If you’re looking to learn all about granular synthesis, you’ve come to the right place!
Granular synthesis is a fascinating and versatile approach to sound design.
It can help take your music production skills to the next level, and impress people in the process.
In today’s article, we’ll explore the ins & outs of granular synthesis.
As well as provide you with pro insights, techniques, and tips to help you excel at this powerful sound creation method.
Here’s a glimpse of what you’ll discover:
- The principles and history of granular synthesis ✓
- Time-stretching & pitch-shifting techniques ✓
- Tips & tricks for mastering granular synthesis ✓
- How granular synthesis can be used in sound design & production ✓
- Popular granular synths & processors ✓
- Advanced granular synthesis techniques ✓
Once you’re done reading today’s article, you’ll be super versed in granular synthesis and granular synthesizers, like a real boss.
So, let’s dive in…
Table of Contents
- What is Granular Synthesis?
- How Granular Synthesis Works
- Granular Synthesis vs. Other Synthesis Methods
- Core Components
- Time-Stretching
- Pitch-Shifting
- Ambient Textures and Pads
- Percussive and Rhythmic Elements
- Tips & Tricks for Mastering Granular Synthesis
- The 6 Best Granular Synth Plugins
- Unconventional Granular Synthesis Methods
- Practical Applications
- Final Thoughts
What is Granular Synthesis?
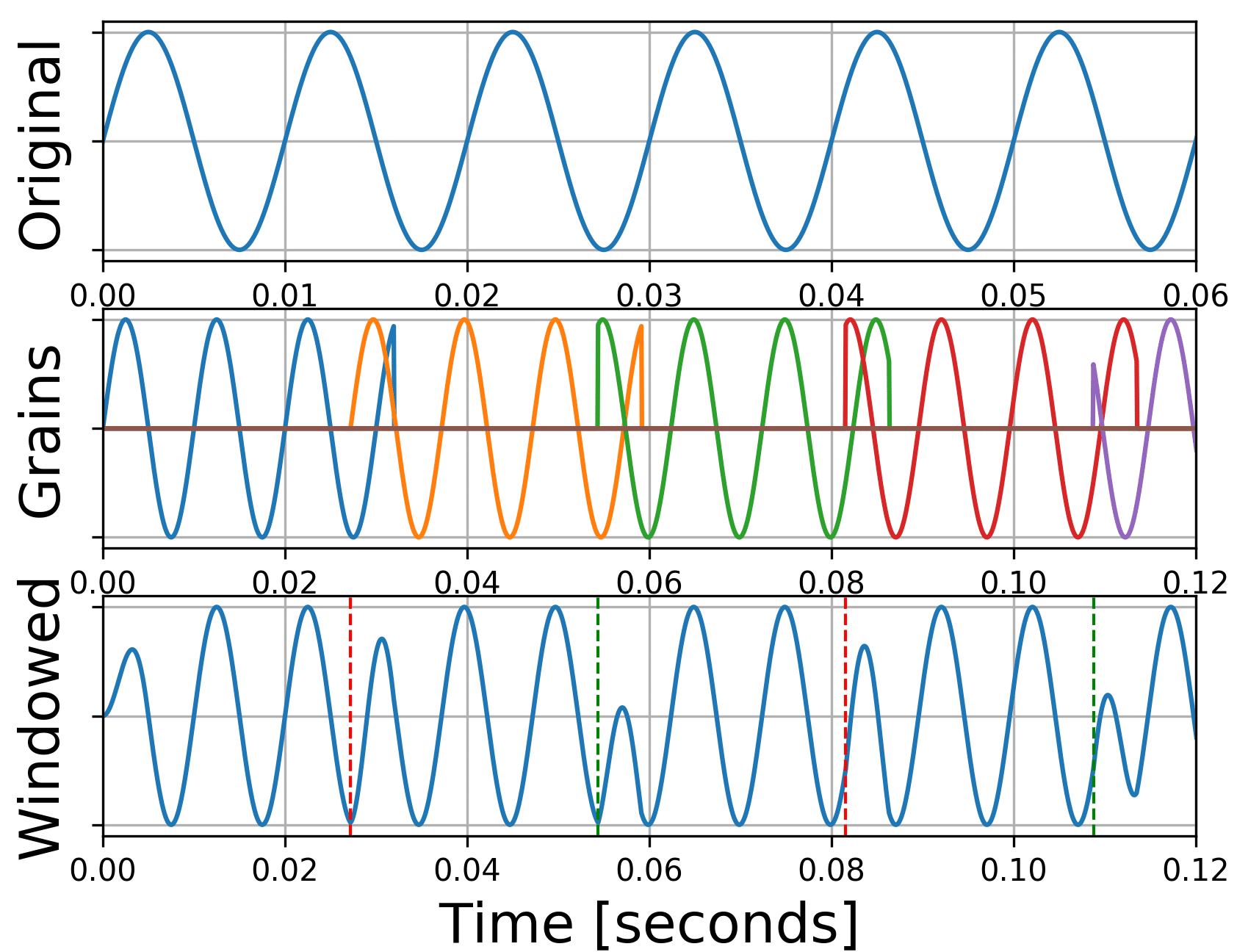
Granular synthesis (GS) is a sound synthesis method that involves breaking audio samples into small segments, or grains.
Then, they can be manipulated and reassembled to create sounds that are fresh, new, and exciting.
The concept of this synthesis was first introduced by Iannis Xenakis in the 1950s and further developed by Curtis Roads in the 1970s.
It was originally accomplished by cutting tiny segments of a recorded audio file on tape and using a variety of methods to paste and playback the audio in a “granular” fashion.
The evolution of digital audio workstations (DAWs) has made granular synthesis more accessible and popular among music producers, like myself, who like to push the boundaries of sound design.
How Granular Synthesis Works
There are many moving parts of granular synthesis, and here are the main two:
1. Grains
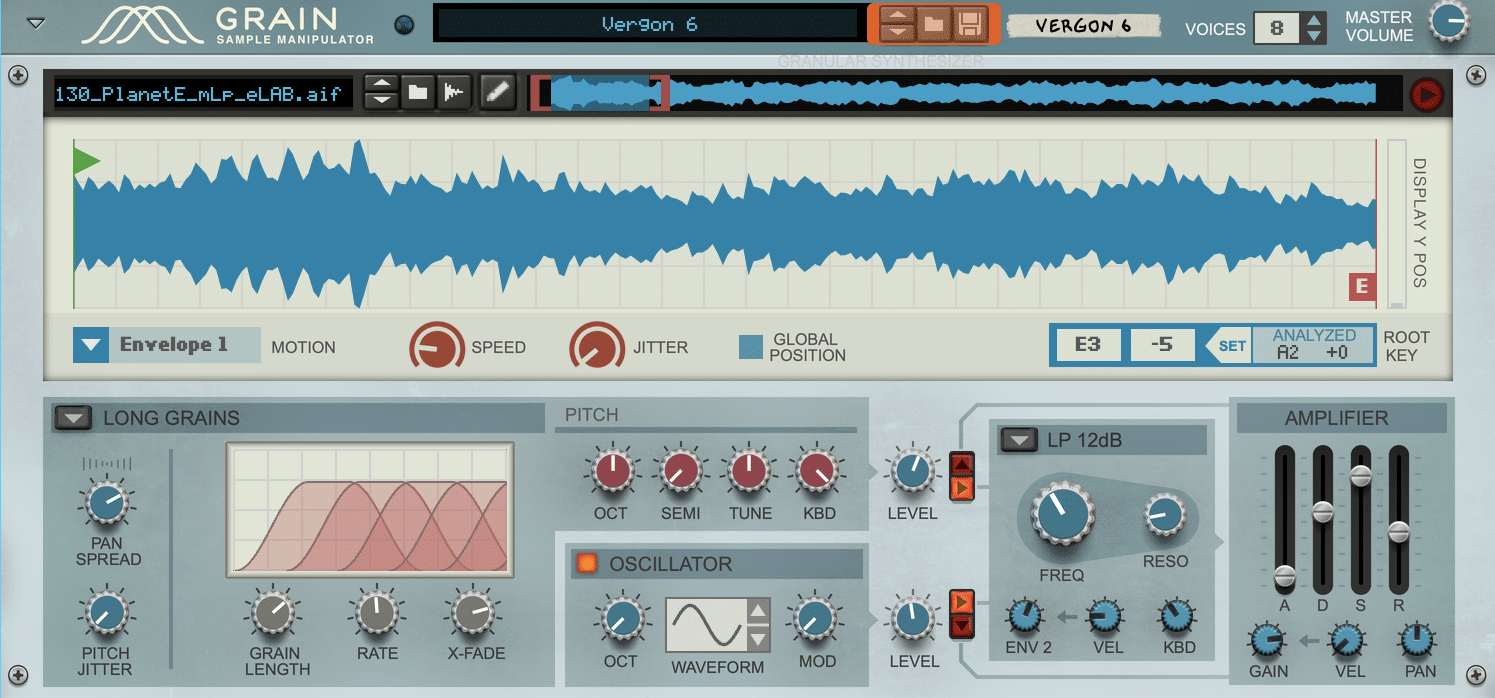
Granular synthesis relies on dividing audio samples into tiny audio grains 一 which can range from a few milliseconds to several hundred milliseconds in length.
These grains can be manipulated independently using various parameters, such as:
- Playback speed
- Pitch
- Length
This can help you create a wide range of different sounds and brilliant textures.
For example, by changing the playback speed of grain, you can create time-stretching effects, where the audio is lengthened without affecting its pitch.
Or, pitch-shifting effects, where the pitch is changed without altering the audio’s length.
Side note, it’s important to have the best pitch shifter plugins in order to become a master of pitch-shifting.
Fun Fact: Pitch-shifting, time-stretching, and manipulation plugins (like Autotune & the Warp modes found in Ableton) actually use a form of GS to perform their pitch/time-preservation effects.
2. Sound Particles
Think of grains as sound particles that can be manipulated and layered to create complex soundscapes.
By controlling the density of grains and their overlap, you can create anything from smooth, ambient textures to harsh, dissonant noise.
Experimenting with grain manipulation can lead to discovering new and interesting sonic possibilities, allowing your music to stand out.
Granular Synthesis vs. Other Synthesis Methods
Granular synthesis differs from other synthesis methods 一 such as subtractive synthesis or wavetable synthesis 一 because it focuses on manipulating audio samples (sample-based synthesis).
As opposed to generating sound from oscillators and other mathematically-based functions.
This unique approach to sound synthesis provides a greater level of control and creativity in sound design.
You can use real-world sounds and samples as raw material, such as creating granular types from non-harmonic sources like foley samples.
You can look at granular synthesis as a fusion of a Sampler and a Wavetable synth because it basically is.
While most advanced Samplers do perform the same modulation capabilities as a subtractive synth, granular synthesis takes it to another level.
It enables you to add anything from subtle to extreme spectral sound-morphing, or even treat it like a wavetable.
You can stack synths and layer both extremes… the possibilities are truly endless.
NOTE: If you’re looking for the craziest subtractive synthesis techniques in the world, we’ve got you covered.
Core Components
The most important part of granular synthesis is the grain parameters and grain controls.
Understanding them will help you master the art of GS as a whole.
-
Playback Speed
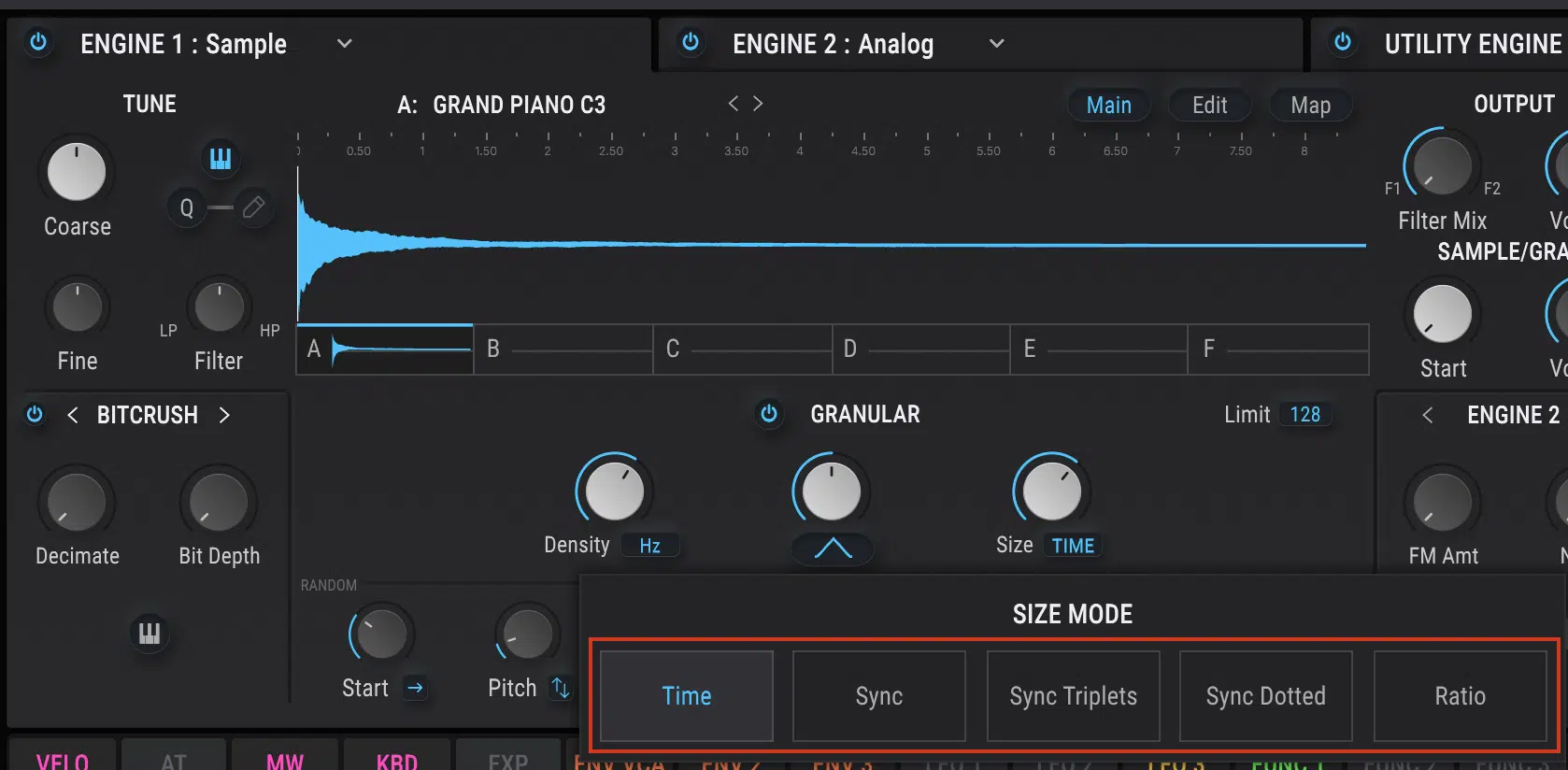
Adjusting the playback speed of individual grains is a primary parameter in granular synthesis.
By increasing or decreasing the playback speed, you can create unique effects.
This includes time-stretching, where the audio is lengthened without affecting its pitch.
Or, pitch-shifting, where the pitch is changed without altering the length of the audio.
We talk about each of these unique processes in detail later on.
Combining time-stretching and pitch-shifting can result in otherworldly sounds that can elevate your productions to new heights.
-
Pitch
Pitch control is another vital parameter in granular synthesis.
By changing the pitch of individual grains over time, you can create harmonies and melodies that wouldn’t be possible using the original sample.
This can be particularly useful when working with melodic content, as it allows you to develop new musical ideas from a single audio sample.
-
Length
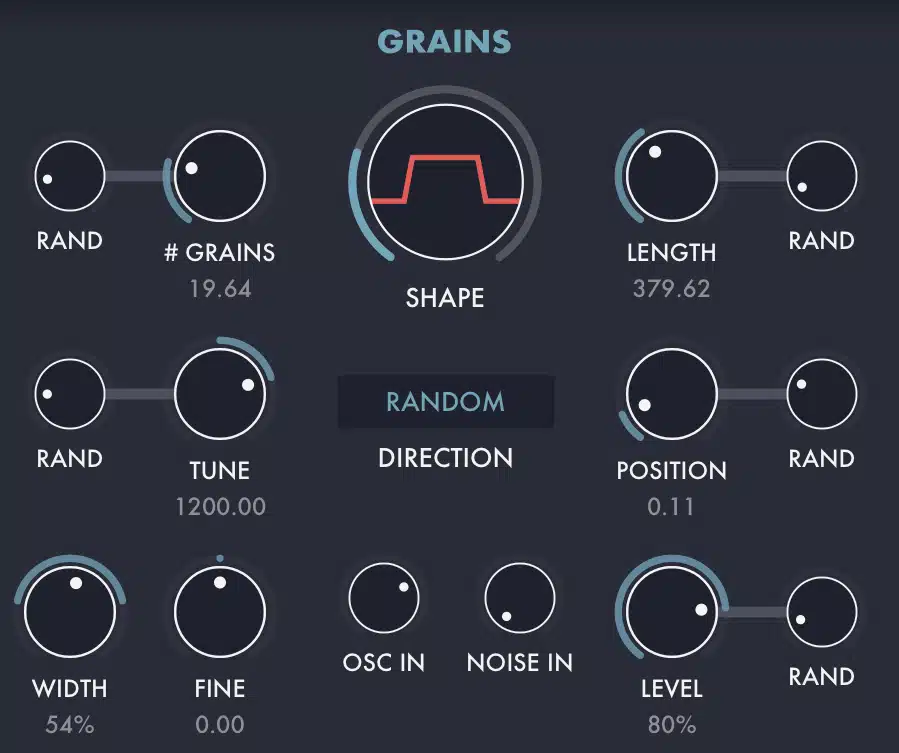
Manipulating the length of grains can significantly impact the resulting sound.
- Shorter grain lengths 一 Create a more granular, textural effect.
- Longer grain lengths 一 Produce smoother, more continuous sounds.
Playing around with different grain lengths can help you find the perfect balance between texture and continuity.
-
Grain Overlaps
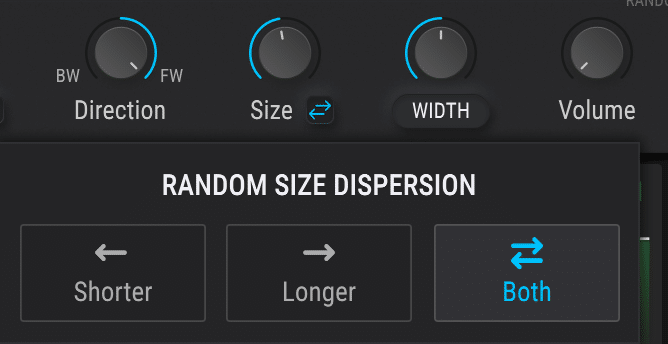
Adjusting the overlap between grains is an essential aspect of granular synthesis, as it can affect the density/texture of the resulting sound.
- Increasing the overlap between grains 一 Creates a smoother, more continuous sound.
- Reducing the overlap 一 Can result in a more fragmented, textural effect.
Experimenting with different overlap settings can lead to a wide variety of sonic textures and gives you even more creative control over your sound design.
-
Density
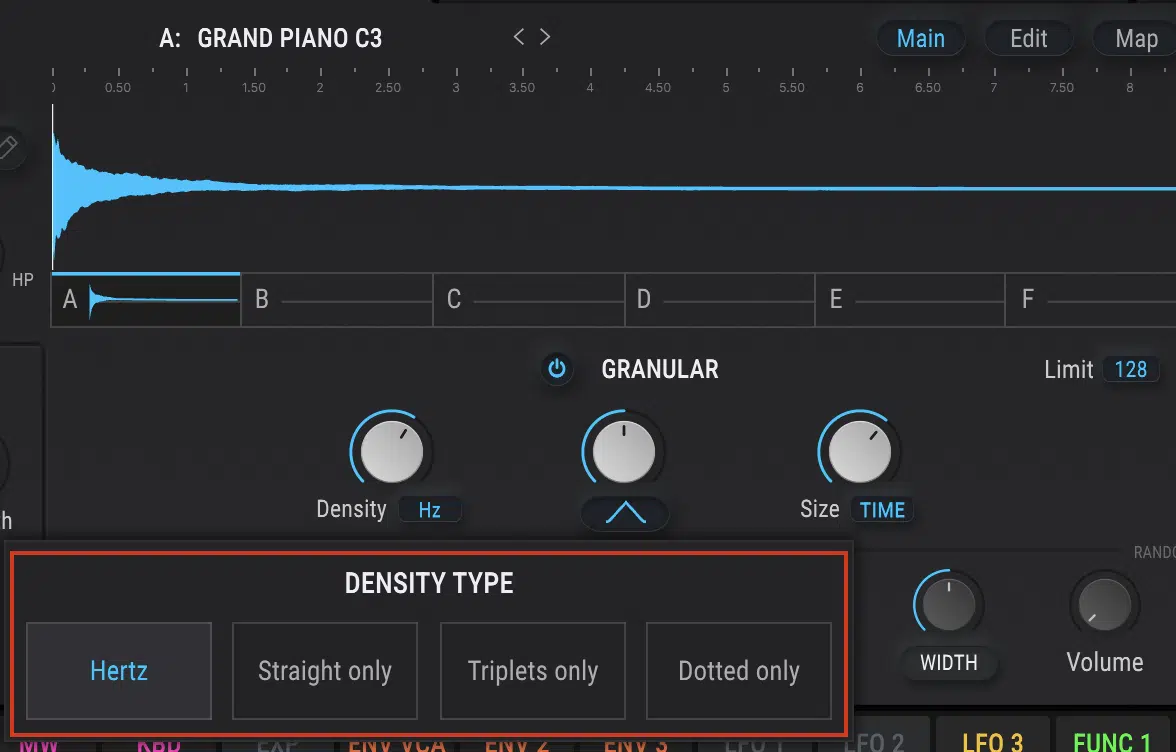
The density of grains in granular synthesis refers to the number of grains present within a given time frame.
- A higher density 一 Creates rich, complex soundscapes.
- A lower density 一 Results in sparse, more transparent, or experimental/glitch-like sounds.
Adjusting the grain density can significantly impact the overall character of your audio, allowing you to fine-tune your GS creations.
-
Grain Shape/Envelope
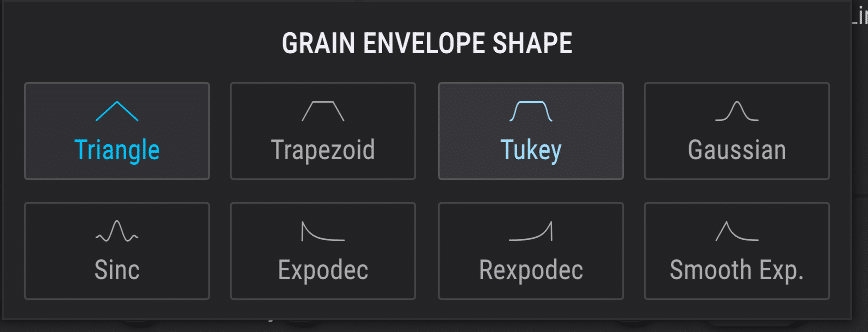
The envelope of a Grain, sometimes referred to as “shape,” determines how the amplitude of one grain evolves over time.
By shaping the envelope of individual grains, you can create a wide range of different effects 一 from sharp, percussive sounds to softer, more ambient textures.
Tweaking different envelope shapes can open up a world of creative possibilities for your GS projects.
NOTE: A classic shape is one that actually makes the grain appear to be playing in reverse.
Time-Stretching
Time-stretching is an essential technique in modern music production, so you should definitely get acquainted with it (if you’re not already).
It allows you to change the length of an audio sample without affecting its pitch.
This is particularly useful when trying to fit an entire sample into a specific tempo or when creating unique, evolving soundscapes.
Granular synthesis plays a significant role in time-stretching by breaking one sample into tiny grains and manipulating their playback speed while maintaining the same pitch.
This process can be achieved through various DAWs and plugins that offer GS capabilities.
In practice, time-stretching can be used to create interesting effects such as slowing down a vocal sample to make it sound more ethereal or stretching a drum loop to fit a different BPM.
When time-stretching with GS, the key is to find the right balance between grain length and overlap to maintain a smooth sound without introducing unwanted artifacts.
Experimenting with different grain settings and playback speeds can help you achieve the desired time-stretching effect for your specific project.
Pitch-Shifting
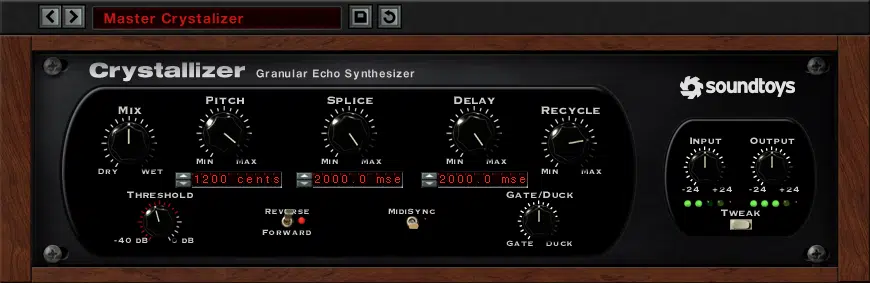
Pitch-shifting is another essential technique, which involves changing the pitch of an audio sample without affecting its length.
This can be useful for creating harmonies, melody loops, or even transforming a sound into something entirely new.
Granular synthesis enables pitch-shifting by breaking down the audio sample into grains and manipulating their pitch independently while maintaining the original playback speed.
This is also how the evolution of pitch-preserving-time-stretching and time-preserving-pitch-stretching started, which is at the forefront of many complex options we have today.
For example, you can use pitch-shifting to transpose a melodic sample into a different key or to create harmonies from a single vocal recording.
GS allows for precise pitch control, enabling you to create smooth pitch transitions or to experiment with more extreme pitch changes for epic sound design.
Ambient Textures and Pads
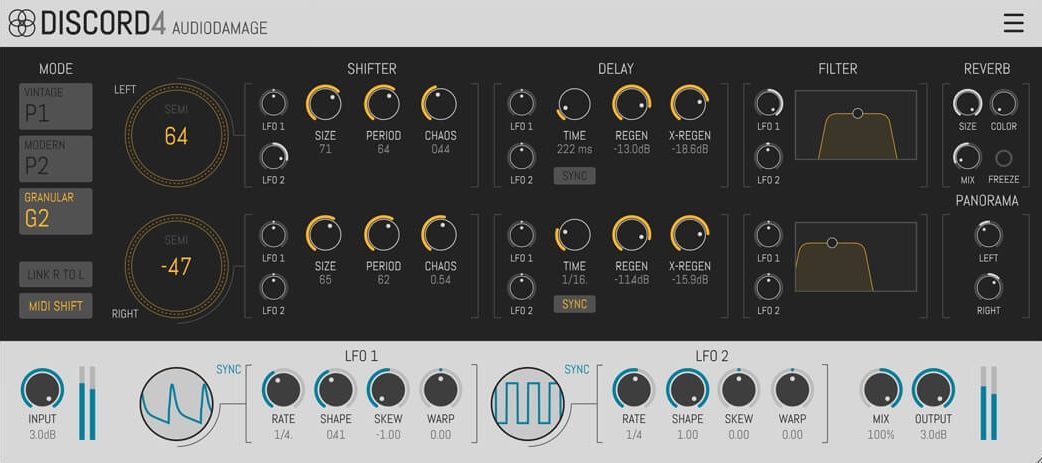
One of the most common uses of granular synthesis in sound design is the creation of lush, atmospheric textures and pads.
By breaking down audio samples into tiny grains and adjusting their pitch, playback speed, length, and envelope, you can create evolving soundscapes that add depth and emotion to your music.
Manipulating different grain parameters and layering multiple grains can result in complex, ethereal textures that can elevate your production.
Percussive and Rhythmic Elements
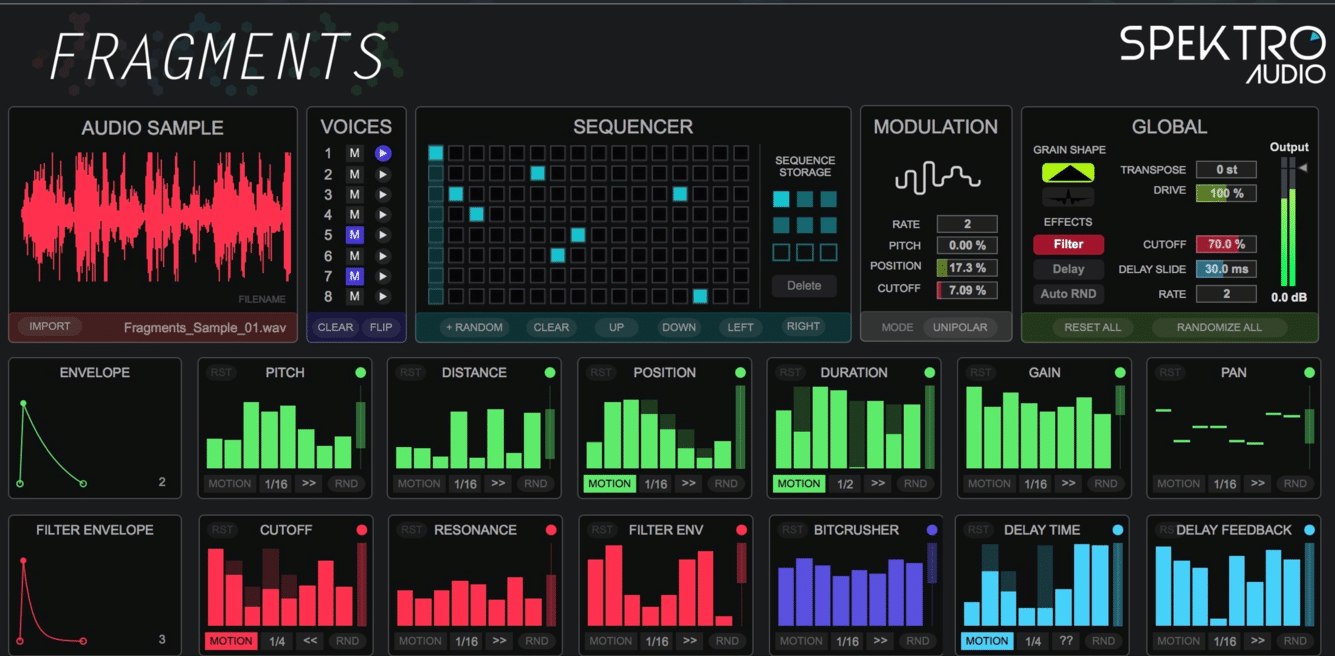
GS can also be used to create unique percussive and rhythmic elements in your music.
By manipulating the pitch and envelope of individual grains, you can transform any sample into an entirely different and intriguing new sound.
This includes drum hits, clicks, glitches, or even complete drum & melodic loops.
Combining these granular synthesis-generated sounds with traditional drum samples can add a unique vibe, unmatched by any other technique.
Tips & Tricks for Mastering Granular Synthesis
In order to master this form of synthesis, there are a few surefire tips and tricks to help you throughout the entire process.
-
Start with a Simple Sound Source
When you’re first diving into granular synthesis it’s a good idea to begin with a simple sound source like:
- A sine wave
- A basic sample
- A Single instrument (one shot) recording
This approach allows you to concentrate on understanding how the various grain parameters impact the sound and makes it easier to hear the results of your manipulations.
Since you’re working with source material that you’re already familiar with, it allows you to fully comprehend what this form of synthesis and its associated parameters are going to the sound.
As you become more comfortable with GS, you can gradually move on to more complex sound sources, which will offer a broader range of sonic possibilities.
-
Experiment with Different Grain Parameters

One of the keys to mastering GS is to explore the full range of grain parameters available in your GS plugin or instrument.
This includes adjusting:
- Grain length
- Pitch
- Envelope
- Density
- More
By experimenting with different settings, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of how each parameter affects the overall sound and texture.
Don’t be afraid to push the boundaries and try extreme settings to see what insane and rare sounds you can create.
Speaking of plugins and instruments, if you’re looking for the absolute best free VST effects on the planet or the most epic free VST instruments, we’ve got you covered.
-
Layer Multiple Grains for Richer Sounds
Another technique for achieving more complex and intricate sounds with granular synthesis is layering multiple grains with different settings.
By combining grains with various pitch, length, density, and envelope settings, you can create rich, multi-layered sounds that would be difficult to achieve with a single grain.
Play around with different combinations of grains.
This way, you can stumble upon exciting and unexpected results and expand the sonic palette available to you.
-
Explore Unconventional Sound Sources

Once you learn how to implement granular synthesis, consider experimenting with unconventional sound sources to further expand your creative possibilities.
This might involve using every day sounds as your raw material, like:
- The hum of a refrigerator
- The rustling of leaves
- The sound of traffic
- Car Engines, Mufflers, etc.
Breaking down these non-musical sounds into grains and manipulating their parameters can produce some truly epic, rare, outstanding sonic textures.
Which, by the way, can’t be replicated with the use of other synthesis methods, like FM synthesis.
-
Granular Effects Processing
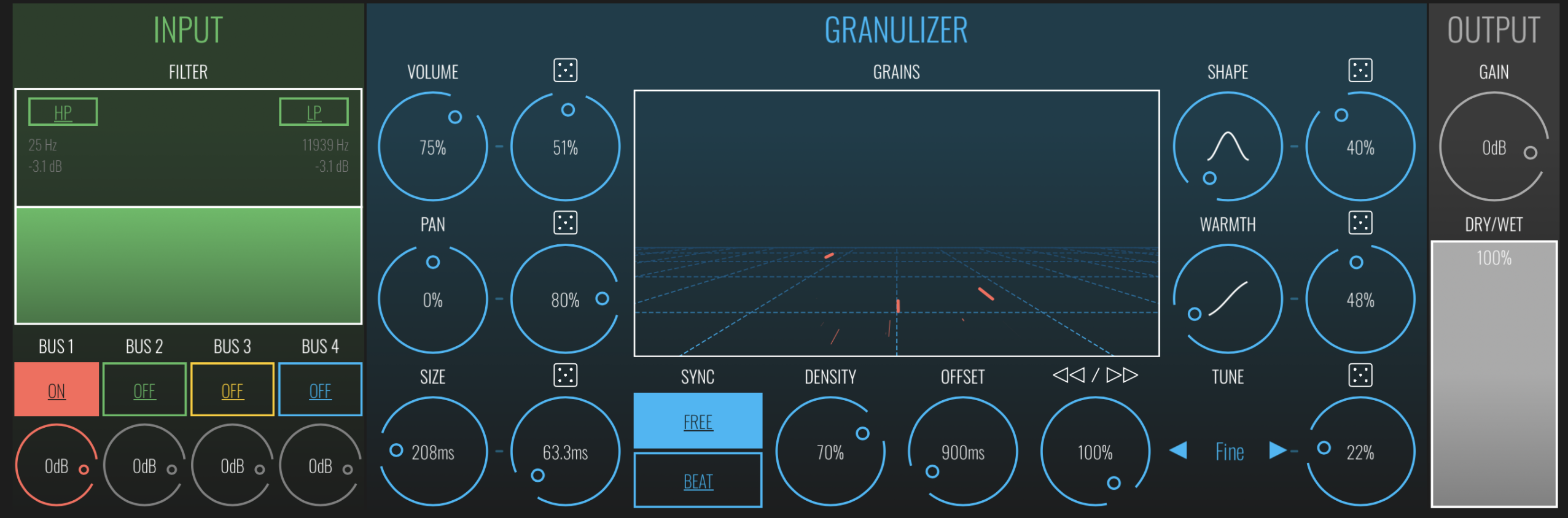
A more advanced GS technique involves using GS as an effects processor for other audio sources.
By feeding the output of a synthesizer, guitar, or voice through a GS plugin, you can create a wide range of effects.
This ranges from basic textures to extreme sound transformations.
Speaking of plugins, if you’re looking for the best mixing plugins, best EQ plugins, best saturation plugins, best mastering plugins, best compressor plugins, or best reverb plugins, we’ve got ALL the best ones!
-
Creating Rhythmic Patterns
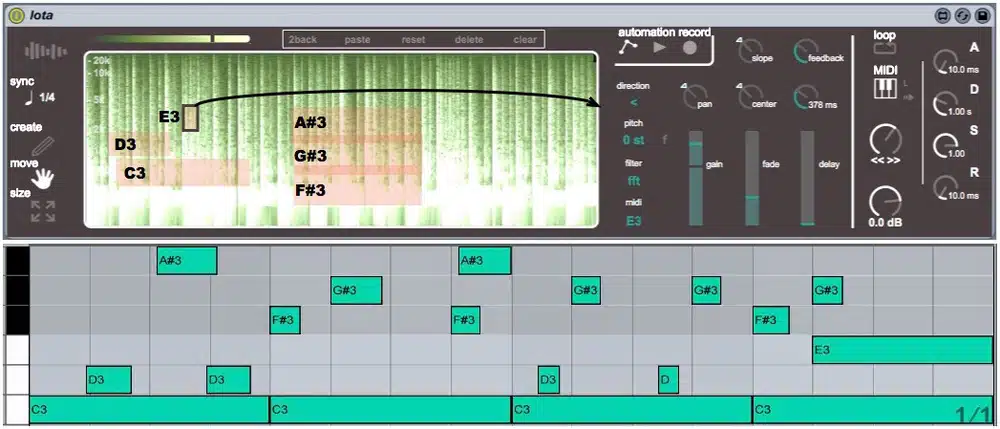
Granular synthesis can be used to create intricate rhythmic patterns from seemingly static sound sources.
For example, you could load a sustained pad sound into your granular synthesizer and adjust the grain length and density to create short, percussive grains.
By automating the pitch and playback speed of these grains in a rhythmic pattern, you can generate complex, pulsating textures that add rhythm and movement to the original pad sound.
Pro Tip:
Try routing one of the parameters, like the grain size or envelope shape, to a knob/slider on your MIDI controller or poly aftertouch (if it supports MPE).
Then record the automation and further edit the data within your MIDI clip to draw moves and patterns otherwise impossible to accomplish in real-time.
The 6 Best Granular Synth Plugins
In order to experiment with GS and all its intricacies, you’ll need the best plugins and tools.
Luckily, we’ve got you covered.
-
Granulator II
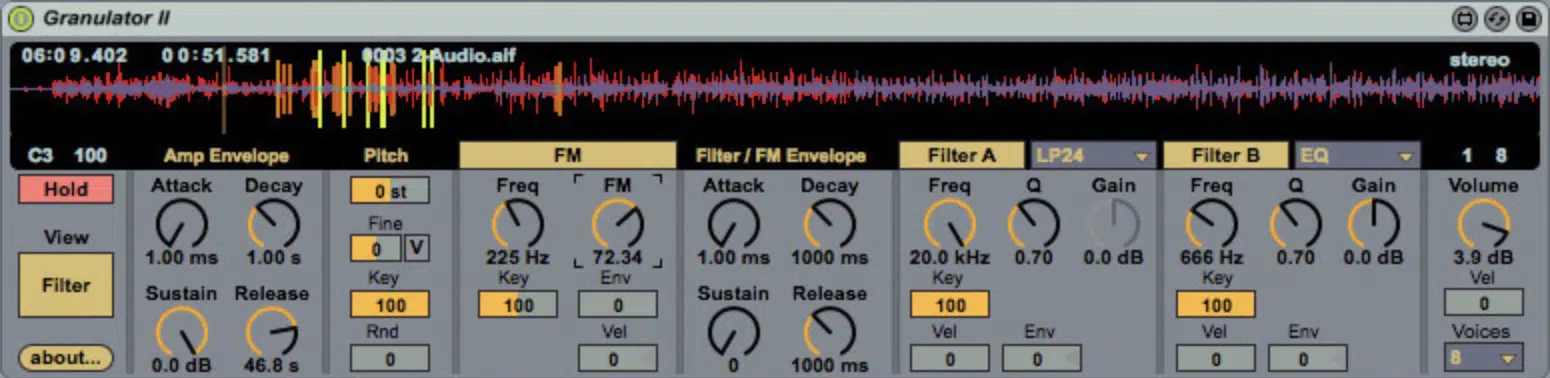
Granulator II is a popular granular synthesizer plugin created by Ableton and Monolake’s Robert Henke.
It offers a user-friendly interface for experimenting with granular synthesis and a wide range of parameters to manipulate, including grain length, pitch, density, and envelope.
Granulator II is perfect for creating complex, evolving soundscapes and is well-suited for both experienced users and those who are first learning how to become a music producer.
-
Native Instruments Reaktor
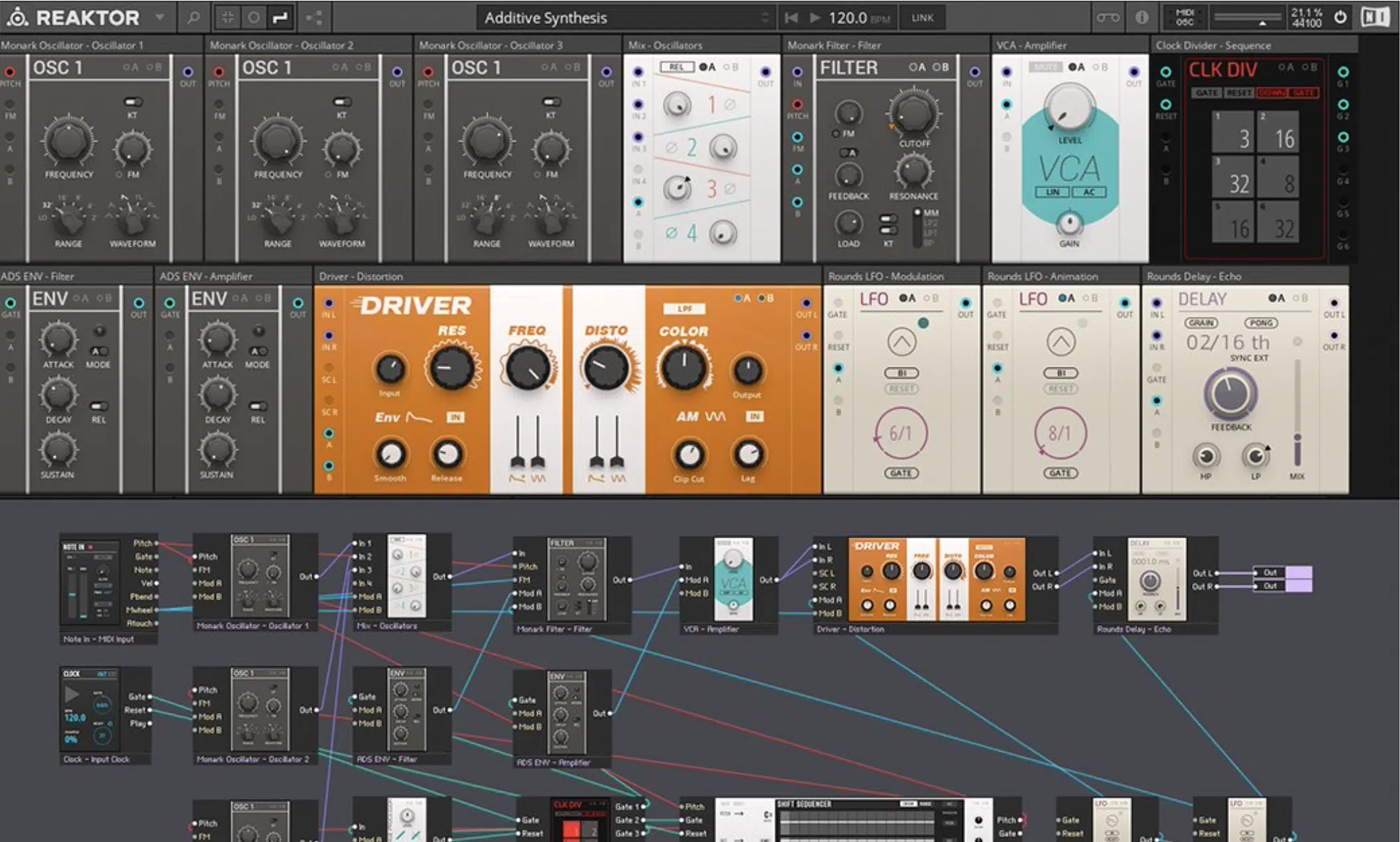
Native Instrument’s Reaktor is a powerful modular software synthesizer that includes several GS modules, such as the Grainstates FX and the Travelizer.
These modules provide extensive control over grain parameters, making Reaktor a highly versatile tool for GS design.
Additionally, Reaktor’s modular environment allows you to combine granular synthesis with other synthesis techniques, such as additive or subtractive synthesis, for even more creative possibilities.
-
Output Portal
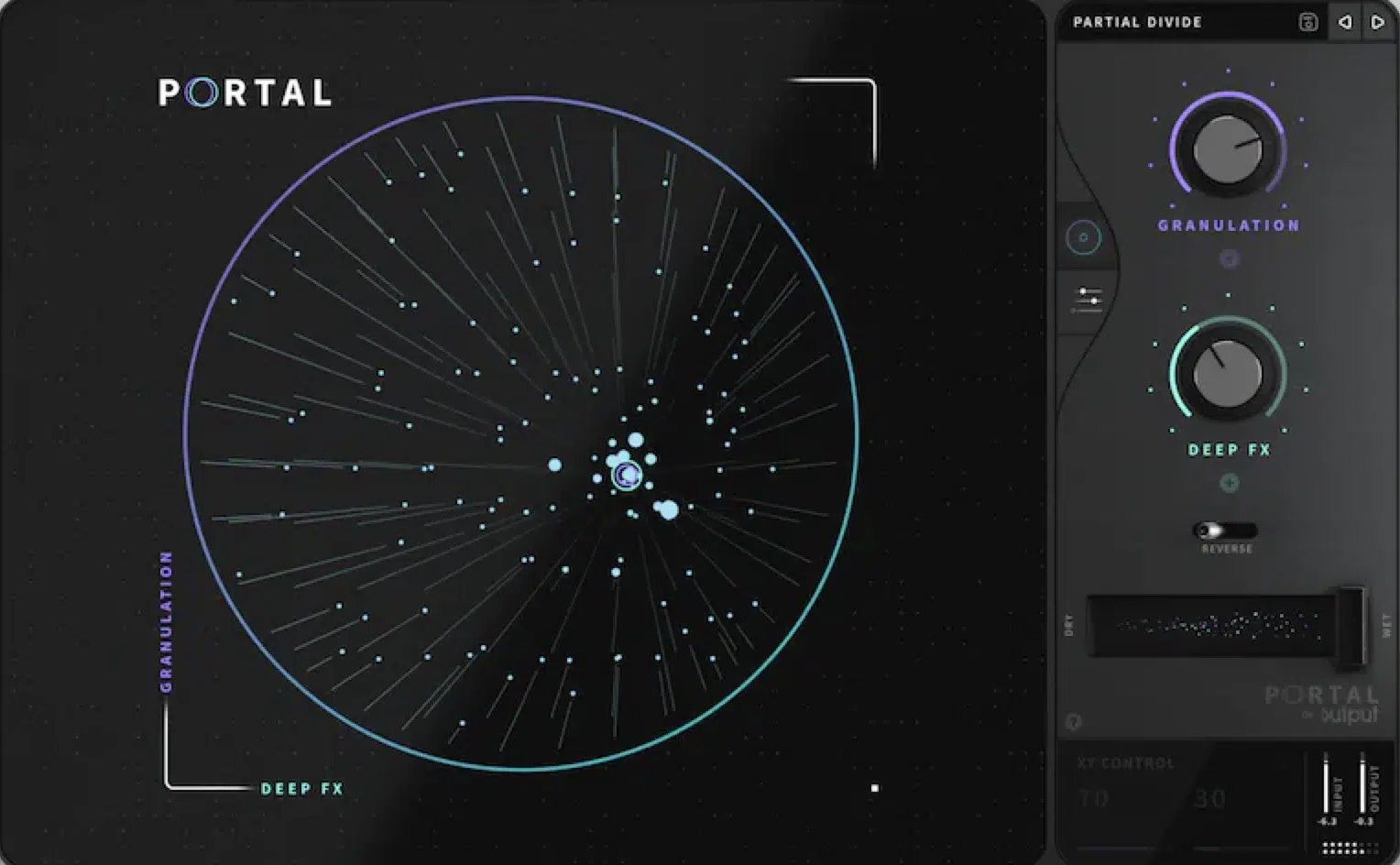
Output Portal is a granular processor that can transform any input sound into a completely new texture.
With its intuitive interface and advanced modulation options, Portal offers a wide range of granular synthesis possibilities.
Including subtle time-stretching and pitch-shifting to extreme glitchy transformations.
Its built-in effects engine and Randomization features make it a versatile tool for creative sound design and experimentation.
-
Arturia’s EFX Fracture
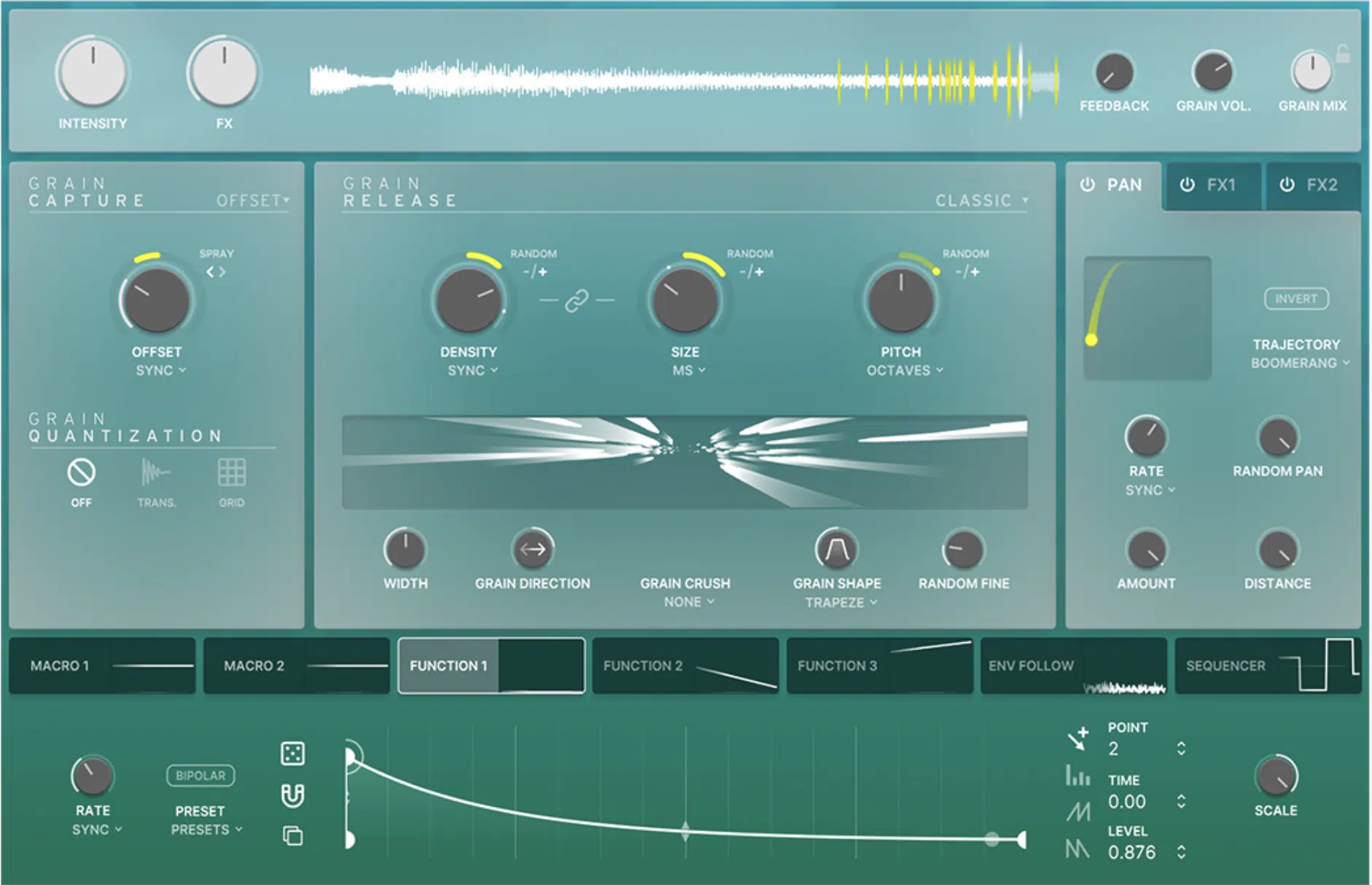
EFX Fracture focuses on creating interesting and complicated textures from a variety of source materials.
With its advanced modulation options and comprehensive effects section, EFX Fracture enables you to manipulate grains in various ways, resulting in intricate soundscapes and evolving pads.
Its versatile MOD matrix and preset system make it a powerful tool for those looking to dive deep into granular synthesis.
Speaking of presets, if you’d like the dopest free presets in the game, check out the Unison YouTube Tutorial Presets… you won’t regret it.
-
Reason’s Grain
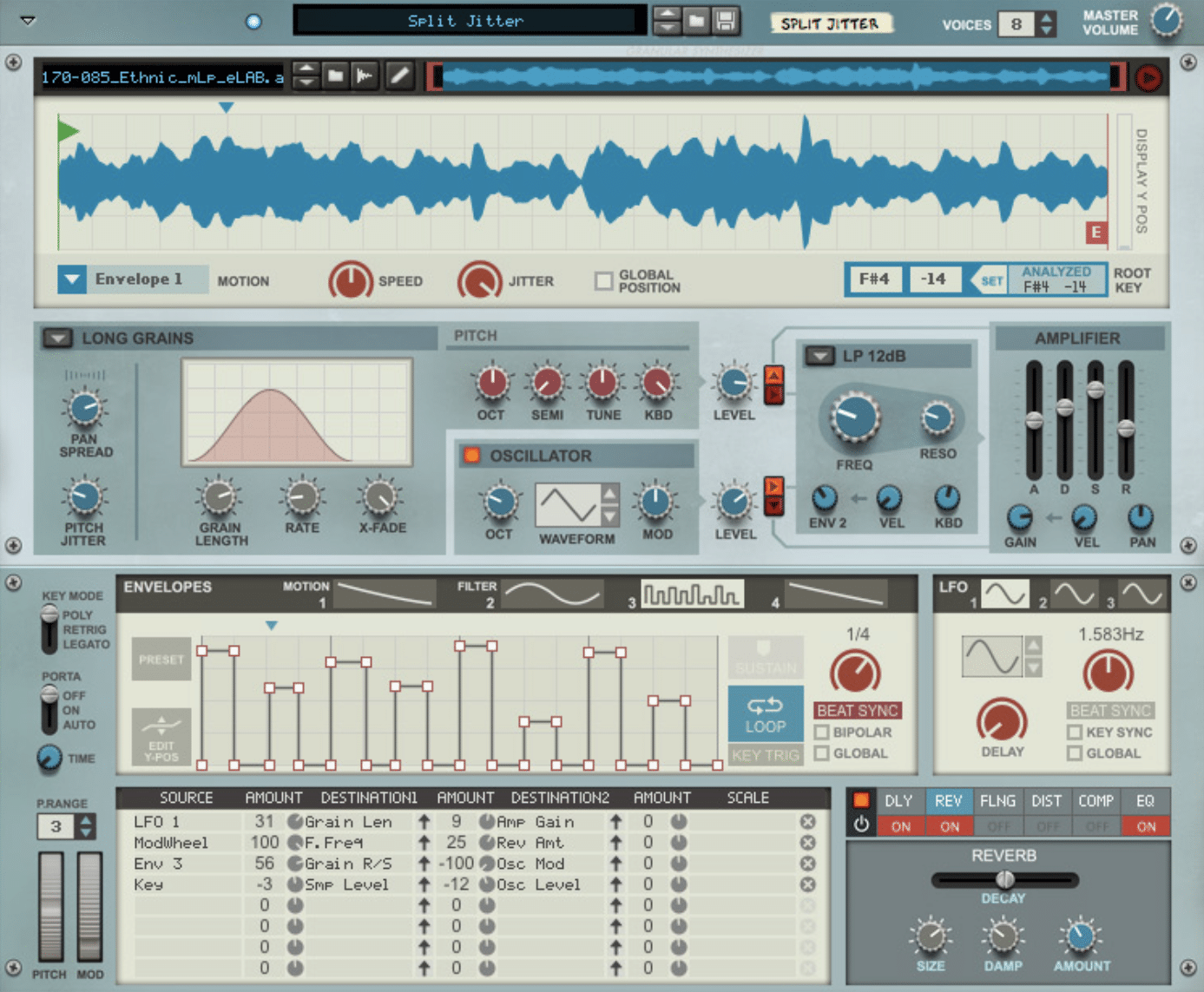
A powerful granular synth included in the Reason music production software.
Grain allows you to load samples and manipulate them using GS techniques, resulting in a wide range of textures & timbres.
It offers many flexible modulation options, built-in effects, and comprehensive parameter controls.
Grain is an excellent tool for creating soundscapes, rhythmic textures, and sound effects, so keep it in your memory bank.
-
Logic’s Alchemy
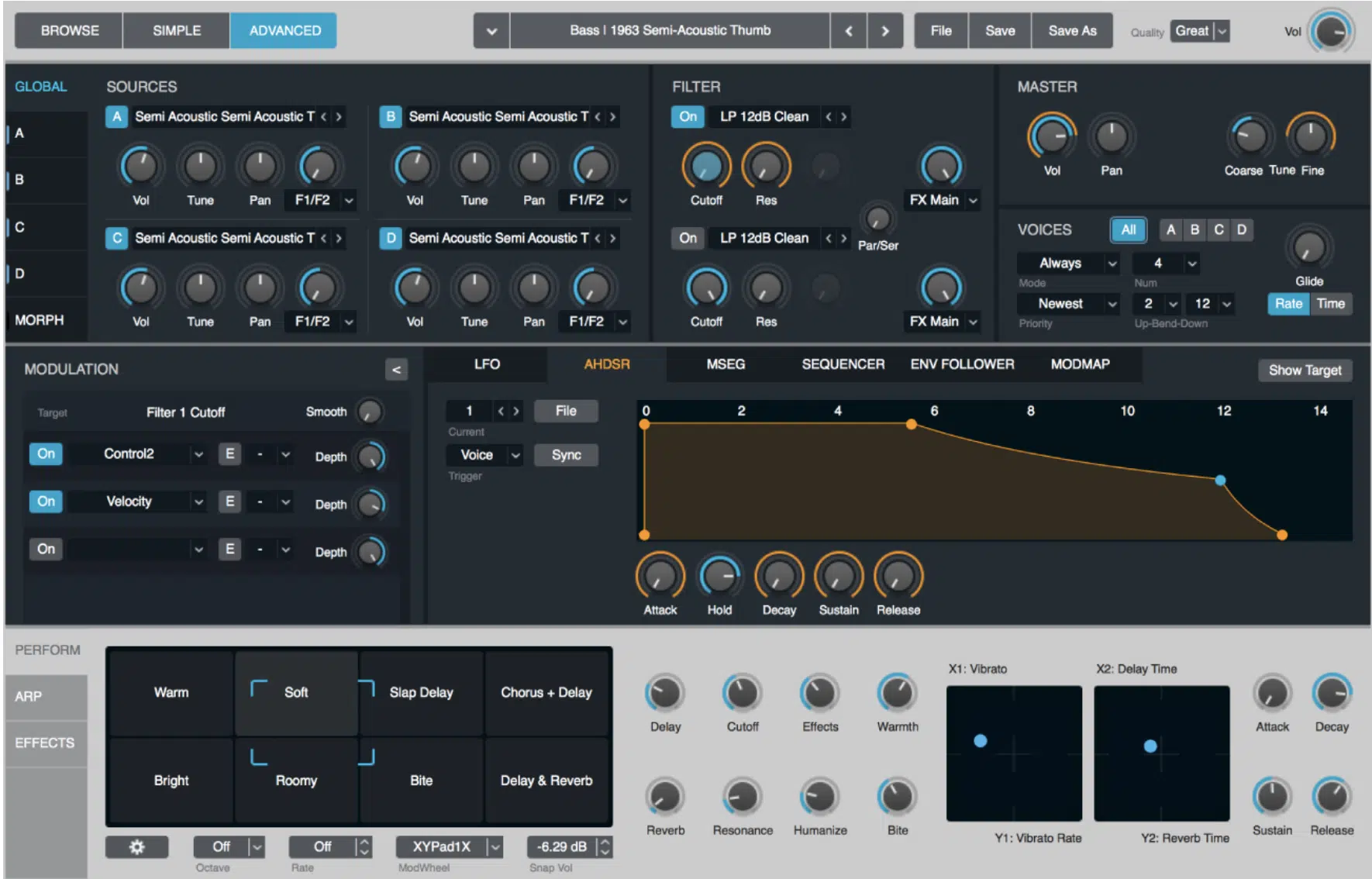
Alchemy, included in Apple’s Logic Pro X, is a powerful and versatile synthesizer that features a granular synthesis engine alongside other synthesis methods.
With its advanced modulation options, integrated effects, and comprehensive sample library, Alchemy offers an extensive range of GS possibilities.
For any and all granular synthesis processes and techniques, Alchemy’s granular engine can help you achieve your sonic goals.
NOTE: When choosing a granular synthesizer or granular processor, it’s important to consider the available granular mode and grain control options.
Some plugins or hardware devices may offer more advanced features, such as multiple granular modes or extensive grain parameter controls.
Others may provide a simpler, more straightforward approach to this type of synthesis.
Consider your needs and skill level when selecting the right granular synthesizer for your projects.
Bonus: Make Noise Morphagene (Hardware)
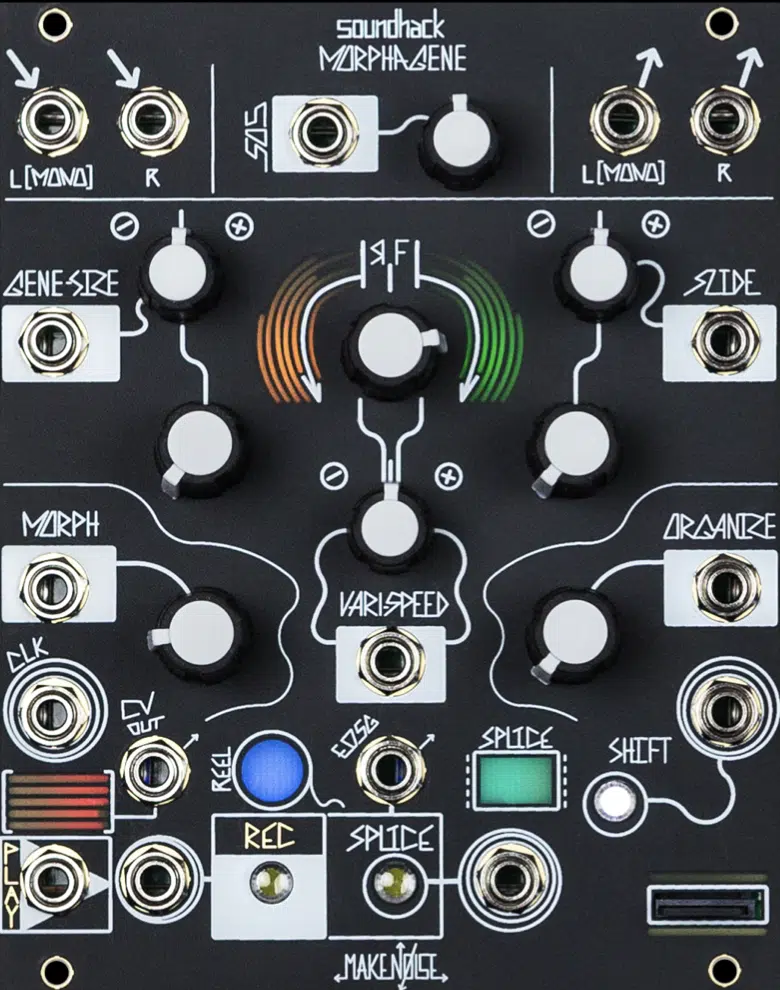

The Make Noise Morphagene is a Eurorack-format granular sampler and processor module that allows you to manipulate an audio clip using GS techniques in a hardware environment (with the same principle as digital replications).
With its hands-on interface and extensive CV control options, the Morphagene is perfect for live performance and experimentation.
It offers a truly unique approach to GS outside of the digital realm.
Unconventional Granular Synthesis Methods
As producers and sound designers, it’s important that you play around with more unconventional methods, especially when it comes to granular synthesis.
Manipulating Drum Hits
Granular synthesis can be applied to drum hits to create unique percussion sounds and rhythms.
For example, you could load a snare drum sample into a granular synthesizer and manipulate the grain parameters to create a new, glitchy snare sound.
Or, something completely different, such as taking a non-harmonious snare and transforming it into something with a lot of melodic character.
Experiment with different grain settings and layering techniques to generate unconventional drum sounds that can add character and interest to your rhythm tracks.
Granular Effects on Stereo Field
Applying GS to the stereo field can create captivating spatial effects that enhance the depth and width of your sound.
By using GS techniques to manipulate the pan position and stereo spread of individual grains, you can create immersive soundscapes that envelop the listener.
Experiment with stereo field manipulation in your GS patches to add an extra dimension to your sound design.
This is particularly popular within electronic music and some hip-hop subgenres.
Practical Applications
Granular synthesis is a popular technique in ambient music production, as it can create lush soundscapes that are perfect for setting a mood or atmosphere.
By manipulating grain parameters such as pitch, length, and density, you can generate textures that range from soothing and calming to eerie and unsettling.
Experiment with different GS techniques to create unique ambient soundscapes for your projects.
GS is also widely used in experimental music, where the goal is often to push the boundaries of conventional sound and create something entirely new.
By using GS to manipulate and transform a variety of sound sources, you can generate mystical textures and timbres that challenge the listener’s expectations.
It’s important to create atmospheres and generate unique sound effects when it comes to making waves with GS, and here is how:
-
Creating Atmospheres
Granular synthesis is a powerful tool for creating atmospheric sounds in film scoring and audio design projects.
By manipulating grains from various source materials, such as field recordings, foley sounds, or musical instruments, you can generate rich, immersive ambiances that evoke specific emotions/environments.
Use GS techniques to craft evocative atmospheres that enhance the narrative and emotional impact of your film or game projects.
-
Generating Memorable Sound Effects
In addition to atmospheric sound design, GS can be used to create unique sound effects for film, television, and video games.
By manipulating grains from a variety of source materials, you can generate sounds that are entirely new and unique, perfect for enhancing on-screen action or adding depth to your audiovisual endeavors.
Incorporate with different grain parameters and layering techniques to create unique sound effects that bring your projects to life.
Final Thoughts
It’s clear that granular synthesis has limitless potential for creating captivating sonic textures and unique audio experiences…
So, go put in that granular synthesis work in order to enhance your skills!
As we mentioned, one-shots of synths or melodic instruments, even loops are perfect for granular synthesis.
Our FREE Unison One-Shot Essentials pack is an absolutely ideal place to start.
It contains professionally-crafted one-shots of all different kinds (all of them mind-blowing).
Simply throw one in and assign the internal tuning, as each one is labeled with the correct note/octave.
Explore the endless possibilities from subtly altering timbre and tonal qualities, to morphing and warping it in extreme ways.
This will provide you with epic results that are crazy different from the original source material (amazing, right?).
With the knowledge and tools you’ve gained from this guide, you’re now ready to embark on your own granular synthesis journey.
You won’t even have to use additional sources like a computer music tutorial, simply save this article for later.
Until next time…







Leave a Reply
You must belogged in to post a comment.