Synths are the beating heart of modern music production, offering a world of sonic possibilities limited only by your imagination.
They can transform a dull track into an aural masterpiece, infusing it with textures and tones that make your music come alive.
However, your tracks will likely fall flat if you don’t know how to use them creatively.
Luckily, we’ll be breaking down everything you need to know about synthesizers.
From their anatomy and setting up your studio to advanced playing techniques and everything in between.
In today’s article, we’ll be breaking down:
- Synth evolution ✓
- Anatomy basics ✓
- Analog vs. digital synths ✓
- Your studio setup ✓
- Playing methods ✓
- Recording & Producing ✓
- Advanced synth tips, tricks & techniques ✓
By the end of this article, you’ll be equipped with all the knowledge needed to use synths like a true professional.
This way, your music will make a powerful impact.
So, let’s dive in…
Table of Contents
A Walk Down Memory Lane: The Synthesizer Evolution
The past, present, and future of synthesizers are nothing short of fascinating.
So, let’s take a trip down memory lane to understand the roots of these game-changing instruments.
-
The Robert Moog Era
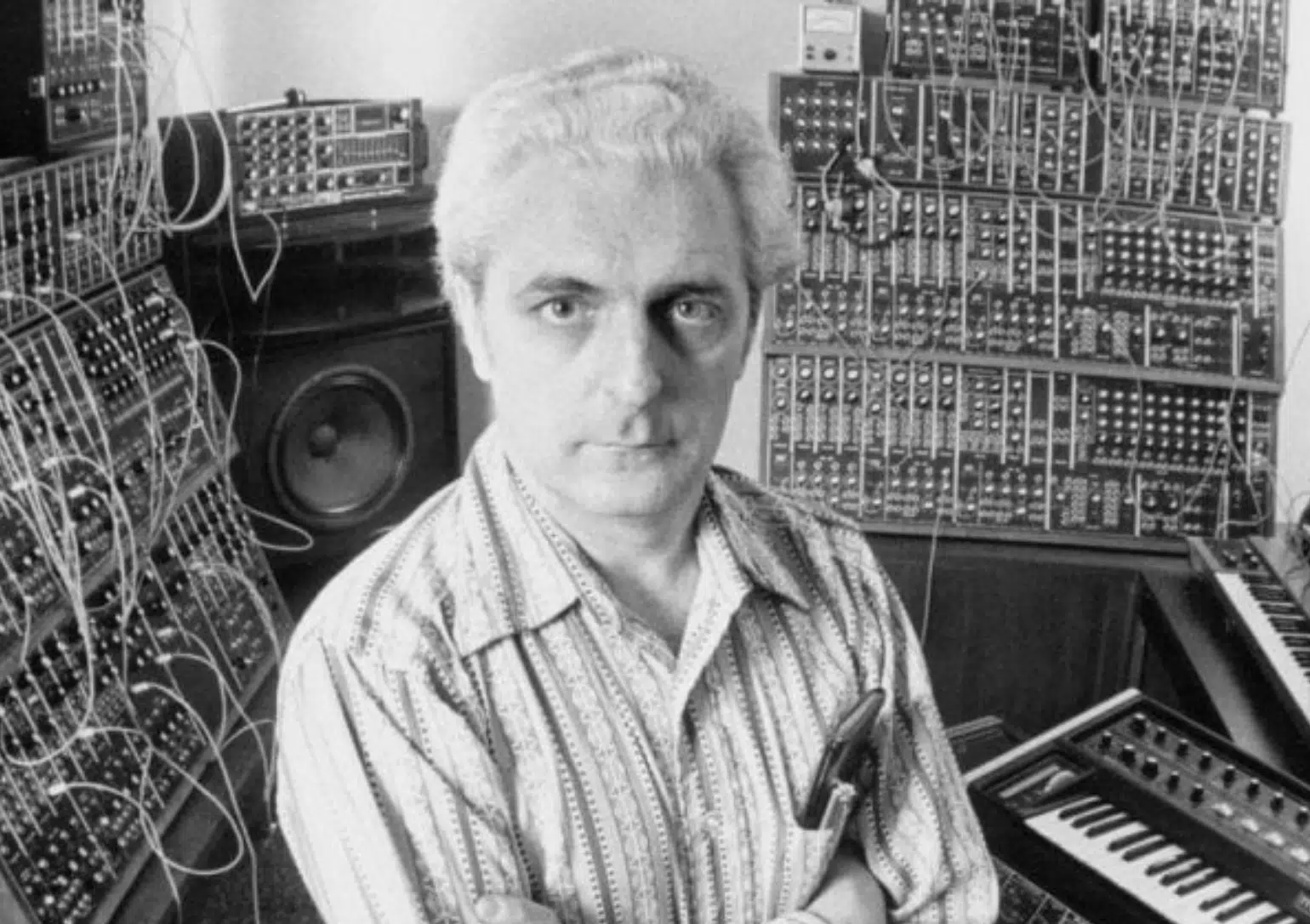

First up is Robert Moog, a name famously synonymous with synthesizers.
When Moog introduced his modular synth in 1964, he laid the foundation for all electronic music genres.
His invention used analog synthesis 一 mimicking traditional instruments’ sounds and creating otherworldly tones.
Unlike previous cumbersome instruments, Moog’s synthesizers were more intuitive.
A musician could play a melody on a compact keyboard interface, which was groundbreaking.
Moog brought certain features into the light, like:
- Filters
- Oscillators
- Envelopes
The Minimoog, for example, had three oscillators and provided various waveform options like sawtooth, square, and triangle.
This allowed musicians to explore a wide range of sounds and timbres.
-
The Yamaha Reign

Yamaha entered the scene with a bang.
Their DX7 synthesizer, released in 1983, took the world by introducing digital FM synthesis.
Imagine the freedom of playing around with 32 algorithms and having 128 presets at your disposal…
That was the DX7 for you.
It was compact, portable, and created complex sounds that analog synths couldn’t match.
Yamaha’s innovations set the bar for future synthesizers.
Models like the CS-80 became iconic in their own right 一 creating unparalleled atmospheres and textures.
-
Digital Revolution: Where We Are Now

Fast forward to today, surrounded by synthesizers powered by advanced digital technology.
Virtual analog synths, like the Arturia V Collection (above), give you the richness of analog synthesis combined with the convenience of digital technology.
Now, right on your laptop, you can have a:
- Moog
- Yamaha CS-80
- Roland Jupiter-8
And the best part?…
Modern digital synths are incredibly affordable.
This allowed even bedroom producers to shop for top-tier sound engines.
Anatomy of a Synthesizer
Before we hop on our musical spaceship, let’s understand the gears, knobs, and other controllers that make it soar and influenced the digital age.
-
The Oscillators
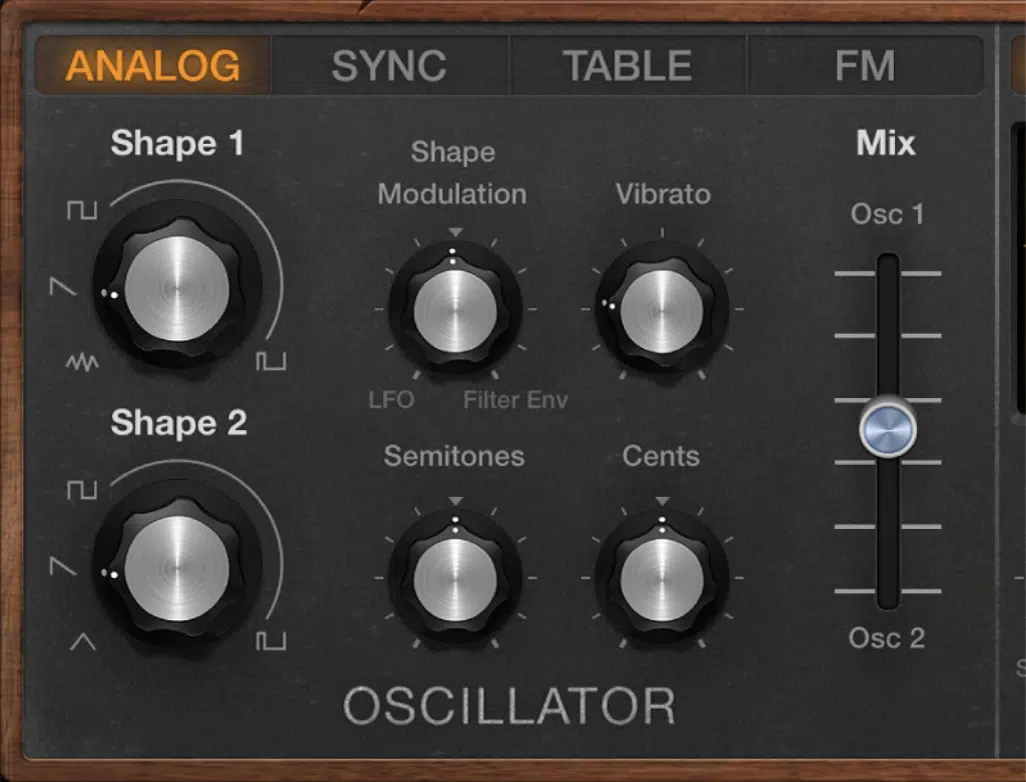
Oscillators are the soul of your synth, generating the raw electronic signal that eventually transforms into lush sounds.
Picture it as your color palette when you’re painting…
You start with primary colors but can mix them to create an endless array.
Synthesizers often come with multiple oscillators, like the Nord Lead 4, which has two per voice.
Layer a square wave with a sawtooth wave to create a rich, textured sound.
Through modulation, you can make one oscillator affect another 一 changing its pitch and creating that iconic “wobble” used extensively in dubstep and other genres.
Oscillators are where your sound journey begins.
Tweak them right, and you can go from replicating a grand piano to creating out-of-this-world sounds.
-
The Filters
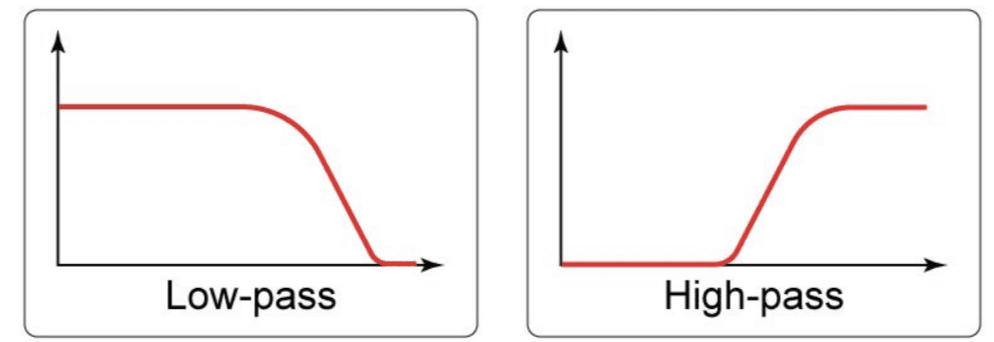
Filters chisel away frequencies to mold your sound.
In order to really master your synths, being familiar with different filters is vital.
- High-pass filters 一 Let high frequencies pass through while cutting off the lows. This is great for creating airy, ethereal textures.
- Low-pass filters 一 Let low frequencies pass and cut off the highs. Perfect for making lo-fi beats or that muffled radio voice effect.
Whether you’re into analog synthesis or leveraging the latest digital technology, filters are at the center stage.
In analog, you often find “ladder filters,” famed for their warm sound.
Digital filters, on the other hand, offer surgical precision.
Don’t overlook resonance; it emphasizes certain frequencies around the cutoff point.
Crank up the resonance, and you’ll get a squelchy sound; perfect for those funky basslines.
-
Envelopes & Other Controls
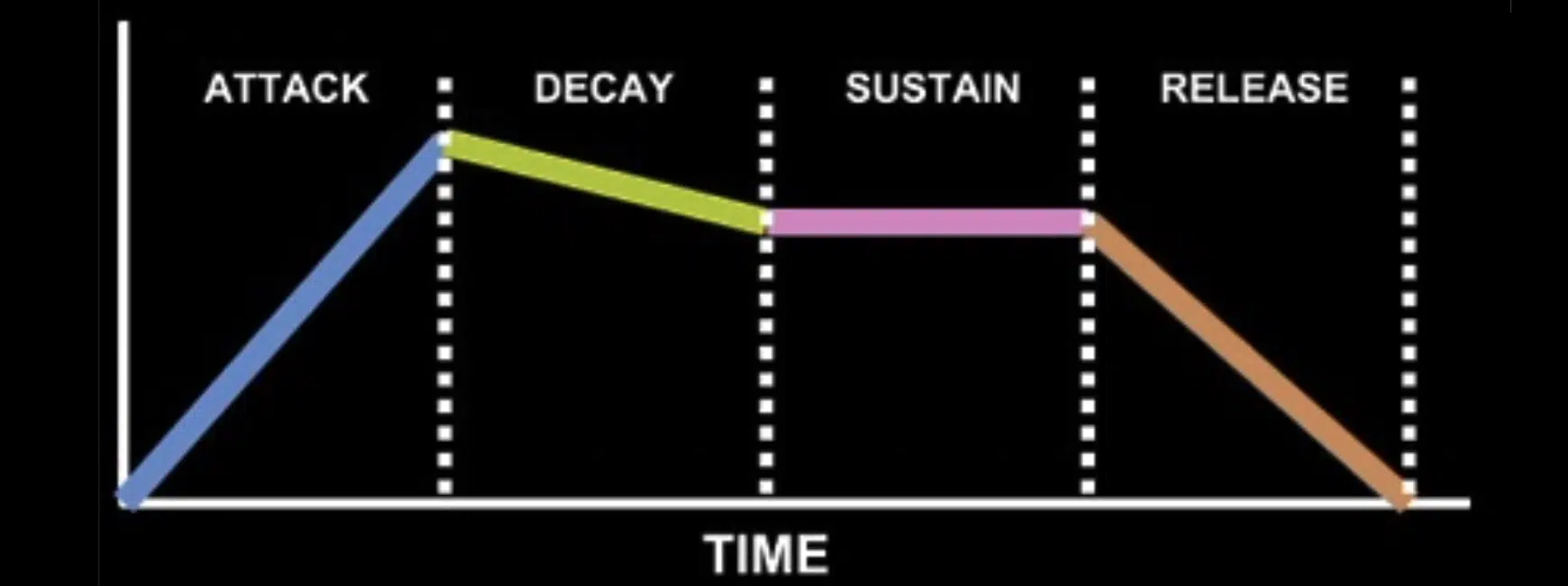
Envelopes shape how a sound evolves over time.
They usually have four signature stages:
- Attack 一 How quickly sound reaches peak volume.
- Decay 一 How it decreases.
- Sustain 一 The level it holds.
- Release 一 How it fades out.
Understanding this ADSR model gives you immense control over your sound’s dynamics.
Other controls like LFOs (Low-Frequency Oscillators) add more modulation options.
You can make the sound wobble, shimmer, or pulse 一 depending on how you set the LFO rate and depth.
Some advanced synths also offer options like “aftertouch,” where the sound can change depending on how hard you press the keys, even after the initial strike.
Knobs and sliders are the physical (or virtual) controls that let you manipulate these parameters in real-time.
This gives you the freedom to tweak your sound on the fly.
-
Keys & Controls
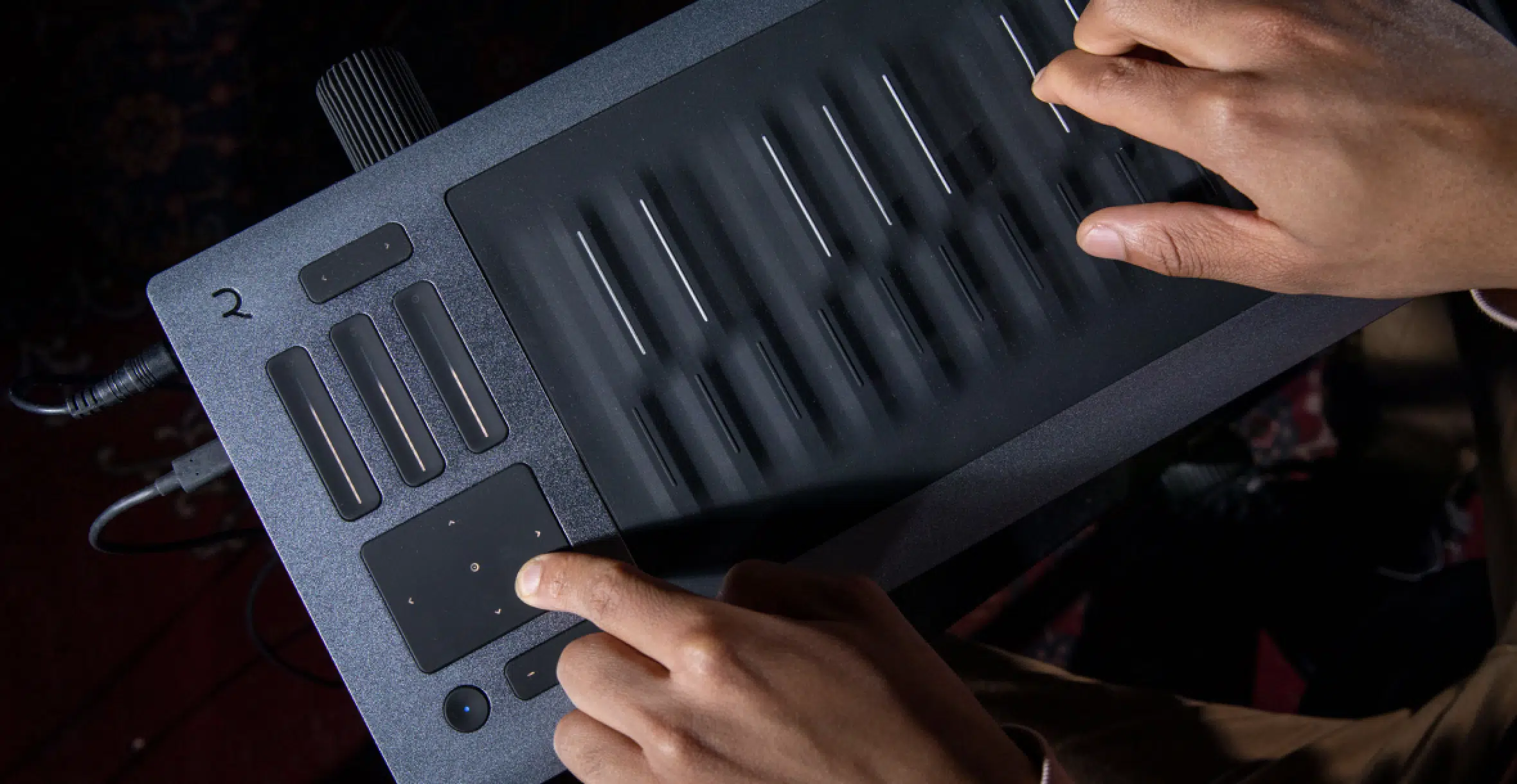

Keys on a synthesizer are your gateway to play those mesmerizing sounds.
These aren’t just simple keys; they’re often velocity-sensitive.
This means the harder you press, the louder the sound, and vice versa.
Modern synths even offer “key tracking.”
Key-tracking is a feature where the filter settings can change based on which key you play 一 giving you a wider sonic palette.
Some synthesizers ditch traditional keys altogether.
Instruments like the ROLI Seaboard (a favorite amongst producers and artists) use a silicone surface that lets you slide between notes and emulate instruments like the violin or piano.
Beyond keys, a synthesizer often includes many:
- Knobs
- Buttons
- Wheels
The mod wheel, for instance, allows you to add vibrato or other modulation effects in real time.
Getting familiar with these features can help you create some epic music production tips and will allow you to master synths quickly.
Synth Types: Analog vs. Digital
Alright, now that you’re familiar with the anatomy of a synthesizer, let’s explore the two main categories: Analog and Digital.
-
What’s Analog Synthesis
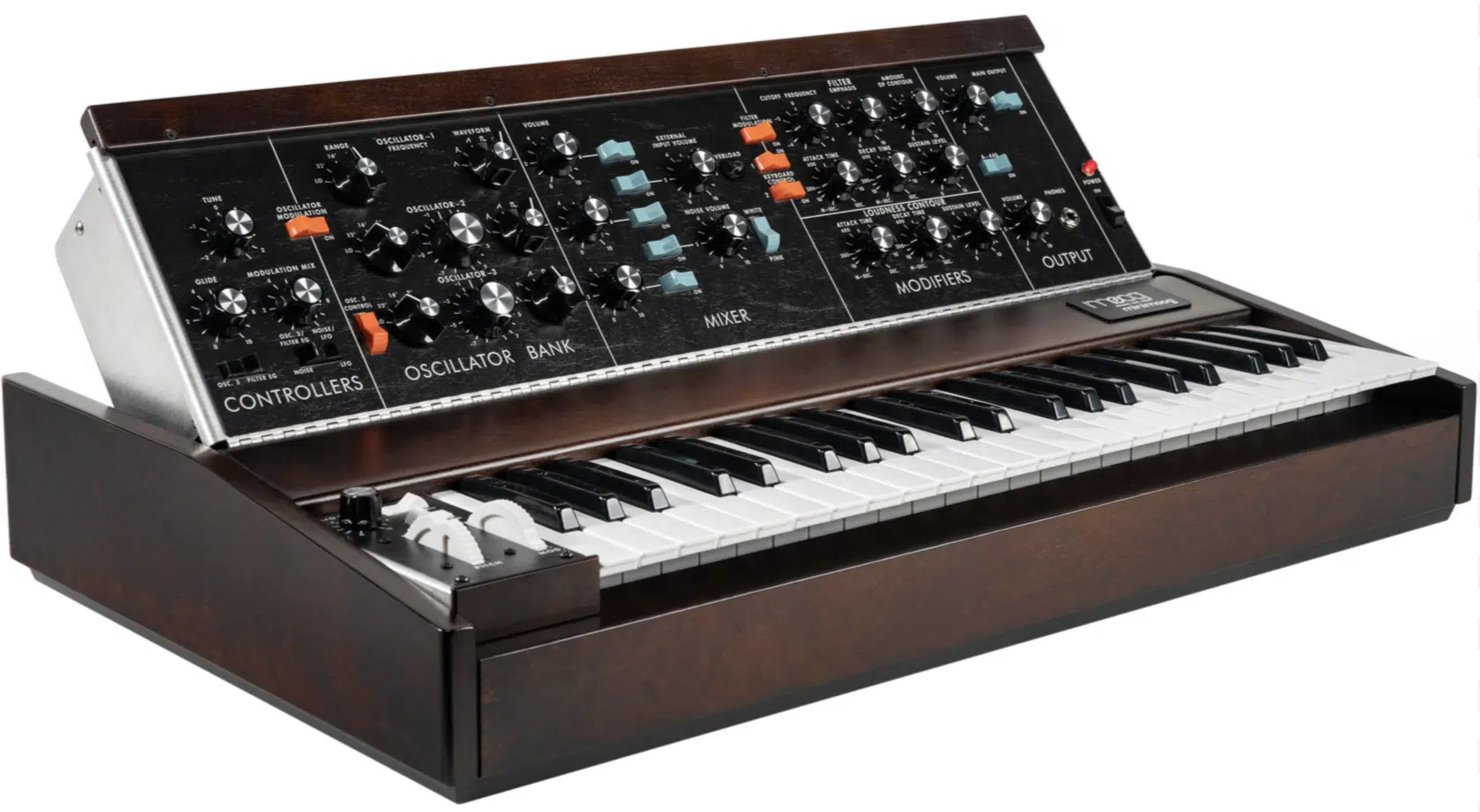

In analog synthesis, you deal with circuitry that shapes and manipulates electric voltage to produce sound.
Think of the Moog Minimoog 一 this classic synth is a perfect example.
One hallmark of analog synths is “warmth,” characterized by its rich overtones.
For example, analog synths often provide a fat, warm sound you can feel in your gut if you’re creating a bass sound.
Analog synthesis is tactile.
Unlike digital synths, you have direct control over:
- Oscillators
- Filters
- Envelopes
This is done through physical knobs and sliders, making it intuitive and hands-on.
-
Digital Synths & Their Flexibility

Digital synths, like the Yamaha DX7, harness digital technology to model any sound, from classic analog tones to complex acoustic instruments.
The flexibility is insane, as you can switch from emulating a grand piano (or other instruments) to mimicking a drum kit with the press of a button.
Ever tried layering a flute sound with a distorted electric guitar?
Well, you can do that here.
With digital, you can also easily switch between different synthesis methods.
Want FM, granular, and wavetable synthesis in one track?… No problem!
Plus, with the advances in digital technology, many of these synths can emulate the warmth of analog to an almost indistinguishable level.
Digital synths often come loaded with a myriad of presets.
So, if you’re in a hurry to find a specific sound, you’re just a few clicks away.
-
Polyphonic Synthesizers: The Best of Both Worlds

Polyphonic synthesizers allow you to play multiple notes at once, a major step from monophonic synths that only produce one note at a time.
Imagine being able to play chords and melodies simultaneously!
Some great polyphonic synthesizers (like the Dave Smith Prophet series) integrate analog and digital elements.
You get the richness of analog oscillators with the flexibility of digital effects.
Modern music often demands widely complex, evolving textures.
With polyphonic synthesizers, you can stack different sounds, like strings and synths, for a rich, orchestral feel.
It’s the definition of innovation.
Setting Up Your Electronic Studio
You’ve got the knowledge; now let’s get you equipped with how to set up your electronic studio.
-
Choosing Your Synthesizer
When choosing a synthesizer, consider the kind of music you want to produce.
You might want a synth that excels at punchy basses and shimmering leads for dance music.
Also, don’t overlook the user interface.
Some synths are menu-heavy 一 while others lay all the controls out on the front panel.
Your budget matters too, but thankfully, digital technology has made synthesizers more affordable.
Software synths like the Arturia V Collection offer a lot of bang for your buck.
-
Making Connections: MIDI and More

MIDI (Musical Instrument Digital Interface) is your best friend in the studio.
It lets you control one piece of gear with another 一 like playing your synthesizer with a separate MIDI keyboard.
Speaking of MIDI keyboards, we’ve got the absolute best options of 2023.
Don’t forget about audio cables.
You’ll need these to connect your synthesizer to your audio interface (standard 1/4-inch cables usually do the trick).
Always make sure your gear is connected to a reliable power source.
Investing in a good surge protector can save you a lot of heartache down the line.
We all know how frustrating it is to have a masterpiece only to lose it.
How To Play Synths: Techniques & Tips
Ready to rock your synth like a true professional? Let’s dig into some techniques.
-
Using & Creating Your Own Presets
Presets can be your best friend when you’re just starting out.
They give you a foundation to build upon 一 offering pre-designed sounds you can modify.
Take some time to review your synths presets; they’ll likely cover a wide range of genres, from ambient to techno.
However, the real fun begins when you start creating your own presets.
For instance, if you like how a certain preset sounds but wish it had a little more reverb, you can easily tweak it and save it as your own.
To create something unique, you could layer a classic ’80s polyphonic synthesizer preset with modern effects.
NOTE: Once you’ve made adjustments that you’re happy with, make sure to save them.
On most digital synths, you can save a set of settings as a new preset.
This can save you a ton of time, especially if you repeatedly use the same sounds in different projects.
-
Incorporating Low-Frequency Oscillators
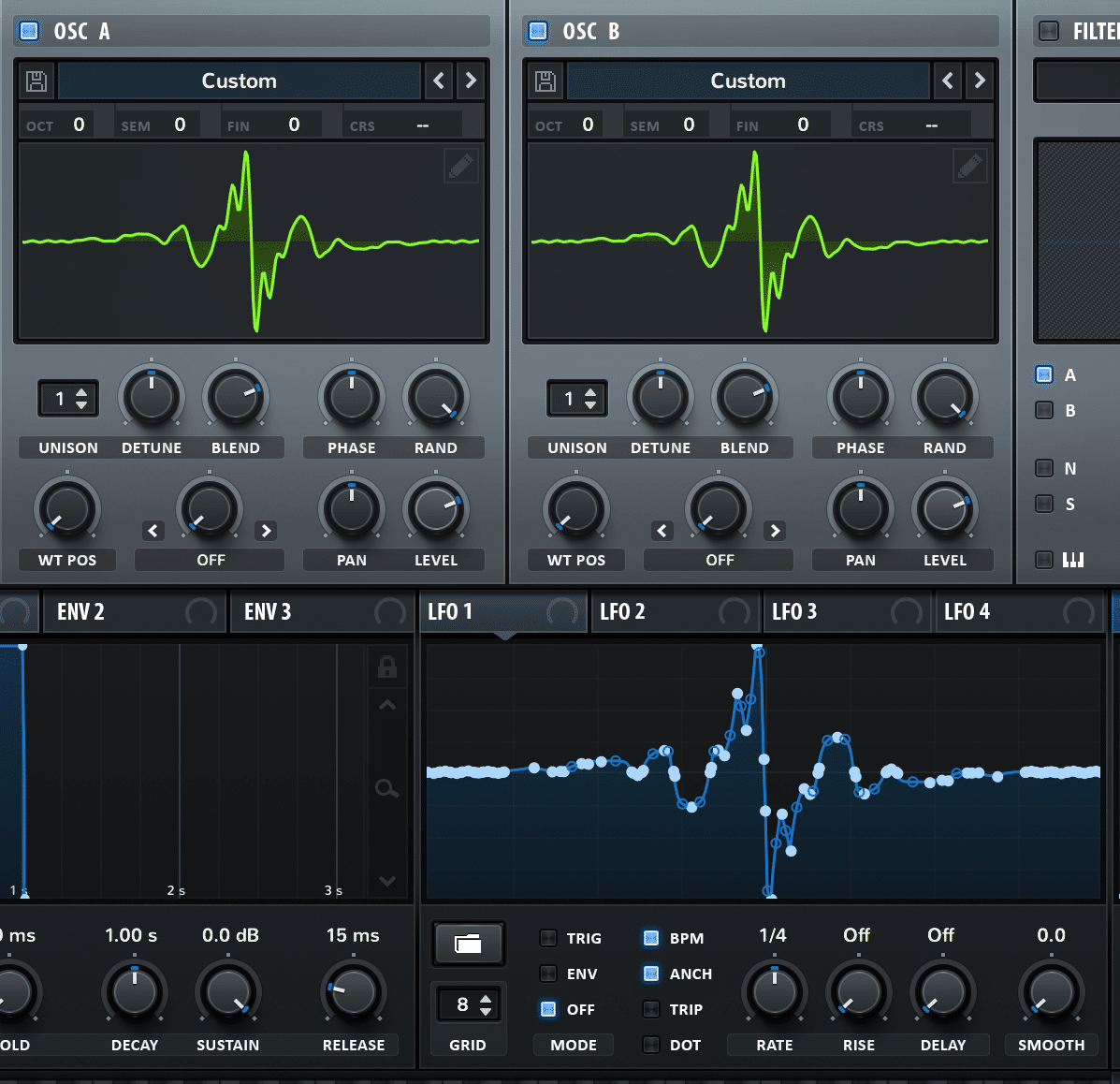
Low-frequency oscillators, or LFOs, can add that extra flair to your tracks.
Think of an LFO as a rhythmical motion that you can attach to various parameters in your synthesizer, like pitch, filter, and volume.
The classic ‘wobble’ sound in dubstep?… That’s an LFO modulating a filter at a fast rate.
Most synths allow you to control the speed and depth of your LFOs.
- Speed 一 Determines how quickly the LFO cycles.
- Depth 一 Controls how much the LFO affects the sound.
Experiment with slower LFOs on pads for an evolving texture or faster LFOs on lead sounds for energetic arpeggios.
Advanced Tip: Some synths even allow you to sync your LFOs with your DAW’s tempo.
This can be incredibly handy for ensuring that your LFO modulation fits perfectly with your project’s BPM.
This makes your music sound more cohesive.
Recording & Producing with Synths
And now, the final piece of the puzzle: laying down those killer tracks with the help of your synths.
-
The Studio Setup

Your electronic studio is more than just a collection of gear; it’s your creative haven.
Make sure your synthesizers and other essential gear are within arm’s reach.
You should consider rack-mounted synthesizers for those looking to save some extra space in their home studio.
These can neatly slide into a studio rack 一 leaving your workspace clutter-free.
Don’t underestimate the power of good studio lighting.
It sets the mood and lets you see all the tiny labels on your synthesizer’s interface.
-
Mixing & Manipulating Sound

Mixing becomes the next crucial step once your sound design is on point and your tracks are recorded.
Speaking of sound design, if you’re looking for the most groundbreaking, innovative sound design secrets in the game, we’ve got you covered.
Your synthesizer often comes with built-in effects like:
However, you can always add more effects through your DAW.
For example, try adding a sidechain compressor on your bass synth to let your kick drum punch through the mix.
Equalization (EQ) is another essential tool in your studio.
For synths, cutting the lower frequencies on your lead sounds can create room for your bass and kick 一 while boosting the high-mids can add clarity.
Always compare your EQ changes in the context of the full mix, not just solo’ed.
Automation is super powerful as well, so don’t underestimate it.
If your synth line sounds too static, try automating parameters like filter cutoff or resonance over time.
This dynamic change can add a layer of complexity and movement to your music, taking it from good to great.
NOTE: Always save your work, and not just the final track.
Save presets, MIDI files, and even your DAW session; trust me, the future you will be thankful.
Synths: Final Thoughts
As you’ve learned, synthesizers are incredibly versatile and complex instruments offering a wide range of sonic possibilities.
From understanding their anatomy to mastering their keys and manipulating sound, the world of synthesizers is expansive and rewarding.
With the right techniques and knowledge, synthesizers can elevate your tracks.
As well as impart them with texture, depth, and a signature sonic palette that sets you apart from the crowd.
To give you a jump-start in applying all this newfound knowledge, you absolutely need this incredibly unique and innovative MIDI Box (Free Teaser).
It’s a comprehensive MIDI package that includes 55 expertly crafted MIDI files to enhance your music production experience.
Whether you’re struggling with melodies, looking for inspiring chord progressions, or need that perfect bassline, this box has got you covered.
These MIDI files are incredibly versatile and can be easily integrated into your synthesizer setup 一 allowing you to apply all the techniques we’ve discussed in this article.
It’s the perfect complement to this guide, ensuring you’re fully equipped to use synths like a true professional.
So go ahead, get your hands on the Unison MIDI Box, and start applying what you’ve learned today.
The world of synthesizers is full of endless possibilities, and you’re now well-equipped to explore them like a professional.
Until next time…







Leave a Reply
You must belogged in to post a comment.