Audio formats are the backbone of digital music production.
They can drastically affect the quality, size, and compatibility of your music projects.
As a music producer, it’s important to understand the intricacies of various audio formats to make informed decisions that align with your creative visions and practical needs.
Whether you’re recording, editing, or distributing music, the right audio file format can be the difference between an average and a professional-sounding track.
In today’s article, we’ll break down:
- Understanding Audio Formats ✓
- Common Audio File Formats ✓
- Uncompressed vs. Compressed Audio ✓
- WAV and AIFF Files ✓
- MP3 and AAC Formats ✓
- Lossless Audio Codecs ✓
- Lossy Audio Compression ✓
- The best audio file format for your projects ✓
- Impact of File Format on Audio Quality ✓
- Storage and File Management Strategies ✓
- Technical Aspects of Audio Data ✓
By the end of this article, you’ll have a deep understanding of audio file formats and their implications in music production.
You’ll be equipped to choose the most suitable formats for various aspects of your projects 一 ensuring the best possible audio quality in all of your tracks.
You will gain insights into managing file sizes and maintaining sound integrity, allowing you to work efficiently and effectively like a professional music producer.
So, let’s dive in…
Table of Contents
Understanding Audio Formats
In the evolving landscape of digital audio production, understanding audio file formats is crucial. Let’s start by defining all the audio file formats and their significance in the music industry, including the most popular audio file format.
-
What Are Audio Formats?
Audio formats are essentially containers for audio data, a way to store and transmit sound digitally.
Each audio format, whether it’s a WAV, MP3, or FLAC file, has its unique way of encoding and compressing audio data.
These audio format types vary in terms of:
- Audio quality
- File size
- Compatibility with different playback systems
The primary distinction in audio file formats lies in how they compress and store audio data, which you’ll need to know as a music producer.
Uncompressed audio formats like WAV and AIFF files preserve the original audio quality by storing raw audio data, but this results in larger file sizes.
On the other hand, compressed audio files like MP3 or AAC reduce file size by removing certain audio data, which can affect sound quality.
The choice of an audio file format has a direct impact on the final output of a project.
High-resolution formats (hi-res audio files) are the most common audio format for studio recordings.
This is because a high-resolution audio format ensures the highest audio quality, while compressed formats are more suitable for online streaming where storage space and bandwidth are limited.
-
The Role of Audio Formats in Digital Music Production

In digital music production, choosing an audio format is a balancing act between maintaining optimal audio quality and managing file size and compatibility.
Uncompressed audio files offer the best sound quality but require more storage space and processing power.
Compressed audio formats are widely used for distributing music due to their smaller size.
This makes them ideal for streaming services and personal music players.
However, they may not be the best choice for professional music production where audio quality is paramount.
Different Audio File Formats
Each audio format serves a specific purpose in music production. Let’s cover the common types of audio formats and compare uncompressed formats and compressed formats.
-
Overview of Common Audio File Formats

The most common audio file formats include WAV, MP3, AIFF, and FLAC.
- WAV files, an uncompressed audio format, are widely used in professional settings due to their high audio quality.
- MP3s, a form of compressed audio, are popular for consumer use due to their smaller size.
- FLAC files offer a middle ground as a lossless compressed format 一 they reduce file size without sacrificing audio quality.
- AIFF files are similar to WAVs but are more commonly used on Apple devices, utilizing the same uncompressed audio file format.
Each format has its specific purposes, functions, and uses.
For example, WAV files are often used in recording studios and for audio editing, while MP3 files are preferred for online distribution.
Understanding these formats is crucial for making informed decisions in music production and will help you achieve supreme audio quality.
Uncompressed Audio Formats
Transitioning into high-quality audio, we’ll start with uncompressed audio formats. These audio file types are crucial for maintaining the purest form of audio data, essential in professional music production settings.
-
WAV Files: The Gold Standard in Uncompressed Audio
WAV files, representing the Waveform Audio File Format, are the backbone of professional audio recording.
As an uncompressed audio format, WAV files maintain all the nuances of audio data, ensuring pristine audio quality.
This makes them the most popular audio format for recording studios, where capturing every detail of the sound is paramount.
However, the high fidelity of WAV files comes at the cost of large storage space requirements.
Each WAV file contains raw audio data in its unaltered form 一 resulting in significantly larger file sizes compared to compressed audio files.
This factor makes the WAV file less suitable for casual use but indispensable for professional audio projects where sound quality is non-negotiable.
-
AIFF Files: The Preferred Choice for Apple Devices
AIFF files, or Audio Interchange File Format, are Apple’s answer to the WAV format.
Like WAV, AIFF is an uncompressed audio format that retains all the audio data from the original recording, ensuring excellent sound quality.
This makes AIFF files a popular choice among Apple device users, especially those engaged in professional music production.
AIFF files share the same drawback of large file sizes as WAV files.
An AIFF file is ideal when working within the Apple ecosystem 一 offering seamless compatibility with Apple’s software and hardware.
This audio file format is often used in settings where Apple’s devices and software are predominant, leveraging their integrated environment for efficient audio production.
-
Pulse Code Modulation

At the heart of both WAV and AIFF files lies Pulse Code Modulation (PCM).
Pulse Code Modulation is a method used to digitally represent sampled analog signals.
It is the standard form of audio data encoding in uncompressed audio files 一 ensuring the audio is captured and reproduced with high fidelity.
This makes Pulse Code Modulation indispensable in settings where preserving the integrity of the audio quality is crucial.
The significance of PCM in professional audio work cannot be overstated.
It provides a reliable way to maintain the audio quality of recordings, making it a fundamental music technology in the production of high-quality uncompressed audio files.
This technology is especially important in studios and for archival purposes, where the accuracy of audio data representation is a top priority.
Compressed Audio Formats
As we shift focus to more storage-friendly audio format types, we encounter compressed audio formats. These formats are designed to balance audio quality with file size, making them versatile for various applications.
-
MP3 Files: The Ultimate Compressed Format
MP3 files, standing for MPEG Audio Layer III, have become synonymous with digital music.
As a compressed audio format, MP3 uses lossy compression to reduce file size significantly while maintaining a reasonable level of sound quality.
This makes MP3 files incredibly popular for consumer use, where the balance between quality and file size is crucial.
The widespread use of MP3 files is largely due to their:
- Versatility
- Flexibility
- Compatibility
They span across a broad range of devices and promotional platforms.
While they may not match the audio quality of uncompressed audio formats, their smaller size makes them ideal for online distribution.
As well as personal music libraries, where storage space is a consideration.
-
AAC Files: Advanced Audio Coding for Efficient Storage
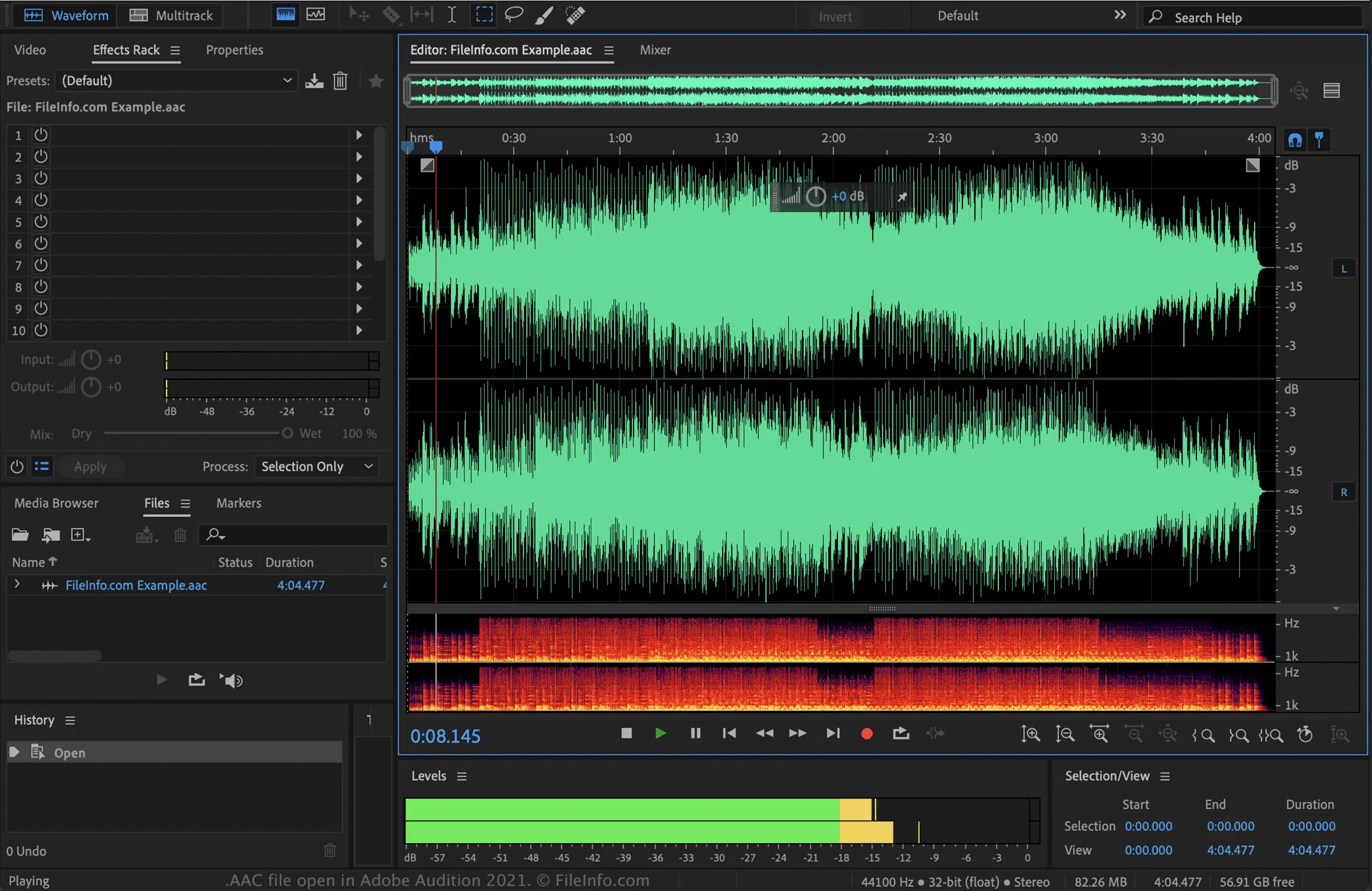
AAC files, short for Advanced Audio Coding, represent a step forward in compressed audio technology.
An AAC file is known for providing better sound quality at similar bit rates compared to MP3 files, making them a more efficient choice in terms of storage.
This has led to their widespread adoption in various digital platforms 一 especially those prioritizing audio quality within limited bandwidth.
The use of AAC files is particularly prevalent in Apple’s ecosystem, where they are favored over MP3 for their superior audio quality and efficient compression.
This makes them a preferred choice for users of Apple devices, offering a good balance between sound quality and file size.
-
WMA (Windows Media Audio) Files: Windows Media Audio’s Role

WMA files, or Windows Media Audio, are a proprietary audio format developed by Microsoft.
As a compressed audio format, WMA was designed to compete with MP3, offering similar levels of audio quality and file size reduction.
WMA files (like those displayed in the WMA lossy format) are often used in the Windows operating system and are compatible with various Microsoft products.
While WMA files may not be as universally accepted as MP3 or AAC files, they hold a significant place in the realm of compressed audio formats.
Especially for users within the Windows ecosystem.
This proprietary format offers a viable alternative to MP3, particularly in environments where Microsoft’s software and devices are predominant.
Lossless Audio Formats
Delving into high-fidelity audio, let’s explore lossless audio formats. Lossless formats (lossless file formats) offer an ideal balance between digital audio quality and file size optimization.
-
FLAC Files: Free Lossless Audio Codec Explained

FLAC files, standing for Free Lossless Audio Codec, present a compelling solution for audiophiles and professionals alike.
This lossless compressed audio format maintains complete audio data integrity, meaning no quality is lost during compression.
This digital audio file type can reduce file size without compromising audio quality, making it an attractive option for high-quality audio storage and streaming.
The versatility of FLAC files extends to their widespread compatibility with a range of:
- Audio playback systems
- Software
The efficient compression algorithm of this popular digital audio format ensures that users can enjoy high-resolution audio.
All without the significant storage space demands typical of uncompressed audio files like WAV or AIFF.
-
Apple Lossless Audio Codec: Optimized for Apple Devices

The Apple Lossless Audio Codec (ALAC) is Apple’s proprietary answer to FLAC.
Designed for seamless integration with the Apple ecosystem, ALAC files offer lossless compressed audio quality.
This ensures that no audio data encoded is lost during the compression process.
Therefore, it makes this audio file format a perfect choice for users of Apple devices who do not wish to compromise on audio quality.
ALAC files, similar to FLAC, manage to compress the audio data without any loss of quality 一 making them ideal for storing large music libraries on Apple devices.
Their optimization for Apple’s hardware and software ensures that they are one of the most popular audio formats among users of Macs, iPhones, and other Apple products.
-
Other Lossless Compressed Formats
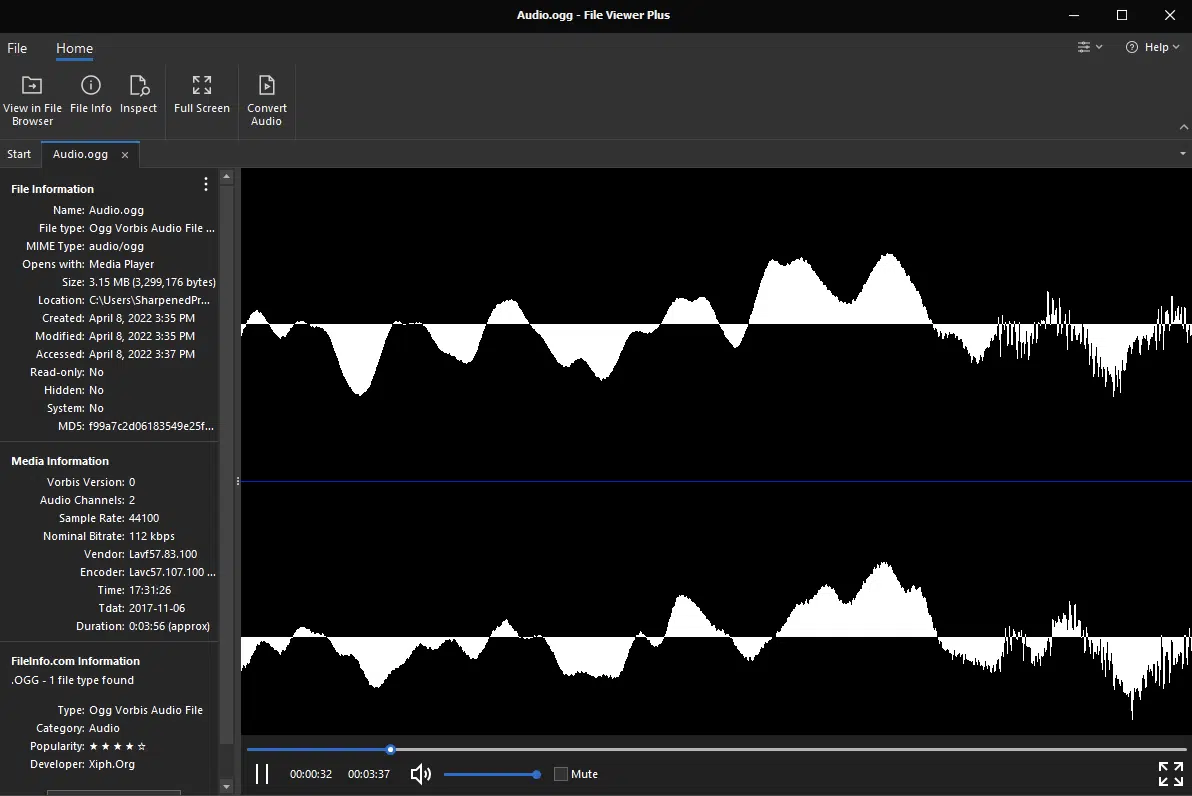
Beyond FLAC and ALAC, there are other lossless compressed formats that cater to specific needs and platforms.
For instance, the Waveform Audio File Format (WAV) offers a PCM-encoded lossless audio codec alternative.
The Monkey’s Audio is another format known for its high-quality audio data preservation.
Each of these audio file formats (while less common than FLAC or ALAC) serves a niche audience and purpose.
They are particularly relevant for users with specific hardware or software preferences or those seeking alternatives to the more mainstream lossless compressed audio files.
Finally, OGG Vorbis files are a type of audio file format that uses free, open-source lossy compression, known for providing high-quality sound at lower bit rates compared to other formats like MP3.
Lossy Audio Formats
Moving to a category that balanced file size with quality, lossy audio formats/lossy audio files offer a practical solution for everyday use and online distribution. So, let’s dive into the interesting world of lossy file formats.
-
Understanding Lossy Formats
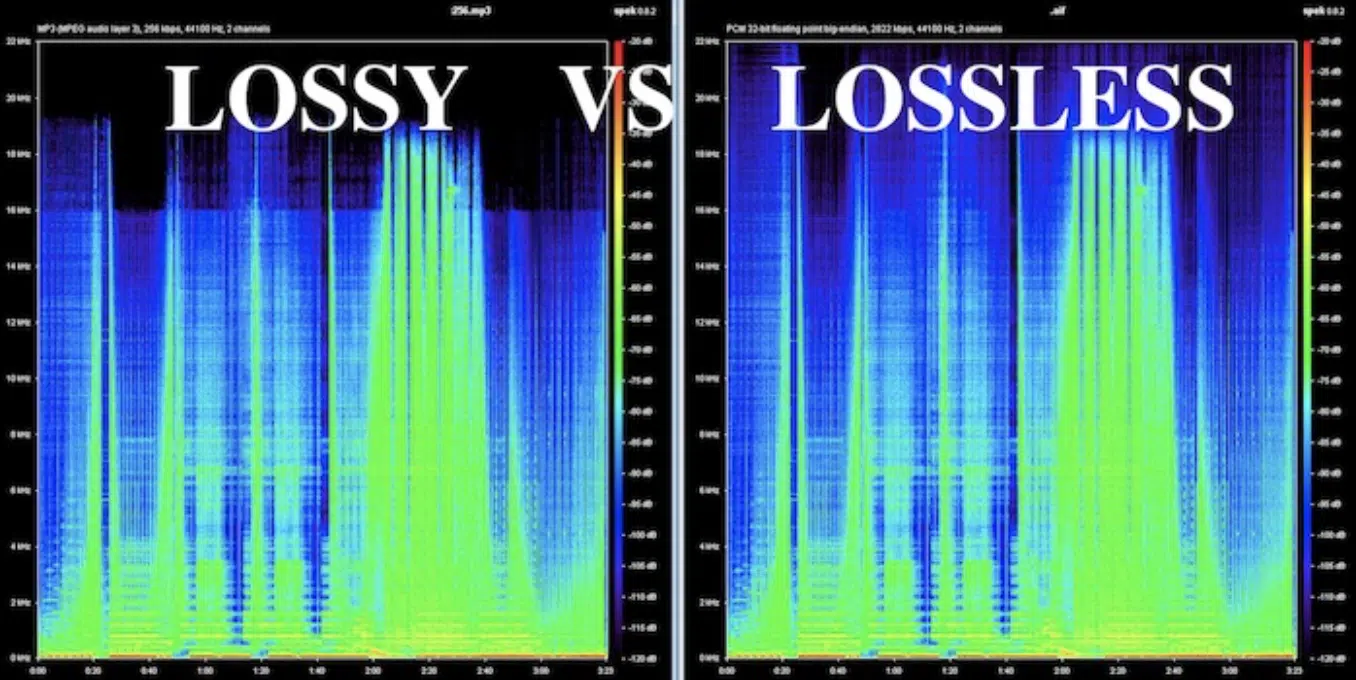
Lossy audio formats like MP3, AAC, and WMA are designed to compress audio data by removing parts deemed less critical to human hearing.
This results in significantly smaller file sizes, making these formats ideal for online streaming, where bandwidth and storage are limited.
The key trade-off with lossy formats lies in their impact on sound quality.
While they are highly efficient in terms of storage and streaming, the compression process inevitably leads to some loss of fidelity.
The extent of this quality loss depends on the compression level and the algorithm used.
Lossy audio is a staple in the consumer market, where convenience and storage efficiency often outweigh the need for perfect audio quality.
These lossy compressed formats have reshaped how we consume music 一 making audio more accessible and portable than ever.
Audio Quality Considerations
When it comes to music production, audio quality (and sound quality) is a paramount consideration. Let’s get into it.
-
Impact of Audio File Format on Audio Quality

The choice of an audio file format directly influences the audio quality of a recording or a music track.
Uncompressed audio formats like WAV and AIFF provide the highest fidelity, preserving the original audio data without any loss.
This is crucial in professional settings where every nuance of the sound is important.
Compressed audio formats, on the other hand (particularly lossy formats) compromise sound quality to varying degrees.
This compression can lead to a loss of detail, especially in the high and low ends of the audio spectrum.
While this might be acceptable for casual listening, it can be a significant drawback for professional audio work.
-
Balancing Sound Quality with Storage Space
A key consideration in choosing an audio file format is finding the right balance between sound quality and storage space.
Uncompressed audio files offer the best audio quality but can be impractically large for some applications, like:
- Streaming
- Distribution
- Portable Listening
Lossless compressed audio files like FLAC and ALAC provide a middle ground, maintaining high audio quality while reducing file size.
Unlike uncompressed files, lossy compressed audio files significantly reduce file size at the expense of sound quality.
The choice depends on the specific requirements of the project and the intended use of the audio.
-
Bonus: Choosing the Best Audio Format for Different Use Cases

The “best” audio file format varies depending on the use case.
For professional recording and editing, uncompressed audio formats like WAV or AIFF are preferred for their fidelity and quality.
These audio formats ensure that the audio data is captured and reproduced accurately.
For consumer purposes (such as music libraries or online streaming) compressed audio files like MP3 or AAC are more practical.
They offer a good balance between sound quality and file size, making them suitable for everyday use.
Lossless compressed formats like FLAC are ideal for those who prioritize audio quality without the bulk of uncompressed files.
Remember, when choosing the audio file format for you, consider the overall purpose.
Audio File Format: Final Thoughts
In mastering the art of music production, the choice of the right audio file format is essential.
It’s not just a technical decision; it’s about bringing your music to its fullest potential.
By understanding and utilizing the appropriate audio file formats, you ensure that your tracks are delivered with the clarity and quality they deserve.
To further enhance your journey, you have GOT to check out the invaluable Free Project Files pack.
This pack includes three professional-grade project files, each available in Ableton, FL Studio, and Logic Pro.
Designed by expert sound designers and producers, these project files exemplify the impact of proper audio file format selection and processing.
They offer a real-world glimpse into the production styles of today’s hit music 一 helping you to instantly recognize the difference quality project files can make.
So, dive into these project files, explore the nuances of audio file formats, and take your music production to the next level.
With these resources at your fingertips, you’re well on your way to creating pro-quality tracks that stand out in the modern music scene.
Until next time…







Leave a Reply
You must belogged in to post a comment.