WAV and MP3 files are two of the most common audio formats in digital audio production.
They’re the key to understanding the balance between audio quality and file size.
So, as a music producer, you’ll need to understand the differences and applications of MP3 vs WAV files in order to choose the right one every time.
That’s why, in today’s article, we’re breaking down:
- MP3 vs WAV files: the big difference ✓
- Compression and uncompressed audio ✓
- Sound quality and audio quality ✓
- File size and storage implications ✓
- Different audio file formats ✓
- Advantages & disadvantages of WAV files and MP3 files ✓
- When to use each one (music production tips) ✓
- Digital audio editing and processing considerations ✓
- Streaming and distribution preferences ✓
- Everything you’ll need to know about MP3 vs WAV files ✓
After this article, you’ll know everything about WAV and MP3 files.
This way, you’ll be able to choose the right audio format for any situation and produce high-quality music like a true professional.
So, let’s dive in…
Table of Contents
MP3 vs WAV Files: Breaking it Down
MP3 and WAV files are two of the most widely used audio formats in digital music production. Understanding all the differences between them is how you’ll make the right choice for different projects.
MP3 Files
MP3 files, also known as MPEG Audio Layer III, are a popular format for compressed audio files.
These files are created using a lossy compression algorithm…
This significantly reduces the file size by eliminating certain parts of the audio data that are less audible to the human ear.
They’re ideal for use in streaming services and portable music players, where smaller file sizes and ease of distribution are everything.
For example, a typical song in MP3 format might be around 3-5 MB in size, compared to 30-50 MB for the same song in WAV format.
One of the main advantages of MP3 files is their widespread compatibility.
Almost all digital devices and audio-editing software support MP3 files so, needless to say, they’re incredibly versatile.
This universal compatibility, combined with their reduced file size, makes MP3 files a convenient choice for different musical situations.
-
Pro Tip

The lossy compression used in MP3 files can result in a noticeable loss of audio quality, especially at lower bitrates.
This trade-off between file size and sound quality is a key consideration when choosing between an MP3 file and WAV file.
WAV Files
WAV files (Waveform Audio File Format files) are uncompressed audio files that preserve the original sound quality of the recording.
Unlike MP3 files, WAV files do not use lossy compression, meaning they retain all the audio data and deliver high-fidelity sound.
For instance, a song in WAV format will capture every single detail of the original recording, which makes it perfect when sound quality is paramount.
The primary downside of a WAV file types is its obnoxiously large file size… because it is an uncompressed audio file, it takes up a crazy amount of storage space.
For example, a five-minute song in WAV format can easily be over 50 MB, which can quickly add up if you are dealing with a large library of audio files.
-
Pro Tip
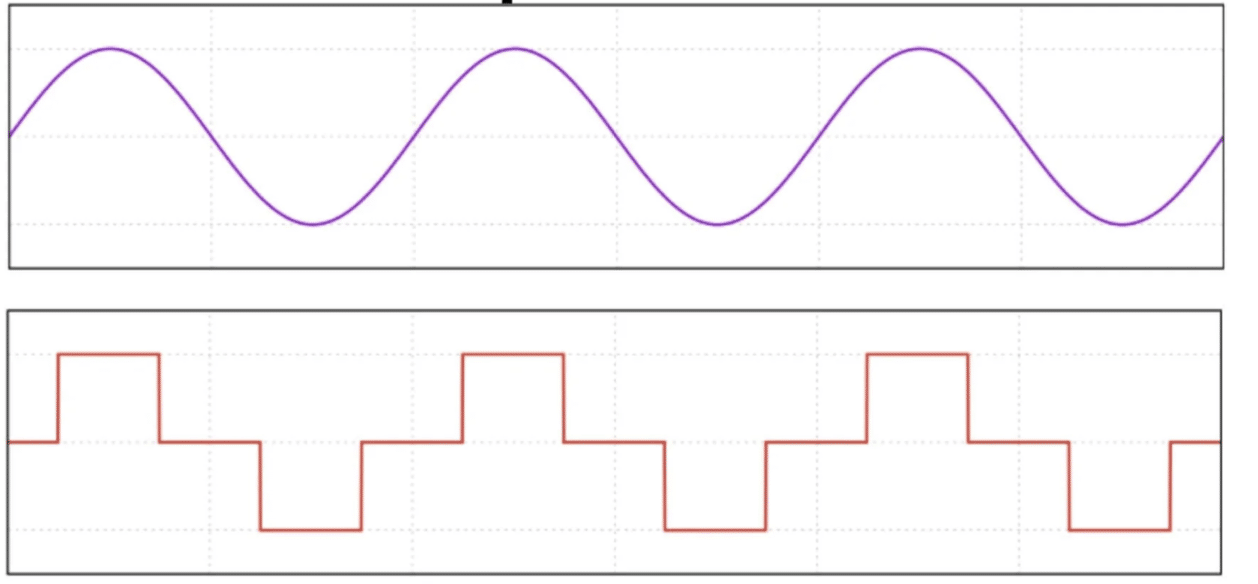
You’re going to hear the phrases “lossless formats” and “lossy formats” all the time when talking about MP3 vs WAV files.
Lossless formats are simply an audio file type that retains all the original data from the recording (no loss in sound quality).
Lossy formats are audio files that use compression to reduce file size, which results in a loss of some audio data and potentially affects the overall sound quality.
As long as you remember that, you’ll be fine.
Key Differences Between WAV and MP3
Understanding the key differences between WAV and MP3 files will help you in choosing the right audio file format for any scenario. So, let’s dive in, starting with compression and uncompressed audio files (MP3 vs WAV).
-
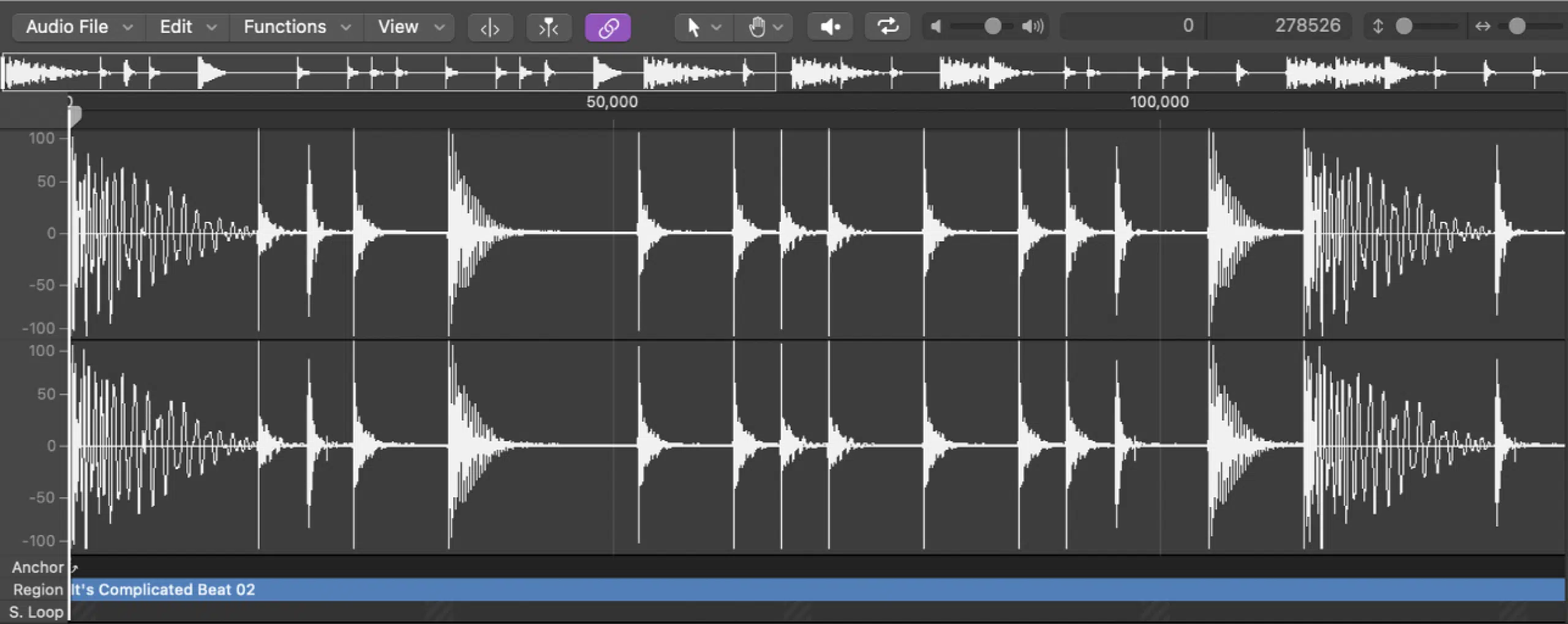
Compression and Uncompressed Audio Files (MP3 vs WAV)
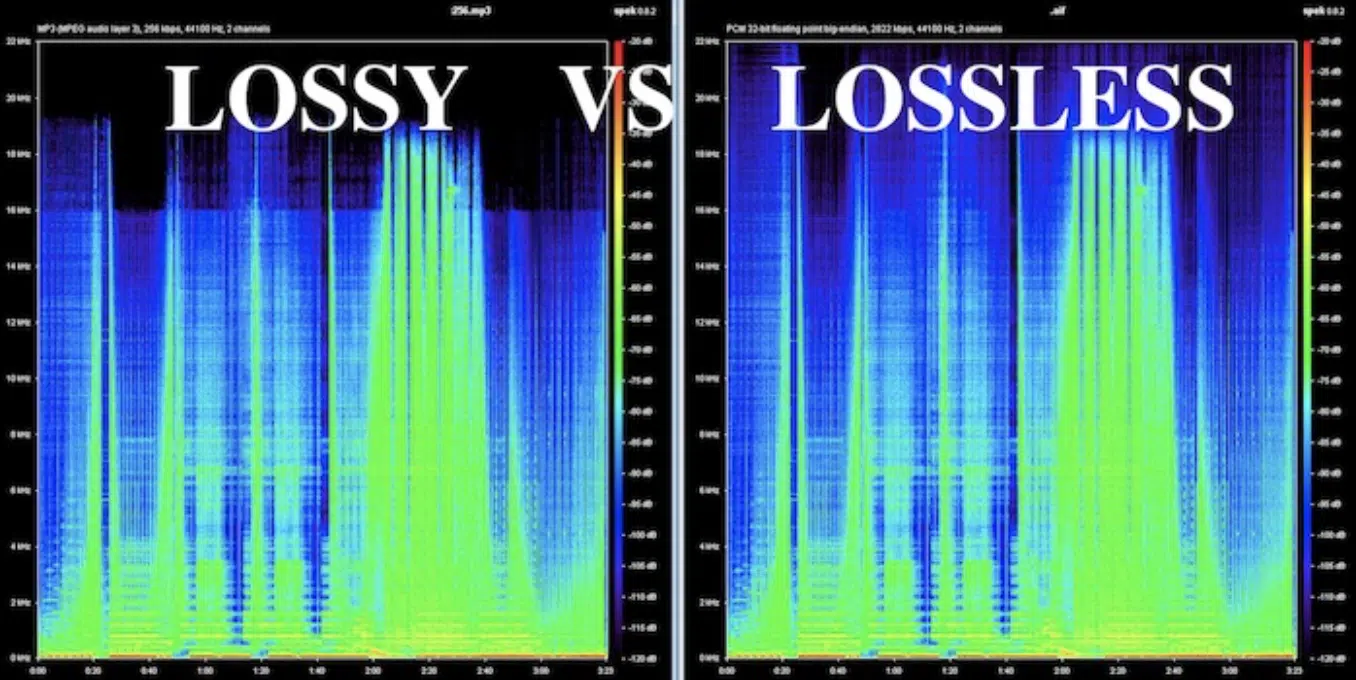
Uncompressed WAV (top); Lossy MP3 (bottom)
MP3 files use a lossy compression algorithm to reduce file size.
This process involves removing parts of the audio data that are deemed ‘less important,’ to get smaller files.
For example, an MP3 file might compress a song to one-tenth of its original size 一 making it easier to store and share.
However, this compression can introduce artifacts and reduce the overall sound quality (particularly at lower bitrates).
On the flip side, a WAV file is uncompressed, so it retains all the original audio data.
This uncompressed nature ensures that your WAV file will deliver the highest possible sound quality; capturing every single nuance of the original audio/recording.
Let’s say you’re in the studio working on your final mixdown on professional sound systems…
You’re going to want to use a WAV file because it ensures the highest audio quality.
Totally free from the compression artifacts that can destroy MP3 files.
-
Sound Quality and Audio Quality (MP3 vs WAV)
When it comes to better sound quality, WAV files have a clear advantage over MP3 files.
A WAV file is an uncompressed audio file, so right off rip it offers superior audio quality because it captures the entire range of frequencies present in the original audio.
This makes them ideal for mixing and mastering because preserving the highest possible sound quality is essential.
For example, audio engineers use WAV files all day so the final product is as close to the original recording as possible.
MP3 files, on the other hand, use lossy compression to reduce file size, which can impact sound quality.
At lower bitrates, MP3 files may exhibit noticeable compression artifacts, such as a “swishing” sound or a loss of high-frequency detail.
However, at higher bitrates, such as 320 kbps, MP3 files can still deliver good sound quality that is acceptable for most casual listening purposes.
For instance, many streaming services use high-bitrate MP3 files to balance sound quality and file size.
Pro Tip

Despite the noticeable difference, MP3 files can still be good for situations where ultimate sound quality is not the primary concern.
For example, when distributing music online or sharing audio files with collaborators, the smaller file size of MP3 files can be a huge advantage.
However, for critical listening and professional audio production, the WAV file remains the preferred choice due to its superior audio quality and lack of compression artifacts.
-
File Size and Storage (MP3 vs WAV)
The difference in file size between MP3 and WAV files is one of the most significant factors to consider, for obvious reasons.
MP3 files are much smaller due to their lossy compression, which makes them easier to store and transfer.
For example:
- A typical MP3 file might be around 3-5 MB for a three-minute song
- The same song in WAV format could be 30-50 MB
This reduced file size makes MP3 files ideal for streaming services, use in portable devices, etc., where storage space and bandwidth are limited.
On the other hand, a WAV file is much larger because they are uncompressed.
This larger file size can be a drawback when dealing with limited storage space or when needing to transfer audio files quickly.
Still, for professional audio production, the superior WAV quality often outweighs the inconvenience of their larger size.
Like we covered, the use of WAV files ensures that every detail of the original recording is preserved 一 providing the best possible starting point for mixing and mastering.
NOTE: The larger file size can also make it more challenging to share WAV files over the internet or through cloud storage services.
When to Use WAV vs MP3 Files

Choosing between WAV and MP3 file formats depends largely on the specific requirements of your music production project.
WAV file types (the Waveform Audio File Format) are the preferred choice and industry standard when it comes to professional:
- Recording
- Mixing
- Mastering
Again, this is because it is an uncompressed audio file format which you should just remember equals better quality.
For example, if you are recording a high-quality vocal track or a live band performance, you’re going to want to use a WAV file so every detail of the original audio is captured without any loss of audio data.
This is key when working in a studio environment where sound fidelity is number one.
Not saying it’s not always important, but you get what I mean.
On the other hand, MP3 files are more suitable for situations where storage space and ease of distribution are more important than perfect audio quality.
For instance, if you are preparing a mix for a streaming service or creating a podcast, the smaller file size of MP3 files makes them ideal for quick uploads and efficient storage.
Despite the potential quality loss, high-bitrate MP3 files (such as 320 kbps) can still provide a listening experience that most audiences generally accept.
This balance makes MP3 files a versatile option for many everyday music production tasks.
Digital Audio Editing and Processing
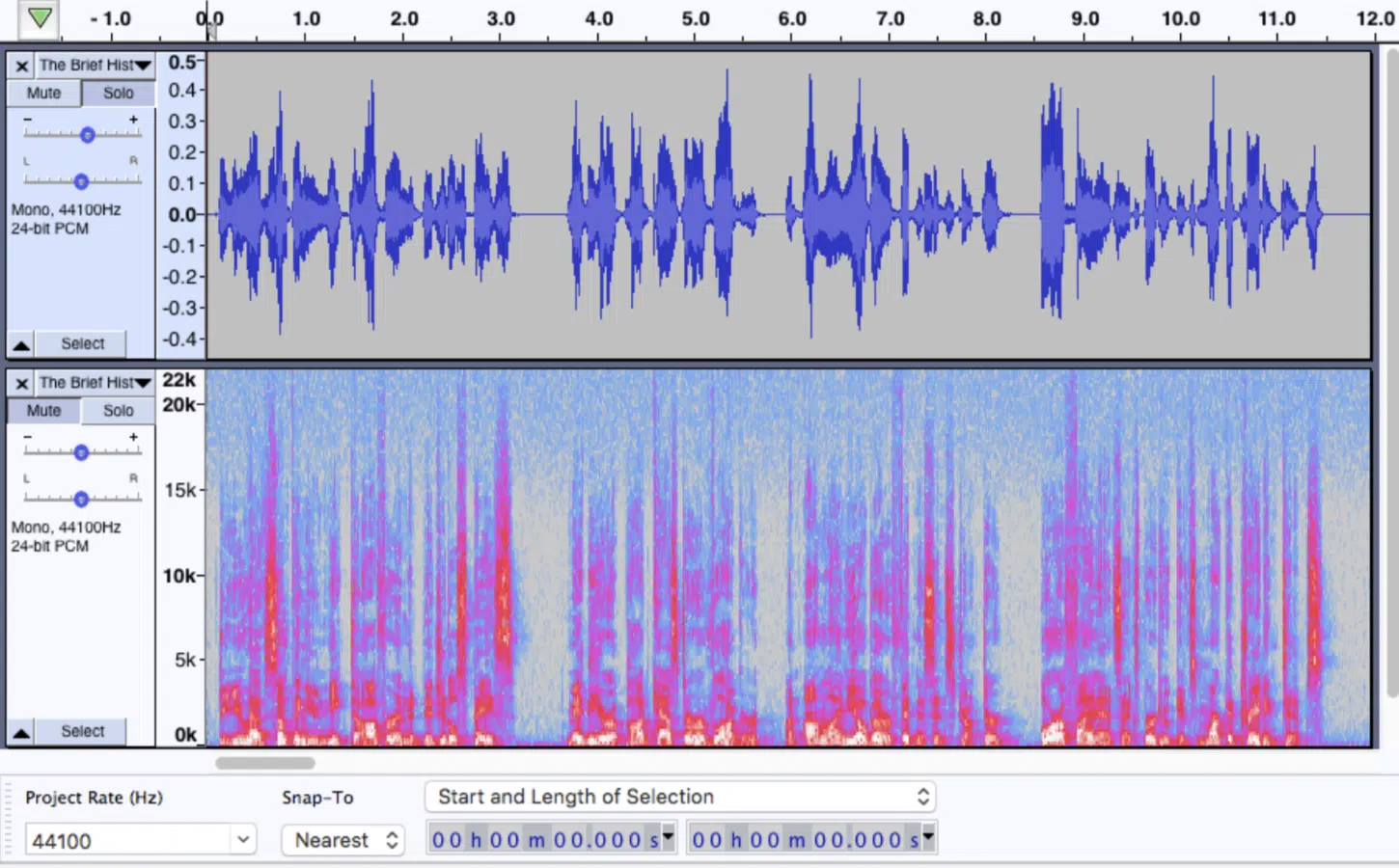
When it comes to digital audio editing and processing, the choice between WAV and MP3 files can significantly impact the outcome of your project.
A WAV file, being uncompressed, provides a grreat starting point for editing and processing.
This means that any modifications, such as EQ, compression, or reverb, will be applied to the full-quality audio signal 一 resulting in a higher-fidelity final product
For example, if you are editing a complex multi-track session, using a WAV file ensures that every track maintains its original audio quality throughout the editing process.
On the other hand, editing MP3 files can introduce additional artifacts and degrade audio quality further due to their lossy compression.
Every time an MP3 file is edited and re-saved, it undergoes another round of compression, which can exacerbate the loss of raw audio data.
So, while MP3 files are convenient for storage and sharing, they’re not ideal for intensive editing and processing.
In a nutshell, when it comes to WAV and MP3, it is recommended to use a WAV file/WAV formats for all audio editing and processing tasks, saving MP3 files for final distribution once the editing is complete.
Streaming and Distribution: MP3 or WAV?

The choice between WAV and MP3 files is, of course, super important when it comes to streaming and digital audio distribution.
For streaming services, MP3 files are the preferred audio format due to their small file size and efficient streaming capabilities.
Services like Spotify, Apple Music, and SoundCloud use MP3 (or any similar compressed file format) to deliver music to listeners quickly and efficiently.
For example, a streaming service can store and stream thousands of songs using MP3 files 一 ensuring that users experience minimal buffering and fast load times.
However, for professional distribution, such as releasing a debut album or single, WAV files are often preferred.
Distributing music in WAV format ensures your listeners receive the highest possible audio quality, free from the artifacts and degradation associated with lossy compression.
Which is, of course, what you always want.
For instance, many online music stores and high-fidelity streaming services, such as TIDAL and Qobuz, offer tracks in WAV (or another lossless format).
This is for my fellow audiophiles and serious music enthusiasts who demand the best sound quality.
Advantages & Disadvantages of MP3 vs WAV Files (Recap)
So, now that you have a solid understanding of MP3 files and WAV files, let’s just quickly recap, so you easily get the full picture.
-
Advantages of WAV Files

The Waveform Audio File Format (WAV) is the industry standard for storing uncompressed audio data.
A WAV file uses the encoding method linear pulse code modulation (LPCM) to encode the audio signal.
The primary advantage of WAV files is their unmatched audio quality.
Because they are uncompressed, WAV files retain all the original audio data 一 making them ideal for professional audio production.
For instance, when recording a live performance, using WAV files makes sure that every detail of the sound is captured.
It provides a high-fidelity recording that can be further processed and mixed without any loss of quality (which is super important).
-
Disadvantages of WAV Files

The main disadvantage of WAV files is their large file size, which is far from desirable.
This can be a major drawback when:
- Dealing with limited storage space
- You need to transfer audio files quickly
For example, a single hour of stereo audio recorded at 16-bit/44.1 kHz can take up more than 600 MB of storage space, which can quickly add up in a large project.
Additionally, the larger file size can make it more challenging to share WAV files over the internet or through cloud storage services.
-
Advantages of MP3 Files

MP3 files use the MPEG audio compression algorithm to reduce file size by removing raw audio data that is less perceptible to the human ear.
This process (lossy compression) results in much smaller files compared to uncompressed formats like WAV.
The main advantage of MP3 files is their small file size.
This makes them easy to store, transfer, and stream, which is why MP3 is the standard audio format for many online and portable audio applications.
Additionally, the widespread compatibility of MP3 files means they can be played on almost any digital device or audio-editing software 一 making them incredibly versatile.
For example, MP3 files are commonly used for podcast distribution, where small file sizes and easy sharing are essential.
-
Disadvantages of MP3 Files

The main disadvantage of MP3 files is the potential loss of audio quality due to lossy compression.
This can result in noticeable artifacts, especially at lower bitrates.
For instance, when comparing the same song in both MP3 and WAV formats, the MP3 version might lack some of the finer details and clarity of the WAV version.
This loss of quality is unacceptable in some musical situations, especially where sound fidelity can’t be compromised.
MP3 vs WAV Files: Final Thoughts
Understanding the differences between MP3 vs WAV files is key for any music producer.
MP3 vs WAV files each have their own strengths and weaknesses, and knowing when to use each format can greatly enhance your production quality.
MP3 files offer the convenience of smaller file sizes, making them perfect for streaming and distribution.
On the other hand, WAV files provide the highest sound quality, essential for professional recording, mixing, and mastering.
With this information, you can now make the right decisions for any project/task.
To take your skills to the next level and further understand music production as a whole, you’ve got to check out these legendary Free Project Files.
It contains 3 invaluable project files that break down exactly how professional tracks are made ─ from start to finish.
Plus, everything is 100% royalty- and copyright-free, so you can use them however you’d like and experiment with both MP3 and WAV files in your projects to see firsthand how they impact your work.
Just make sure to stay dedicated, always keep learning, and pumping out sick music.
Until next time…







Leave a Reply
You must belogged in to post a comment.