In today’s competitive industry, it’s important to incorporate innovative techniques in order to create captivating sounds.
Enter: Additive Synthesis.
Additive synthesis is often overlooked, due to its sheer complexity, but we’re going to break it down today so you can incorporate it with confidence.
In today’s article, we’ll dive into the exciting world of additive synthesis, including:
- Its definition, benefits, and uses ✓
- How it compares to other synthesis types ✓
- The 5 best additive synthesizers of 2023 ✓
- Expert tips, tricks & techniques to master additive synthesis ✓
- How to incorporate it in your own tracks ✓
So, let’s dive into this powerful synthesis technique, in order to skyrocket your skills and enhance your tracks.
Table of Contents
- What is Additive Synthesis?
- How Additive Synthesis Works
- The History of Additive Synthesis
- Additive Synthesis vs. Other Types of Synthesis
- Understanding Additive Synthesis
- The 5 Best Additive Synths of 2023
- #1. Razor by Native Instruments
- #2. Loom II by AIR Music Tech
- #3. Pigments 3 by Arturia
- #4. Alchemy by Apple (Logic Pro)
- #5. Harmor by Image-Line
- Tips & Tricks for Additive Synthesis
- Final Thoughts
What is Additive Synthesis?
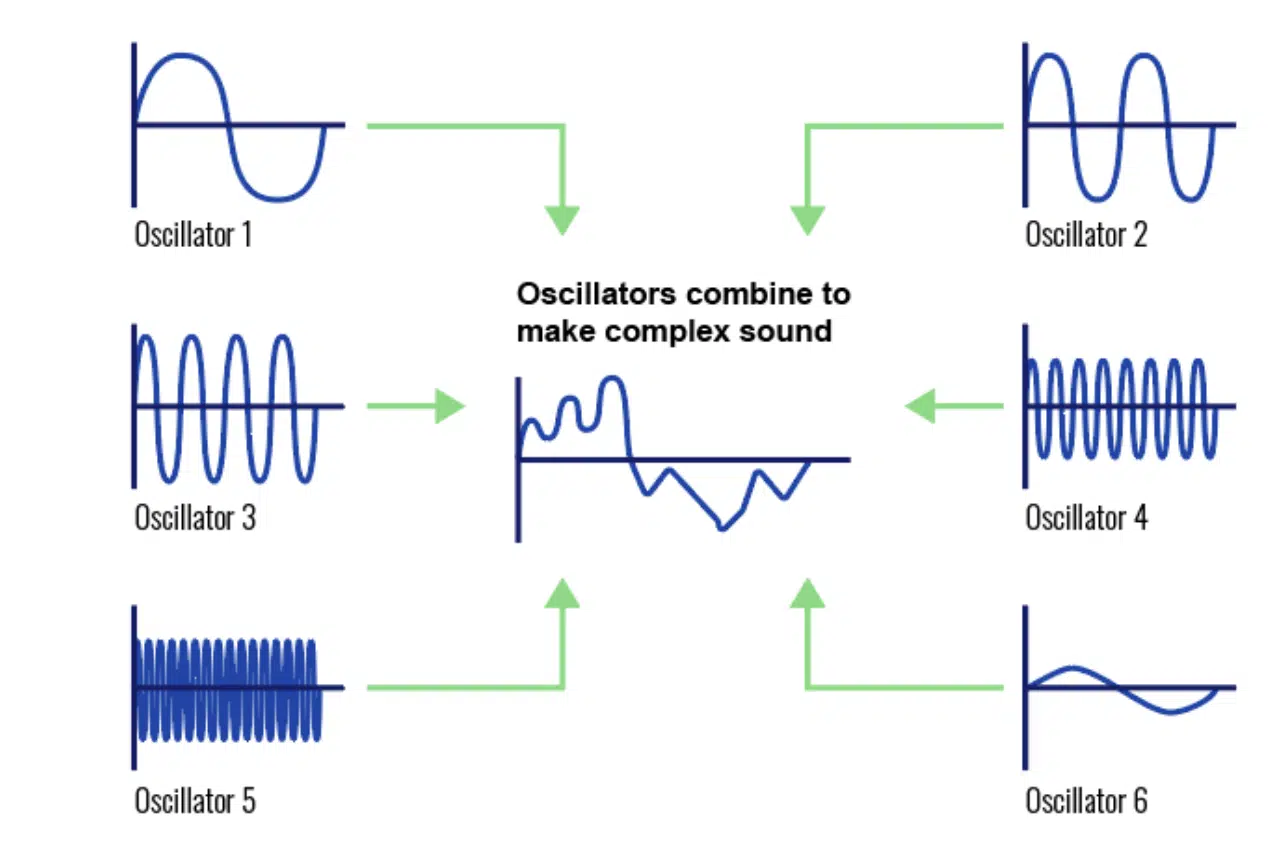
Additive synthesis is a sound synthesis technique that generates complex sounds by combining multiple sine waves of different frequencies, amplitudes, and phases.
Each sine wave represents a harmonic component, and together, they form the unique timbre of the resulting sound.
The additive synthesis process allows you to create a virtually limitless variety of sounds, making it a valuable tool for music producers seeking original, expressive tones.
The beauty of additive synthesis lies in its ability to produce rich, organic sounds by carefully controlling the individual harmonics.
This level of control gives you the freedom to shape your sound precisely, allowing you to craft anything from simple, pure tones to intricate, evolving textures.
It’s exceptionally great at reproducing virtually any sound.
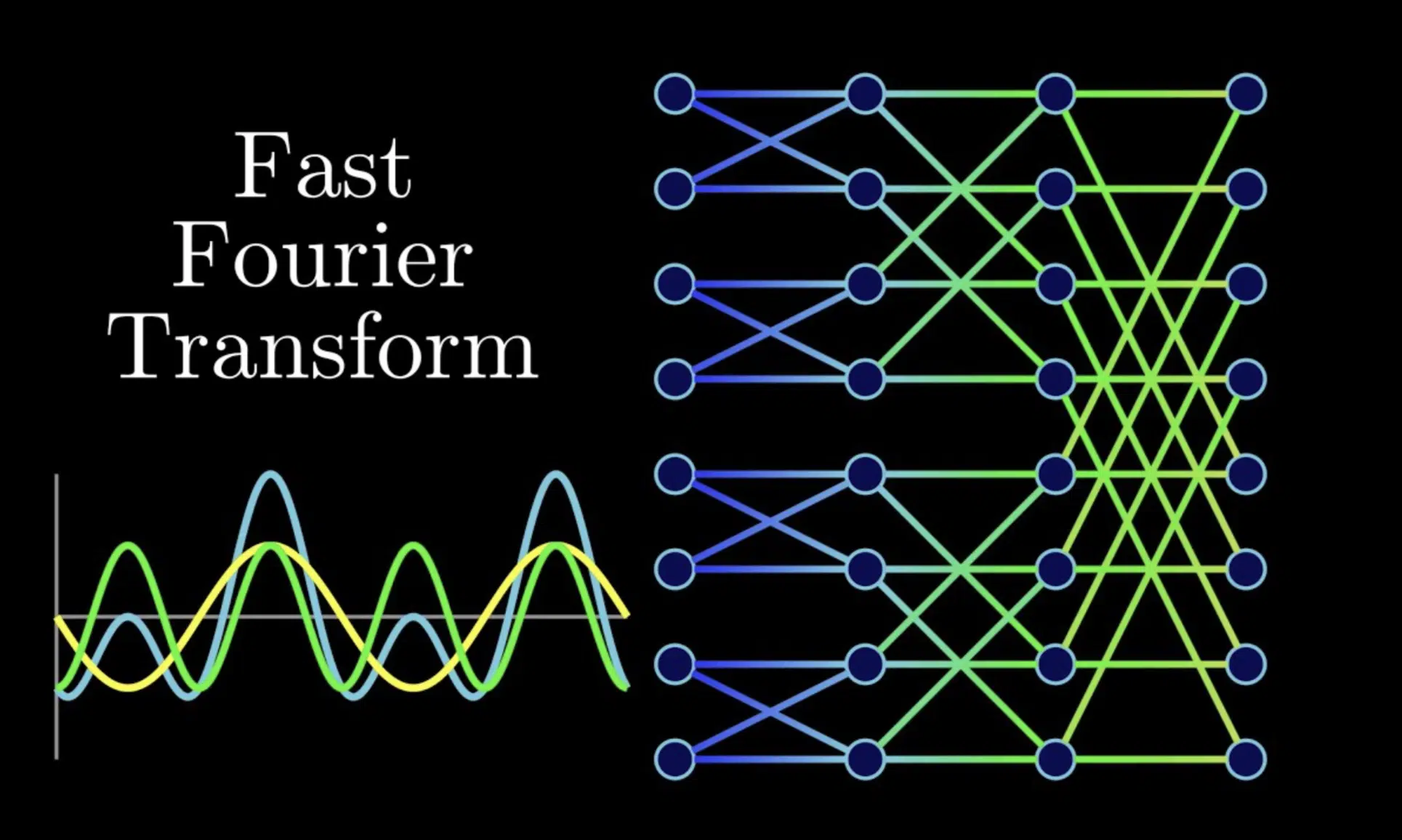
This lies in the FFT Theory that states “any sound in existence can be reproduced using (and summing) a large number of sine waves, at various frequencies, amplitudes, and phases.”
To understand the mechanics of additive synthesis, it’s also essential to grasp the concept of harmonics.
Harmonics are integer multiples of a fundamental frequency, and they determine the character of a sound.
For example, a fundamental frequency of 100 Hz will have harmonics at 200 Hz, 300 Hz, 400 Hz, and so on.
These harmonics, when combined, create the distinctive timbre of a sound.
How Additive Synthesis Works
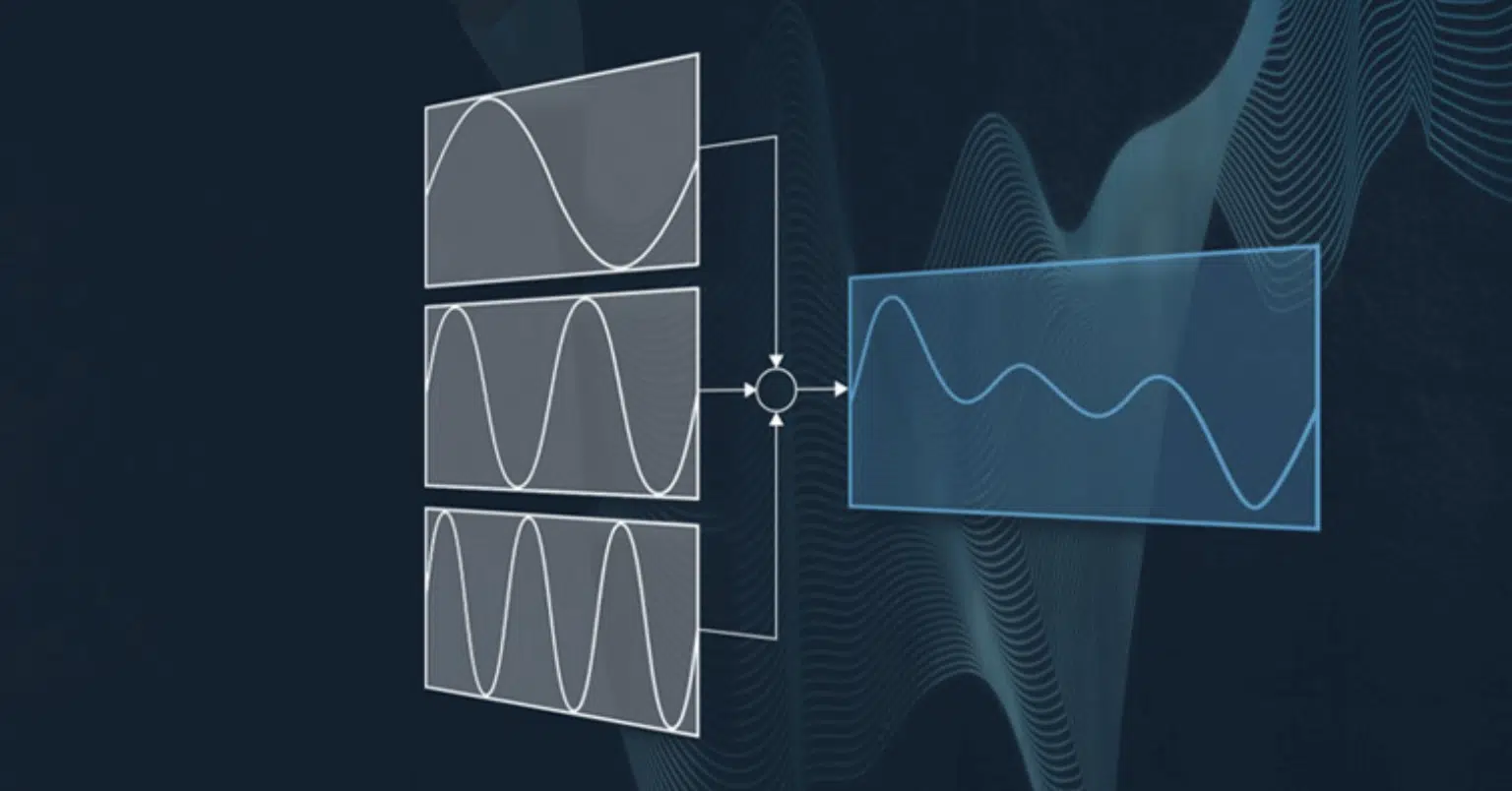
In additive synthesis, the sound is generated by summing individual sine waves, each representing a harmonic.
The combination of these sine waves, with their specific frequencies, amplitudes, and phases, creates the resulting sound’s unique timbre.
This process can be thought of as constructing a sound from the ground up.
As opposed to other synthesis techniques, like subtractive synthesis, which involves sculpting a sound by removing specific frequencies.
To create a sound using additive synthesis, you start by defining the fundamental frequency, which is the lowest frequency and the foundation of the resulting sound.
Then, you add harmonics by introducing sine waves at integer multiples of the fundamental frequency.
Each sine wave’s amplitude determines the relative strength of that harmonic, and the phase defines the harmonic’s position within the waveform.
By carefully controlling the frequencies, amplitudes, and phases of the sine waves, you can create a wide variety of sounds.
This level of control allows you to emulate existing instruments, like a piano or a flute, or create entirely new, otherworldly sounds.
The possibilities are truly endless.
The History of Additive Synthesis

The concept of additive synthesis dates back to the early days of sound synthesis, with some of the first examples being mechanical instruments like the Telharmonium, invented in the late 19th century.
The Telharmonium used rotating disks and electrical alternators to generate sine waves, which were then combined to produce different sounds.
Despite its technical limitations, Telharmonium laid the groundwork for future developments in additive synthesis.
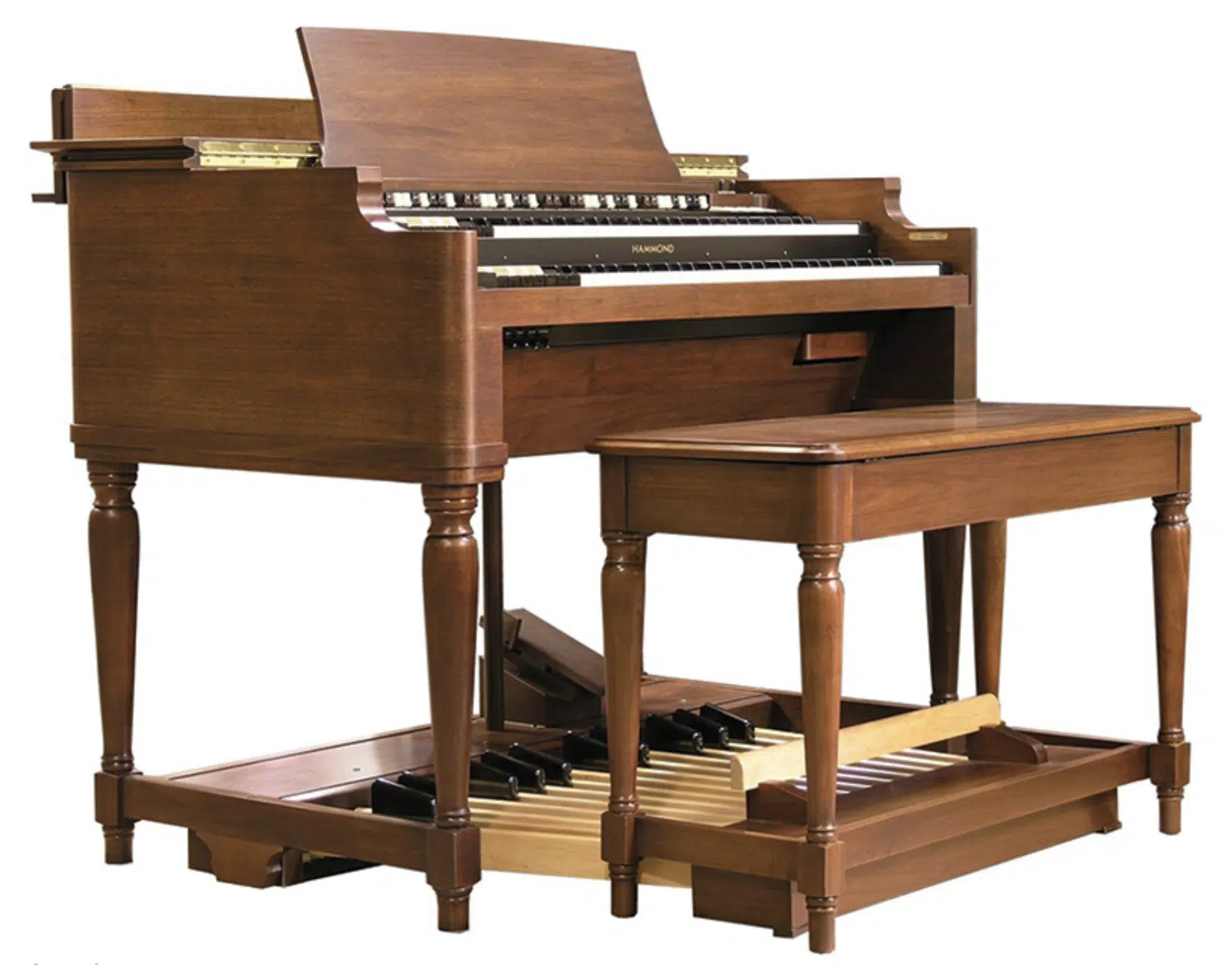
One of the most iconic examples of additive synthesis in action is the Hammond organ, introduced in the 1930s.
The Hammond organ utilizes a system of spinning tonewheels to generate sine waves, which can be combined and manipulated through drawbars to create a wide variety of tones.
The Hammond organ’s unique sound and the flexibility of its additive engine made it a popular choice for musicians across various genres and subgenres, from jazz to rock.
Digital Technology’s Impact
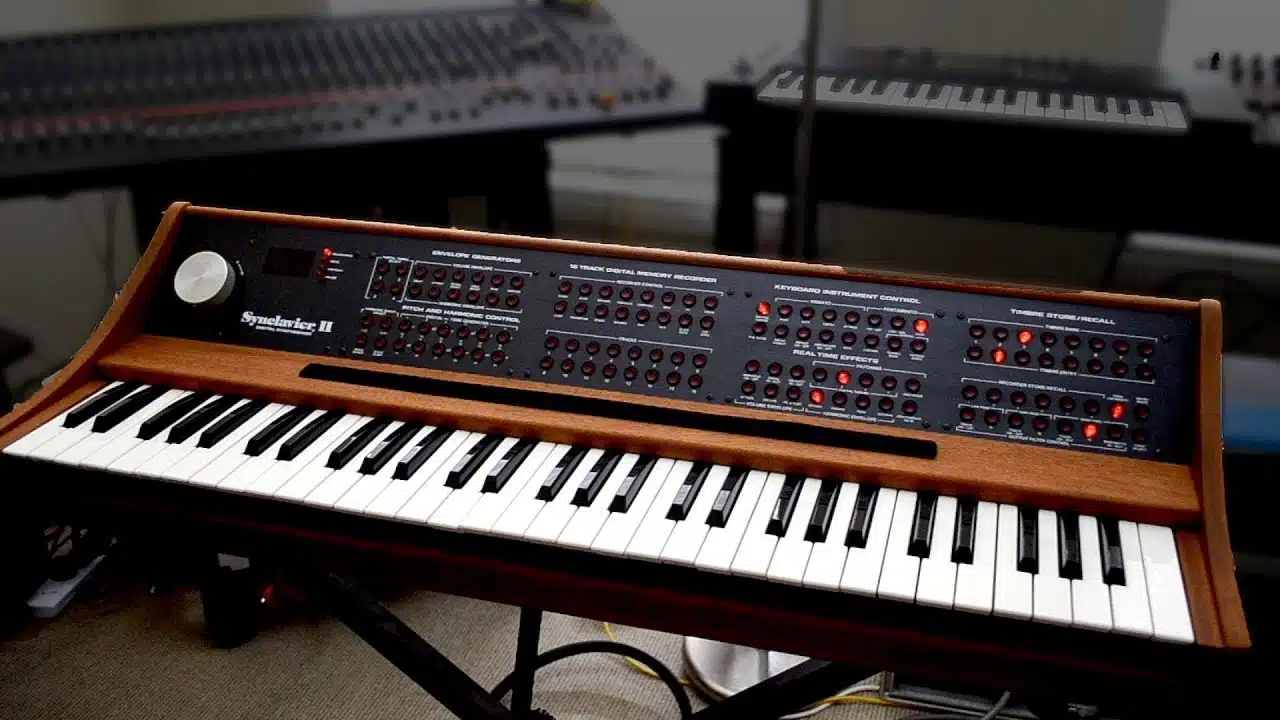

With the advent of digital technology in the 1970s and 1980s, additive synthesis became more accessible and practical for electronic musicians.
The Synclavier was the first full-blown “additive synth” and, since it was so ahead of its time, had sampling abilities (believe it or not).
The development of digital synths and computer-based music production software allowed for precise control over individual harmonics.
It enabled the creation of more complex and intricate sounds.
Today, additive synthesis continues to be a powerful tool in the modern music production landscape.
It offers a wealth of creative possibilities for music producers and sound designers alike.
Additive Synthesis vs. Other Types of Synthesis
Before we move on, let’s quickly compare additive synthesis to the 2 other forms of synthesis, so you can truly understand the difference.
Subtractive Synthesis
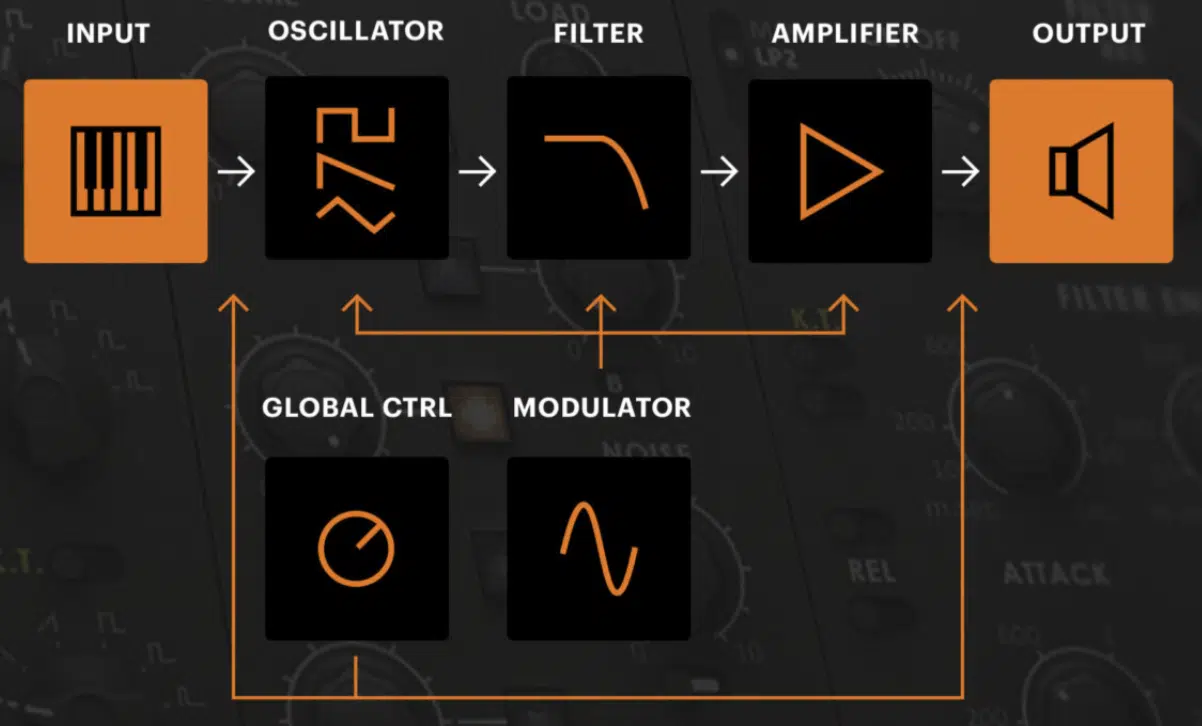
While additive synthesis builds a sound from the ground up, subtractive synthesis takes a different approach.
You start with a rich, harmonically complex sound source, such as a sawtooth wave, and then use filters to remove the appropriate frequencies and shape the resulting sound.
It’s often associated with analog synthesizers and remains relevant in modern music production for its warm, organic sound quality.
The primary difference between subtractive and additive synthesis lies in the sound generation method.
- Additive 一 Focuses on combining sine waves to create complex sounds.
- Subtractive 一 Involves removing frequencies from a harmonically rich waveform.
Both techniques offer unique benefits and have their place in modern music production.
However, additive synthesis provides a greater level of control over the individual harmonics, allowing for a wider range of sound possibilities.
FM Synthesis
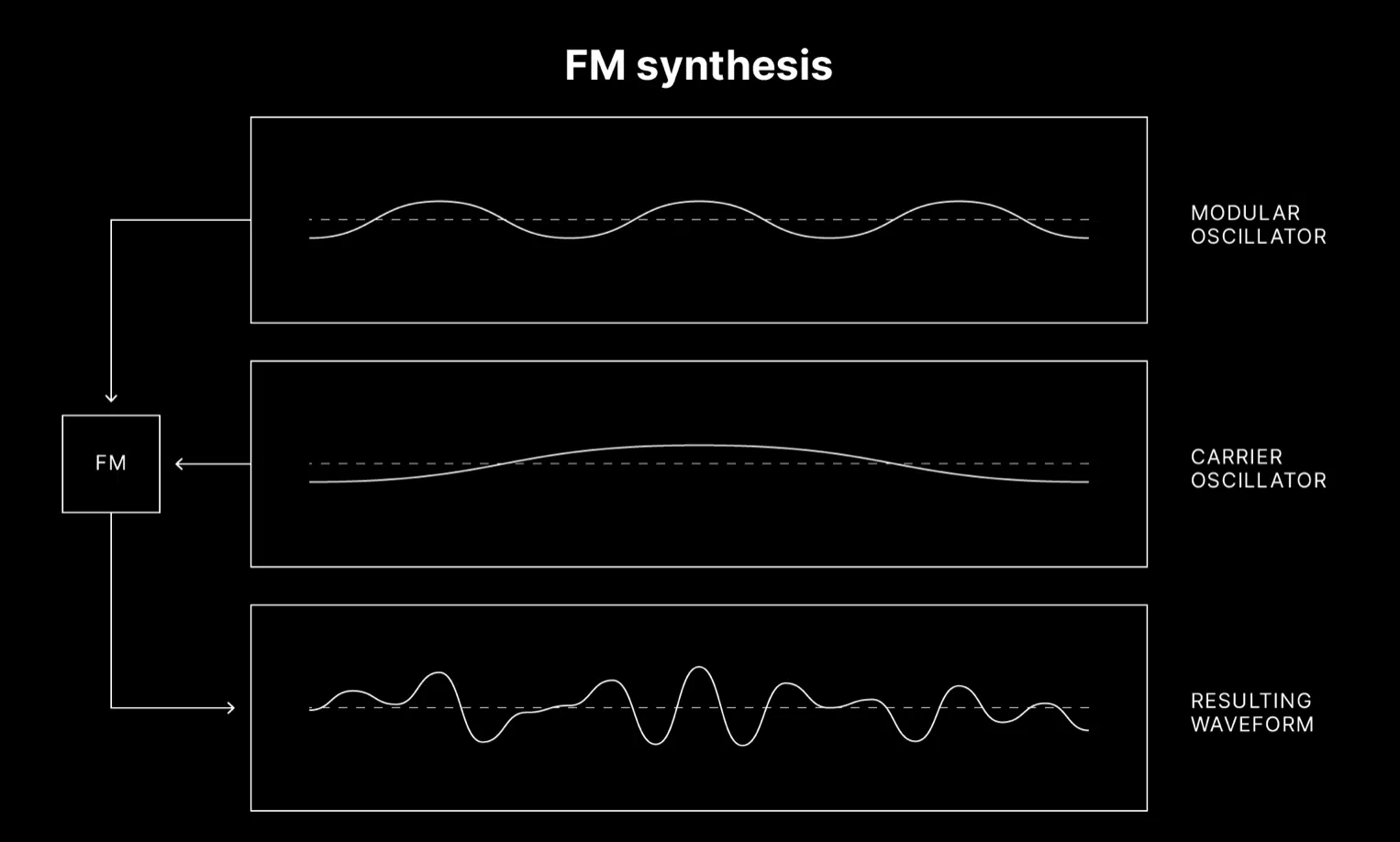
Frequency modulation (FM) synthesis is another popular synthesis method, known for its ability to create a wide array of sounds, from realistic acoustic instruments to electronic timbres.
In frequency modulation synthesis, the frequency of a waveform (called the carrier) is modulated by another waveform (called the modulator).
The interaction between these waveforms generates new harmonics, which can be manipulated to create complex, evolving sounds.
Though this type of synthesis can create a diverse range of sounds like additive synthesis, their approaches differ significantly.
- Additive 一 Focuses on combining individual sine waves to create the desired sound.
- FM 一 Relies on the interaction between waveforms to generate new harmonics.
Side note, if you’re interested in learning all about wavetable synthesis (an additional synthesis type) as well, we break it all down.
Understanding Additive Synthesis
In order to truly understand additive synthesis, you need to be aware of all its moving parts.
-
Sine Waves & Harmonics
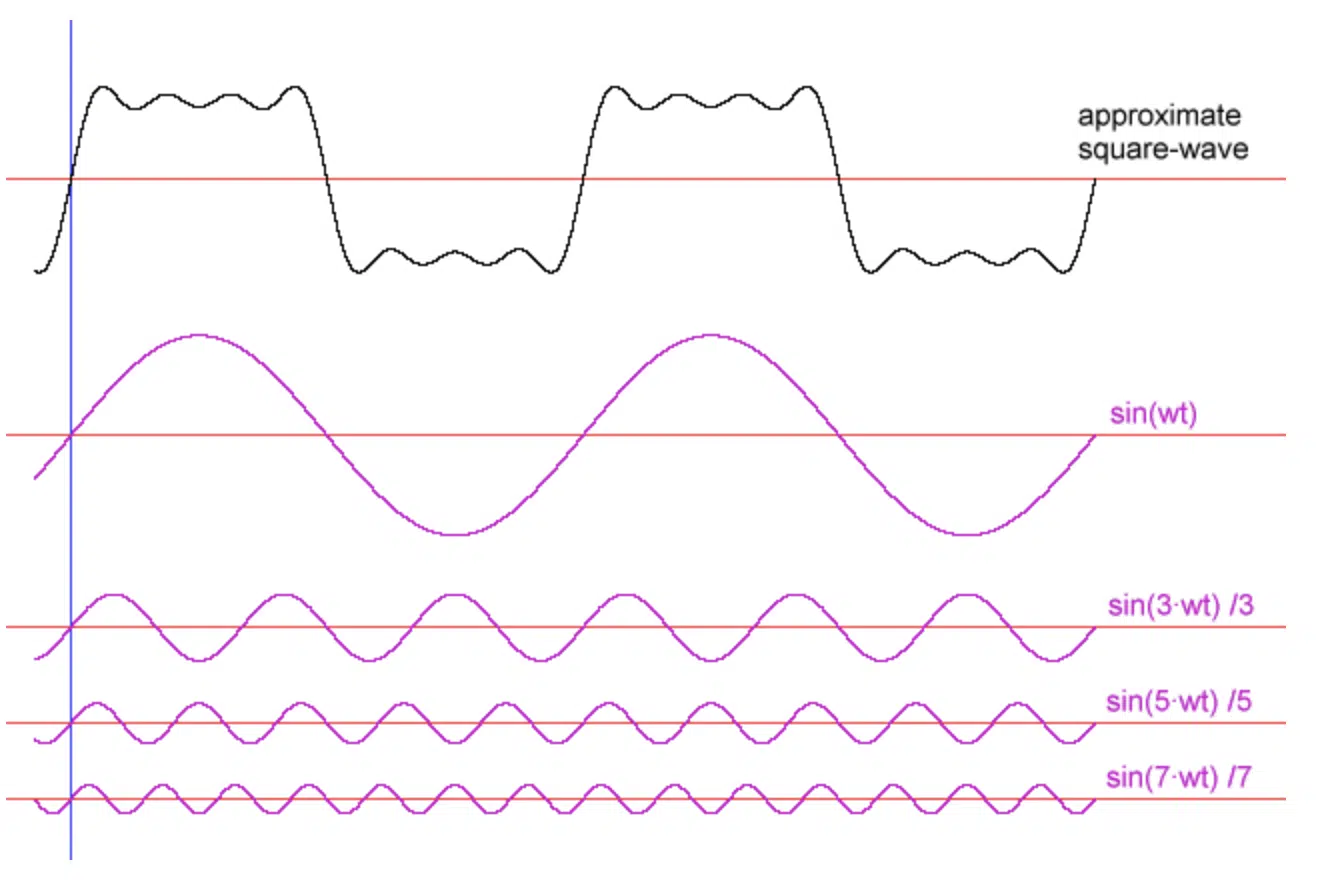
The core building blocks of additive synthesis are sine waves, which are the simplest type of waveform, containing only a single frequency.
In additive synthesis, more sine waves are combined to create complex sounds, with each sine wave representing a harmonic component of the resulting sound.
By manipulating the frequencies, amplitudes, and phases of these sine waves, you can create a wide array of timbres and textures.
Harmonics play a crucial role in shaping the character of a sound.
In general, lower harmonics contribute to the fundamental pitch of a sound, while higher constituent harmonics add complexity and richness to the timbre.
Speaking of pitch, if you’re looking for the absolute best pitch shifter plugins around, look no further.
By carefully controlling the balance of only harmonics in additive synthesis, you can achieve a wide variety of tones and textures.
This ranges from simple, pure sounds to intricate, evolving soundscapes.
-
Envelopes & Modulation
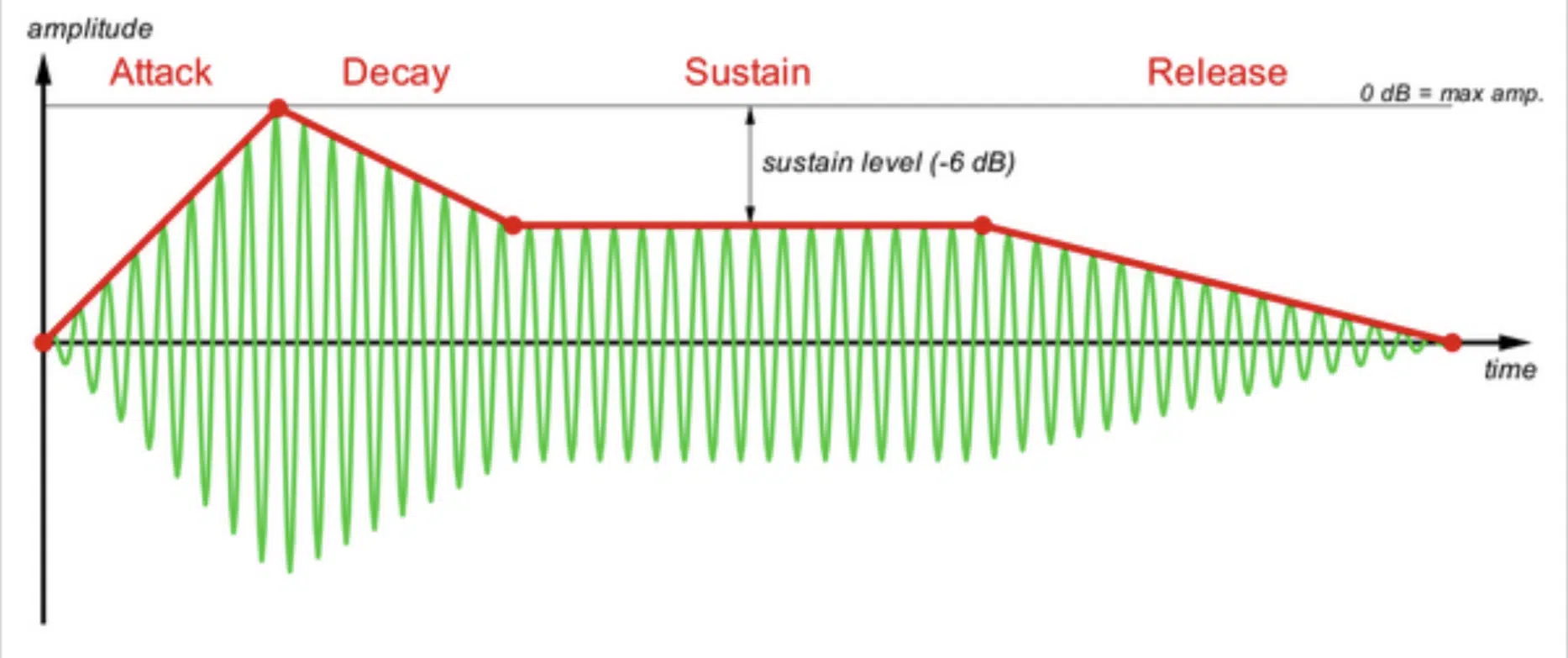
Envelopes and modulation are essential tools in additive synthesis, allowing you to shape the dynamics and movement of your sound over time.
Envelopes are used to control the amplitude, frequency, and phase of individual harmonics.
They help you create evolving sounds that change in character throughout their duration.
Modulation is another powerful technique that can be used to add movement and complexity to your additive synth patches.
Speaking of synth patches, we broke down the top VST synths of 2023 for you!
By modulating parameters such as amplitude, frequency, or phase, you can create dynamic, evolving sounds that respond to your playing or external inputs.
For example, a MIDI controller or sequencer.
-
Spectral Resynthesis
Spectral resynthesis is an advanced technique used in some additive synths that allows you to analyze and recreate the harmonic content of an existing sound.
By analyzing the frequency content of a sample or recording, you can break the sound down into its individual harmonics (through FFT).
Which can then be recreated using additive synthesis.
This process enables you to recreate and manipulate the timbre of existing sounds, offering a unique approach to sound design and synthesis.
Spectral resynthesis can be a valuable tool for creating unique, expressive sounds that incorporate elements of real-world recordings or samples.
Speaking of samples, we break down the absolute best FREE sample packs of 2023 (a must-read!).
The 5 Best Additive Synths of 2023
Now that you’re familiar with all additive synthesis has to give, let’s talk about the 5 best additive synths (digital synths) of 2023.
Most additive synthesizers are lacking in some departments, but not these!
#1. Razor by Native Instruments
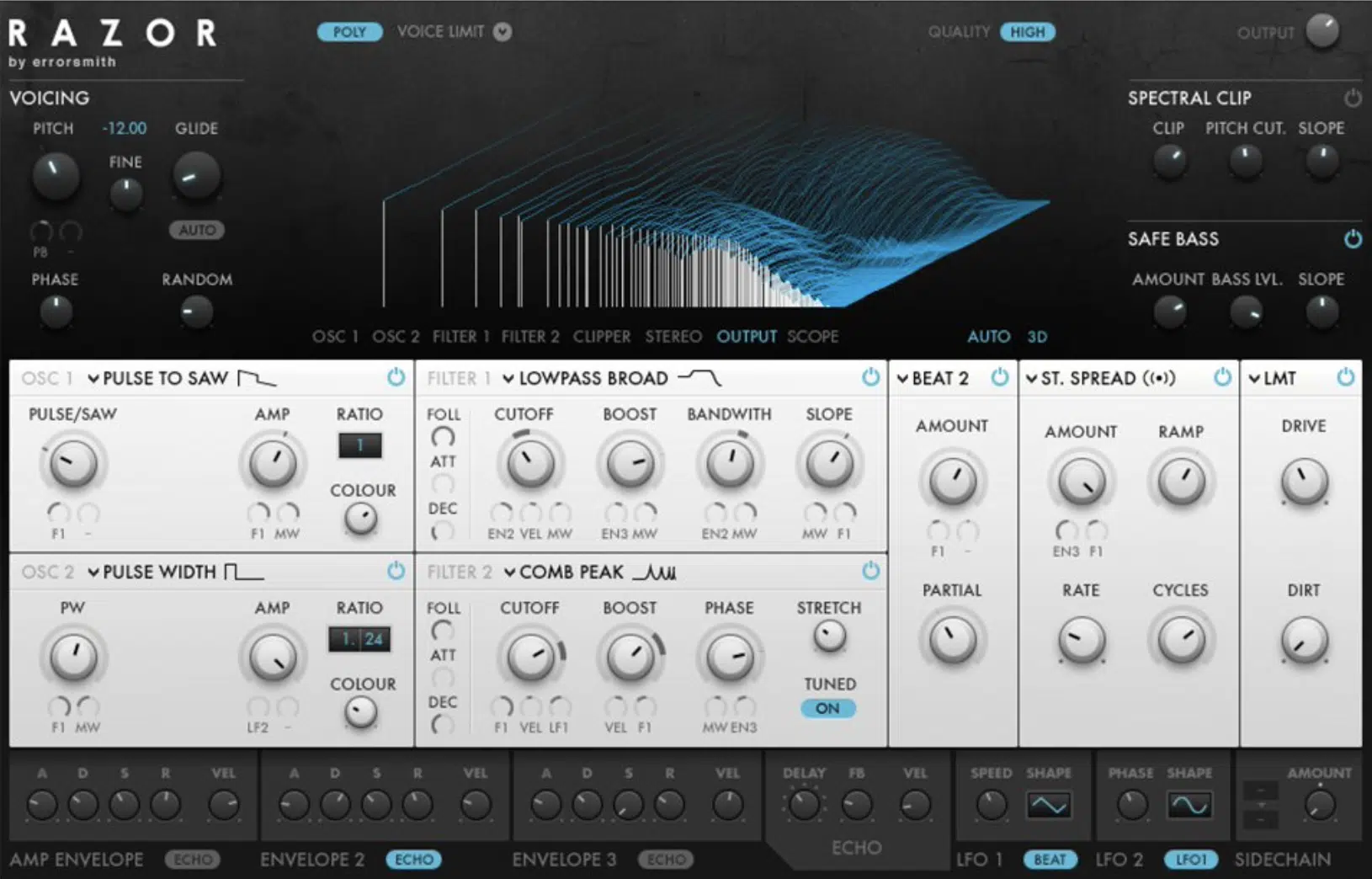
Razor is an innovative additive synthesizer available in Native Instruments’ powerful Reaktor modular synthesis environment.
With its intuitive interface and flexible modulation options, Razor is capable of producing a diverse range of sounds, from lush pads to aggressive leads.
Its unique additive engine allows you to manipulate up to 320 partials in real-time, providing precise control over your sound’s harmonic content.
Its unique system offers multiple modules for each section, which allow you to start off with string-like modulation.
As well as create otherworldly sounds, as these modules interact with the inharmonic partials in very unique ways.
Another notable aspect of Razor is its extensive modulation capabilities, which include multiple LFOs, envelopes, and sequencers.
These modulation options allow you to create evolving, dynamic sounds that respond to your playing or external inputs.
Standout Features:
- Up to 320 partials for detailed sound manipulation
- Wide variety of modules that allow you to creatively affect the partials
- Extensive modulation options
#2. Loom II by AIR Music Tech
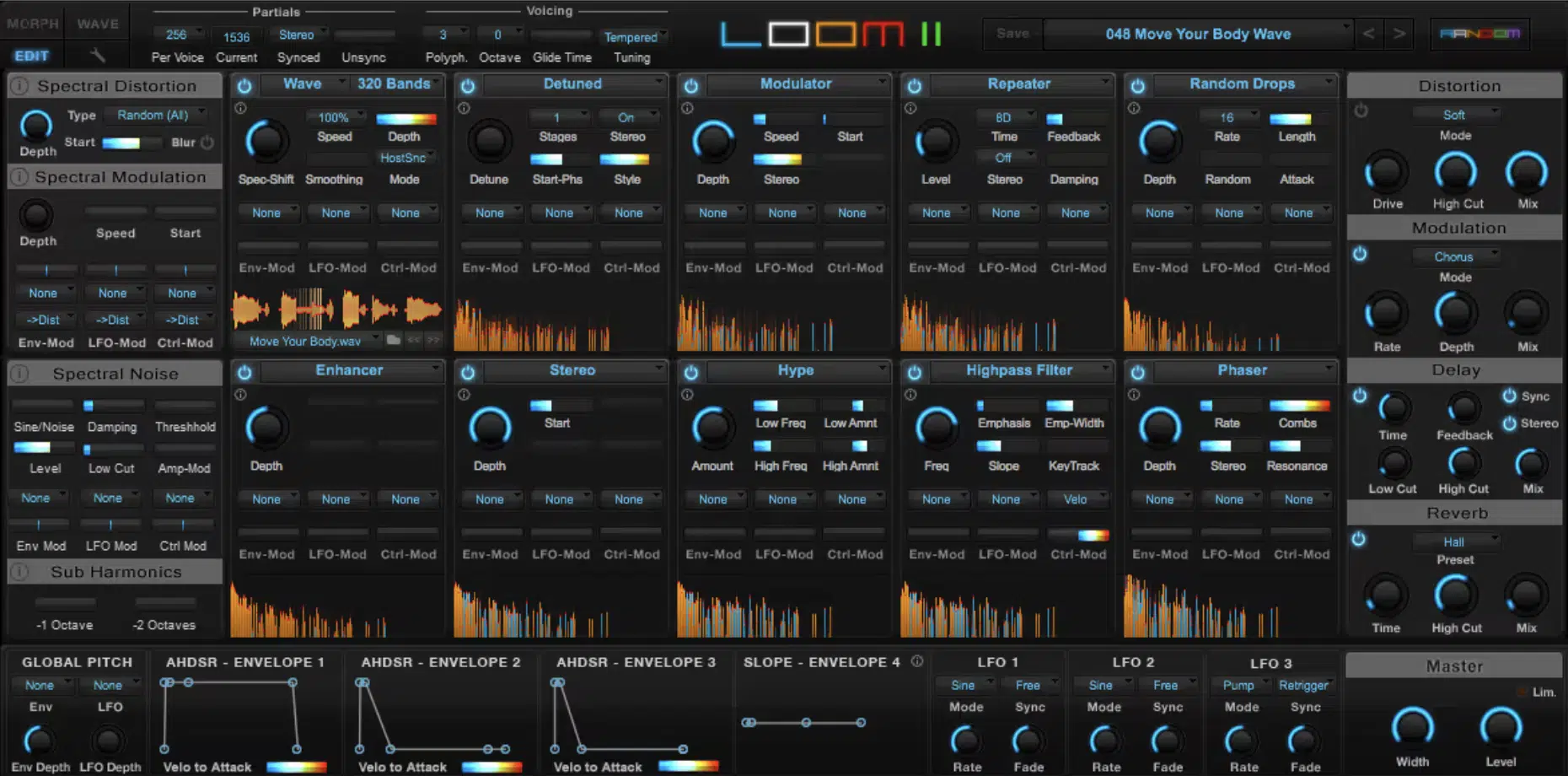
Loom II is a powerful, easy-to-use additive synthesizer developed by AIR Music Tech.
Designed with a sleek, modern interface, Loom II offers a unique approach to additive synthesis, combining 30 editable modules to create mind-blowing, evolving sounds.
With its modular architecture, it encourages experimentation, making it an excellent choice for electronic music producers and sound designers alike.
The standout feature of Loom II is its Morph Pad, which other additive synths typically don’t offer.
It allows you to morph between different presets in real-time.
This feature enables you to create dynamic, evolving sounds that can be controlled via MIDI controller or automated within your DAW.
Loom II also offers a range of built-in effects, including reverb, delay, and distortion, which can be used to further enhance your sounds and add depth and character.
Speaking of reverb, if you’re searching for the best reverb plugins of 2023, we divulge all the top industry picks.
Standout Features:
- Modular additive synthesis architecture
- Morph Pad for real-time preset morphing
- Built-in effects
#3. Pigments 3 by Arturia
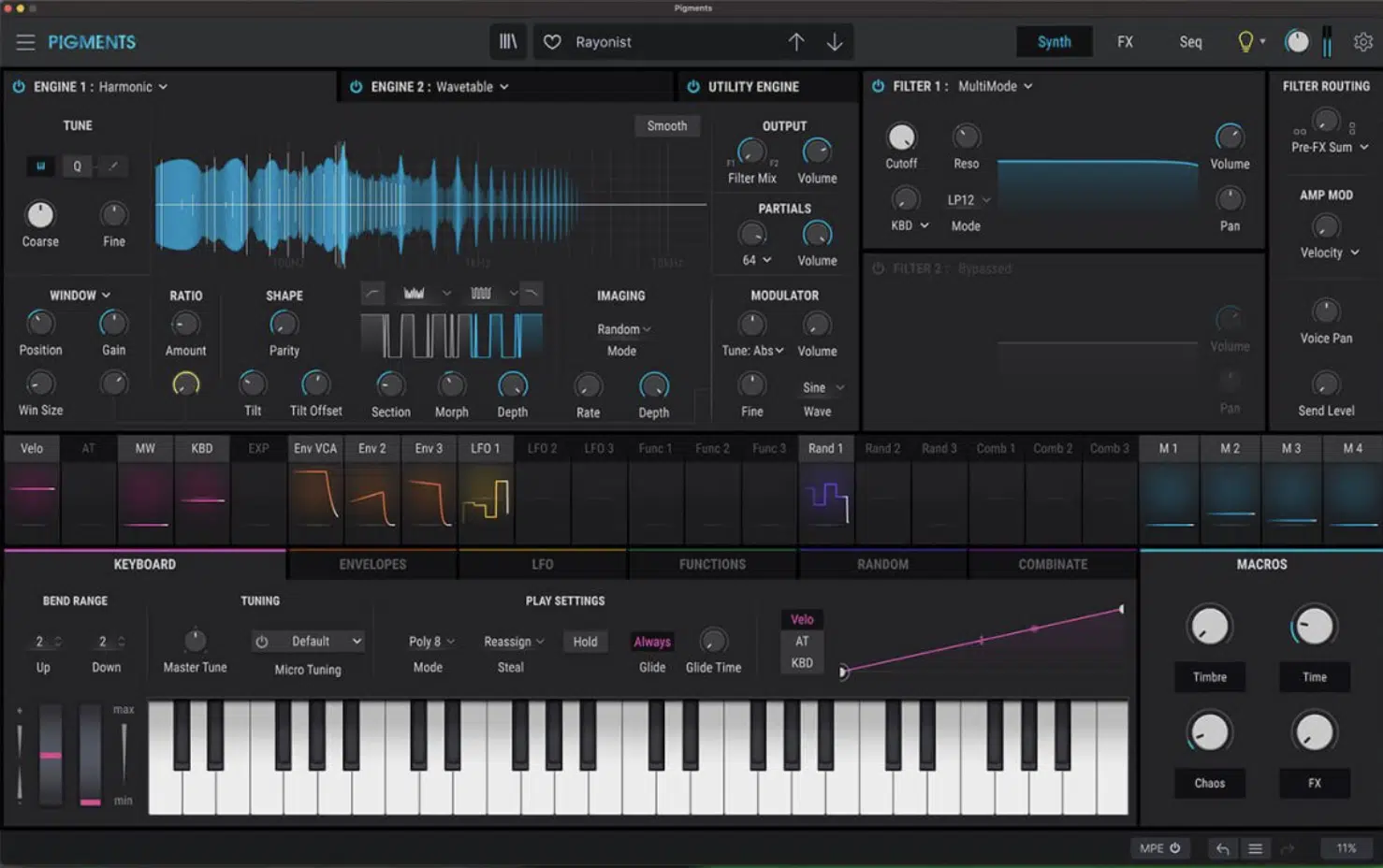
Pigments 3 is a true additive synthesizer by Arturia that combines additive synthesis with other synthesis techniques, including wavetable, virtual analog, granular synthesis, and multi-sample engine.
With its powerful sound engine and intuitive interface, Pigments 3 is a comprehensive tool for modern music producers and sound designers, offering a wide range of sonic possibilities.
One of Pigment 3s’ standout features is its comprehensive modulation capabilities.
This include multiple LFOs, MSEG (multi-stage) envelopes, random generators, and a sequencer/arpeggiator.
These modulation options provide a high level of control over your sound’s dynamics and movement, allowing you to create intricate, evolving textures.
Additionally, Pigments 3 offers a range of high-quality built-in effects, many of which are taken directly from Arturia’s analog-modeled plugins.
This includes filters, reverb, delay, and multi-band compression, which can be used to further sculpt and enhance your sounds.
Standout Features:
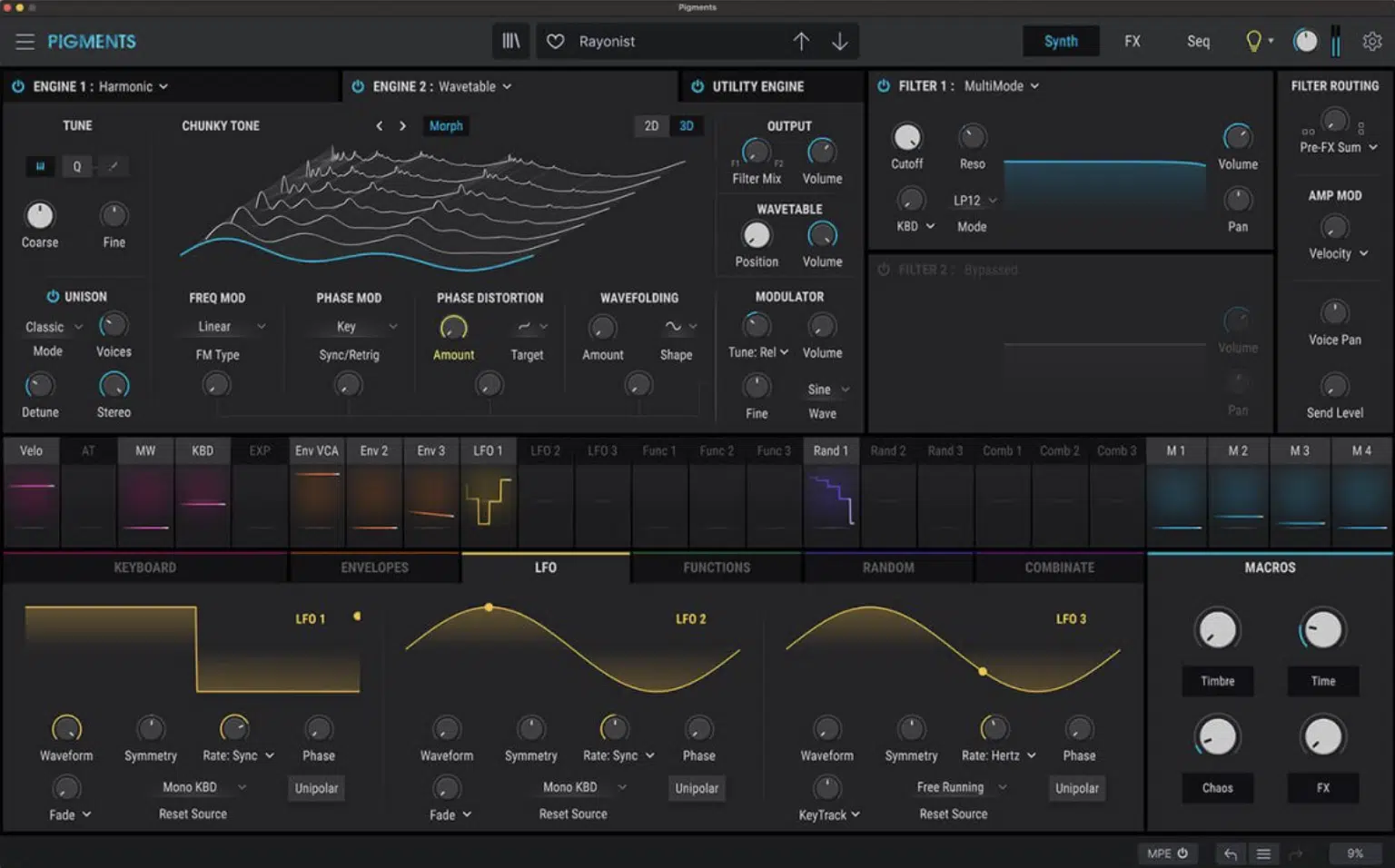
- Multiple synthesis techniques, including additive
- Comprehensive modulation capabilities
- High-quality built-in analog-modeled effects
- Full-blown sequencer/arp with unique randomization options
#4. Alchemy by Apple (Logic Pro)
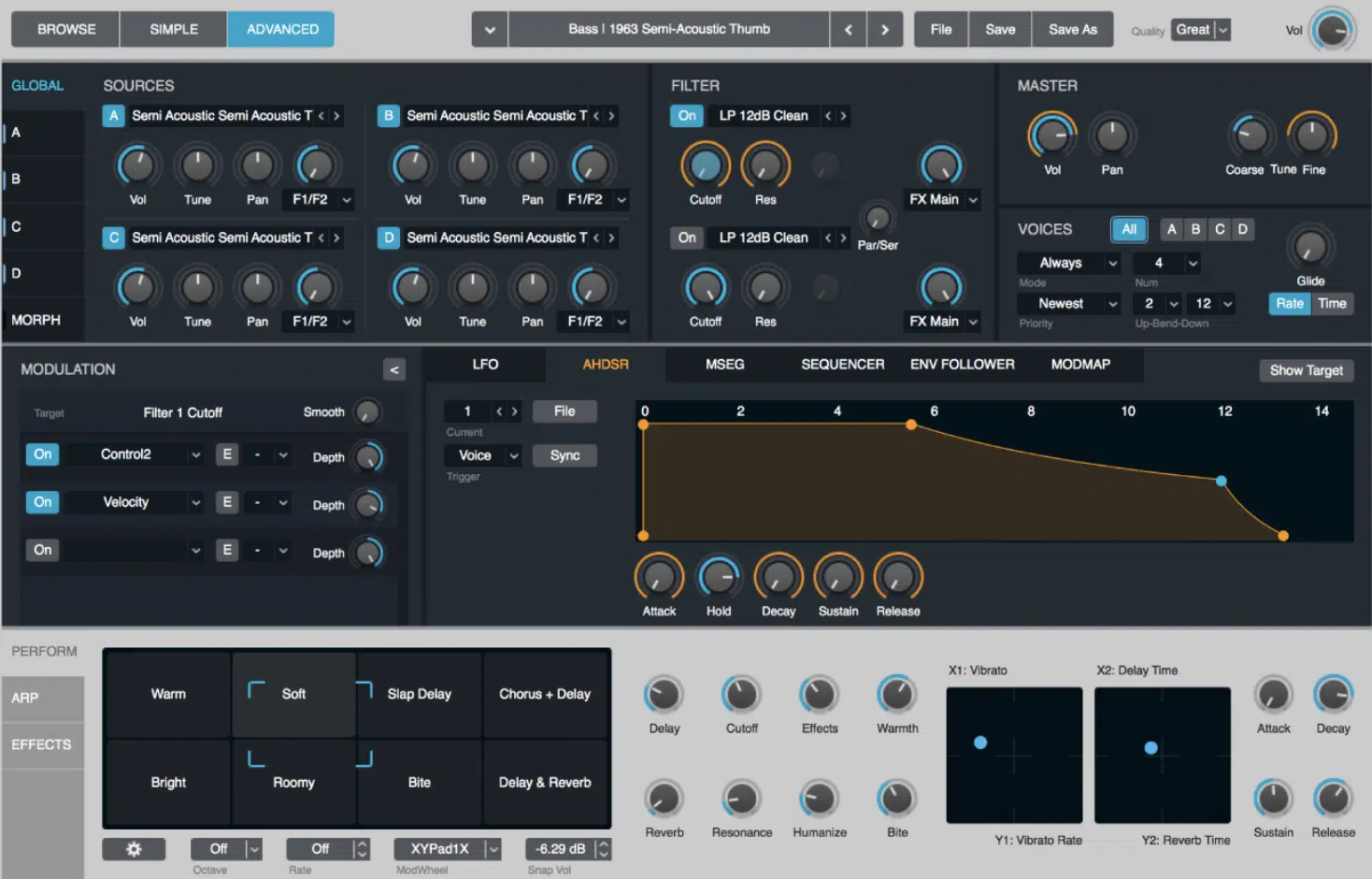
Alchemy, included in Apple’s Logic Pro DAW, is a powerful synthesizer that combines additive synthesis with other synthesis techniques, including granular, spectral, and virtual analog synthesis.
It even loads all of Logic’s sampler patched (stock or custom) for further sample manipulation in any of the included synthesis methods.
With its extensive sound manipulation capabilities, Alchemy is a versatile tool (and noise generator) for electronic music producers and sound designers looking to create unique music.
One of Alchemy’s standout features is its advanced spectral resynthesis capabilities, which allow you to analyze and recreate the harmonic content of existing sounds.
This feature enables you to use real-world recordings or samples as the basis for your additive synth patches, offering a unique approach to sound design and synthesis.
Alchemy essentially has a “morph pad” of its own.
However, instead of switching parameter values between presets, it lets you alter preset parameters, which other additive synths traditionally don’t come equipped with.
You can even move between “scenes” in real-time, and have internal modulators modulate its every movement (sick, right?).
All presets already include these pre-set scenes plus one hack: set up and save a preset, import it into Garageband IOS and you’ll have full control over your preset’s pad!
Another notable aspect of Alchemy is its extensive modulation options, which include multiple LFOs, envelopes, and sequencers.
These modulation options allow you to create dynamic sounds that respond to your playing or external inputs.
Standout Features:
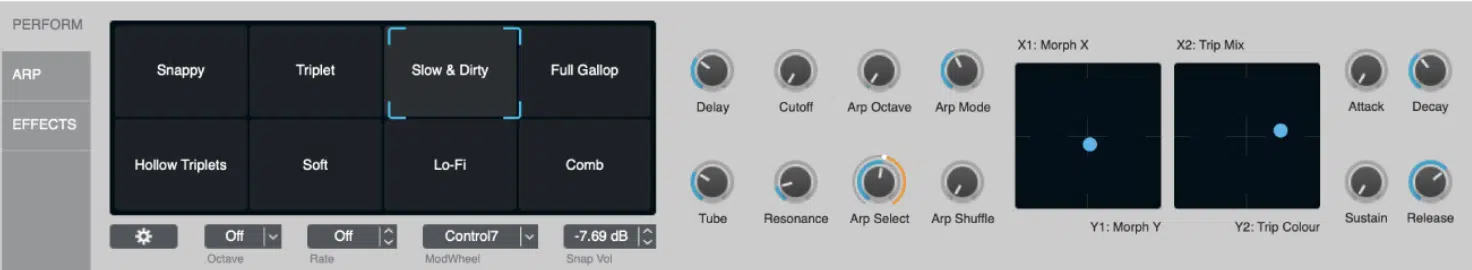
- Multiple synthesis techniques, including additive, granular, subtractive/VA, and full ESX-style multi-sample engine
- Advanced spectral resynthesis capabilities
- Extensive modulation options
- Morph Pad
- IOS preset import
#5. Harmor by Image-Line
Harmor, developed by Image-Line, is a powerful additive synthesizer that offers a unique approach to sound design and synthesis.
It includes all the familiar subtractive language, but with a much more powerful additive engine, which makes it an incredible first additive synth if you’re a beginner.
With its innovative resynthesis engine and intuitive interface, Harmor allows you to manipulate audio samples.
Or, create sounds from scratch using its built-in additive synthesis capabilities.
One of Harmor’s standout features is its advanced image resynthesis, which allows you to import images and convert their pixel data into audio (audio normalization).
This feature offers a unique, creative approach to sound design, enabling you to create one-of-a-kind sounds based on visual data.
Harmor also provides an extensive range of modulation options, including multiple LFOs, envelopes, and X/Y controllers.
They can be used to create dynamic, evolving sounds that respond to your playing or external inputs.
Standout Features:
- Innovative resynthesis engine
- Advanced image resynthesis capabilities
- Extensive modulation options, including IL’s famous custom envelopes
- Can double as a standard (yet advanced) subtractive synth
Tips & Tricks for Additive Synthesis
Now let’s dive into tips & tricks that can help you optimize and enhance your additive synthesis skills.
-
Optimizing Your Synth Sounds

When working with additive synthesis, it’s essential to explore different combinations of harmonics and partials to create unique timbres.
Start by adjusting the amplitude and phase of individual harmonics to see how they impact the overall sound.
Then, add more harmonics to increase the complexity of the sound, or focus on a few strong harmonics for a purer, more straightforward tone.
Don’t be afraid to push the limits of your additive synth to discover new sonic possibilities.
For example, try detuning some harmonics slightly to create subtle inharmonic textures.
Alternatively, experiment with automating the amplitude or phase of individual harmonics over time to create evolving, dynamic sounds.
-
Harnessing The Power of MIDI Controllers

MIDI controllers can be a powerful tool for controlling and shaping your additive synth sounds.
By mapping MIDI controllers to parameters like amplitude, frequency, or phase, you can create dynamic, expressive performances that respond to your playing in real-time.
For example, you might use a MIDI keyboard MOD wheel to control the balance of harmonics in your sound.
This allows you to shift between simple and complex timbres as you play.
You could also use an expression pedal to control the amplitude of individual harmonics, creating swells and fades that add movement to your sound.
In addition to hardware controllers, many DAWs offer built-in MIDI automation tools that can be used to control your additive synth parameters.
Play around with drawing automation curves for parameters like amplitude or phase to create evolving, dynamic sounds that change over time.
-
Using Phasers To Enhance Your Sound
Phasers are a type of effect that can add depth and movement to your additive synth sounds.
By applying a phaser to your synth patch, you can create subtle shifts in phase that add intrigue and complexity to the sound.
To get started, try applying a gentle phaser with a low-depth setting to a simple sine wave patch.
As you increase the depth and sample rate of the phaser, you’ll notice the sound becoming more complex and animated.
Try tweaking different phaser settings to find the sweet spot that enhances your sound without overpowering it.
Don’t forget you can use parallel processing to blend the original sound signal in with the processed version.
For more advanced applications, consider using a multiband phaser that allows you to apply different phase settings to different frequency ranges.
This can create even more intricate textures and help you sculpt the perfect sound for your mix.
-
Different Frequency Ranges & Fundamental Frequencies
Additive synthesis offers a vast range of sonic possibilities, and one of the best ways to explore its potential is by experimenting with different frequency ranges and fundamental frequencies.
By focusing on specific frequency areas, you can create a wide variety of textures & timbres that can be used to add interest and depth to your music.
For instance, try creating a patch that emphasizes the lower harmonics to produce a deep, bass-heavy sound.
Alternatively, you can focus on the higher harmonics to create bright, shimmering textures that sit on top of your mix.
By playing around with different frequency ranges and fundamental frequencies, you can unlock new sonic possibilities.
-
Balancing Harmonics
The key to creating rich, expressive sounds with additive synthesis lies in finding the right balance between harmonics.
By carefully adjusting the amplitude, frequency, and phase of individual harmonics, you can create dope timbres and textures that enhance your music.
Start with the amplitude of different harmonics and adjust their levels to create a harmonically rich sound.
You can also try detuning individual harmonics slightly to create subtle inharmonic textures that add depth and complexity to your sound.
NOTE: Keep in mind that small adjustments can have a significant impact on the overall timbre, so be prepared to spend some time fine-tuning your patch.
Another technique for balancing harmonics involves modulating the amplitude, frequency, or phase of individual harmonics over time.
By automating these parameters using envelopes, LFOs, or MIDI controllers, you can create evolving, dynamic sounds that change in character throughout their duration.
Remember that achieving a rich, balanced sound often requires a combination of careful harmonic manipulation and complementary processing, such as EQ, compression, and reverb.
By combining these techniques, you can create additive synth patches that are full, expressive, and well-suited to your professional beats.
Speaking of compression and EQ, we dropped the absolute best EQ plugins and best compressor plugins of 2023.
Final Thoughts
Additive synthesis is a powerful tool for music producers and sound designers alike.
By understanding its principles and mastering its techniques, you can create an endless array of unique sounds and take your tracks to new heights.
Don’t forget to check out our top 5 additive synths for 2023 and experiment with the tips & tricks we’ve shared throughout this article.
One final suggestion to further enhance your sound design is to combine additive synths with these outstanding Serum presets, which feature an array of high-quality wavetable synths.
By layering or combining additive and wavetable synths, you’ll be able to harness the power of sound design in ways that would be impossible using just one method of synthesis alone.
So, go ahead and dive into the world of additive synthesis, using our article as a guide.
Explore its vast possibilities and let it inspire your creativity, pushing your music production skills to new heights.
Until next time…







Leave a Reply
You must belogged in to post a comment.