The term ‘studio engineer’ is thrown around quite a bit lately, but what does it really mean, and how can you become a professional studio engineer yourself?…
Well, it might seem like a mystical, inaccessible field only open to a select few.
However, that is far from the truth.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know about studio engineering.
From understanding the basics of sound engineering to launching a successful career in the music industry, we’ve got you covered.
In today’s article, we’ll be breaking down:
- Sound engineering tips, tricks, and techniques ✓
- The role of a studio engineer ✓
- Essential recording equipment ✓
- The recording process: from silence to masterpieces ✓
- The makings of a successful studio engineer ✓
- Education & career opportunities ✓
- Breaking into the music industry ✓
- A day in the life of a studio engineer ✓
- Crafting your unique sound ✓
By the end of this article, you’ll have all the knowledge needed to embark on an exciting new career as a studio engineer.
Or, simply fine-tune your technical skills for your own production benefits.
Whether you’re a musician looking to understand the recording process or an aspiring audio engineer ready to take that initial leap 一 this guide is designed to provide a clear path to success.
So, let’s dive in…
Table of Contents
- Understanding Sound Engineering
- What Exactly is a Studio Engineer?
- The Nitty-Gritty of Recording Engineering
- Sound Engineering: The Tools of the Trade
- The Recording Process: From Silence to Music
- The Makings of a Successful Studio Engineer
- Education & Career Path
- The Job Title Dilemma: Sound Engineer, Mixing Engineer, Audio Engineer & Recording Engineer
- The Responsibilities of Studio Engineers
- Pro Tip
- Studio Engineer: Final Thoughts
Understanding Sound Engineering

Audio engineers are responsible for adjusting, balancing, and enhancing the different sound sources in a recording.
They work their magic on sounds, both captured during a recording session or those created digitally.
Essentially, sound engineering ensures a seamless blend of harmony and rhythm.
Every beat you tap your foot to, every bass drop that gives you goosebumps, and every melody that lingers in your mind long after the song is over, that’s the craft of sound engineering.
This field merges the technical aspects of sound manipulation with creative input 一 transforming raw music into a polished audio track that captivates the audience’s ears.
But, let’s break it down a bit more…
You see, sound engineering is a broad term encompassing various sub-disciplines.
These include:
- Audio engineers
- Recording engineers
- Mix engineers
- Mastering engineers
- Others engineers
All of them play critical roles in the recording process, but each specializes in a different area of sound manipulation.
And today, we’ll be breaking them all down for you.
What Exactly is a Studio Engineer?

A studio engineer is like the conductor of an orchestra, overseeing all elements of the recording process.
From managing the recording equipment to adjusting the audio tracks and sound sources, their role is multifaceted and ever-evolving.
Studio engineers, though often behind the scenes, are vital to creating the music we all love.
They work closely with artists, producers, and other engineers 一 turning the artist’s vision into a sonic reality.
The studio engineer knows the ins and outs of the recording studio and can manipulate its equipment to produce the desired sound.
More than just a technical job, being an audio engineer requires creativity.
It’s all about understanding:
- The music itself
- The artist’s overall vision
- The audience’s expectations
Each decision an audio engineer makes (be it adjusting the volume or adding a sound effect) can drastically change how the audience hears the song.
The Nitty-Gritty of Recording Engineering

While the term “recording engineer” is often used interchangeably with “studio engineer,” there’s a subtle difference.
A recording engineer focuses primarily on the recording process itself.
They’re the ones dealing with the microphones and ensures the sound sources are adequately captured during recording sessions.
A recording engineer’s work can be as straightforward as setting up microphones in a live sound mixing session.
Or, as intricate as deciding the best recording techniques to capture the sound of different instruments.
They’re often deeply involved in the technical aspects of the recording process and work closely with the audio engineer to ensure the raw recordings are top-notch.
Sound Engineering: The Tools of the Trade
The artistry of an audio engineer lies not only in their skills but also in their tools.
So, let’s now discuss the equipment that helps transform sound into beautiful music.
-
Essential Recording Equipment
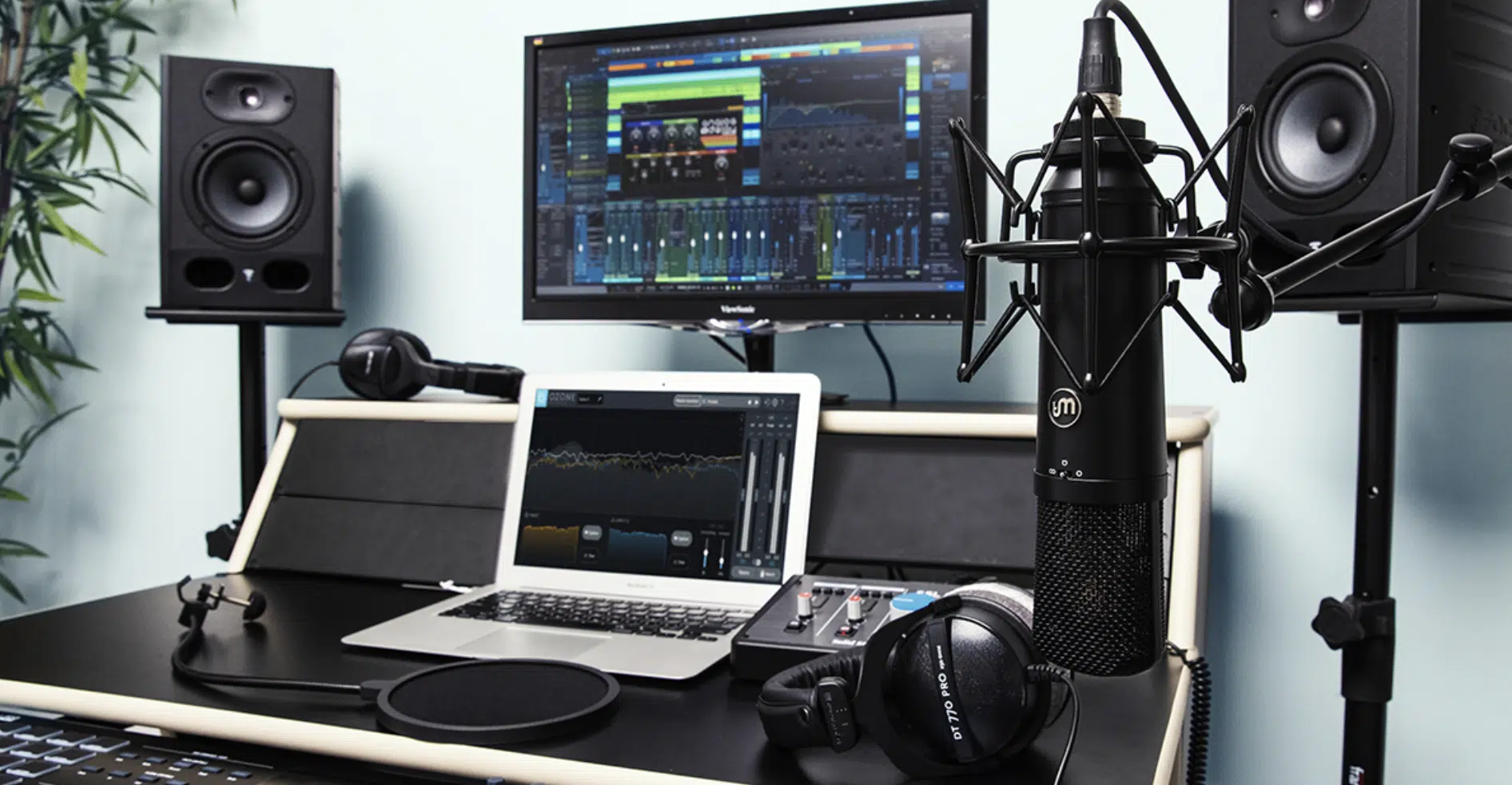

A studio engineer’s ability to do their job effectively is deeply intertwined with their understanding of the tools they use.
This includes both:
#1. The physical recording equipment: Microphones, mixing consoles, and audio interfaces.
#2. Software tools: Digital Audio Workstations (DAWs), plugins, and sound libraries.
Understanding how these tools work, how to use them efficiently, and how they affect the audio they are working with is an essential part of a studio engineer’s job.
If you’re setting up a home recording studio, there are a few key pieces of equipment you’ll need, such as:
- A reliable computer
- A quality audio interface
- The microphones themselves
- A pair of studio monitor speakers
- A good pair of closed-back headphones
All of this equipment is super crucial if you’re planning on becoming a studio engineer or enhancing your music production skills.
-
Making the Most of Your Home Studio
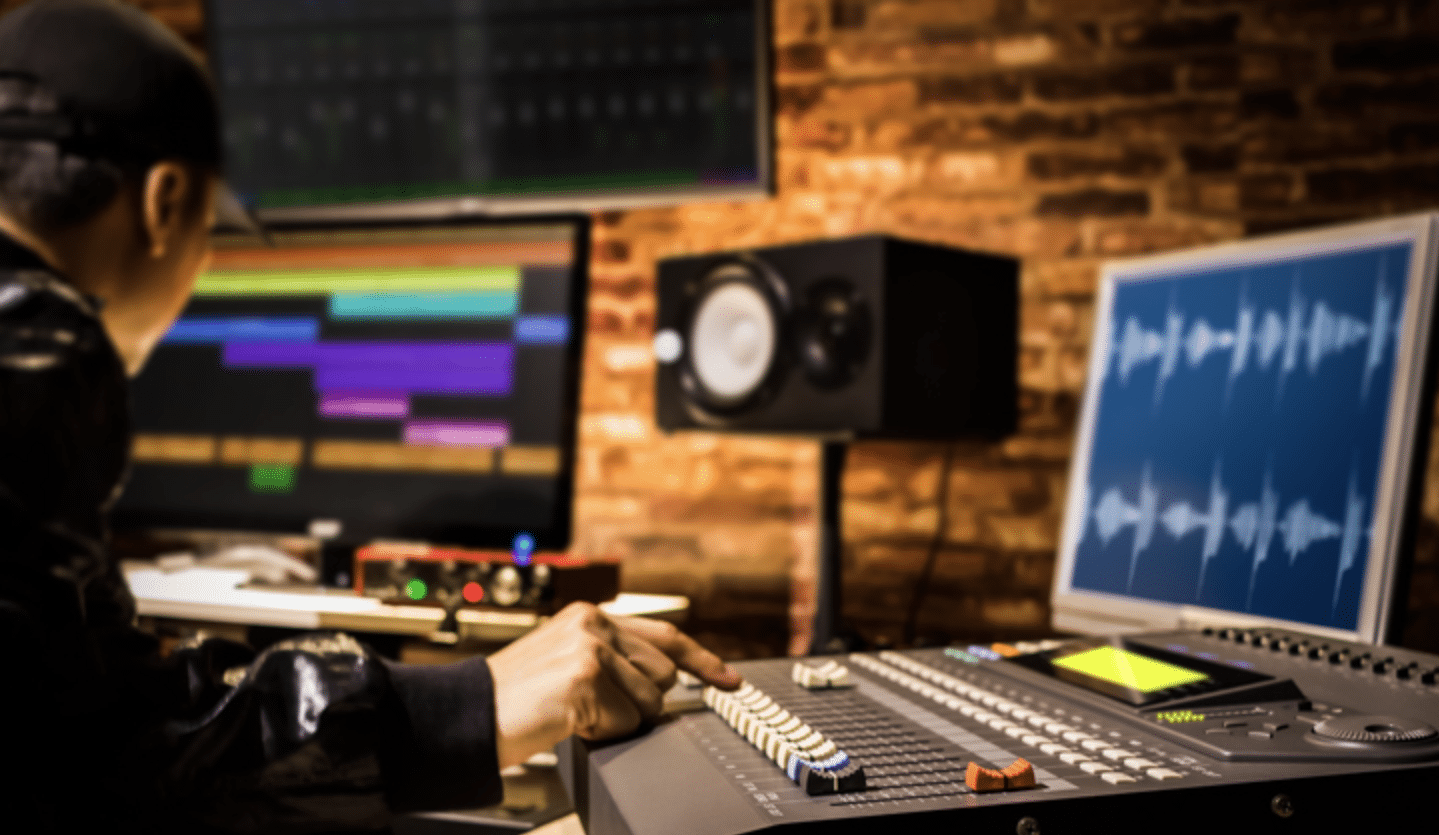

Optimizing your recording studio (or, home studio) goes beyond merely owning the equipment.
When learning how to become a studio engineer, there are certain things you’ll need to do to ensure your home studio is at its most optimal and functional layout.
This includes:
#1. Proper positioning of microphones, speakers, and the artist can greatly influence the sound quality.
#2. Consider soundproofing and acoustically treating your space to reduce noise and echo.
#3. Make use of your equipment’s full capabilities.
#4. Learn the difference between cardioid, omnidirectional, and bidirectional microphone patterns and when to use each.
#5. Make sure to familiarize yourself with your audio interface’s features, like preamps and phantom power.
Also, investing in quality cables can prevent signal loss and interference.
Make sure to organize your cables neatly, label everything, and ensure all gear is well maintained.
This not only keeps your studio looking super professional but can save you time troubleshooting later on.
-
Digital Audio Workstation (DAW): The Heart of Your Studio

The role of a Digital Audio Workstation (DAW) in the life of a studio engineer cannot be overstated.
This sophisticated software is essentially your main control panel.
It’s the digital platform where the magic of music production happens 一 from recording to editing and mixing.
Professional-grade DAWs like Pro Tools, Logic Pro, FL Studio, Reaper, and Ableton Live are packed with robust features that allow for intricate sound manipulation.
Understanding the ins and outs of your DAW, learning the plethora of options and tools at your disposal, is an ongoing process.
But, the more adept you become, the more you can bend it to your creative will.
Your DAW is not merely a tool, it’s an extension of your creative vision.
If you want to become a studio engineer, knowing how to work with it to its full potential will greatly enhance your proficiency as a studio engineer.
It’s essentially your canvas for creating and refining audio masterpieces.
The Recording Process: From Silence to Music
From silence to a symphony of sounds, let’s discover the step-by-step process of music recording.
-
Demystifying the Recording Sessions
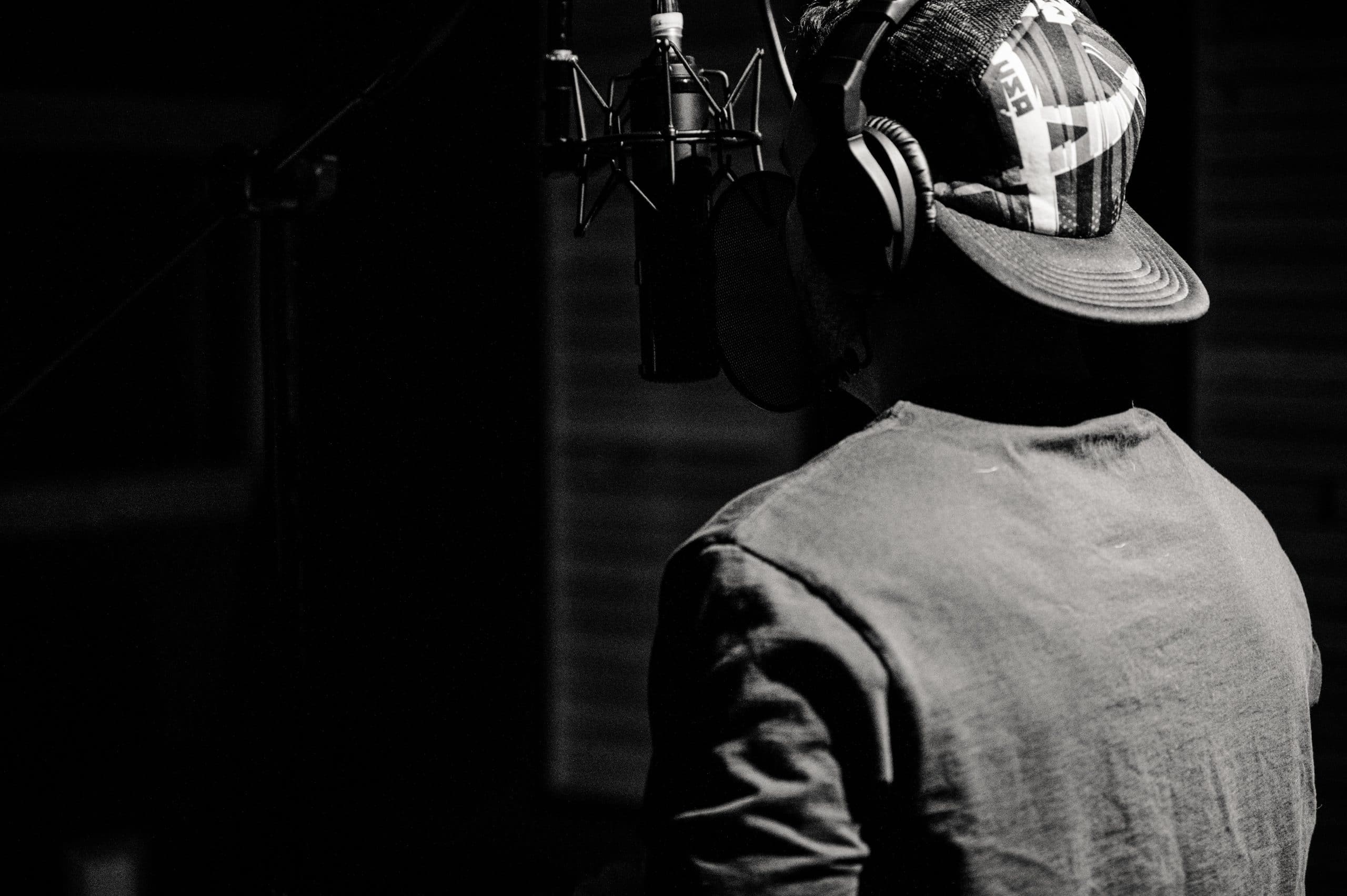

Recording sessions form the foundation of the music production process.
They are crucial periods where you, as a studio engineer, collaborate with musicians to create raw audio material.
This isn’t merely a case of hitting the record button.
It’s about understanding the process 一 from the technical setup to managing the energy in the room.
Each recording session is a unique challenge, requiring:
- Careful preparation
- Sound equipment knowledge
- Strong communication skills
It’s a balancing act between managing the technical details and ensuring a conducive creative environment for the artists.
Furthermore, the ability to adapt on-the-fly during recording sessions is a hallmark of a skilled studio engineer.
Technical hiccups, last-minute changes, or unforeseen circumstances often arise during these sessions.
The ability to navigate through these hurdles while maintaining a smooth recording process is key.
-
Working with Audio Tracks
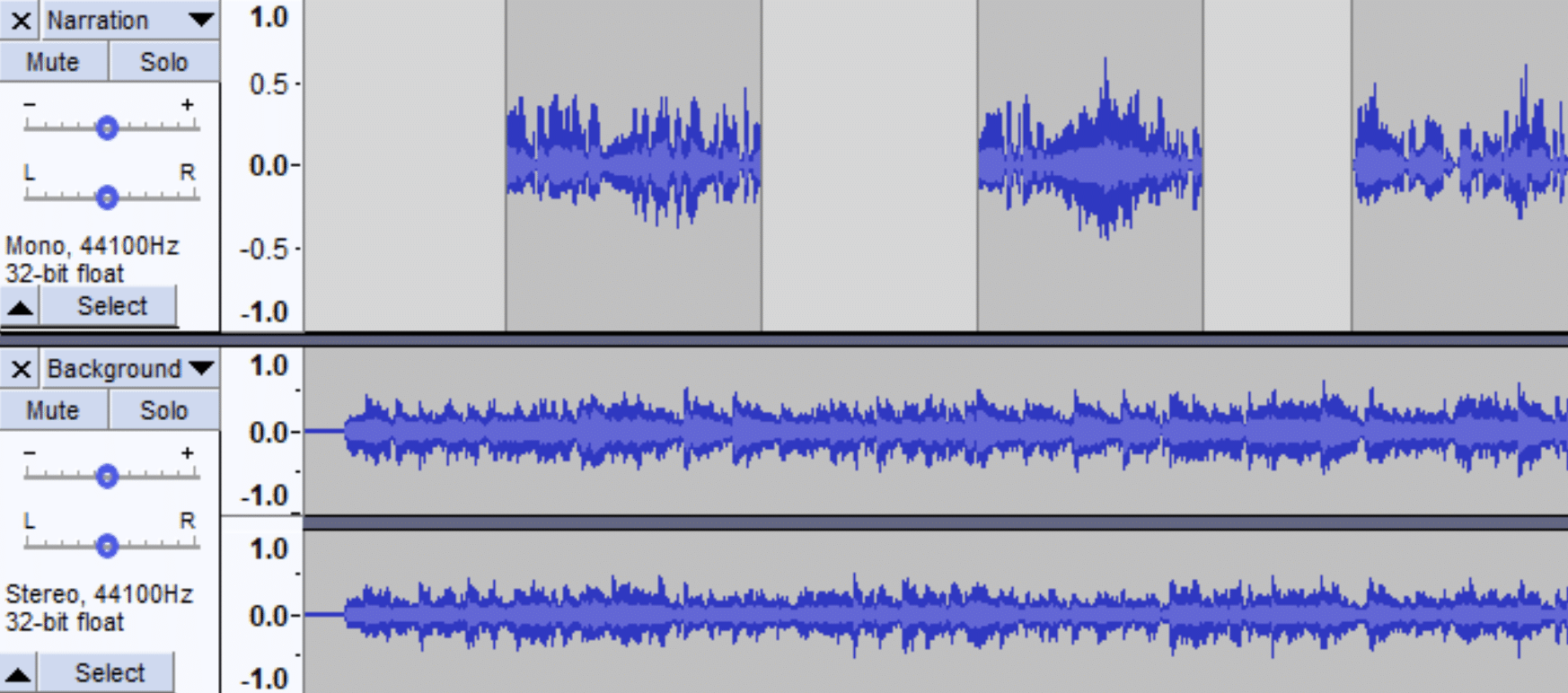
In essence, audio tracks are the building blocks of any music piece.
As a studio engineer, one of your primary tasks is layering and arranging these tracks to construct a cohesive and balanced sound landscape.
Mixing, however, is where your technical skillset dovetails with your artistic flair.
In this process, you:
- Balance levels
- Apply audio effects
- Pan sounds to sculpt a unique sonic image
More than just turning the volume up or down, mixing is about enhancing the emotive power of the music.
Furthermore, working with audio tracks involves careful listening and a deep understanding of how different sounds interact within the mix.
Knowing when to highlight a track or when to pull one back can be the difference between a good mix and a great mix.
-
The Art of Adjusting Sound Sources
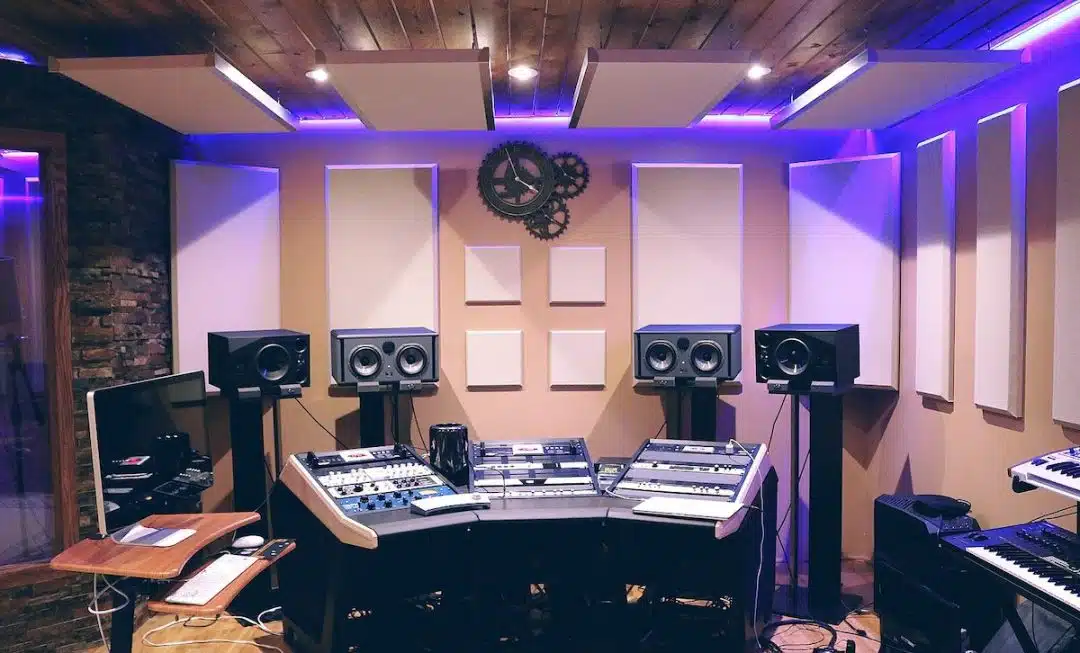

Adjusting sound sources forms a crucial part of sound engineering.
This entails making decisions on:
- The positioning of microphones
- The treatment of the recording room
- The type of microphone used to capture the audio
Sound sources aren’t confined to just instruments 一 they include vocals, ambient sounds, and electronic sounds as well.
Each source has its unique characteristics and understanding how to capture them at their best is a crucial skill in the studio engineer’s arsenal.
As an engineer, you will need to adjust and experiment constantly to achieve the best possible recording.
This could involve moving microphones, changing the environment, or altering the source itself.
Your ability to optimize sound sources will greatly impact the quality of your recordings.
The Makings of a Successful Studio Engineer
Not that you have a basic understanding of what studio engineering is, let’s break down the true makings of a successful studio engineer.
-
Technical Skill or Creative Input: What Matters More?

Being a successful studio engineer requires a blend of technical knowledge and creative input.
Having a firm understanding of the technical aspects of recording, mixing, and mastering is crucial.
However, it’s equally important to appreciate the creative process that goes into making music.
Every decision a studio engineer makes (from mic placement to mixing adjustments) impacts the final product.
While technical skills can guide these decisions, creativity is what allows an engineer to use these tools to enhance the artistic intent of the music.
Ultimately, the best engineers understand that technical skills and creative input are not mutually exclusive.
They’re two sides of the same coin.
Mastering both aspects can help an engineer bring a musical vision to life in the most effective and engaging way.
The audio engineering world is constantly evolving, with new technologies and software continually emerging.
Successful studio engineers are those who stay up-to-date with these advancements.
This might involve:
- Learning new DAW features
- Experimenting with cutting-edge plugins
- Exploring emerging audio formats like immersive audio
Embracing technology can open up new creative possibilities and streamline your workflow.
-
Ensuring the Best Overall Sound: Tips & Tricks

A good studio engineer strives for the best possible sound in all their productions.
But what makes a ‘good sound’ can be subjective and can vary greatly depending on the genre (like lo-fi or hip-hop), artist, and even individual tracks.
Therefore, an understanding of music and its many facets is as essential as mastering technical skills.
The tricks to achieving the best sound often lie in the details…
It can be as technical as understanding how to use EQ to clean up a mix or as intuitive as knowing when a performance, despite its flaws, captures the right emotion.
Continual learning, experimenting with new techniques, and keeping up with the latest technologies in audio engineering are also key to ensuring the best overall sound.
An open mind and an eagerness to try different things can often lead to surprising and satisfying results.
Education & Career Path
Becoming a studio engineer is a journey of constant learning and discovery.
In this section, we’re going to explore the steps on this rewarding and beneficial career path.
-
How to Become a Studio Engineer: Formal Training & Beyond

Aspiring to become a studio engineer involves more than just a love for music.
It requires a combination of:
- Formal education
- Practical experience
- A deep understanding of both the technical and creative aspects of music production
Many engineers start their journey with formal training in music technology or by acquiring an audio engineering degree.
This provides a solid theoretical foundation and introduces students to the technical skills required as an aspiring sound engineer.
However, beyond formal education, gaining hands-on experience is invaluable.
Whether through internships, apprenticeships, or volunteering in local sound recording studios, practical experience allows aspiring audio engineers to apply their knowledge.
As well as refine their skills in real-world scenarios.
-
Career Paths in the World of Studio Engineering

A career as a studio engineer can take many different forms.
Some audio engineers prefer working in recording studios, collaborating with different artists on various projects.
Others may choose to specialize in live sound, working at concerts and live events.
Some studio engineers find their niche in:
- Post-production
- Working on audio for film
- Television
- Video games
Here, the work can be quite different but requires the same foundational knowledge of sound and how to manipulate it.
Lastly, with the rise of home recording, some engineers choose to work independently 一 setting up their own studios and offering their services remotely.
This path provides more creative control and flexibility but requires a more entrepreneurial approach.
No matter the path chosen, the world of studio engineering offers a plethora of opportunities for those passionate about music and sound.
NOTE: The role of an assistant engineer is often a stepping stone for aspiring studio engineers.
This role offers invaluable hands-on experience and mentorship from a more experienced sound engineer.
Responsibilities may include setting up microphones, maintaining gear, and even running recording sessions under supervision.
It’s an opportunity to apply the skills learned in school (or a college course) to real-world situations.
As well as learning the less tangible aspects of the job, like studio manager responsibilities and juggling multiple sessions.
-
Advanced Apprenticeships & Other Learning Opportunities
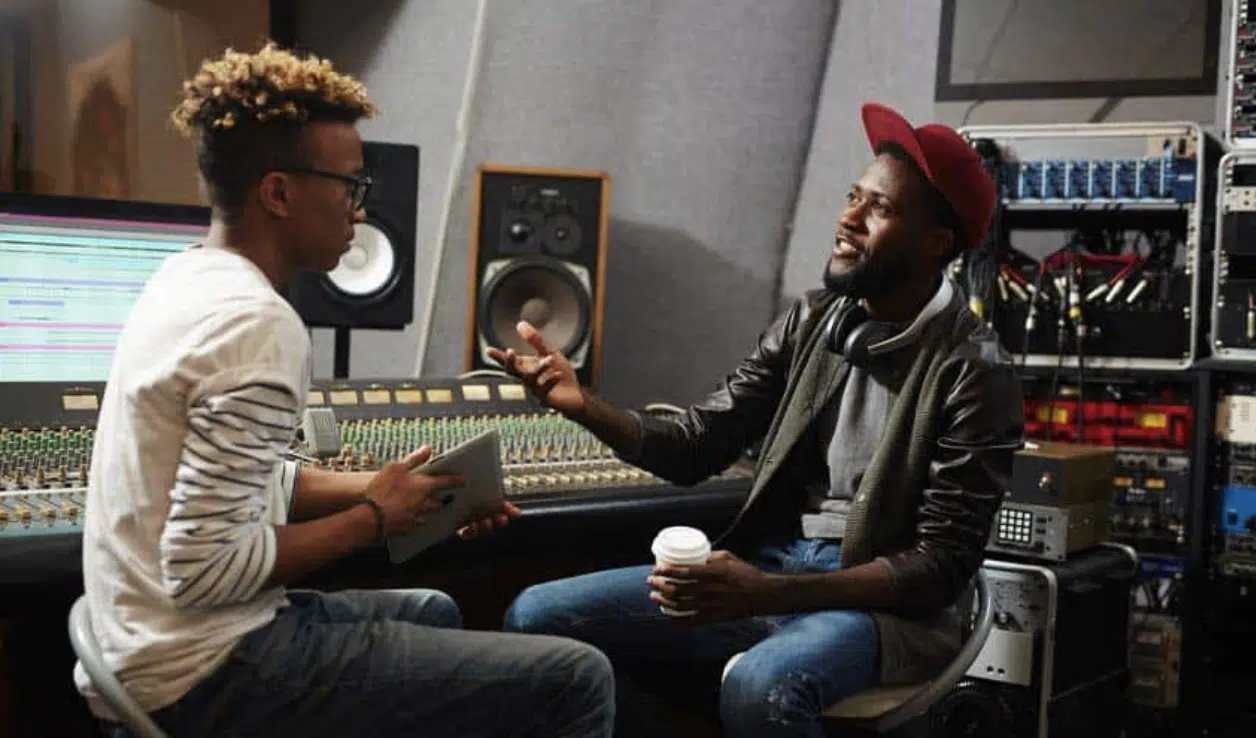

Aspiring studio engineers can further their skills through an advanced apprenticeship, working under a seasoned engineer or producer.
These offer the opportunity to:
- Observe and assist in professional sessions
- Gain insight into the industry
- Learn new technical skills
Additionally, workshops and masterclasses, often offered by equipment manufacturers or professional bodies, can provide deeper knowledge of specific topics.
Online resources, such as video tutorials, blogs, and forums, are also abundant.
They offer a wealth of knowledge for self-driven learners 一 covering everything from basic recording techniques to advanced mixing concepts.
NOTE: Attending community music industry events and networking is a valuable way for budding studio engineers to get their foot in the door.
These corporate events (or community music events) provide opportunities to meet industry professionals, learn from their experiences, and potentially open doors to job opportunities.
Networking can also lead to collaborations with local musicians or other engineers.
These experiences not only enhance your skill set but also help you break in to the audio engineering society.
The Job Title Dilemma: Sound Engineer, Mixing Engineer, Audio Engineer & Recording Engineer

In the music industry, job titles can be confusing.
Sound engineer, mix engineer, audio engineer, recording engineer… what’s the difference?
Generally, these terms are often used interchangeably, but there can be subtle differences in roles depending on the context.
- Sound engineers 一 Typically work in live sound settings.
- Recording engineers 一 Focus more on capturing sound in a studio environment.
- Audio engineers 一 A broad term encompassing both of these roles and more.
- Mixing engineers 一 A mixing engineer specializes in mixing tracks, balancing levels, and adding effects to create a polished final product.
In many cases, especially in smaller studios or home studios, the same person may fulfill multiple or all these roles.
Remember, these titles are less important than the skills and experience you bring to the table.
It’s your ability to capture, manipulate, and enhance sound that will set you apart in the music industry.
The Responsibilities of Studio Engineers
What does a typical day for a studio engineer look like? Well, let’s explore the unique responsibilities of this complex and exciting role.
-
Handling Volume and Recording Levels
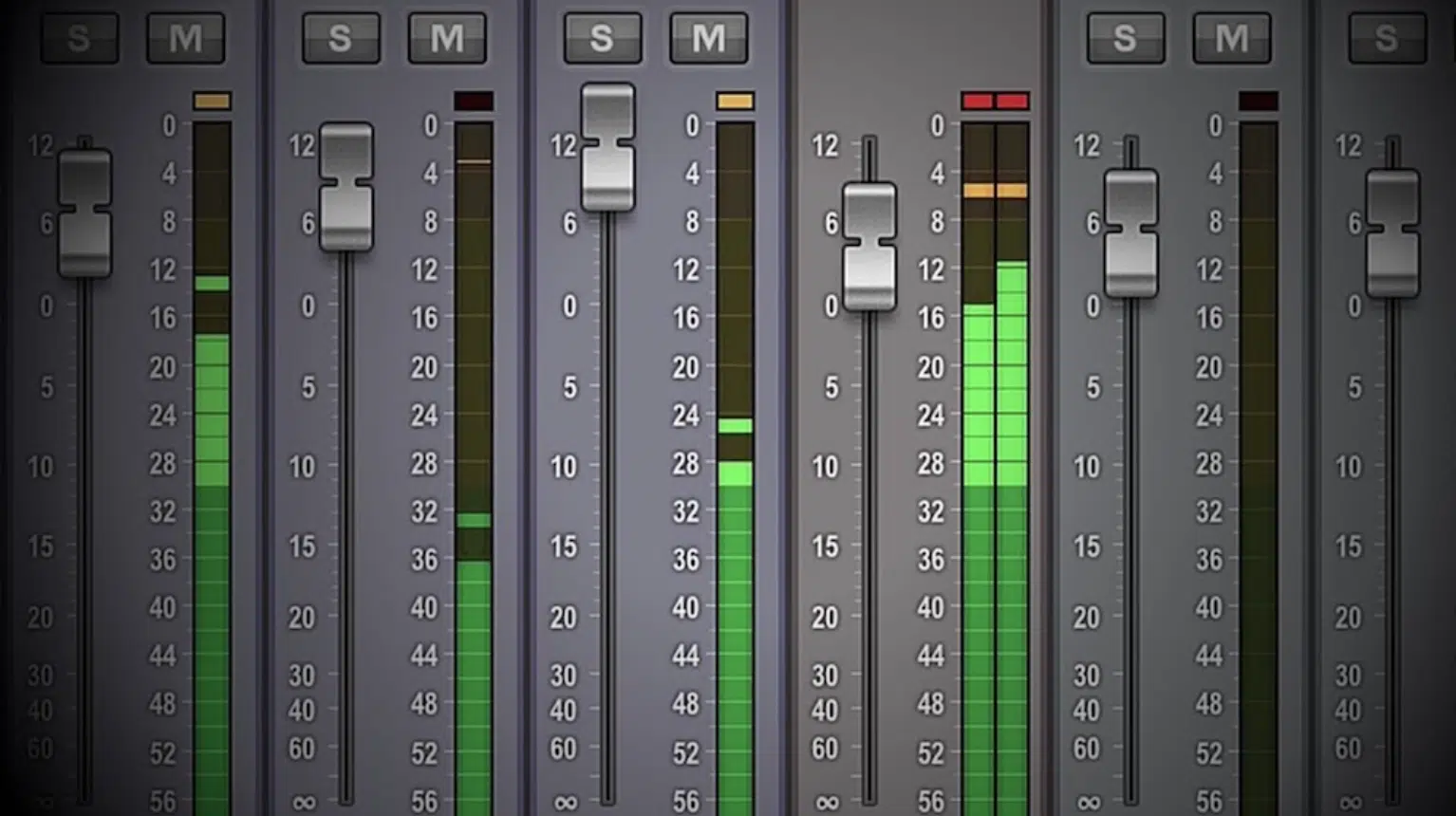
A significant part of a studio engineer’s day is spent managing recording levels.
This process starts with setting the gain on the microphone preamp during the soundcheck, ensuring a strong signal without clipping or distortion.
The engineer must continuously monitor these levels throughout the recording session 一 making adjustments as necessary.
During mixing, the sound engineer works on balancing the volume of different tracks.
This requires a keen ear and understanding of musical elements to create a cohesive and dynamic mix.
Volume automation might be used for more precise control.
It allows the audio engineer to adjust levels within different parts of a song.
-
Working with Different Instruments
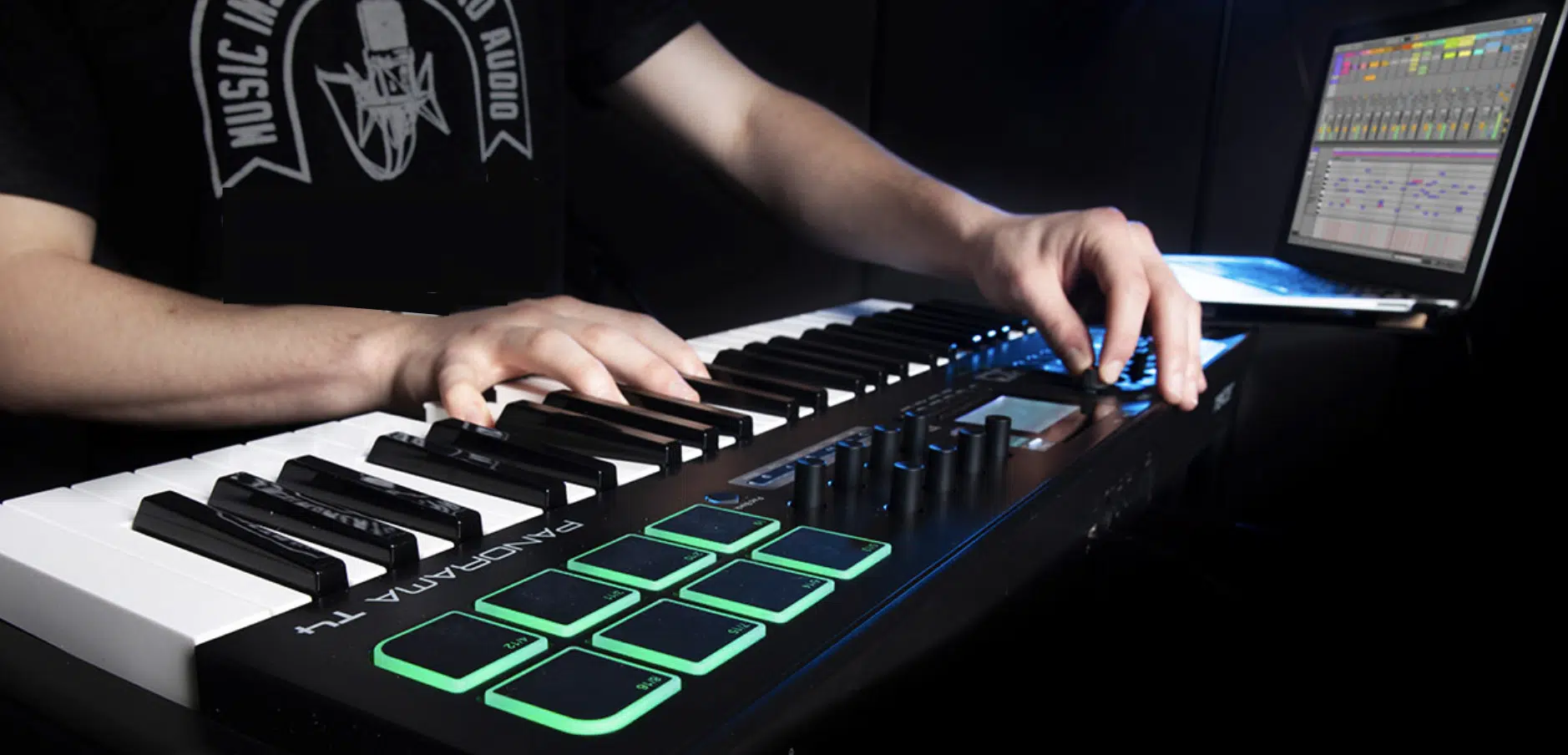

Working with different instruments presents unique challenges as an audio engineer.
Each instrument has its own frequency range, dynamic characteristics, and tonal nuances.
The sound engineer must understand these to capture the instrument’s sound accurately and make it sit well in the mix.
It can help you:
- Create dope sound effects
- Record music properly
- Truly understand recorded sound as a whole
That’s super important in the audio production process, and as a music producer in general.
For instance, recording a drum kit involves multiple microphones 一 each capturing a different drum or cymbal.
These tracks must be carefully balanced and phased-aligned to achieve a coherent drum sound.
On the other hand, recording vocals requires a sensitive microphone and a controlled environment to capture the subtleties of the human voice.
Pro Tip
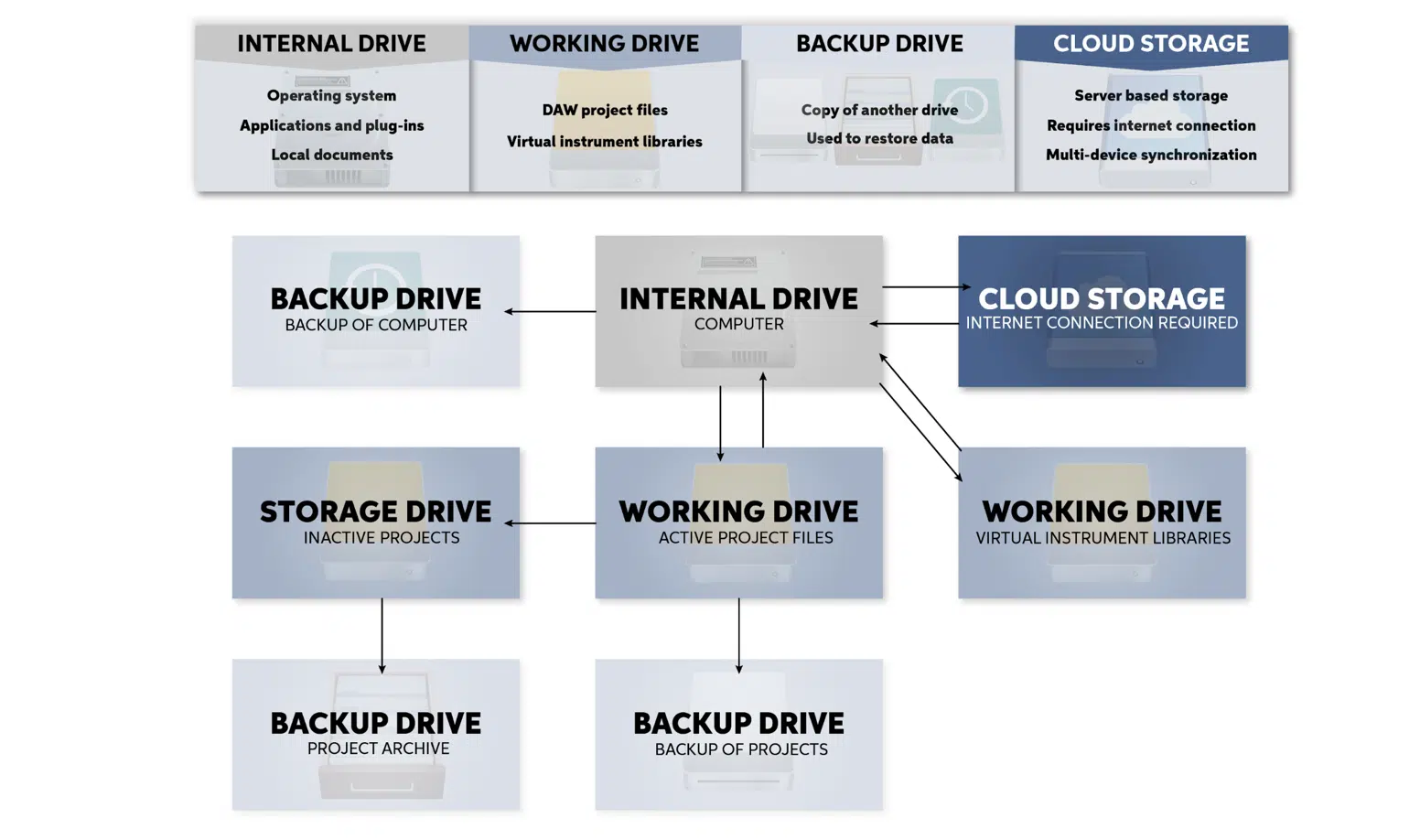
A studio engineer also needs to manage music and recording technology like a studio archive, which involves cataloging and storing all the recordings made in the studio.
This helps to keep track of the numerous sessions and takes 一 allowing easy retrieval of files when needed.
Creating a studio archive also involves backing up data to protect against potential data loss.
This can be done using external hard drives or cloud storage.
A good archiving system saves time and prevents potential headaches down the line.
Also, a sound reinforcement system, such as PA systems or speaker arrays, are crucial in live settings, but they can also impact your studio recordings.
For instance, the choice of monitor speakers in your studio can influence how you perceive and mix your music.
Similarly, the headphones you use for tracking and mixing music can color the sound and impact your decisions.
It’s all an intricate balance of continuous education, persistence, and a true love for music.
Studio Engineer: Final Thoughts
As we reach the end of our exploration into the world of a studio engineer, just remember that while the path may seem overwhelming at times, your passion for music can guide you through.
From honing your skills at adjusting sound sources to exploring different musical career paths, the road to becoming a studio engineer is as exciting as it is challenging.
If you’re looking to see the work of a master studio engineer in action and want a practical and accessible tool to help guide you, you’ve got to check out these (free) famous beatmaker templates.
These template essentials are a great way to delve deeper into the nuances of studio engineering.
They’ll give you a firsthand look at how professionals like us craft music that actually resonates.
With these templates, you can better understand the processes, techniques, and skills required to create music that not only sounds good but also moves the listener.
The templates break it all down for you; from the initial recording to the final mix.
They can help you to see the intricate web of decisions that a studio engineer makes when creating a track.
With this newfound knowledge and the right tools at your disposal, you’re well on your way to mastering the art of studio engineering.
Whether you’re embarking on a new career path or refining your technical skills for your own music production benefits, remember to keep the beat of your passion alive.
After all, at the end of the day, it’s all about the music.
Until next time…







Leave a Reply
You must belogged in to post a comment.