The job of an audio engineer is like that of an unseen maestro, conducting an orchestra of sounds and shaping them into a beautiful masterpiece.
From capturing the raw musical performance to manipulating and balancing sound elements in post-production, audio engineers make the magic of music possible.
If you’re a music producer, understanding the intricacies of audio engineering can offer you a profound advantage.
It can enhance your production skills, expand your creative possibilities, and even open up new career avenues.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll embark on a deep dive into the realm of audio engineering.
Today, we’ll be breaking down:
- The foundation & importance of audio engineering ✓
- Different types of audio engineering ✓
- Steps and traits to become a successful audio engineer ✓
- Essential audio engineering tools ✓
- The unique challenges and responsibilities in live sound ✓
- Advanced concepts in audio engineering ✓
- Career paths in audio engineering ✓
- Transitioning from music production to audio engineering ✓
By the end of this guide, you’ll have a solid understanding of audio engineering.
You’ll learn how to blend your existing skills as a music producer with newfound audio engineering techniques.
More importantly, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge and insights to pursue a rewarding career in audio engineering if you so choose.
Table of Contents
- The Core of Sound: Understanding Audio Engineering
- Dive into Different Types of Audio Engineering
- Stepping into the Shoes of an Audio Engineer
- Audio Engineering Tools of the Trade
- The Magic of the Recording Studio
- Live Sound: A Different Beast
- Advanced Concepts in Audio Engineering
- Navigating a Career in Audio Engineering
- Audio Engineering: Final Thoughts
The Core of Sound: Understanding Audio Engineering
Now that you’re primed and ready to uncover the secrets of audio engineering, it’s time to start with the basics.
First, we’ll peel back the layers of this fascinating field to grasp its fundamental concepts and relevance in today’s music landscape.
-
What is Audio Engineering?
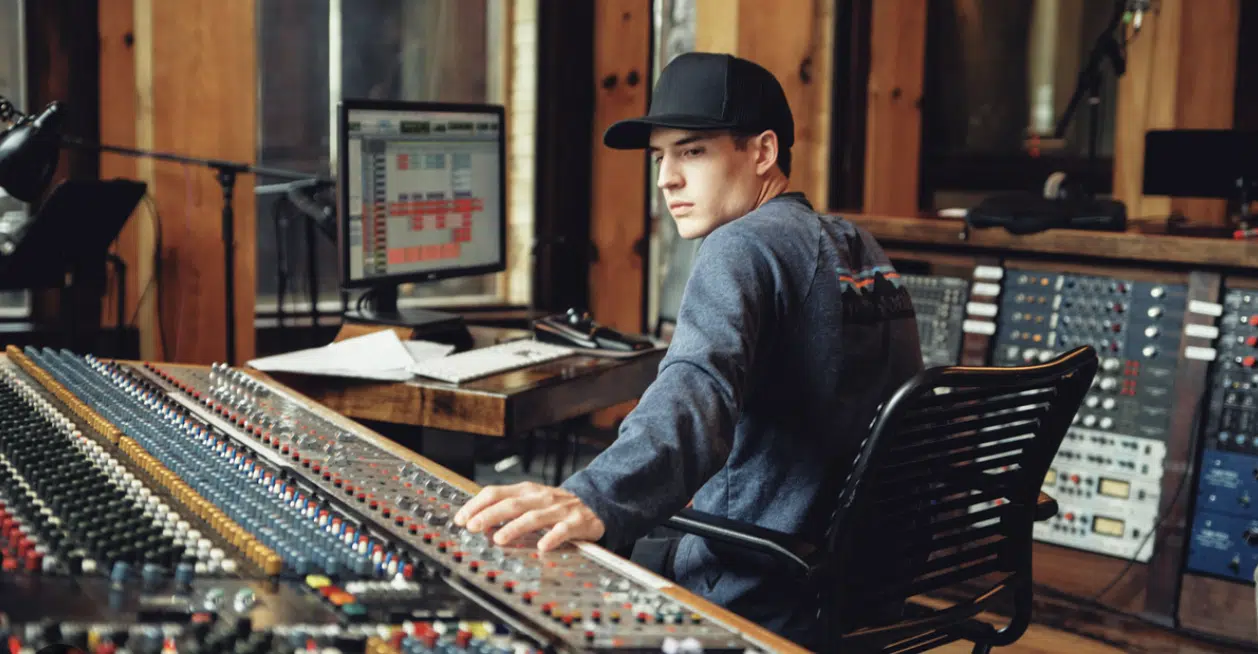

When people ask me, “What is audio engineering?” I often compare it to being a painter…
But instead of colors and a canvas, we use sound and silence as our medium.
In the most basic terms, it’s the technical and creative process of recording, manipulating, reproducing, and mixing sounds.
At the heart of audio engineering lies the science of sound.
It’s about understanding:
- How sound works
- How sound travels
- How sounds interact with the environment
- How it’s perceived by the human ear
However, it’s also about the art of sound 一 creating aural experiences that evoke emotions, telling stories, or simply making people move to the beat.
Audio engineering is a vast field with many sub-disciplines, each requiring its unique set of skills and knowledge.
Whether it’s working in a recording studio, creating soundscapes for video games, or ensuring that a live concert sounds perfect, an audio engineer wears many hats.
They play a pivotal role in the world of audio production, which we’ll break down today.
-
Importance of Audio Engineering in Music Production
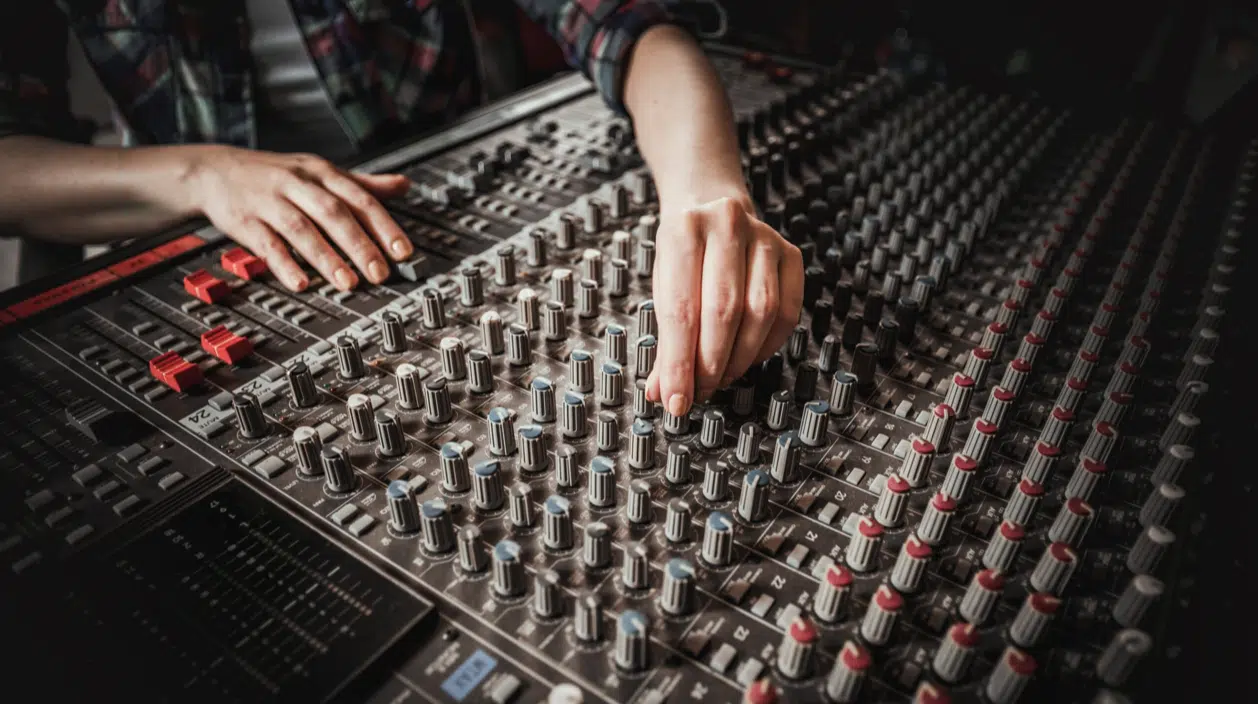

When it comes to music production, audio engineering is the foundation that everything else is built upon.
The audio engineer’s role in music production is critical 一 they turn an artist’s vision into a tangible, auditory experience.
The intricate beats, the booming bass, the crisp vocals; every element you hear in a track has been carefully crafted by an audio engineer.
Audio engineers ensure that:
- Each element is recorded with the best sound quality
- Processed to fit the mix
- Mastered to sound great on all sound systems
Audio engineering in music production isn’t just about the technical aspects… It’s also about creativity.
They use their technical skills to enhance musical ideas and contribute to the overall artistic direction of a track.
They might suggest adding certain sound effects to elevate a part of the song or adjusting the tone of an instrument to better suit the track’s mood.
In the realm of digital hip-hop music production, the role of the audio engineer is even more crucial.
The genre’s heavy reliance on electronic elements, intricate beats, and vocal processing calls for a deep understanding of sound engineering.
-
The Role of an Audio Engineer
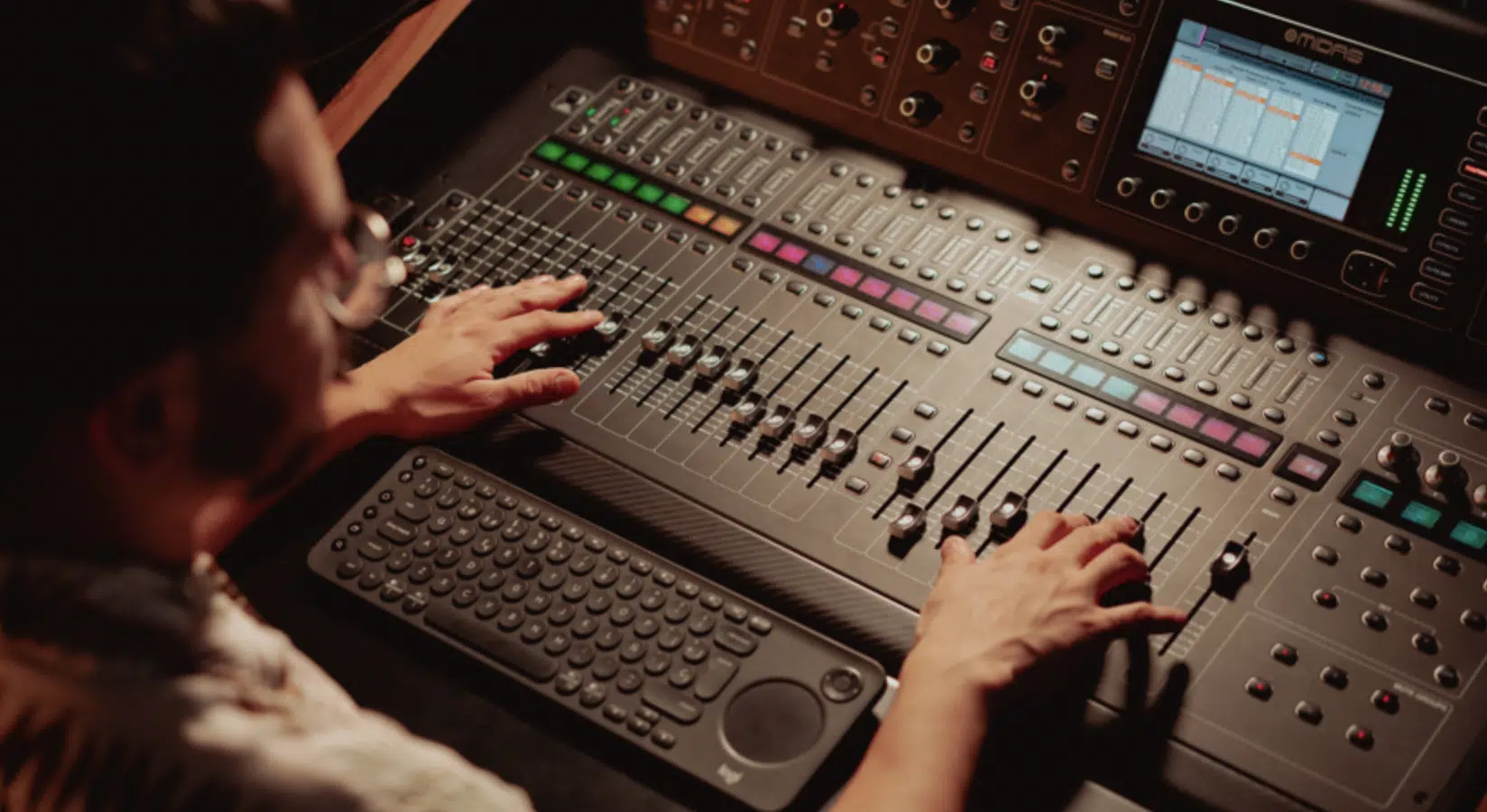

As an audio engineer or aspiring engineer, you are essentially the gatekeeper of sound.
You are responsible for capturing, shaping, and balancing the elements of a track to create the final product.
As well as have the power to highlight a vocal, suppress background noise, or enhance a bass line.
The role of most audio engineers varies, depending on the context.
In a recording studio, an audio engineer is responsible for:
- Setting up microphones
- Managing sound levels
- Recording high-quality audio
Here, a keen ear and technical skills are essential to capture the best possible sound quality from the start.
For a mix engineer, the role involves blending and balancing the various elements of a track to create a harmonious mix.
This requires a deep understanding of musical elements, the overall creative vision, and the technical skills to manipulate sound in a precise manner.
For mastering engineers, the role is about polishing the mix and preparing it for distribution.
They ensure the track sounds good on all sound systems and formats, maintaining the balance and consistency of the overall album.
In the realm of live sound, an audio engineer ensures that the sound in a live performance is clear, balanced, and impactful.
This involves working with complex live sound systems and handling the unpredictable nature of a live event.
In all these roles, an audio engineer also serves as a collaborator and a problem solver.
They have to use their technical and creative skills to enhance the music and overcome challenges.
-
The Influence of Sound Quality

The importance of sound quality in audio engineering cannot be overstated.
Sound quality is what separates a professional recording from a garage band demo, or a headlining concert from a local gig.
It’s what draws listeners in and makes them stay.
A good audio engineer has the skills and knowledge to deliver the best sound quality.
This involves:
- Understanding the science of sound
- Having a familiarity with audio equipment and signal processing
- Procuring an ear for detail
Sound quality also plays a crucial role in listener perception.
High-quality sound can make a track feel more immersive, evoking stronger emotional responses.
It can also affect the perceived quality of the music itself 一 a well-engineered track can make good music sound great.
In the digital hip-hop music production scene, where beats and samples are prominent, sound quality takes on an even more significant role.
The clarity of the drum hits, the punch of the bass, and the texture of the samples all contribute to the overall impact of the track.
As an audio engineer, your role is to ensure that these elements shine in the best possible light, delivering a powerful listening experience.
Dive into Different Types of Audio Engineering
Now that you have the basics of audio engineering down, let’s compare it to different types of engineering, as there are plenty.
-
Studio Engineering
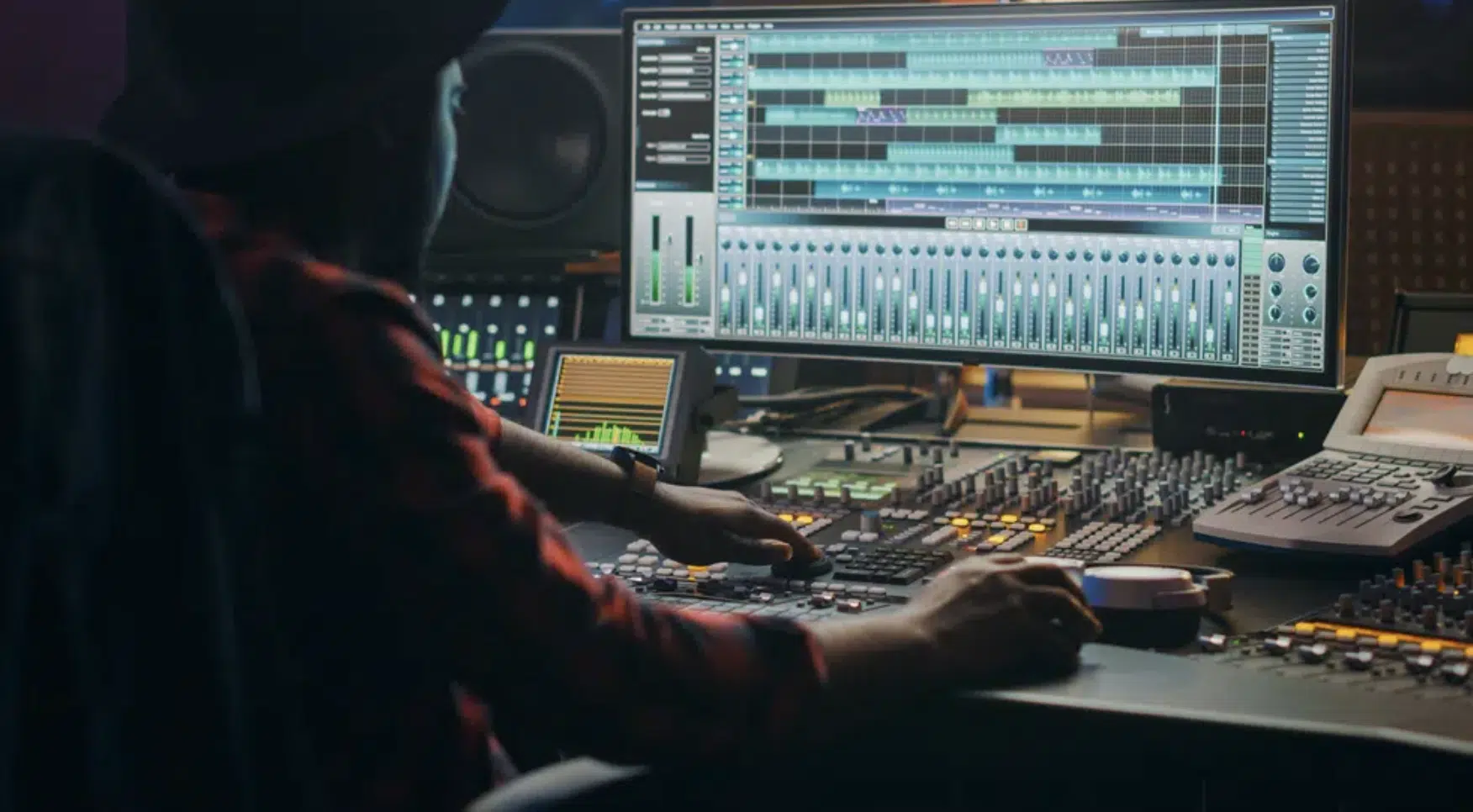

Studio engineering is one of the most well-known aspects of audio engineering, and for a good reason.
It’s here that raw musical ideas are translated into polished tracks ready for the world to hear.
Studio engineers are responsible for overseeing the physical recording process.
This involves:
- Setting up microphones
- Adjusting audio levels
- Capturing high-quality recordings
They need to understand the acoustics of the recording space and how to get the best sound out of each instrument and vocal.
Studio engineers also work closely with artists during the recording process.
They help to create an environment where artists feel comfortable and able to deliver their best performances.
The studio engineer also uses their technical knowledge to advise on recording techniques that could enhance the overall sound or feel of the track.
A studio engineer often manipulates samples and beats and adjusts the timing, pitch, and tone to fit the artists’ unique vision.
The aim is always to achieve the best possible sound, capturing the unique vibe of the track.
-
Sound Engineering

Sound engineering, often interchanged with audio engineering, covers a broader spectrum of responsibilities and skills.
While a sound engineer may work in a studio, their job can also involve live sound, audio post-production for film or TV, sound design, and more.
The role of a sound engineer is multi-faceted.
It involves capturing sound 一 whether it’s a guitar riff, a vocal harmony, or the ambient noise in a film scene.
But it also involves manipulating that sound, using a range of processing tools to adjust pitch, volume, timing, and tone as well.
For hip-hop producers, the sound engineer’s role is especially vital.
They’re responsible for:
- Ensuring that the beat hits hard
- The vocals sit perfectly in the mix
- Every sound in the track is balanced and polished
As well as work with an array of digital tools to manipulate and tweak sounds, ensuring that the final product is as impactful as possible.
-
Live Sound Engineering
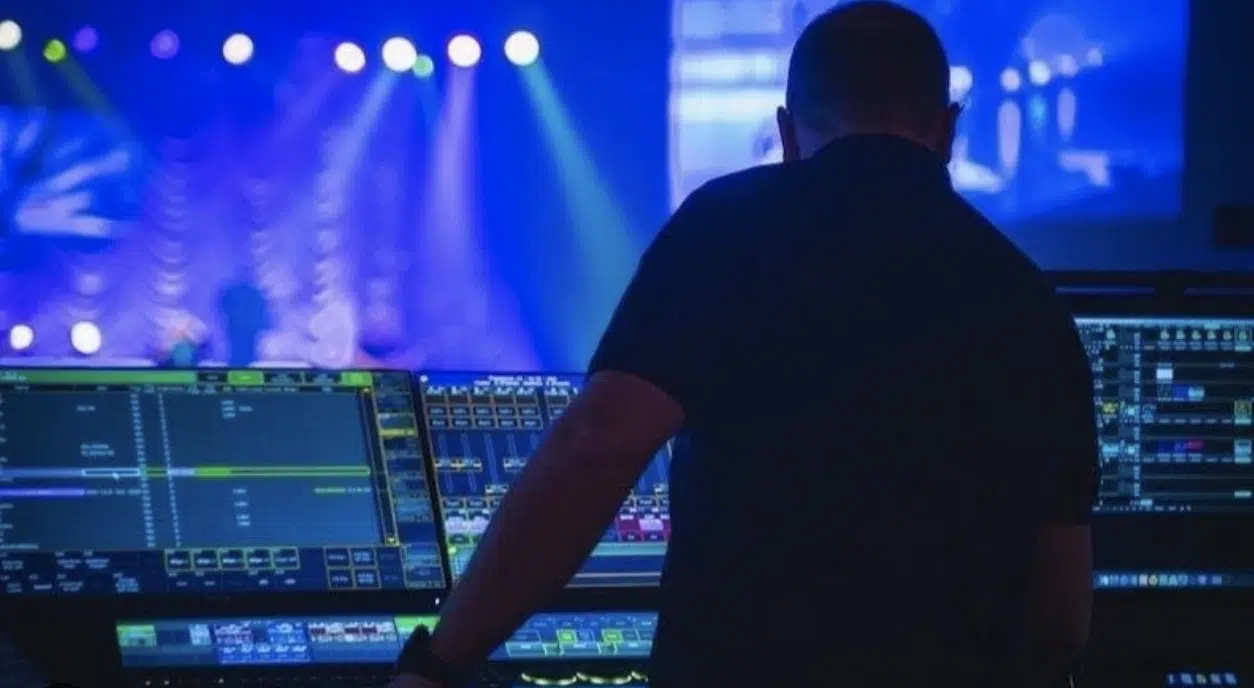

Live sound engineering is a whole different beast.
Instead of working in a controlled studio environment, live sound engineers work in a variety of venues 一 from intimate clubs to large arenas.
Their role is to ensure that the sound at a live event is clear, balanced, and impactful.
As a live sound engineer, your job would be to manage:
- The sound system
- Balance the mix live
- Troubleshoot any issues that arise during the performance
This requires a deep understanding of acoustics, as every venue has different characteristics that affect the sound.
In the context of hip-hop music, where live performances often involve DJs, MCs, and sometimes live instrumentalists, the live sound engineer must handle a range of sound sources.
They need to ensure that the beats are powerful, the vocals are clear, and the overall sound is engaging for the audience.
-
Mastering Engineering
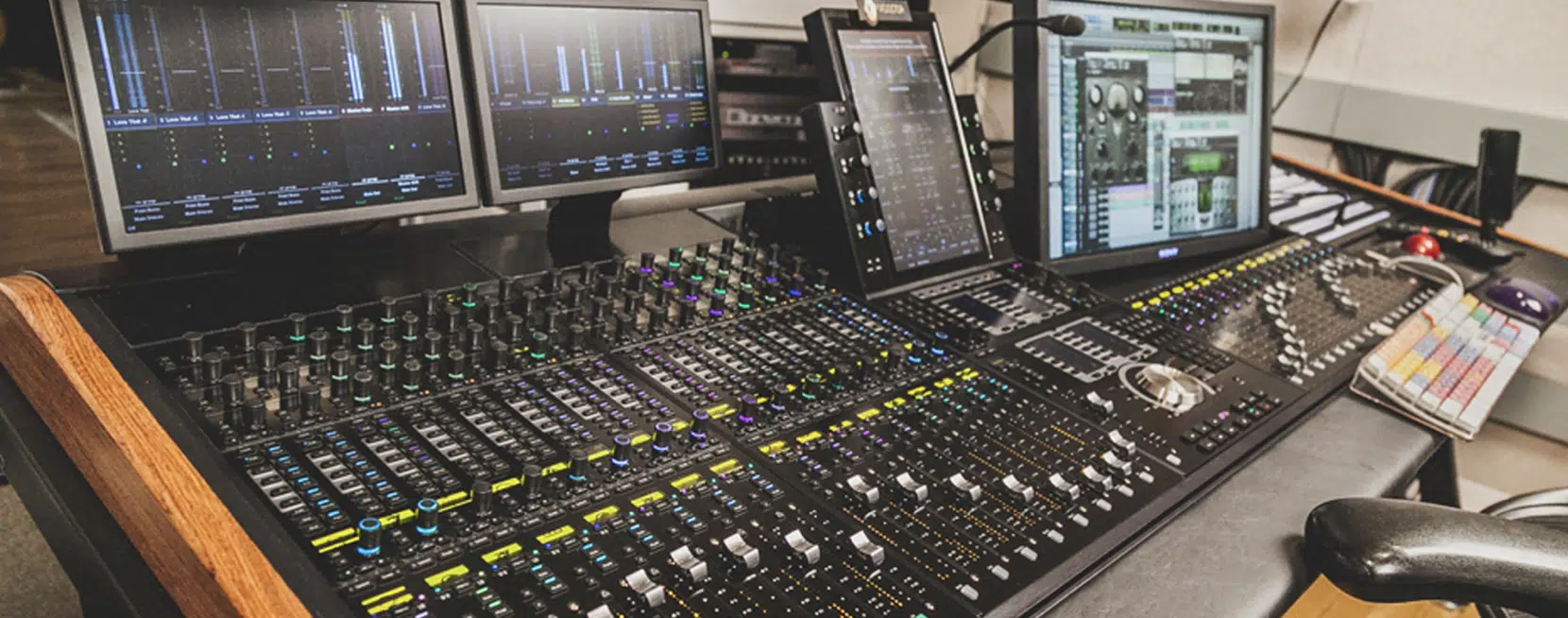

Mastering is the final step in the audio production process.
A mastering engineer takes the final mix of a track and polishes it, preparing it for distribution.
They ensure the track sounds good on all sound systems & formats and maintain the balance/consistency of the overall album.
Mastering is a critical process that requires a keen ear, technical skills, and a deep understanding of music and sound.
The mastering engineer:
- Tweaks the EQ
- Adjusts the stereo image
- Applies dynamic processing
- Sets the overall volume level of the track
In the realm of digital hip-hop, where heavy beats and complex samples are prominent, mastering can make or break a track.
The mastering engineer ensures that the track’s power and impact are preserved.
While also ensuring that it sounds good whether it’s played on a club sound system, a car stereo, or a pair of headphones.
If you’d like to find out, in detail, about mastering engineers, we’ve got you covered.
Stepping into the Shoes of an Audio Engineer
Now that you understand what audio engineering entails and its diverse facets, let’s explore how you can walk this path.
We’ll delve into the process, traits, and training needed to become a successful audio engineer and the promising career prospects it holds.
-
How to Become an Audio Engineer
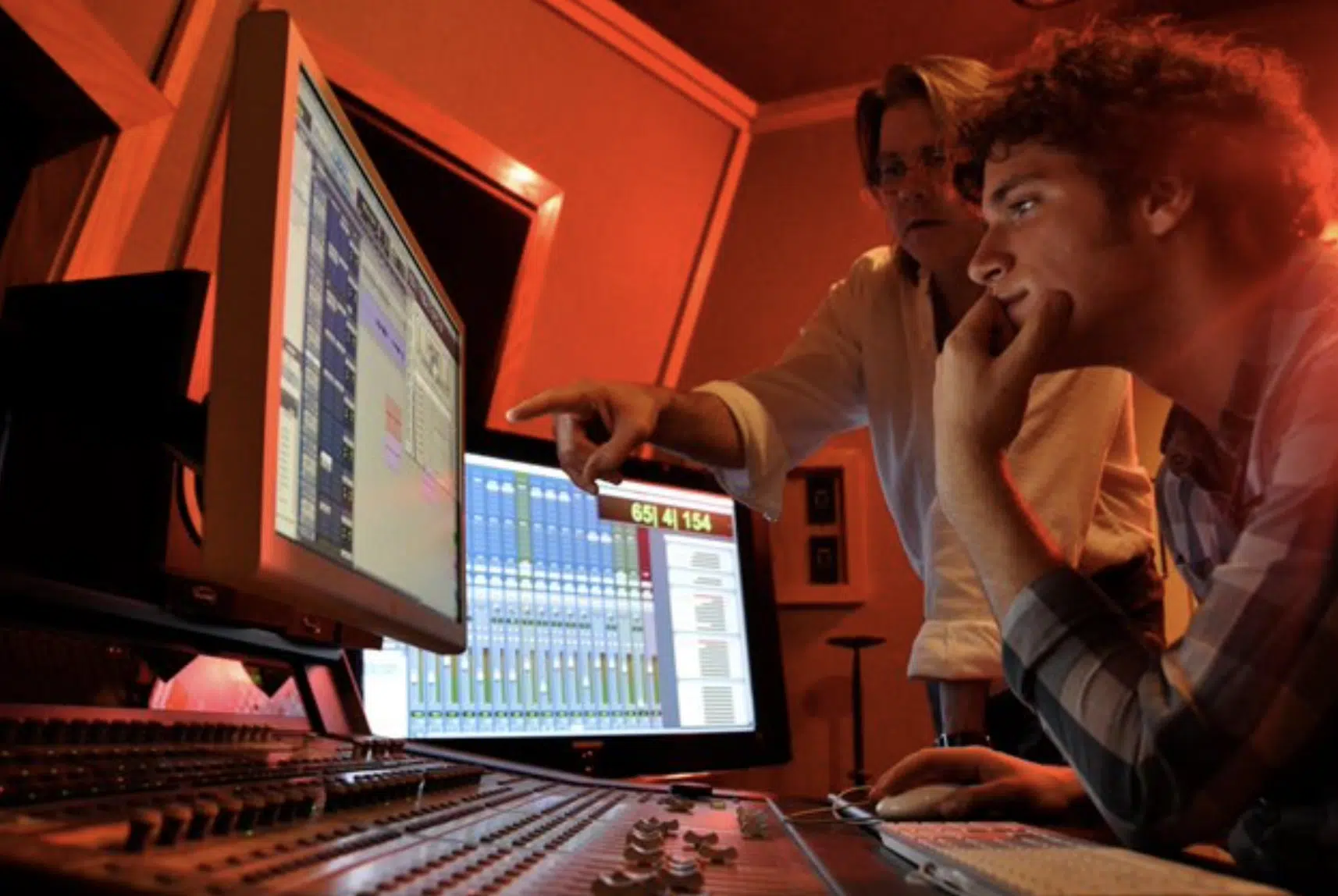

Becoming a professional audio engineer requires a mix of technical knowledge, practical experience, and creative sensibility.
You may start by taking audio engineering programs or professional courses, which provide a solid foundation in the technical aspects of sound.
Audio engineering courses cover a range of topics, including:
- Sound design
- Signal processing
- Audio equipment
- Studio engineering
- Live sound
Some aspiring audio engineers even pursue an audio engineering degree to gain a comprehensive understanding of the field.
However, formal training alone isn’t enough to become an audio engineer…
Hands-on experience is crucial.
This could involve working as an assistant engineer in a recording studio, doing live sound for local gigs, or even setting up your own home studio and recording your own music.
The more practical experience you get, the better.
For established music producers looking to delve into audio engineering, getting hands-on with your own music is a great start.
Using software like Ableton, Reaper, FL Studio, Logic or Pro Tools, you can practice recording, mixing, and mastering, all while honing your ear for sound.
-
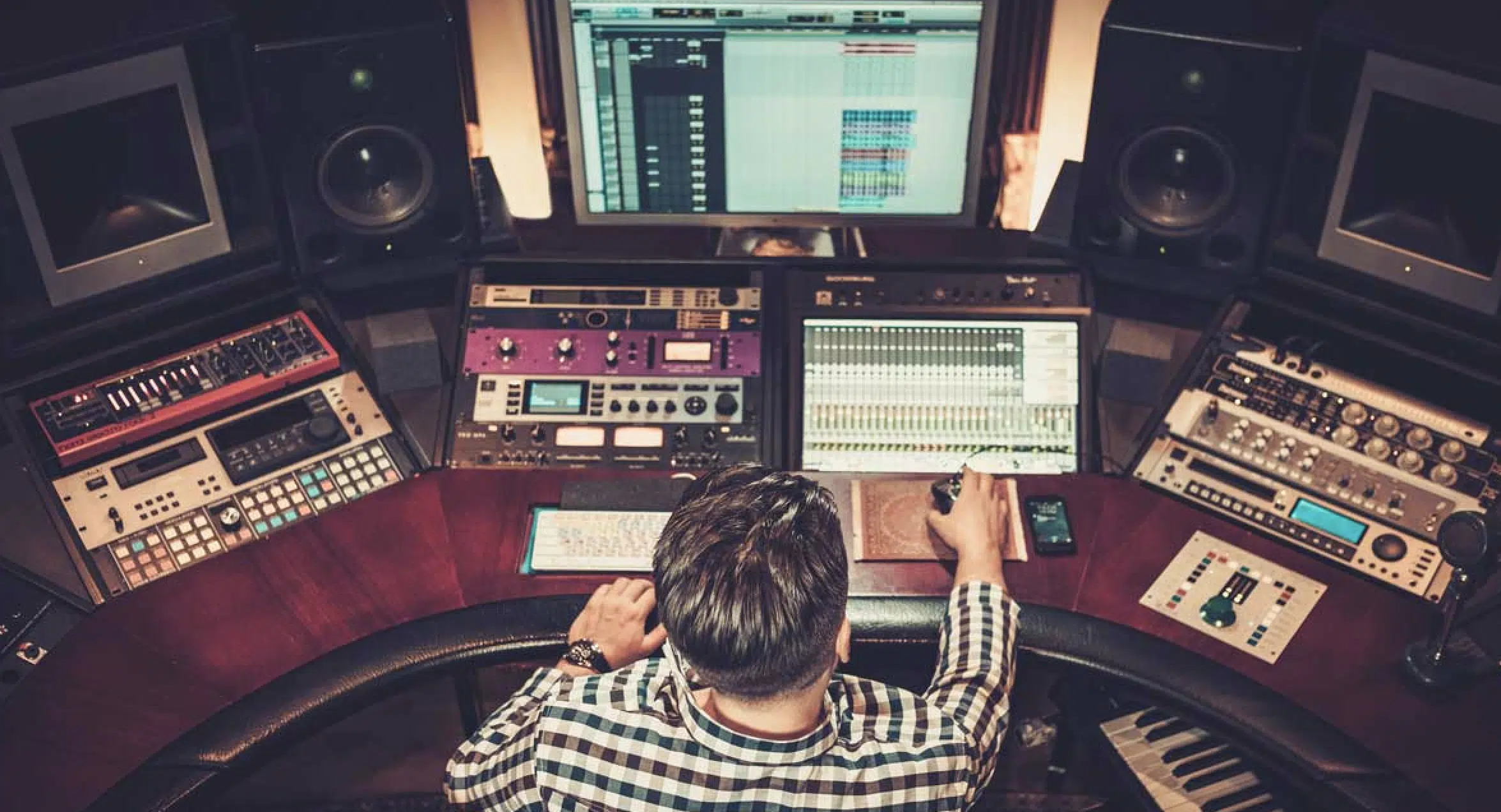
Traits of Successful Audio Engineers

Successful audio engineers share several traits.
1. The most prominent one is, of course, technical proficiency.
Audio engineers need to understand a wide range of audio equipment 一 from microphones and mixers to digital audio workstations and plugins.
They also need to understand acoustics, signal flow, and a host of other technical aspects.
2. Another key trait is good listening skills.
Audio engineers need to be able to listen critically to music and sound, identify subtle issues, and know exactly how to correct them.
This requires a well-trained ear and a deep understanding of sound.
3. A third trait is adaptability.
Every project is different, and audio engineers need to be able to adapt to different artists, genres (like pop or lo-fi), recording environments, and sound systems.
For example, mixing a trap beat requires a different approach than mixing a soulful R&B vocal.
-
The Need for Formal Training

While you can learn a lot through hands-on experience, formal training in audio engineering provides a structured way to learn the fundamentals.
Formal training can come in many forms 一 from college degrees and diploma programs to short courses and online tutorials.
An audio engineering program typically covers a broad range of topics, including:
- Recording techniques
- Signal processing
- Audio equipment
- Sound design
- The music industry
- Audio post-production
- Live sound
For those looking to specialize, programs like electrical engineering or music technology can provide a more focused route.
Whatever path you choose, formal training can provide a strong foundation on which to build your audio engineering career.
-
Job Prospects in Audio Engineering

The audio engineering field offers a range of job prospects.
Many audio engineers work in recording studios 一 handling everything from setting up microphones to mixing and mastering tracks.
Others work in live sound, managing the sound at concerts and other live events.
Then there are roles like:
- Broadcast engineers: who handle the sound for TV and radio broadcasts.
- Audio post engineers: who work on the sound for film and TV post-production.
Some audio engineers even go on to become music producers, using their understanding of sound to guide the creative process.
For those with a passion for hip-hop and digital music production, the opportunities are vast.
From mixing beats to mastering full albums, audio engineering skills can open up new avenues for creative expression and career advancement.
Audio Engineering Tools of the Trade
With a clear path in sight to become an audio engineer, it’s time to familiarize yourself with the tools you’ll need in your arsenal.
We’ll take a look at the essential audio equipment, understand the nuances of signal processing, and explore the art and science behind sound systems and audio effects.
-
Audio Equipment Essentials

Audio equipment forms the backbone of any audio engineer’s setup.
Microphones, preamps, monitors, and mixers; these are all integral to capturing and manipulating sound.
Understanding these tools and how they interact is crucial for an audio engineer.
But it’s not just about hardware, audio or musical technology.
In the digital age, software is just as important.
Digital Audio Workstations (DAWs) are where much of the audio engineering magic happens.
Plugins offer a huge range of possibilities for manipulating sound 一 from EQ and compression to reverb, delay, and beyond.
For hip-hop producers, specific tools like drum machines and samplers are often key parts of the setup.
Software like Serato Sample or hardware like the Akai MPC can be powerful tools for creating and manipulating beats.
-
Understanding Signal Processing

Signal processing is a core part of audio engineering.
It’s all about manipulating audio signals to achieve the desired sound.
This can involve:
- Boosting or cutting certain frequencies (EQ)
- Controlling dynamics (compression)
- Adding space and depth (reverb, delay)
- Much more
In the digital realm, signal processing is typically done using innovative plugins.
There’s a huge range of plugins available 一 each offering different ways to manipulate sound.
Knowing how to use these tools, and when to use them, is a crucial part of an audio engineer’s skillset.
For hip-hop production, signal processing plays a key role in shaping the sound of beats and vocals.
Techniques like sidechain compression can give your track a professional polish.
While creative effects like bit-crushing or saturation can add unique character to your beats.
-
Exploring Sound Systems

Sound systems are another important part of audio engineering.
Whether it’s the monitors in a recording studio or the speakers in a home studio, understanding how sound systems work (and how to optimize them) is essential for any audio engineer.
Different systems have different strengths and weaknesses.
- Studio monitors 一 Designed for accuracy.
- PA systems 一 Designed for volume and coverage.
- Home studios 一 Vary widely, from high-end monitors to simple desktop speakers.
Understanding these differences and knowing how to work with them is a crucial part of audio engineering.
For example, knowing how to mix on studio monitors can help you achieve a balanced, professional mix.
While understanding live sound systems can help you ensure the best possible sound at gigs.
-
The Art of Sound Effects

Sound effects are a major part of many types of audio engineering.
In music production, sound effects can add depth and character to a mix.
In film and TV post-production, sound effects play a crucial role in creating the world on screen.
Creating and manipulating sound effects is a whole art in itself.
It can involve everything from field recording and Foley work to digital synthesis and sample manipulation.
For hip-hop producers, sound effects can be a great way to add unique touches to your tracks.
A well-placed riser, crash, or vocal sample can take a beat from good to great.
And with tools like samplers and software like Ableton Live, the possibilities are virtually endless.
The Magic of the Recording Studio
Now that you’re equipped with the necessary tools, let’s step into the enchanting realm of the recording studio.
We’ll discuss the unique experiences it offers, compare sound and audio recording, and understand the pivotal role of a recording engineer in ensuring the best sound quality.
-
The Recording Studio Experience
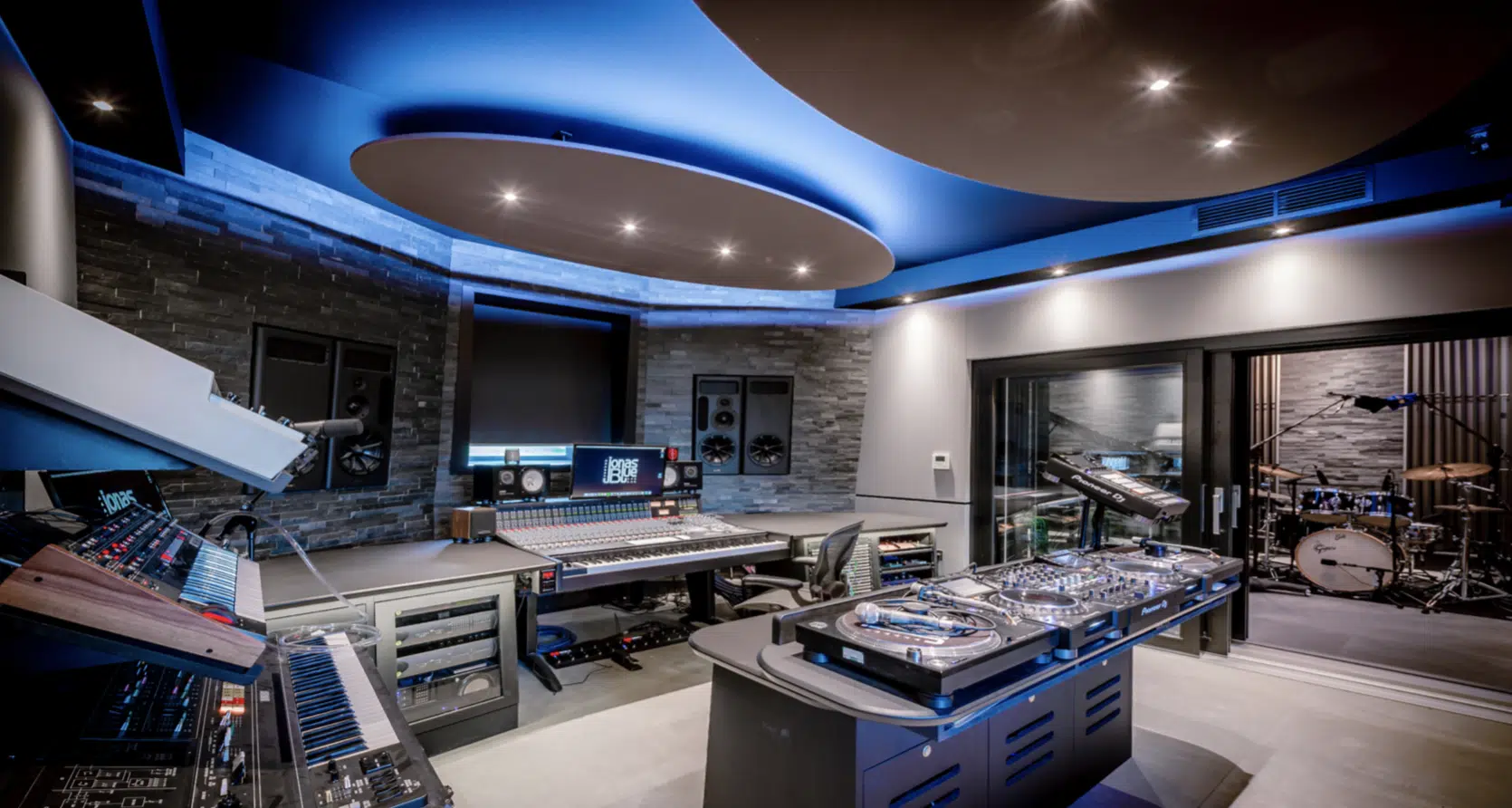

Stepping into a professional recording studio is a unique experience.
From the humming of the machines to the acoustically treated walls, it’s a haven for creatives.
It’s where the magic happens 一 where raw talent meets technical expertise to birth a complete masterpiece.
At the heart of the studio is the control room, housing the mixing console, a vast array of knobs, faders, and switches.
The live room, soundproofed and equipped with state-of-the-art microphones, awaits the artists.
As an audio engineer, you command the bridge between these two worlds.
For producers, the studio is both a workshop and a playground.
Laying down beats, recording bars, and orchestrating the flow of a song; it’s here where the vision transforms into audible reality.
-
Sound Recording vs. Audio Recording
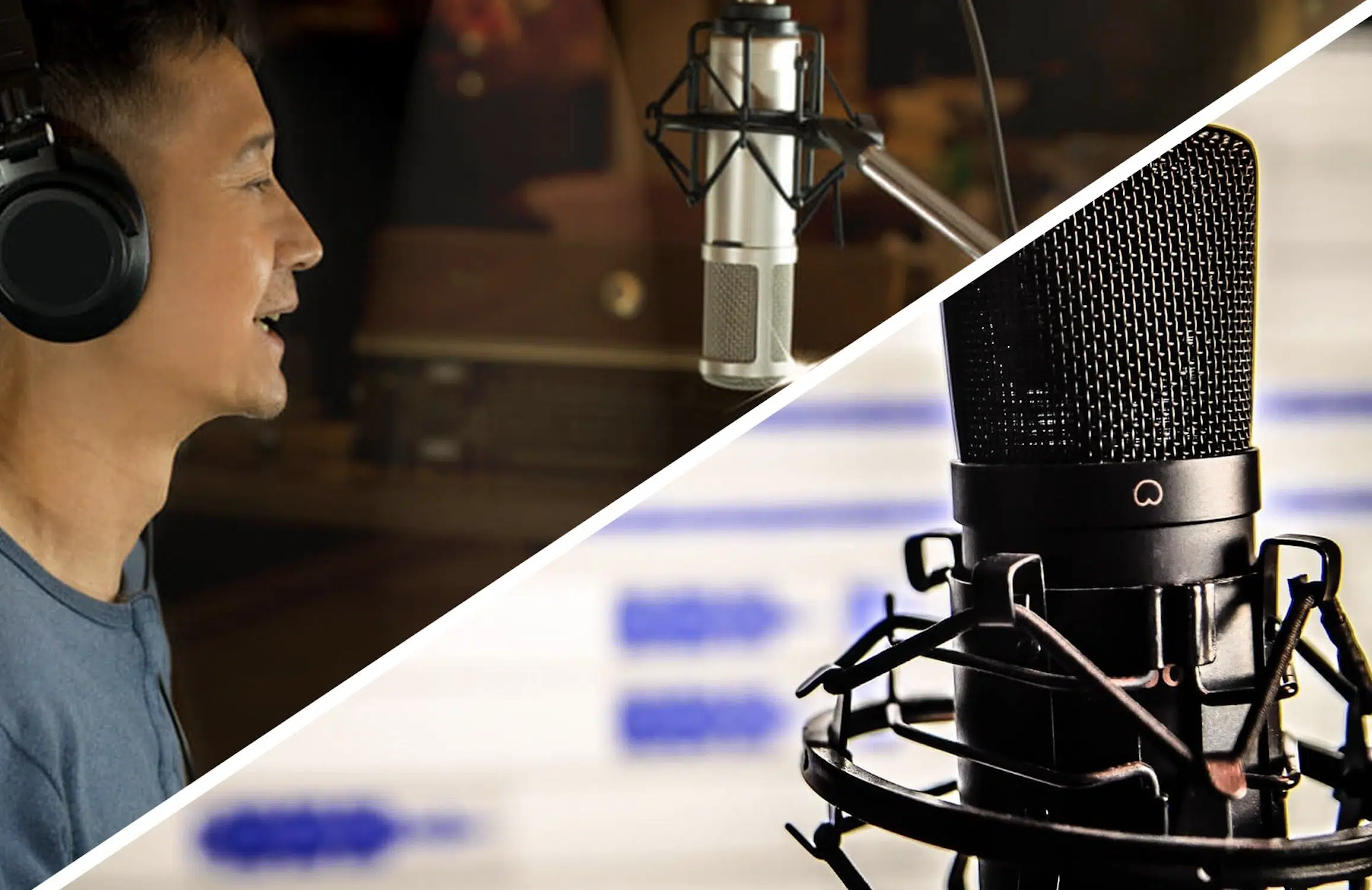

Sound recording and audio recording might seem synonymous, but they’re not quite the same.
- Sound recording 一 Refers to the capture of acoustic sounds, like voices and instruments, using a microphone.
- Audio recording 一 Covers digital and synthesized sounds as well.
In today’s world, these two often intertwine, especially in genres like hip-hop.
A beat might be constructed digitally but layered with samples recorded from vinyl or live instruments.
Mastering both these aspects of recording is vital.
Whether you’re capturing the raw energy of a live rapper or programming a slick beat on a drum machine, your skills as an audio engineer come to the fore.
-
The Role of a Recording Engineer
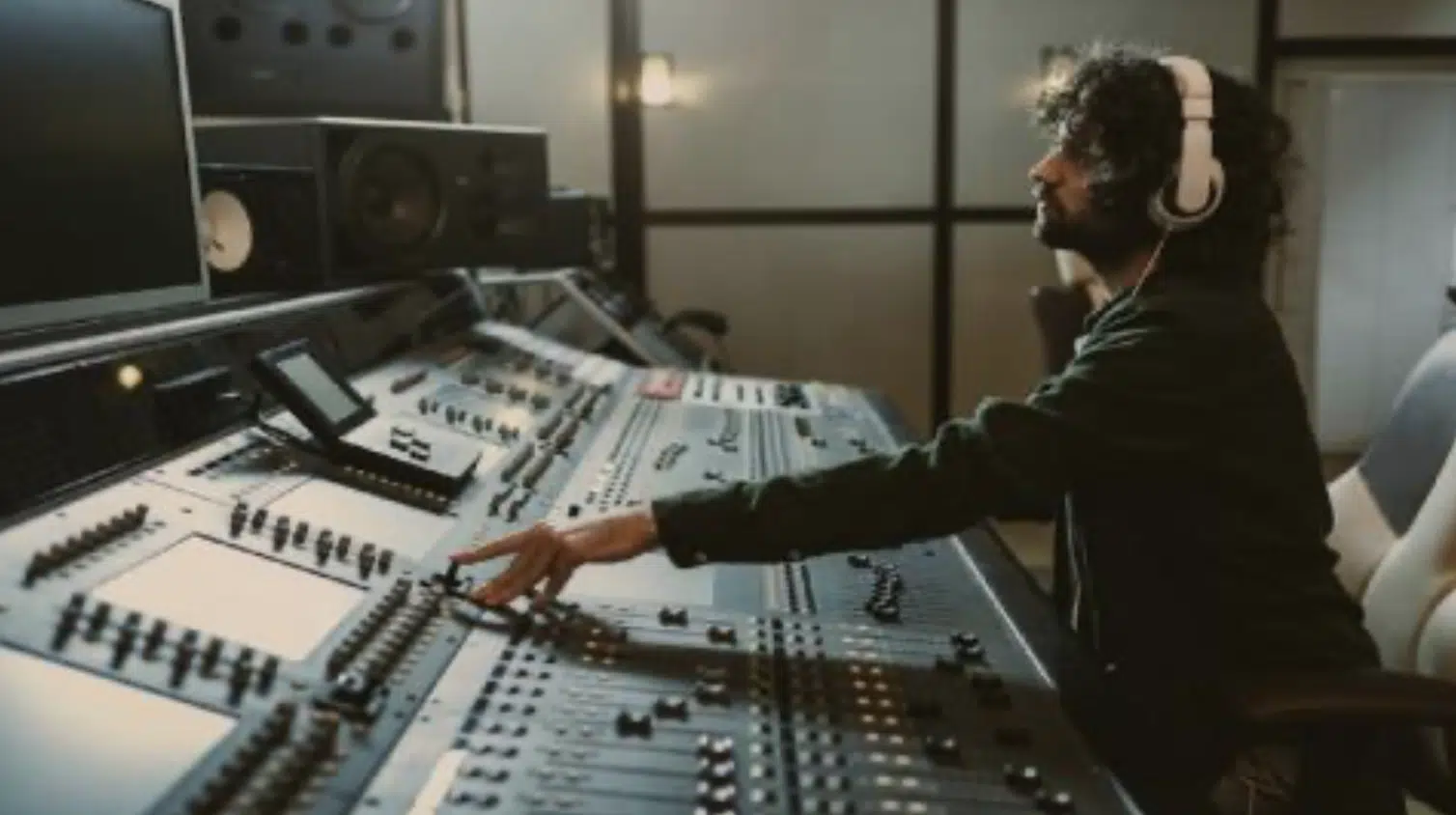

A recording engineer is the technical guru of the studio.
Their job is to:
- Capture the best possible sound
- Set up mics
- Control levels
- Ensure everything is recorded cleanly and clearly
But the role of a recording engineer isn’t purely technical.
It’s also about understanding the artists, and the music, and helping to shape the sound of the record.
This could mean suggesting a different mic for a particular voice or adjusting the acoustics in the room to suit a specific instrument.
For a hip-hop producer, working with a good recording engineer can make a world of difference.
They can help you capture the perfect vocal take, lay down fire beats, and ultimately bring your music to life.
Live Sound: A Different Beast
Diving into the dynamic world of live sound, we find a different set of challenges and thrills.
Here, we will learn about the unique responsibilities of a live sound engineer, managing live sound systems, the art of mixing live sound, and monitor engineers.
-
The Role of a Live Sound Engineer
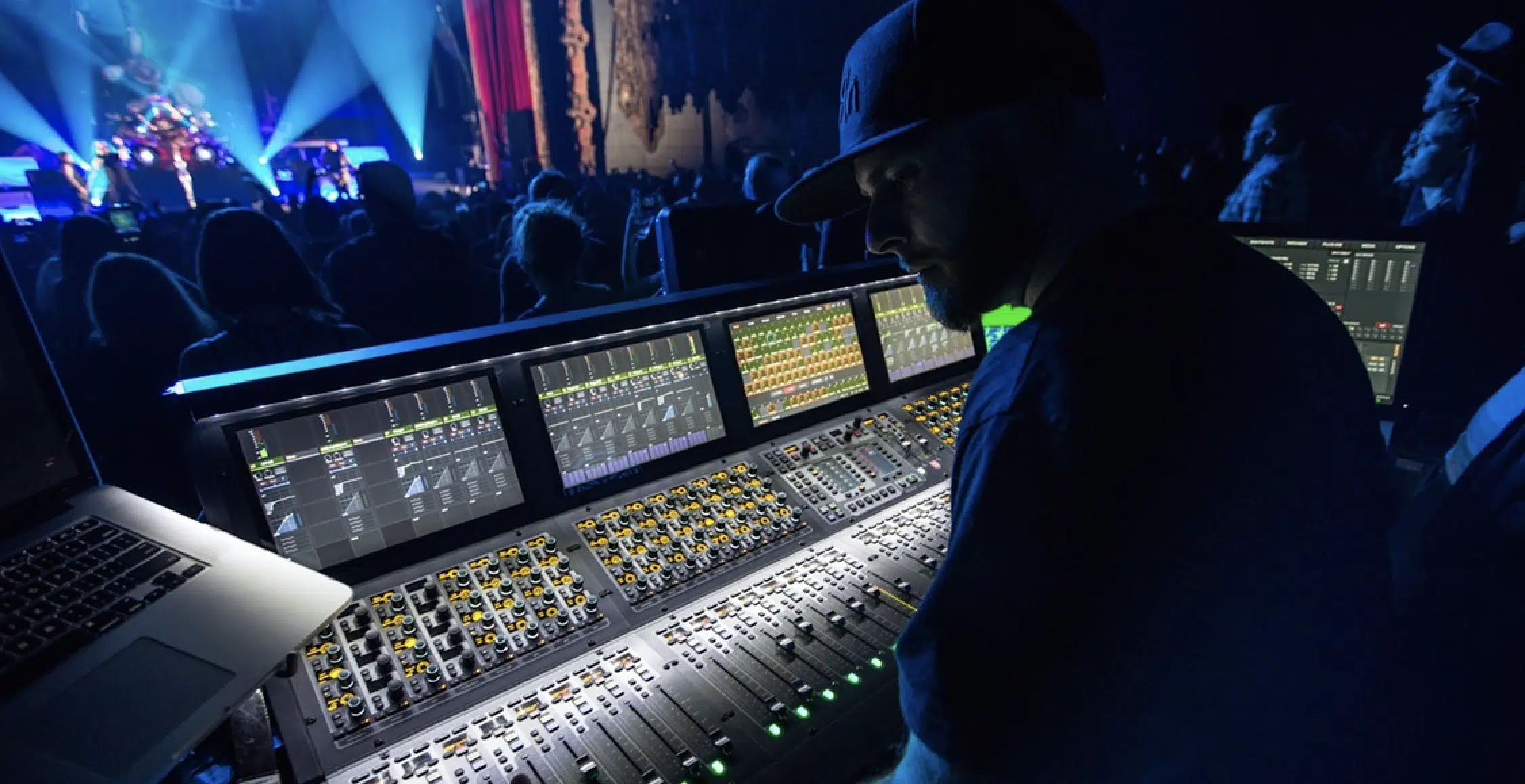

The job of a live sound engineer is an entirely different beast compared to studio work.
From the unpredictable nature of live performances to managing complex sound systems under pressure, this role is not for the faint-hearted.
Imagine you’re working at a major hip-hop festival…
As the live sound engineer, you’re responsible for making sure that every beat, every bar, every ad-lib sounds crisp and clear to the thousands of fans in attendance.
You’ll need to:
- Balance levels on the fly
- Fix issues as they arise
- Adapt to the unique acoustics of the venue
It’s a challenging role, but it can also be incredibly rewarding.
There’s nothing quite like the thrill of a live show, and as the live sound engineer, you’re a crucial part of the team making it all happen.
-
Managing Live Sound Systems
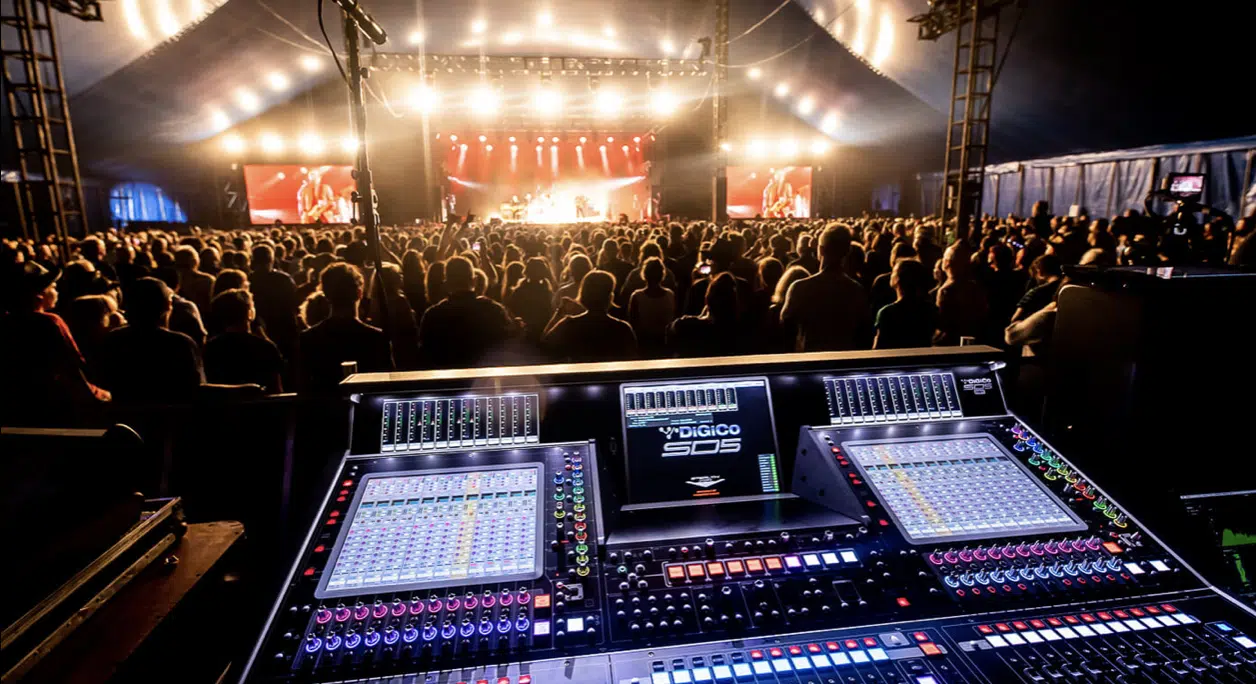

Managing live sound systems is a crucial part of the job for a live sound engineer.
From the PA speakers to the monitors on stage, every piece of sound equipment plays a role in delivering quality sound to the audience.
Picture this: You’re at a packed hip-hop show, and the crowd is going wild, but suddenly, the lead vocalist’s monitor cuts out.
They can’t hear themselves, and their performance starts to falter.
As the live sound engineer, it’s your responsibility to:
- Identify the issue
- Quickly find a solution
- Get the show back on track as quickly as possible
This is where your technical expertise and problem-solving skills truly shine.
Knowing your equipment inside and out, and being able to react quickly and efficiently to issues, is what separates the good audio engineers from the great.
-
Mixing Live Sound
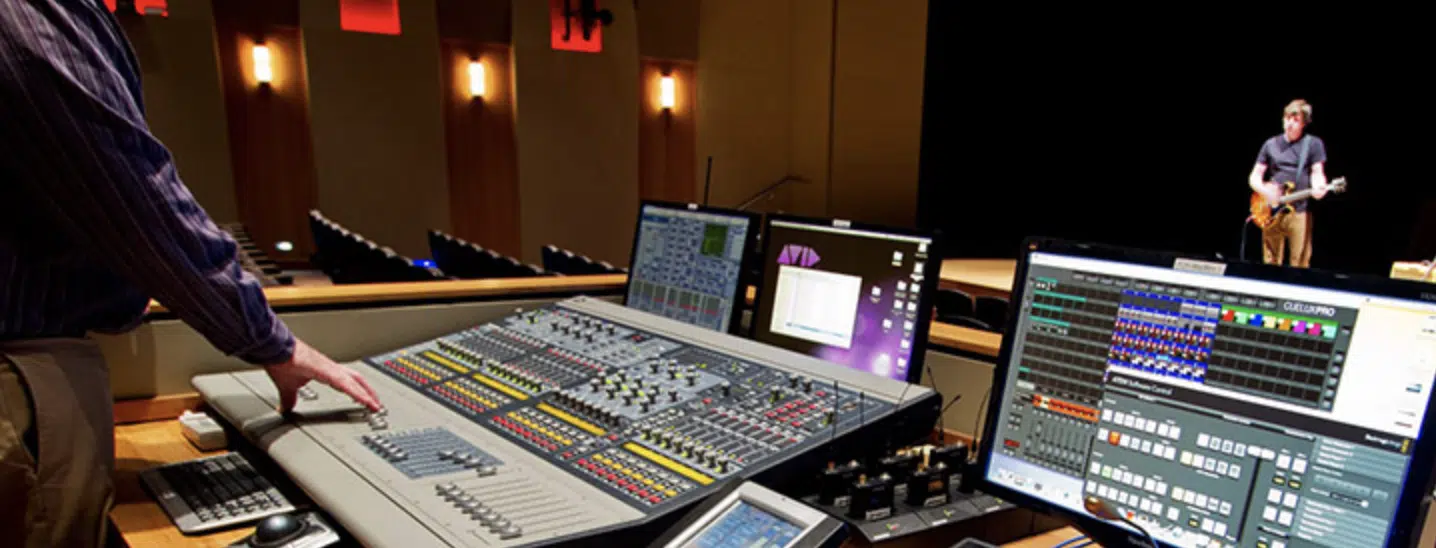

Mixing live sound is both an art and a science.
It’s about balancing the elements of the performance, adjusting levels in real time, and creating an immersive audio experience for the audience.
Take a hip-hop concert, for example…
The thumping kick drum, the booming bass, the crisp snare, the rapping; all of these elements need to come together in the mix.
- Too much bass 一 The vocals could get drowned out.
- Too little bass 一 The beats won’t hit as hard.
As a live sound engineer, you’re not just adjusting levels and mixing sound.
You’re interpreting the music, understanding the dynamics and all the technical aspects, and shaping the sound to deliver the best possible live experience.
Pro Tip: Monitor Engineers
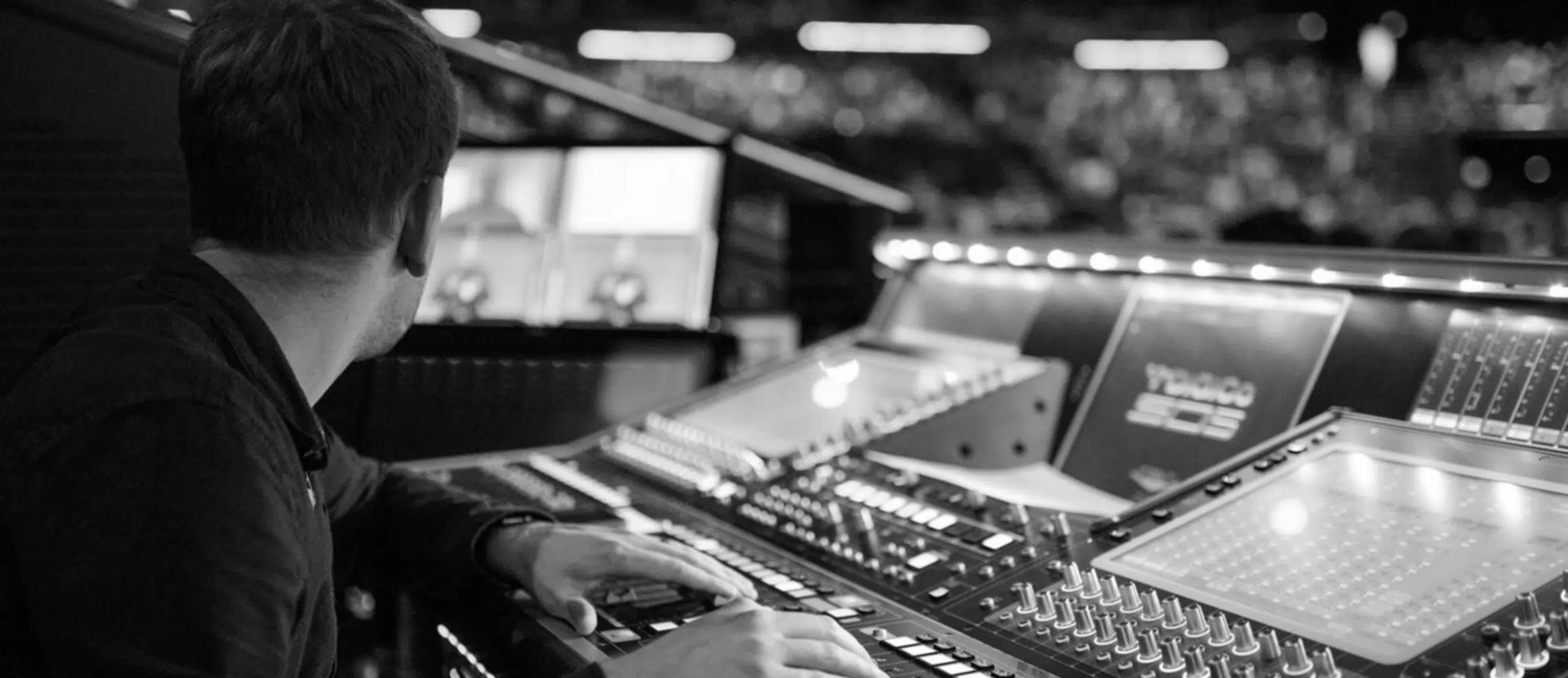

While the front-of-house engineer gets the spotlight, the monitor engineers are the silent guardians of a live show.
They’re responsible for what the artists hear on stage, which is vital for their performance.
Imagine a rapper performing to a beat.
They need to hear the rhythm clearly to stay on time.
Or a DJ syncing their tracks, they need a precise monitor mix to nail the transitions.
As a monitor engineer (or audio design engineer) you’re serving the artists, helping them give their best performance.
Advanced Concepts in Audio Engineering
With a solid foundation and practical insights in place, let’s delve deeper into the advanced aspects of audio engineering.
In this section, we’ll touch upon audio post engineering, systems engineering in the audio domain, the manipulation and mastering of sound, and the collaborative essence of music engineering.
-
Audio Post Engineering
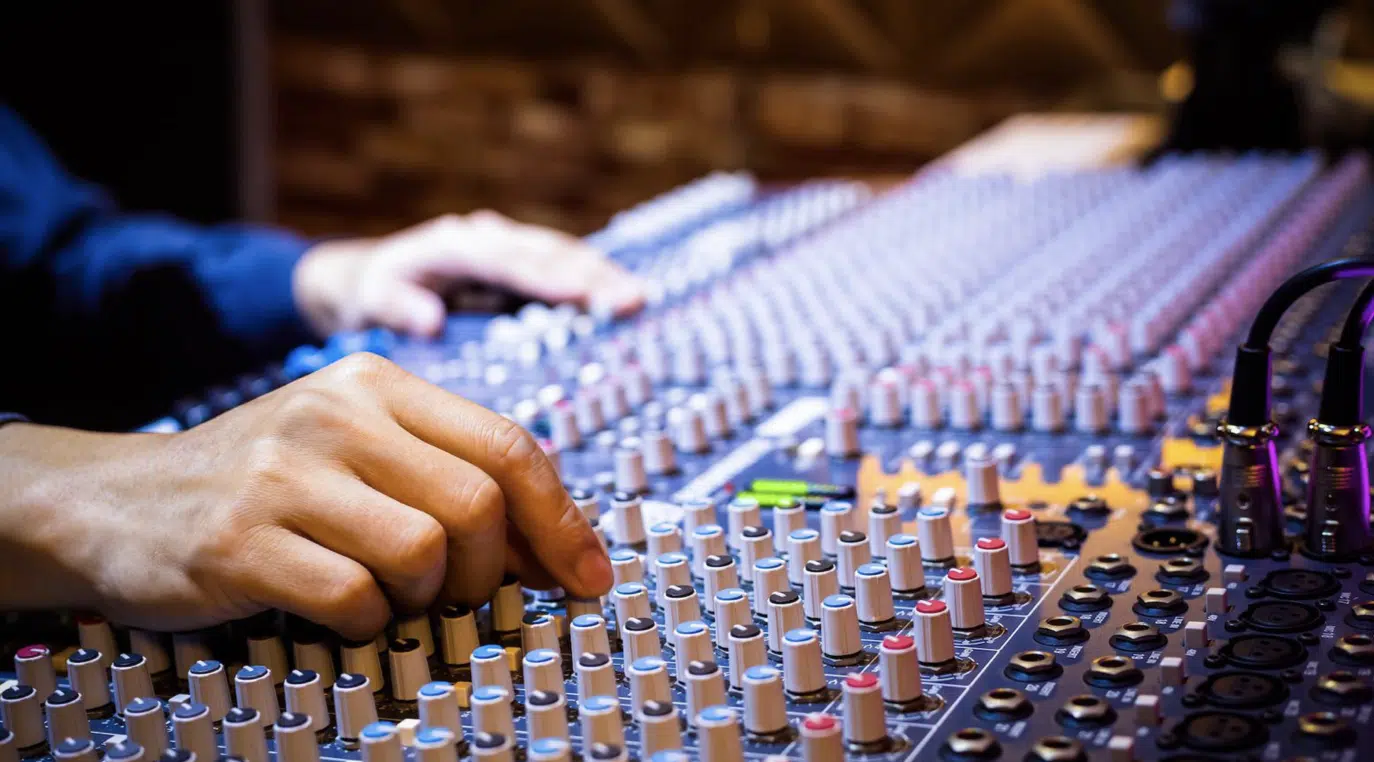

In the world of audio post-engineering, the rules can be a bit different.
This area involves the manipulation and modification of audio elements after the initial recording process (music recording).
Say you’re working on a hip-hop track that was recorded in a home studio.
The recording may be solid, but it lacks the polished sound quality of professional tracks.
As an audio post engineer, your job is to clean up and enhance that recording.
You might use noise reduction to:
- Remove unwanted background noise
- EQ to balance the frequencies
- Add audio effects to give the track a unique sound
The end goal is to create a final product that sounds professional and pleasing to the listener.
This is where the technical aspects of reproducing sound engineering truly come into play.
-
Systems Engineering
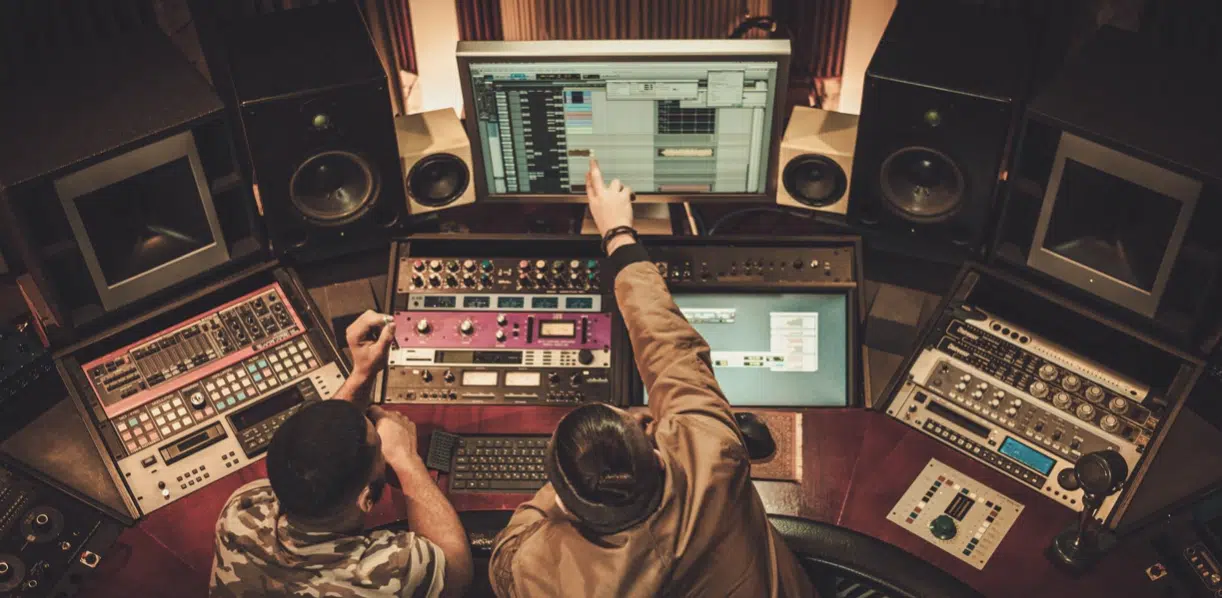

Systems engineering in audio involves looking at the big picture, considering the whole audio system from the source to the listener.
This concept is vital for both live sound and studio work.
Think about setting up a live sound reinforcement system for a concert…
You’re not just running around and plugging in microphones, speakers, and other audio equipment.
You’re considering the whole system:
- The acoustics of the venue
- The positioning of the speakers
- The type of microphones used
- The technical and mechanical aspects
- The software and hardware integration
- How all these elements work together
Or in a studio setting, you’re not just considering the microphone and the audio interface.
You’re considering the whole signal chain 一 the preamps, the cables, the converters, the monitors, and how they all interact.
Systems engineering is all about seeing the forest, not just the trees.
Armed with all the technical knowledge and skills, the question arises:how can you carve out a successful career in audio engineering?
In this section, we’ll trace the potential career paths from an assistant to a mix engineer, discuss the industry realities, and further understand the lifestyle of a professional audio engineer.
-
Career Paths: From Assistant to Audio Engineer

The journey to becoming an audio engineer is a gradual climb.
It often starts with an entry-level role such as an assistant engineer, where you’ll:
- Learn the ropes of the recording studio
- Get hands-on experience with audio equipment
- Understand the workflow of a recording session
Take my own career path, for instance.
I started as an intern at a local recording studio, where I helped set up and break down sessions, maintained the studio equipment, and soaked up as much knowledge as I could.
Over time, I worked my way up to an assistant engineer, then to a recording engineer, and finally to a mix engineer.
At this point, I was responsible for balancing the individual elements of a track to create a cohesive mix.
The journey wasn’t easy, but each step offered invaluable experience and knowledge.
Audio engineering is also a vital part of the music industry.
Without audio engineers, the polished, high-quality music we listen to wouldn’t exist.
-
Transitioning from Music Production to Audio Engineering

Making the leap from music production to audio engineering can seem like a daunting task…
But trust me, it’s a worthwhile transition that can open up a whole new world of sound and opportunity.
As someone who began as a music producer and later ventured into audio engineering, I can tell you the journey has been nothing short of exhilarating.
The first thing you need to understand about this transition is that the skills you’ve honed as a music producer 一 rhythm, melody, and harmony 一 are incredible assets to bring into the world of audio engineering.
Your understanding of song structure and musical composition lays a solid foundation upon which to build your technical skills.
However, becoming one of the best audio engineers out there means delving deeper into the scientific aspects of sound.
You’re not just shaping the musical content, but you’re also managing the technical aspects that ensure the best possible sound quality.
This involves:
- Understanding various audio equipment
- Comprehending the principles of acoustics
- Mastering the technical aspects of recording, music mixing, and mastering
When I made this transition, I had to expand my skillset beyond musical intuition.
I spent countless hours studying the physics of sound, understanding how different audio equipment works, and learning how to balance the technical and artistic aspects of sound.
It was an eye-opening experience that completely transformed how I approach music.
And you can also totally elevate how you approach music as well.
-
Audio Editing: Breaking it Down
Now, let’s talk about how different musical instruments influence audio editing.
Every instrument produces a unique timbre or tone quality, and understanding these nuances is key to achieving an optimal mix in your audio engineering work.
Let’s take, for instance, a hip-hop track I recently worked on.
The beat was thick with layers of snare drums, bass, samples, and synths, each contributing to the track’s overall sound.
The challenge?…
Each instrument has a unique frequency range that needs to be acknowledged and addressed in the mixing process.
- For the bass 一 I focused on the low-frequency range, making sure it was clear but not overpowering.
- The snare drum needed to cut through the mix 一 I focused on its mid-to-high frequencies.
- The samples and synths had a broad frequency range 一 So their placement in the mix required careful attention to ensure they complemented rather than competed with the other elements.
In essence, understanding the unique frequency characteristics of each instrument and how they interact is key to successful audio editing.
Each instrument has its own space within the mix, and a successful audio engineer knows how to make them all play nicely together.
-
Understanding Background Music

Let’s shift gears and discuss background music in music production.
Whether it’s subtle mood-setting tunes in a podcast or the score underscoring a film scene, background music plays a vital role in shaping the emotional landscape of a project.
Recently, I worked on a podcast where we utilized background music to enhance the storytelling.
We had to select pieces that complemented the tone of the narrative without distracting from the spoken content.
- Too prominent 一 The music would overshadow the story.
- Too subtle 一 It might as well not be there.
My role as an audio engineer involved delicately balancing the volume levels, ensuring the music sat well in the mix without overwhelming the dialogue.
I also paid attention to the sonic characteristics of the music, ensuring they didn’t clash with the speaker’s voice frequencies.
It’s a subtle art, but getting it right can drastically enhance the listener’s experience.
-
Bonus: Overcoming Challenges

Finally, let’s discuss the challenges you may face in music production and how to overcome them.
One of the most common difficulties is achieving a well-balanced mix.
This involves managing a wide range of elements 一 from volume levels and panning to EQ and other effects.
Consider a project I recently tackled.
It was a complex hip-hop track with multiple vocalists, intricate beats, and a handful of unexpected sound effects.
The challenge was to ensure all these elements could coexist in the mix without stepping on each other’s toes.
To navigate this, I spent a significant amount of time on detailed sound engineering.
I tweaked EQ settings to carve out a unique sonic space for each element.
I adjusted volume levels to prioritize key elements at different moments and made liberal use of panning/spatial effects to create a sense of depth and movement.
Overcoming challenges in music production involves a combination of:
- Technical knowledge
- Creativity
- Patience
- Flexibility
- A bunch of trial and error
But, as any seasoned audio engineer will tell you, the satisfaction of nailing that perfect mix makes it all worth it.
Audio Engineering: Final Thoughts
After reading this article I hope you agree that the world of audio engineering is indeed fascinating and complex.
We’ve covered everything from the fundamentals to advanced concepts, and everything in between.
But remember, knowledge is only as good as its application…
The real test begins now, and it’s time to put what you’ve learned into practice.
As you venture into your audio engineering journey, having the right resources by your side is essential.
A great starting point that I personally recommend is this insanely beneficial, completely free Beatmaker Box (teaser).
This pack is loaded with a variety of professionally-crafted loops 一 perfect for you to experiment with, tweak, and manipulate to your heart’s content.
Not only will it spark your creativity and inspire you to create phenomenal music, but it will also give you a practical playground to apply your newly-acquired audio engineering skills.
It’s all about merging your technical understanding of sound with your creative instincts as a music producer, and this Beatmaker Box is an excellent tool to facilitate that.
By combining your knowledge of audio engineering with your music production skills, you can unlock an unparalleled level of control and creativity over your sound.
This journey is challenging but equally rewarding.
So, keep exploring, keep learning, and above all, enjoy the beautiful process of crafting sound.
Until next time…







Leave a Reply
You must belogged in to post a comment.