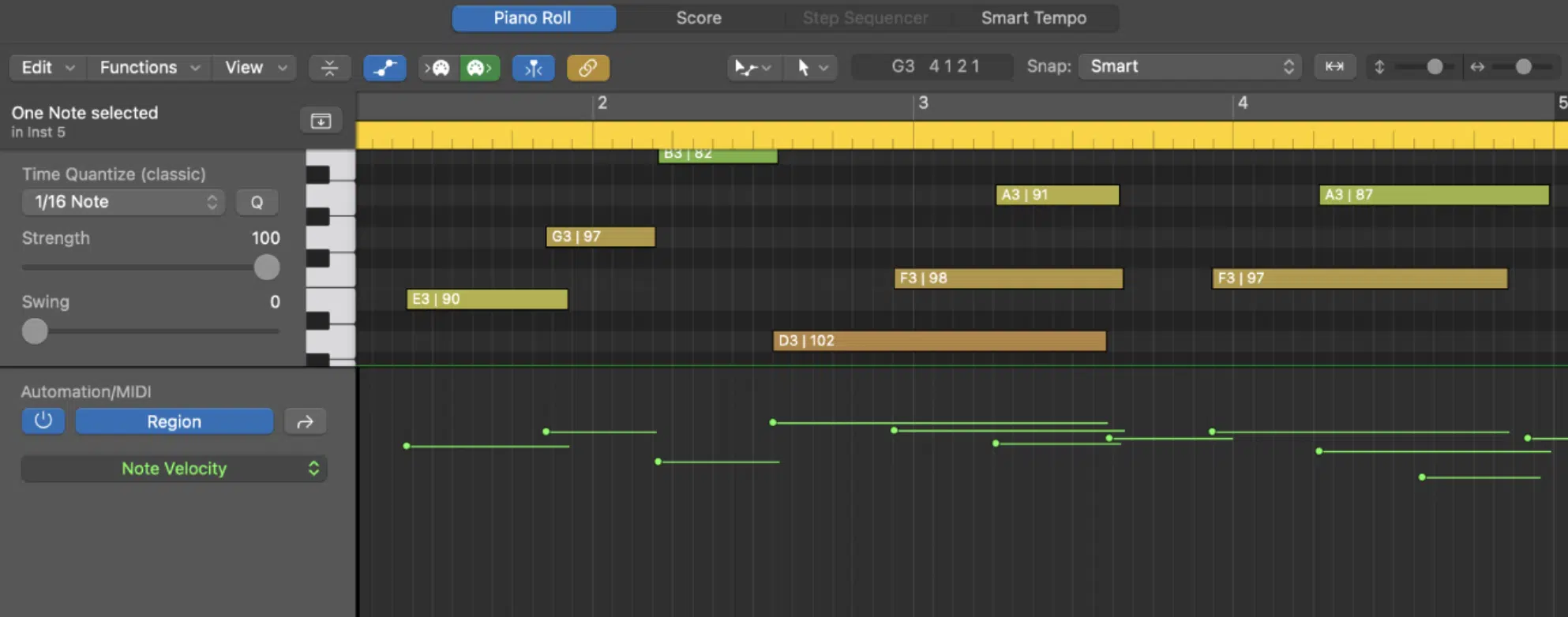
MIDI data is the language through which all MIDI devices communicate.
It consists of a series of messages that tell a MIDI instrument or software what to do.
These messages range from:
- NOTE-ON/NOTE-OFF messages 一 Indicate when a MIDI note is played/released
- Control change messages 一 Alters various parameters like volume or modulation within the software or hardware.
One of the most significant advantages of MIDI data is its precision and flexibility.
MIDI notes, for example, carry information not just about pitch but also velocity, which reflects how hard a key is pressed.
When you play notes with MIDI it allows for versatile performances, where the intensity of each MIDI note can be precisely controlled and replicated.
MIDI data can also be easily edited after recording, allowing you to perfect your performances or automate changes over time.
MIDI data also includes system-exclusive messages (which are specific to certain brands or models of instruments).
These MIDI messages allow for deeper control and customization of MIDI instruments, enabling unique sound design and performance capabilities.
Understanding MIDI data is crucial for effectively harnessing the capabilities of your MIDI devices and software instruments.
-
MIDI Messages & MIDI Information: The Basics
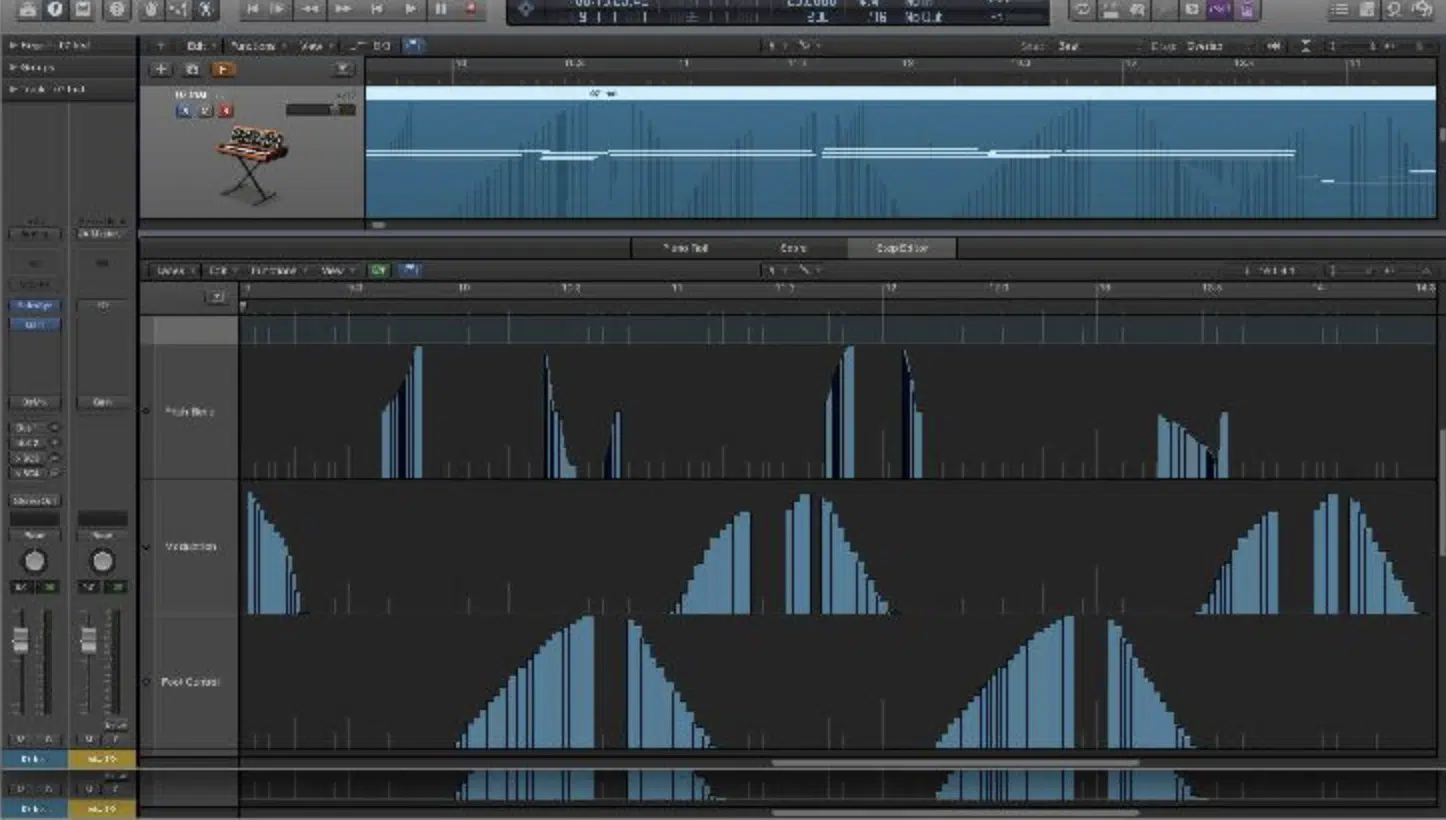
MIDI messages are the building blocks of MIDI data, each serving a specific purpose in the communication between MIDI devices.
The most common type of MIDI message is the note message, consisting of note-on and note-off events.
These messages indicate when a MIDI note is pushed and released, and are fundamental for sequencing melodies and harmonies.
Control change messages are another vital type of MIDI message.
They allow for the manipulation of various parameters in virtual instruments and MIDI-compatible hardware.
For example, a control change message could adjust the filter cutoff on a synthesizer or tweak the reverb level on a virtual piano 一 adding depth and character to your sounds.
Program change messages are used to switch between different sounds or presets within a MIDI instrument.
This is particularly useful in live performance settings, where quick changes are needed.
Pitch bend messages, another type of MIDI message, provide expressive control over the pitch of notes, allowing for smooth transitions and more expressive performances.
Understanding these various types of MIDI messages is essential for effective MIDI sequencing and sound manipulation in your music production process.
-
Pro Tip: Working with MIDI Files
MIDI files can be a game-changer in your music production process.
The MIDI protocol, the nucleus of the MIDI music instrument digital world, allows you to interact with and manipulate these MIDI files across various digital music devices.
By understanding the nuances of MIDI files, you can enhance your potential to create, edit, and refine your tracks as a whole.
Each MIDI file contains information, from note sequences to velocity and timing, all encoded in a format that the MIDI protocol seamlessly communicates with your software and hardware.
Mastering the use of MIDI files also means leveraging the MIDI protocol to its fullest.
MIDI files not only contain the framework of your tracks but also offer invaluable flexibility for experimentation.
Whether you’re rearranging chord progressions, manipulating drum patterns, or layering different instrument tracks, MIDI files are key.
They bridge your creative ideas with the technical prowess of digital music devices 一 transforming how you approach composition and production in the digital age.
MIDI Connectivity and Your MIDI Setup
Now that we’ve covered the essentials of MIDI data and messages, let’s move on to the practical side: connecting and setting up MIDI devices. This is where MIDI interfaces, a MIDI cable, MIDI ports, and other MIDI events come into play, forming the physical link in our music production setup.
-
Connecting with MIDI Cables and Ports
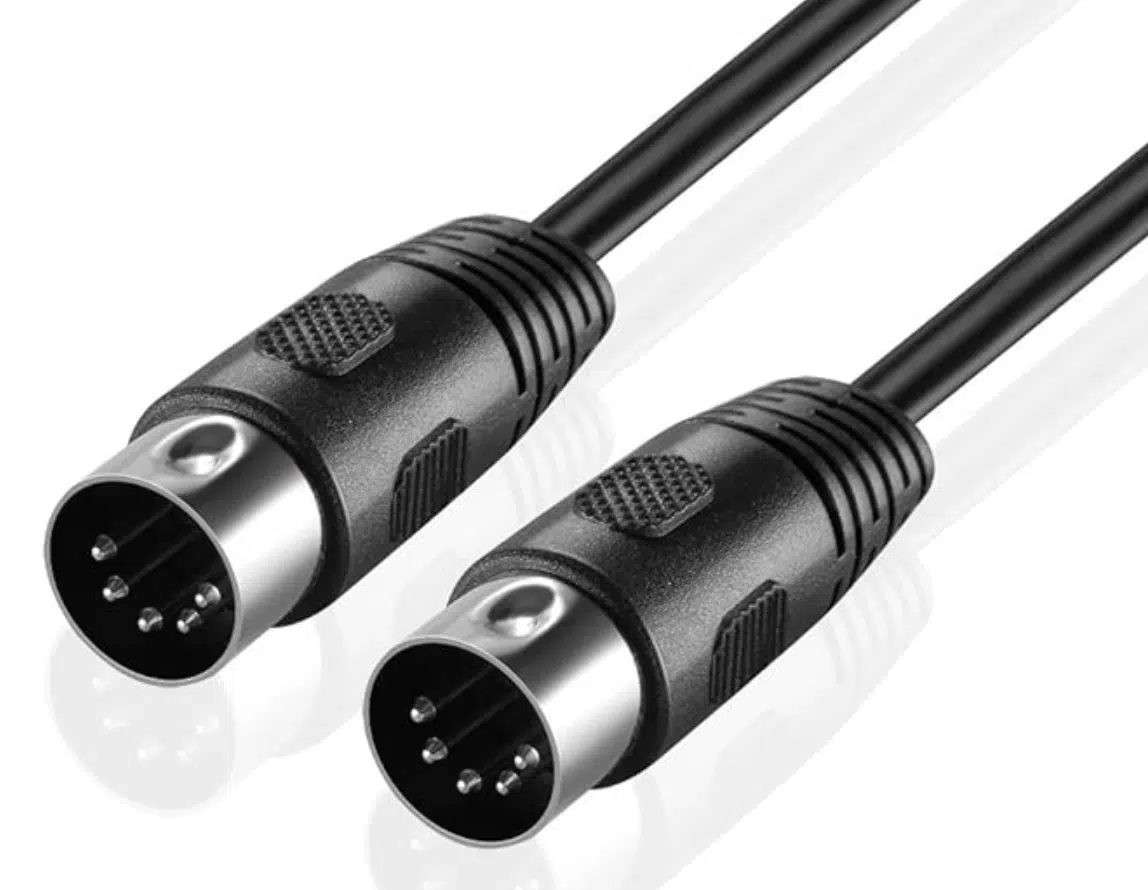

MIDI cables and ports are fundamental for linking various MIDI devices in your studio.
A standard MIDI cable carries MIDI data over 5-pin DIN connections, commonly found in traditional MIDI hardware.
For a seamless music production process, ensuring that every MIDI cable is correctly connected to the MIDI ports – MIDI In, MIDI Out, and MIDI Thru – is crucial.
- The MIDI In port 一 Receives data from other devices.
- MIDI Out 一 Sends data from the device.
- MIDI Thru 一 Duplicates the MIDI Out data to chain multiple devices.
In modern setups, USB MIDI has become prevalent, simplifying connections between MIDI keyboards, controllers, and computers.
USB MIDI eliminates the need for a separate MIDI interface, allowing MIDI keyboards and controllers to connect directly to a computer via a USB port.
This advancement has streamlined the music production workflow, making it more accessible and efficient, especially for home studios.
-
Setting Up Your MIDI Interface for Optimal Performance
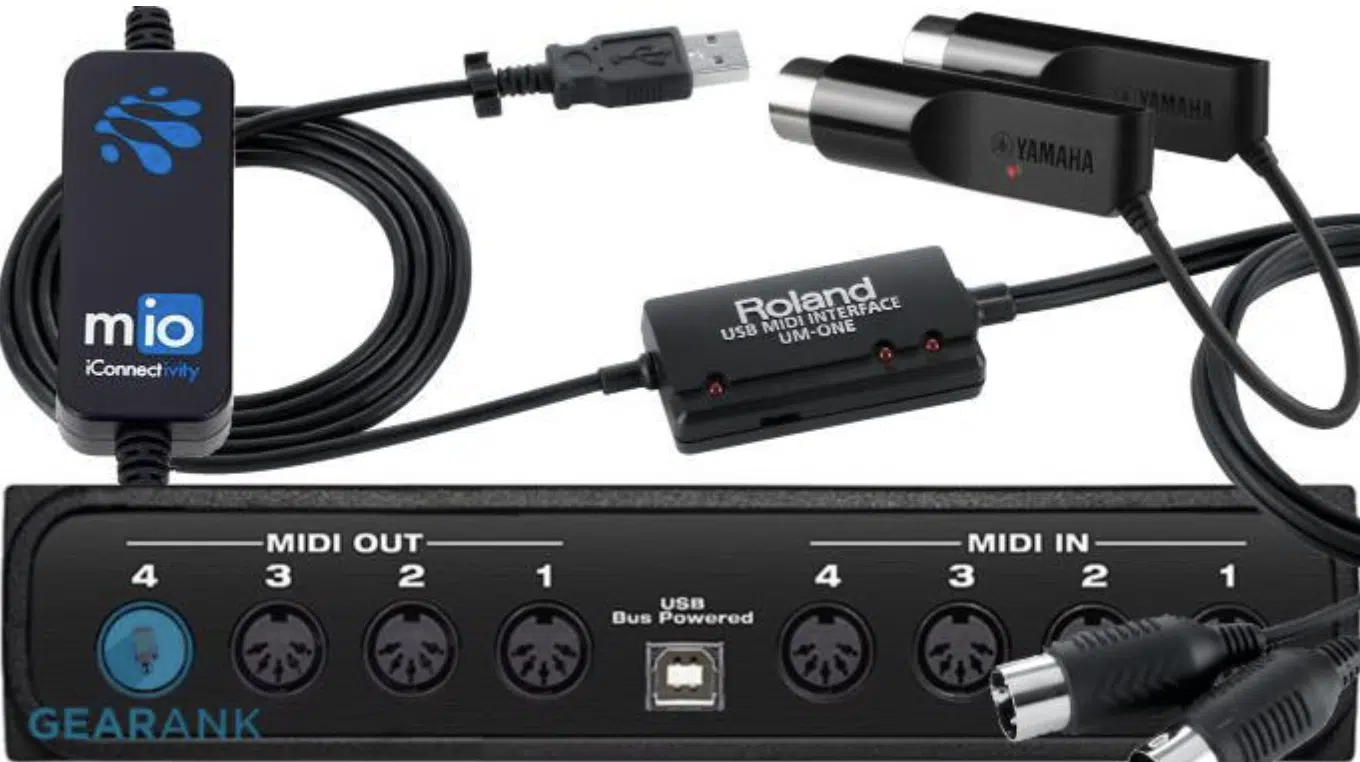

A MIDI interface is essential for bridging the gap between traditional MIDI hardware and modern computer-based systems.
It acts as a translator, converting MIDI data to a format that digital audio workstations (DAWs) can understand and vice versa.
Choosing the right MIDI interface depends on:
- The number of MIDI devices you have
- The complexity of your setup
Configuring your MIDI interface correctly is key for ensuring smooth communication between your devices.
This involves setting the correct MIDI channels (channels through which MIDI messages are sent and received).
A well-configured MIDI setup ensures that the right data reaches the intended device, be it a drum machine, hardware synth, or virtual instrument.
Another crucial aspect is managing MIDI latency (the delay between triggering a MIDI event and hearing the sound).
A good MIDI interface should minimize latency to ensure real-time responsiveness, which is especially important when playing live or recording intricate parts.
Adjusting buffer sizes and sampling rates in your DAW can also help in reducing latency 一 providing a more fluid and productive music creation experience.
-
Ensuring Compatibility with MIDI Devices and Software
Compatibility is key in a MIDI setup, especially considering the variety of MIDI devices and software available.
MIDI keyboards, controllers, and interfaces must be compatible with the software instruments and DAWs you use.
Checking for MIDI compatibility, which refers to the ability of devices to understand and correctly interpret MIDI messages, is essential.
Most modern MIDI controllers and keyboards are class-compliant 一 meaning they don’t require specific drivers to operate with most operating systems.
However, ensuring that your MIDI hardware and software are updated to the latest versions can prevent compatibility issues and take advantage of the latest features.
This includes advanced features like MIDI 2.0.
NOTE: MIDI 2.0, the latest standard, offers enhanced features like increased resolution for MIDI messages, improved expressiveness, and better interoperability between devices.
Ensuring your MIDI devices support MIDI 2.0 or can be updated to it is a forward-looking approach, keeping your setup future-proof and versatile.
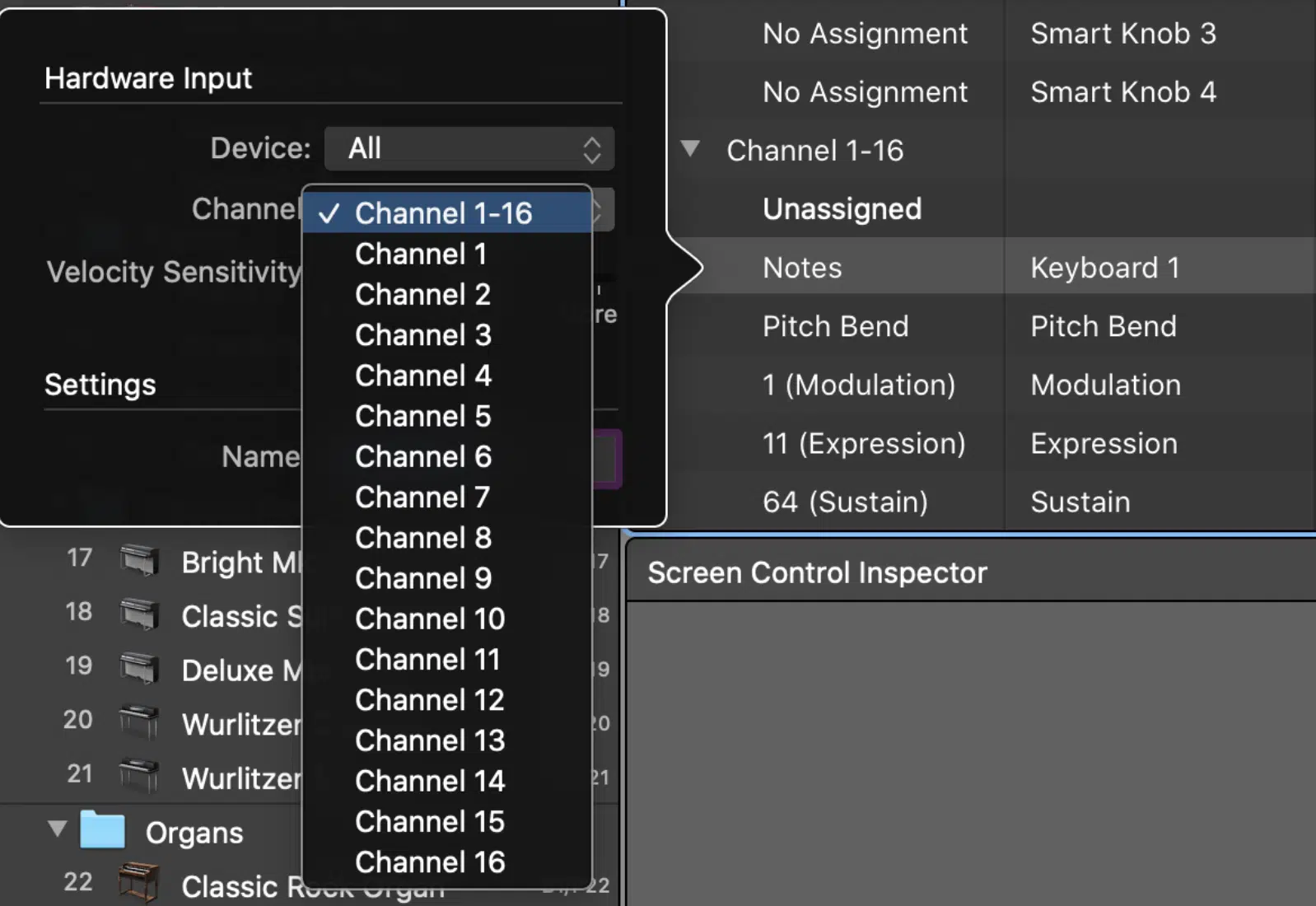
MIDI channels are fundamental to organizing and directing MIDI data in a music production environment.
A single MIDI cable can transmit information over 16 different channels, which allows you to control multiple instruments separately.
Understanding and correctly setting MIDI channels on your devices is crucial for effective MIDI sequencing and layering of sounds from your sound library.
When setting up a MIDI channel, consider the role of each device in your setup.
For instance, you might dedicate:
- One channel 一 To a MIDI keyboard controlling a virtual piano
- Another channel 一 For a drum machine
- Another channel 一 For a MIDI controller manipulating a synthesizer
- Etc.
This organization ensures that MIDI messages are correctly routed, preventing conflicts and ensuring that each device responds as intended.
It’s also essential to understand the difference between MIDI channel messages, which are directed to a specific channel, and system-wide messages that affect every MIDI channel.
Managing MIDI outputs is crucial, especially when dealing with complex MIDI setups.
Each MIDI device in your setup should have your MIDI output correctly routed to either your DAW or other MIDI hardware.
For example, a MIDI keyboard might send its output to a DAW for recording, while a MIDI controller might output to a music hardware synthesizer for live performance.
Properly configuring your MIDI output ensures a smooth and error-free music production process.
Remember, incorporating digital music gear into your setup enhances the way recorded MIDI translates a piano sound into a rich audio signal.
This is a key factor in how we record music and execute MIDI tasks efficiently.
MIDI Wizard 2.0: The Ultimate MIDI Software
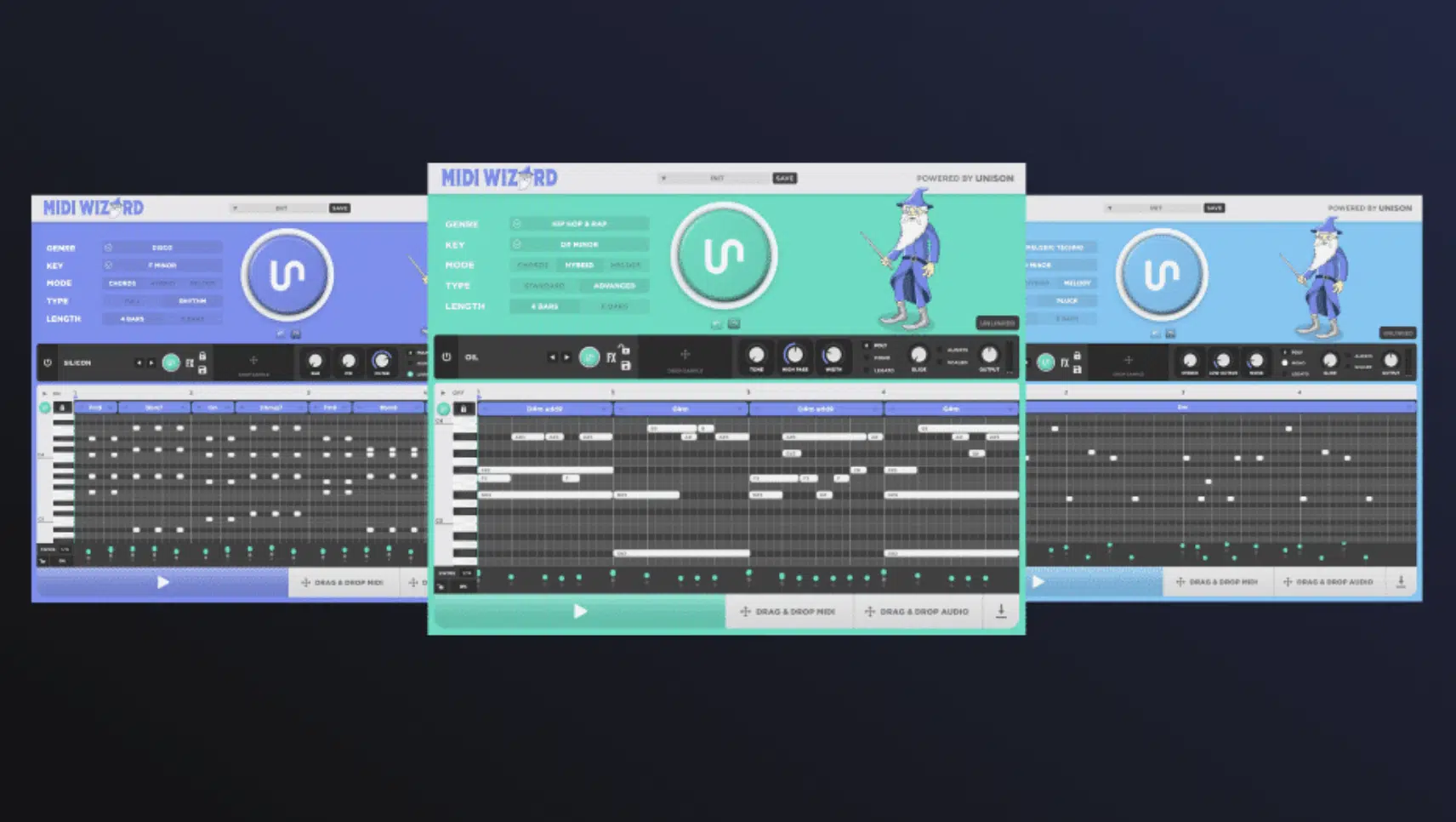
MIDI Wizard 2.0, developed by Unison Audio, represents a significant leap in MIDI software technology.
It’s an AI-powered plugin designed to instantly generate hit melodies and chord progressions across a wide variety of genres.
MIDI Wizard 2.0 is especially beneficial for music producers looking to enhance their creative process and efficiency.
It’s packed with features that cater to the diverse needs of music producers.
It offers three main modes:
- Chord mode: Generates impressive chord progressions in either block format or rhythm.
- Melody mode: For creating catchy melody top lines as longer leads or short plucks.
- Hybrid mode: Combines chord/melody algorithms with AI to produce truly innovative results.
These modes provide producers with a versatile toolkit for crafting intricate musical pieces across various genres.
Additionally, the MIDI Wizard 2.0 comes with a built-in synthesizer, a sampler, and over 200 factory presets, enhancing its usability in music production.
The software also includes 16 built-in effects 一 allowing users to add depth and character to their sounds.
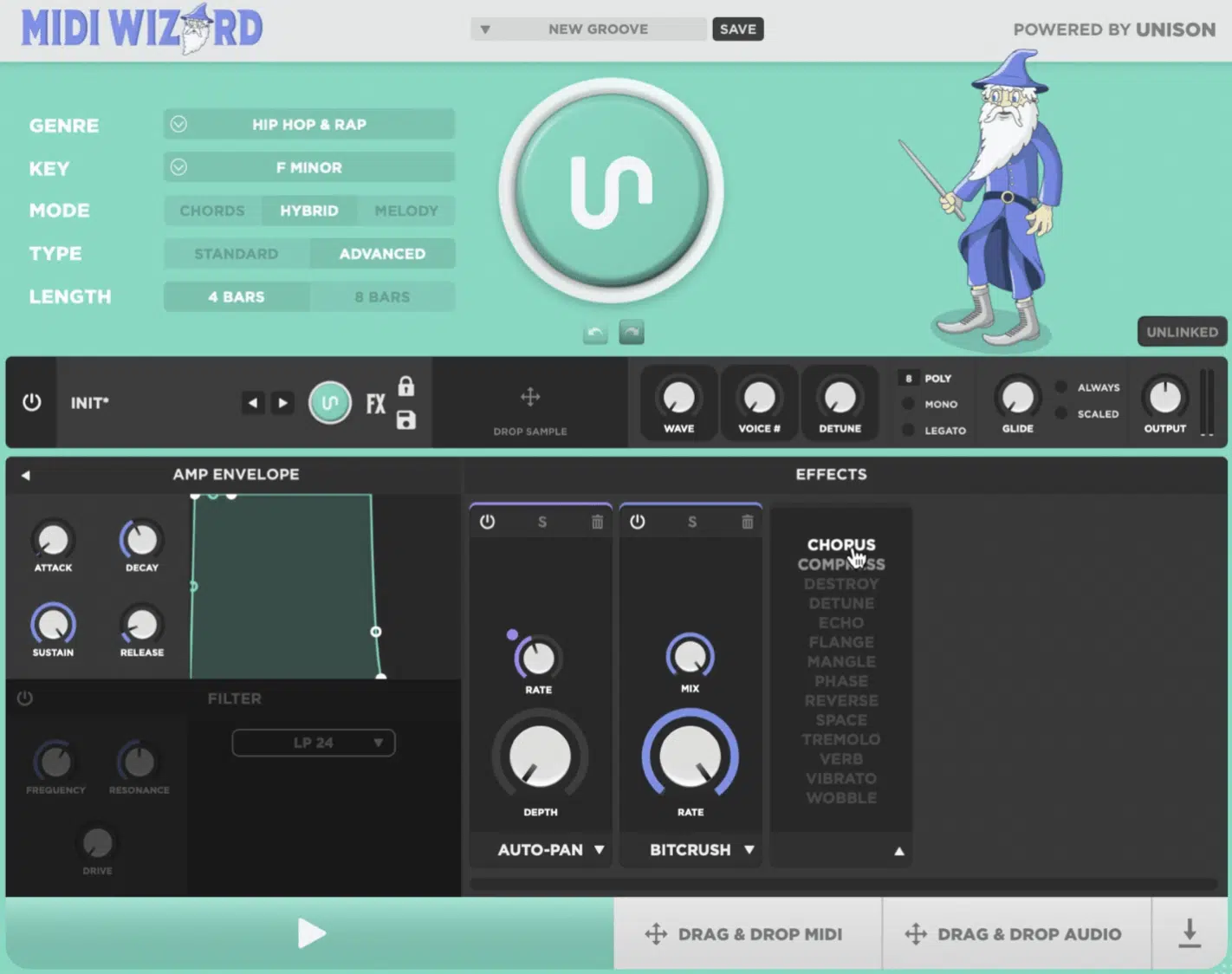
One of its standout features is the AI chord progression detection, which can intelligently produce matching melodies based on the input chords.
MIDI Wizard’s ability to label chord progressions and offer drag-and-drop functionality, or export as audio files, makes it a highly user-friendly tool for producers.
Integrating seamlessly with other Unison tools, MIDI Wizard 2.0 can be linked with tools like Bass Dragon, which can completely change the game.
Plus, included features such as swing and velocity sensitivity add a more humanized touch to chord progressions and melodies.
These features collectively make MIDI Wizard 2.0 a must-have for music producers seeking to create emotionally impactful music.
As well as stand out in the competitive field of music production.
Advanced MIDI Features
Having covered the basics of MIDI connectivity and MIDI setup, let’s explore some of the advanced features that MIDI offers. These features, including MIDI sequencing and the use of MIDI 2.0, open up new possibilities for creativity and expression in music production.
-
The Power of MIDI Sequencing
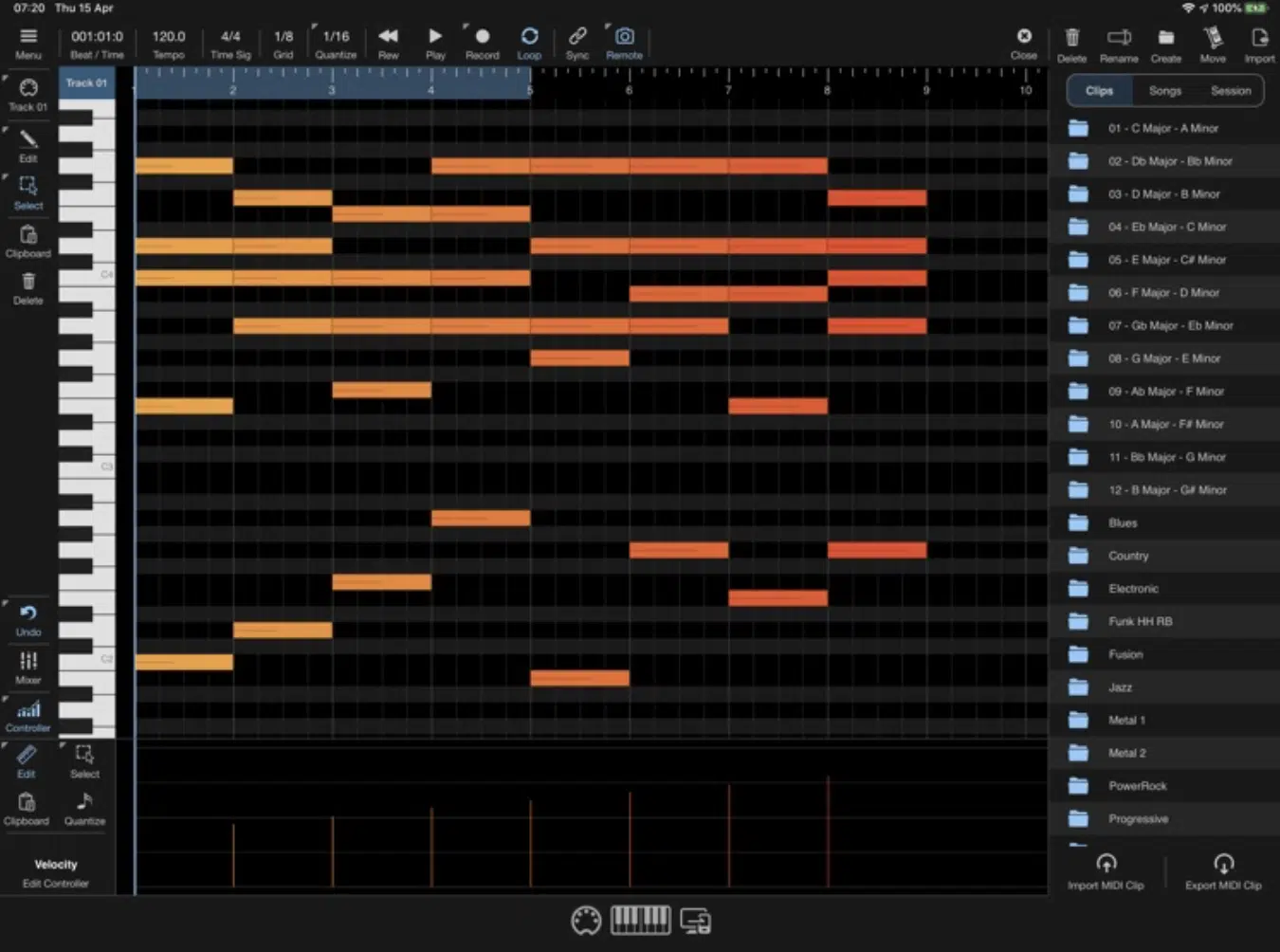
MIDI sequencing is a process where MIDI data is recorded, edited, and played back in a sequence, typically within a DAW.
This allows for the creation of intricate tracks and arrangements 一 layering multiple MIDI tracks to create a full arrangement.
Using a MIDI sequencer, be it hardware sequencer or software, you can create each aspect of your tracks with precision, from drum patterns and chords to melodic lines.
One of the strengths of MIDI sequencing is its non-destructive nature.
You can, without permanently altering the original performance:
- Edit MIDI notes
- Change velocities
- Adjust timing
This flexibility is invaluable in the music production process 一 allowing for endless experimentation and refinement.
For example, a MIDI sequencer can be used to create complex chord progressions or evolving drum patterns, which brings extra depth and complexity to your tracks.
MIDI sequencers also often offer advanced features like quantization, which corrects timing inconsistencies, and automation, allowing allows for dynamic changes over time.
These tools (software/hardware sequencers) are essential for achieving a polished and professional sound in your songs.
Whether you’re working with standalone MIDI sequencers or the sequencer within your DAW, mastering these tools is a key aspect of modern music production.
Exploring MIDI 2.0 and Its Advancements
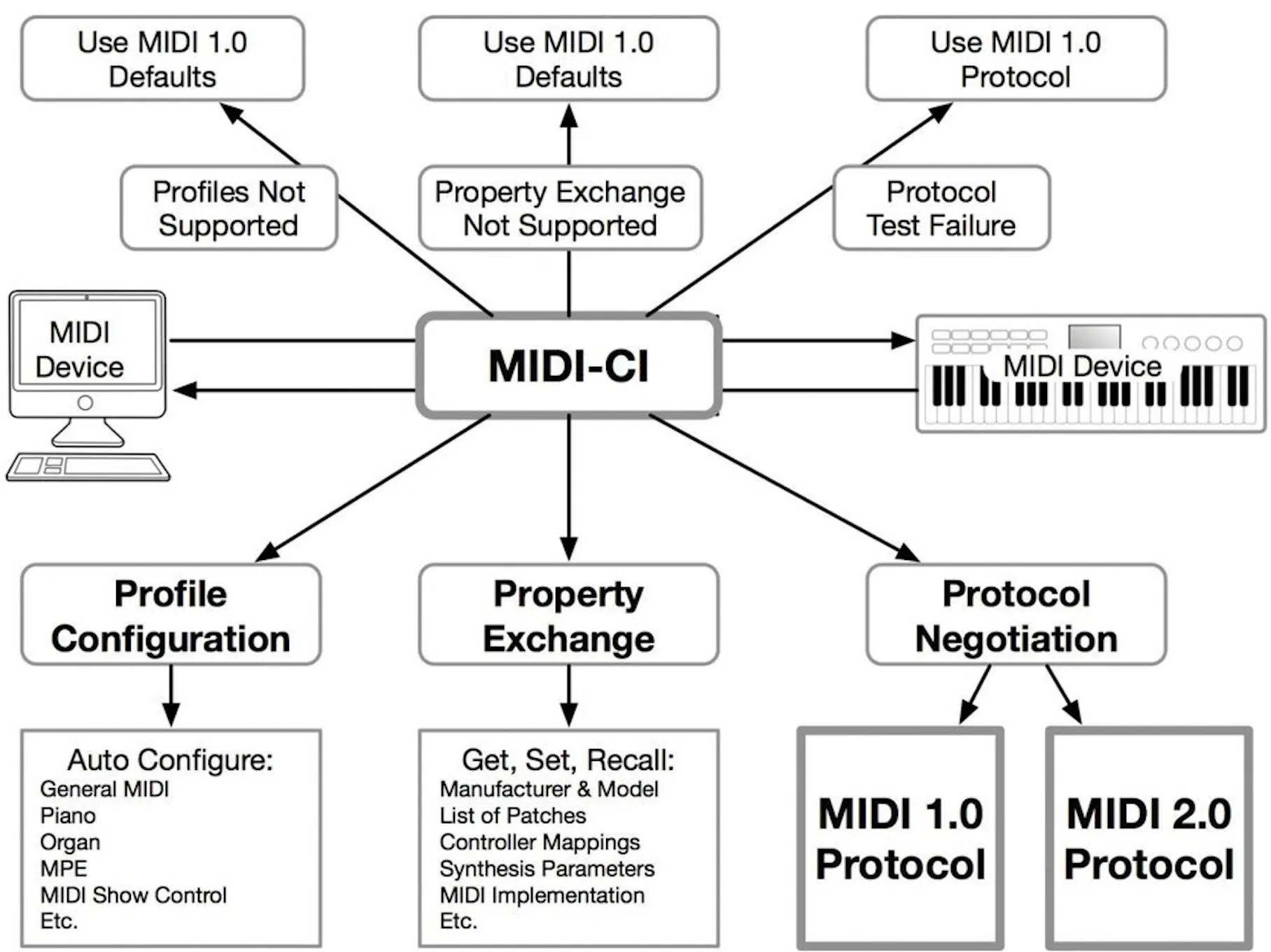
MIDI 2.0 is the latest evolution in the MIDI standard, introducing several advancements that enhance the capabilities of MIDI in music production.
One of the most notable improvements is the increased resolution of MIDI messages 一 allowing for more detailed and expressive performances.
This higher resolution means subtler nuances in playing can be captured and reproduced (a significant leap from the limitations of the original MIDI standard).
Another key feature of MIDI 2.0 is improved interoperability between devices.
It ensures better communication and compatibility because it links more devices seamlessly.
This is particularly beneficial in complex setups where multiple MIDI controllers, keyboards, and interfaces interact.
MIDI 2.0 also introduces new types of MIDI messages and expanded capabilities like enhanced control over dynamics and articulation.
These advancements open up new possibilities for sound design and performance, allowing producers to achieve greater expressiveness and control in their music.
Adopting MIDI 2.0 in your setup can significantly elevate your music production capabilities, keeping you at the top of technological advancements in the field.
Building Your MIDI Setup: Essential Components
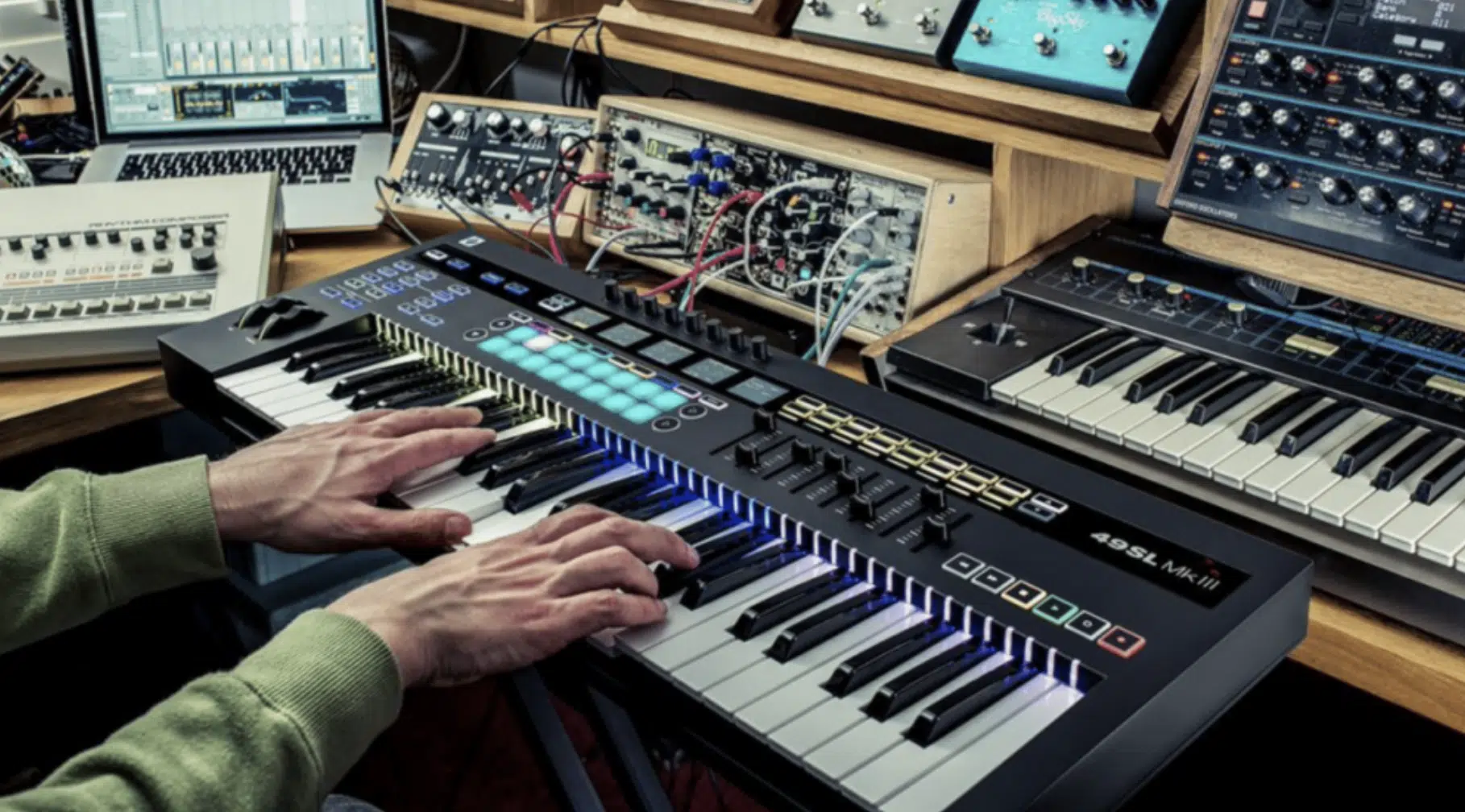

Building a MIDI setup that suits your music production needs involves selecting the right combination of MIDI:
- Controllers
- Interfaces
- Software
A MIDI keyboard is often the centerpiece, providing a tactile and intuitive way to input MIDI notes.
Adding a drum pad controller can enhance your ability to program rhythms and add percussive elements.
A reliable MIDI interface is crucial, especially in setups that include hardware synthesizers or drum machines.
It ensures smooth communication between your computer and MIDI hardware, reducing latency and ensuring synchronization.
For those who incorporate a lot of hardware, a MIDI interface with multiple ports is key.
Software is the final piece of the puzzle, with DAWs serving as the hub for all MIDI activities.
A DAW not only records and processes MIDI data but also hosts virtual instruments and FX plugins.
NOTE: Choosing a DAW that aligns with your workflow and preferences is critical, as it greatly influences your efficiency and creativity in the studio.
What is a MIDI Setup? Final Thoughts
From the basics of MIDI controllers to advanced features like MIDI 2.0 and the innovative MIDI Wizard 2.0, the knowledge we covered today is invaluable.
MIDI is more than just a bunch of cables and codes 一 it’s your partner in bringing those melodies and rhythms in your head to life.
Whether you’re setting up your first home studio or looking for new ways to elevate your sound, remember that MIDI is all about flexibility, creativity, and innovation.
So go ahead, apply these insights, experiment with new sounds, and most importantly, enjoy the process of making music.
With a solid understanding of MIDI and how to use it effectively, you’re well on your way to creating something truly special.
Until next time…







Leave a Reply
You must belogged in to post a comment.