Music staffs are fundamental frameworks in the world of music composition.
They serve as a canvas where musical ideas are painted, a guide that dictates how notes and rhythms are read, and a bridge that connects various elements.
As a digital music producer, it’s crucial to understand what a staff is because it supports every aspect of music creation.
From simple melodies to complex orchestral arrangements and everything in between.
Knowing how to navigate a staff is key to translating musical concepts into digital formats 一 ensuring your compositions are technically sound and creatively fulfilling.
In today’s article, you’ll learn:
- What is a staff in music ✓
- The role of the staff in music notation ✓
- Significance of staff lines ✓
- Understanding Middle C ✓
- The use of ledger lines ✓
- Exploring treble and bass clefs ✓
- Key signatures and their placement ✓
- Time signatures as rhythm guides ✓
- The grand staff and its importance ✓
- Tips for reading and writing staff music ✓
- Much more ✓
By the end of this article, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of what a music staff is and its significance in both traditional and digital music realms.
You’ll be equipped to read and write music with confidence and translate traditional scores into digital formats.
As well as create compositions that resonate with both technical precision and artistic expression, just like a professional.
So, let’s dive in…
Table of Contents
What is a Staff in Music?

A musical staff is the foundation of written music (sheet music) and how it’s interpreted.
It consists of five horizontal lines and four spaces, each representing a different musical pitch.
The musical staff serves as a framework for musicians to understand and communicate musical ideas effectively.
Understanding what a staff in music is can enhance the skills of anyone aspiring to read or write music.
The musical staff in music is versatile and universal.
It adapts to various musical genres and instruments 一 making it an essential tool for composers and performers alike.
The arrangement of musical notes on the staff lines and spaces determines the pitch and rhythm of the music.
This makes the staff a powerful tool for creating complex musical compositions.
The evolution of the musical staff reflects music history itself.
From its early beginnings in medieval chants to its current form in modern music notation, the staff has been integral in the development of music.
For digital music producers, understanding the musical staff is key to translating musical ideas and scales into digital formats.
The Role of the Staff in Music Notation

The musical staff plays a critical role in music notation by providing a visual representation of musical sounds.
Notes placed on the staff lines and spaces correspond to specific pitches, allowing musicians to read and perform music accurately.
This system of notation is fundamental to learning and sharing music.
Music notation on the staff goes beyond pitch representation, also encompassing:
- Rhythm
- Dynamics
- Expression
This makes it a comprehensive language for musicians.
The staff enables composers to convey their musical vision precisely and performers to interpret it with fidelity.
In digital music production, the musical staff is more than just a traditional tool 一 it’s a bridge between acoustic and digital realms.
It allows producers to visually organize and manipulate musical elements, enabling creativity and precision in their work.
The Components of a Musical Staff
The musical staff is not just a set of lines and spaces on a page; it’s a complex system with various components, each carrying significant musical information. Let’s delve into the specifics of these components to better understand their roles in music creation.
-
Staff Lines and Spaces
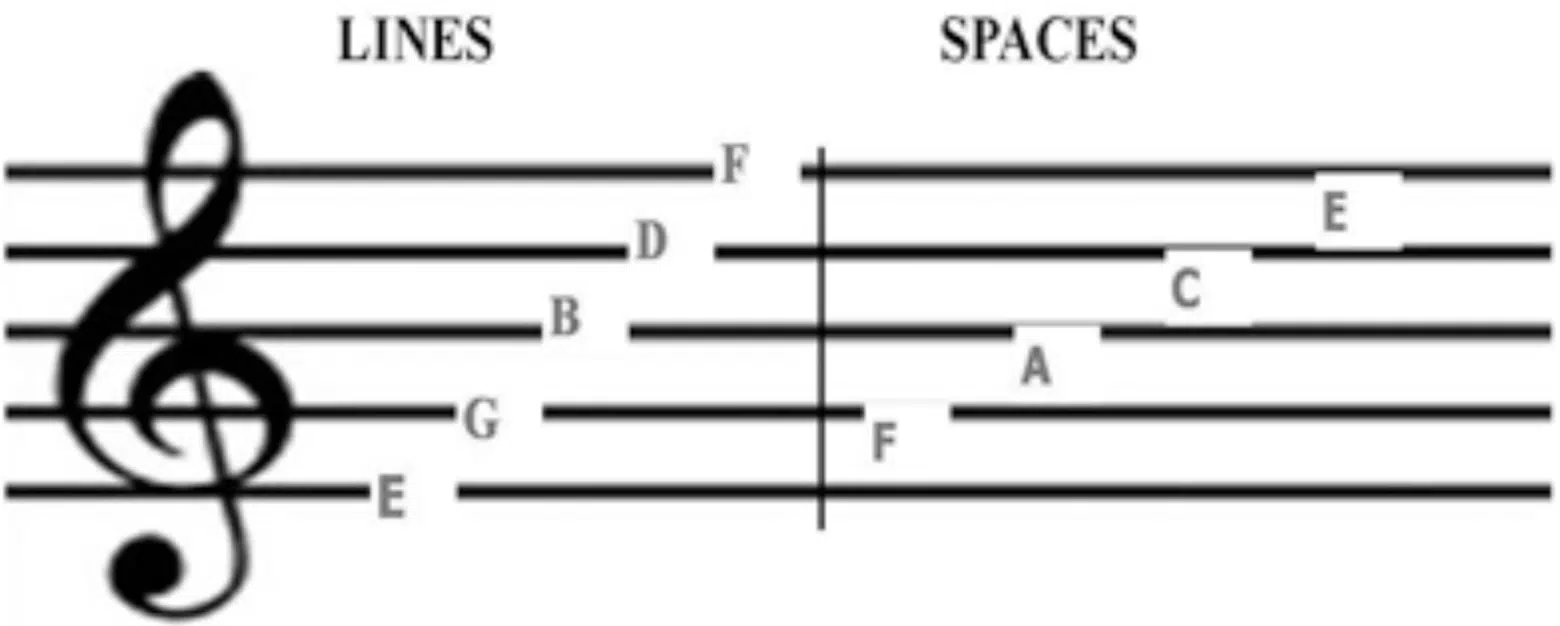
Staff lines are the backbone of music notation; each particular line represents a different musical pitch.
Between them, each space represents the corresponding pitches as well, creating a comprehensive system for music notation.
Understanding staff lines is fundamental for any musician, as they translate musical ideas into concrete symbols.
The musical staff consists of five lines (standard five line staff) and four spaces, and each, from the first line to the last, has a specific note associated with it.
This system allows for a wide range of pitches to be represented, accommodating the diverse needs of various musical instruments.
In music production, this translates to a vast array of sound possibilities.
NOTE: When a vertical line drawn at the end of a set of five parallel horizontal lines signifies the end of a musical piece, it’s important to remember that on a four line staff, this vertical line may appear slightly lower.
It will align with the top line of the staff.
The staff lines are not just static symbols 一 they interact with other elements like clefs and key signatures to give precise meaning to the individual notes.
This interaction is crucial to understanding the exact pitch and quality of the musical notes you are reading or composing.
-
The Importance of Middle C
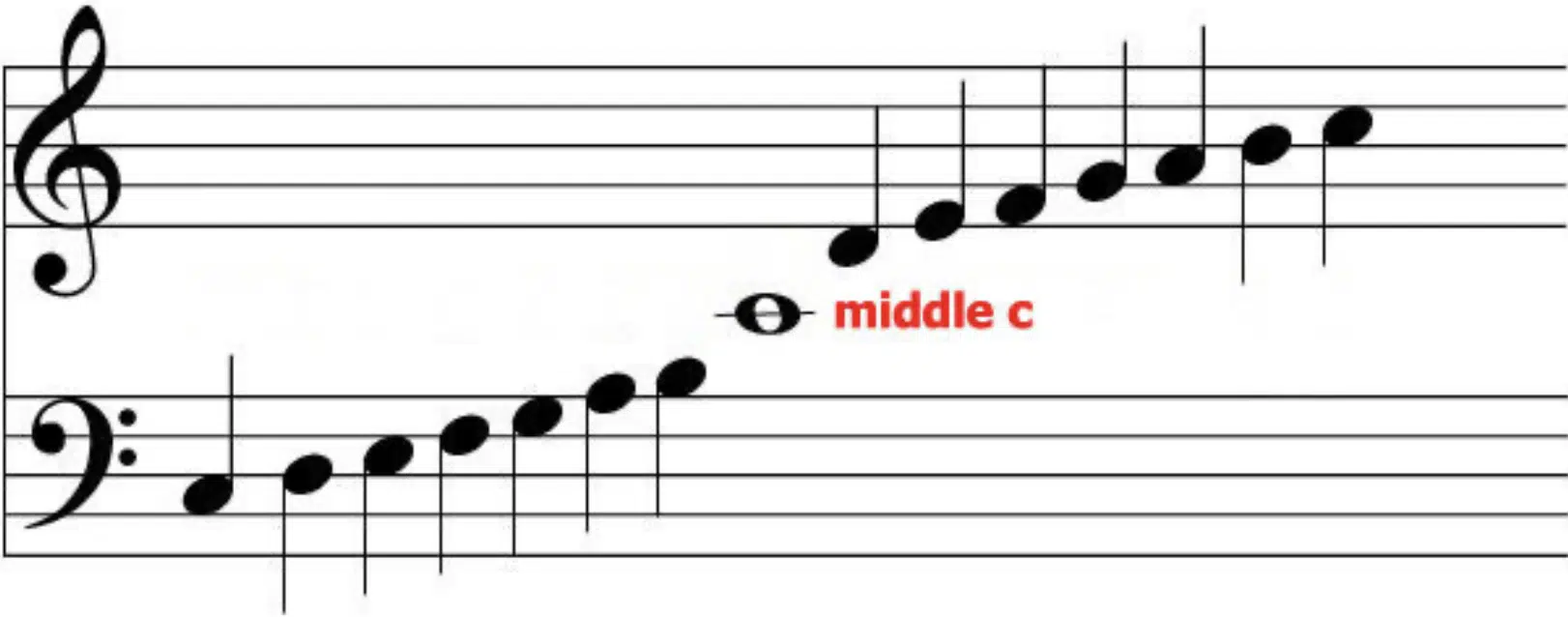
Middle C holds a pivotal position in music theory and practice.
It is the central note around which the two most common clefs 一 the treble and bass 一 are centered.
For anyone learning music, whether on traditional instruments or digital platforms, mastering the concept of Middle C is essential.
In digital music production, Middle C serves as a reference point for:
It helps producers maintain pitch consistency across various digital/keyboard instruments and tracks.
Understanding its position on the musical staff also aids in transposing music effectively.
Middle C’s significance extends to its role as a bridge between the treble and bass clefs, forming the grand staff.
This makes it indispensable in complex compositions, especially in orchestral and choral music, where a wide range of different musical pitches is required.
-
Key Signatures and Their Placement

Key signatures are an integral part of music staff, positioned at the very beginning of each line.
They indicate the key of the piece by showing which individual notes are to be played as sharps or flats throughout.
This simplifies the notation and provides a clear understanding of the harmonic structure of the piece.
For digital music producers, a key signature is essential for maintaining harmonic consistency in their compositions.
A key signature guides you in choosing appropriate chords and melodies that align with the overall tonal center of the piece.
Key signatures also play a crucial role in transposing music for different instruments (like a percussion instrument) or voices.
This is particularly important in digital music production, where a single composition may be adapted for various synthetic sounds or virtual instruments.
-
What Makes the Grand Staff Essential
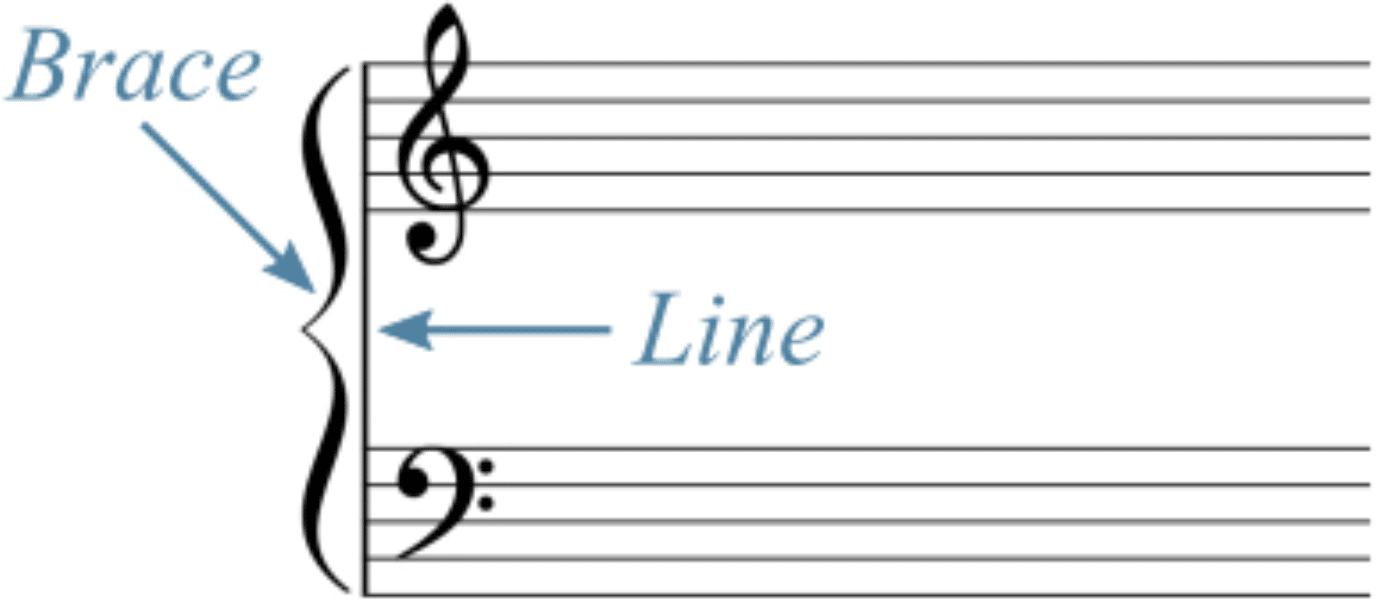
The grand staff, a combination of the treble and bass staffs connected by a brace, is essential for music that spans a wide range of pitches, like piano keyboard music.
It allows for a seamless integration of high and low pitches, creating a full sound spectrum.
For digital music producers, the grand staff provides a comprehensive view of the musical landscape.
It aids in composing layered pieces where multiple instruments or sounds are played simultaneously, ensuring that each element is in its correct pitch range.
The grand staff is not just a tool for notation 一 it’s a visual guide that helps you conceptualize and organize your musical ideas.
It’s particularly beneficial in genres that require intricate arrangements, such as orchestral or complex electronic music.
Diving Deeper: Ledger Lines and Clefs
As we explore further into the intricacies of the musical staff, ledger lines, and different clefs emerge as critical elements. These aspects enhance the staff’s ability to convey a broader range of musical pitches and nuances.
-
Understanding Ledger Lines in Music
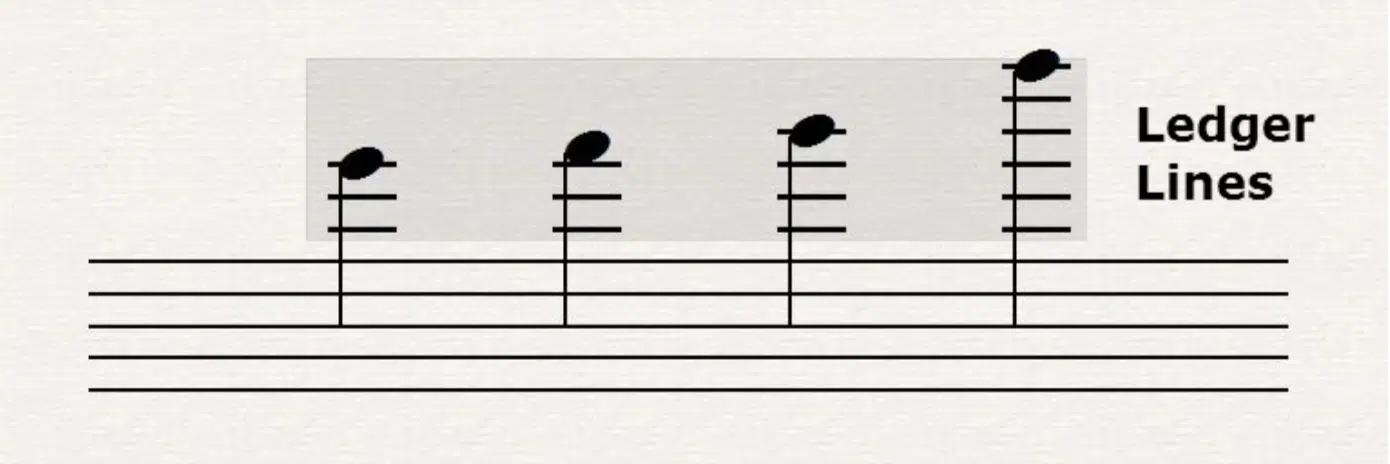

Ledger lines extend the range of the staff beyond its standard five lines.
They appear as short horizontal lines above or below the staff, allowing for the notation of pitches that fall outside the main staff lines.
Ledger lines maintain the same sequential order of notes, providing continuity in musical notation.
Understanding what a ledger line is, is crucial for composing and arranging music that spans a wide range of pitches.
A ledger line offers the flexibility to write complex melodies and harmonies that go beyond the limitations of the standard staff.
The application of ledger lines (like the first ledger line) in music notation follows a systematic approach that preserves the linear progression of notes.
This ensures that even when notes venture far from the central staff, their pitch relationships remain clear and consistent.
This aspect is particularly useful in music production, where visual clarity in notation can greatly aid in the composition process.
NOTE: When a note is written on the top line of one of the two staves, it makes sense to compare its pitch with notes placed on the fourth line or the second line.
Or, even in the space above or below to understand their harmonic relationship.
-
Exploring Different Clefs: Treble and Bass
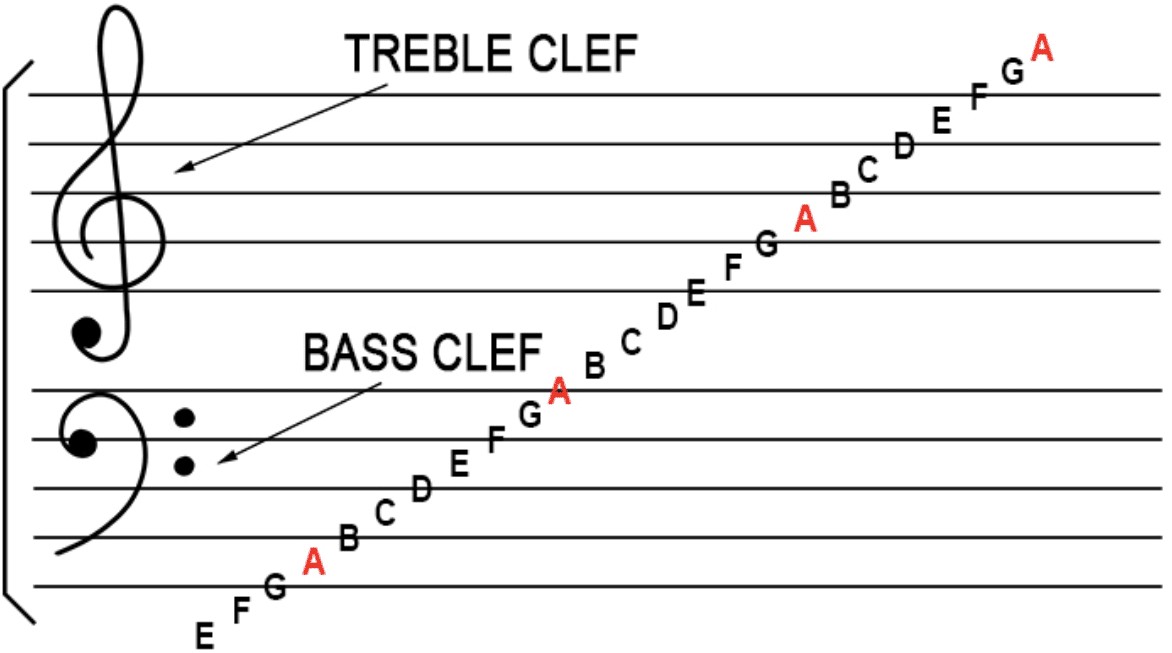
Clefs are symbols placed at the beginning of the musical staff to indicate the pitch of the notes.
The two most common clefs in sheet music are the treble clef and the bass clef.
- The treble clef, associated with higher-pitched instruments and voices, spirals around the G clef note above Middle C.
- The bass clef, used for lower pitches, centers around the F note below Middle C.
Understanding these clefs is crucial for musicians, as they determine the note names for each particular line and space on the staff.
In digital music production, this knowledge is essential for accurately creating and interpreting music across various software and synthesizers.
The use of these clefs goes beyond traditional instruments.
In the digital realm, they help in visualizing how different sounds and frequencies interact within a composition.
Therefore, enhancing the producer’s ability to craft balanced and harmonically rich music.
Special Staff Types and Their Uses
Music notation also includes special types of staff, each catering to specific musical needs. Exploring these staffs reveals the versatility of music notation in accommodating various musical styles and instruments.
-
The Percussion Staff and Its Unique Features
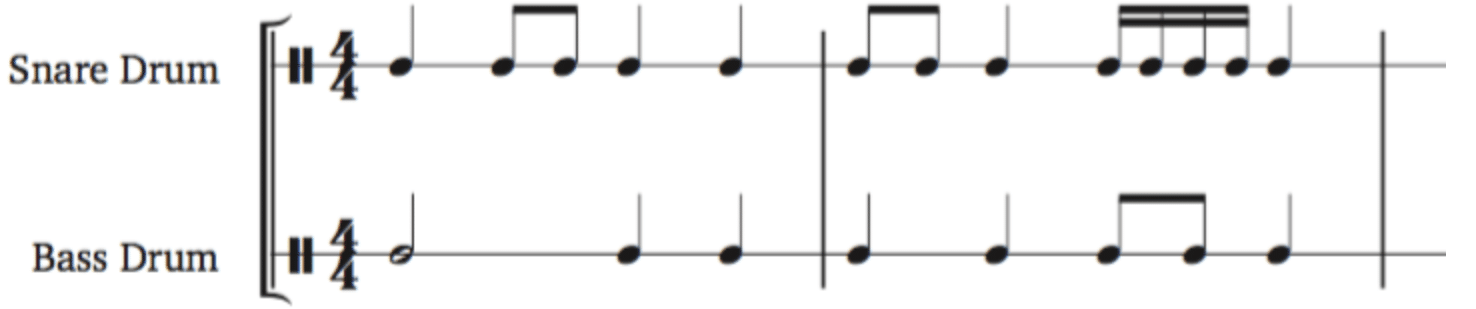
The percussion staff, often using a single line or a simplified staff, is tailored for non-pitched percussion instruments.
Unlike traditional staffs, it uses note symbols to represent different percussion sounds rather than pitches.
The percussion staff is instrumental in programming:
- Drum patterns
- Rhythmic sequences
It provides a clear and concise way to visualize and arrange complex rhythmic components within a composition.
-
Treble Staff and Bass Staff in Digital Music Production

The treble staff and bass staff are not only fundamental in traditional music notation but also in digital music production.
They serve as a visual guide for producers to map out:
- Melodies
- Basslines
- Harmonies
It facilitates a structured approach to composition.
The separation of treble staff and bass staff allows for greater clarity in arranging different elements of a composition.
In digital music production, this clarity is crucial when layering multiple tracks and ensuring that each element sits well in the mix.
Producers can more effectively balance the high and low frequencies 一 creating a more harmonious and dynamic track.
The integration of the treble staff and bass staff in digital music interfaces also simplifies the process of transcribing and modifying music.
Producers can easily switch between other clefs to accommodate a variety of instruments, from synthesizers to sampled sounds.
Practical Tips for Reading and Writing Staff Music
Mastering the art of reading and writing music on a staff is essential for any music producer. Here are some practical tips to enhance these skills.
-
Techniques for Mastering Staff Reading

Familiarity with note names and their positions on the musical staff is the first step toward mastering staff reading.
Regular practice with different types of music can help solidify this knowledge, making it easier to read and interpret musical scores quickly.
Utilizing technology, such as piano music notation software or digital learning tools, can also aid in improving staff reading skills.
These tools often offer interactive exercises and real-time feedback, which can be particularly beneficial for those transitioning from traditional to digital music production.
-
Writing Effective Music Notations on a Staff
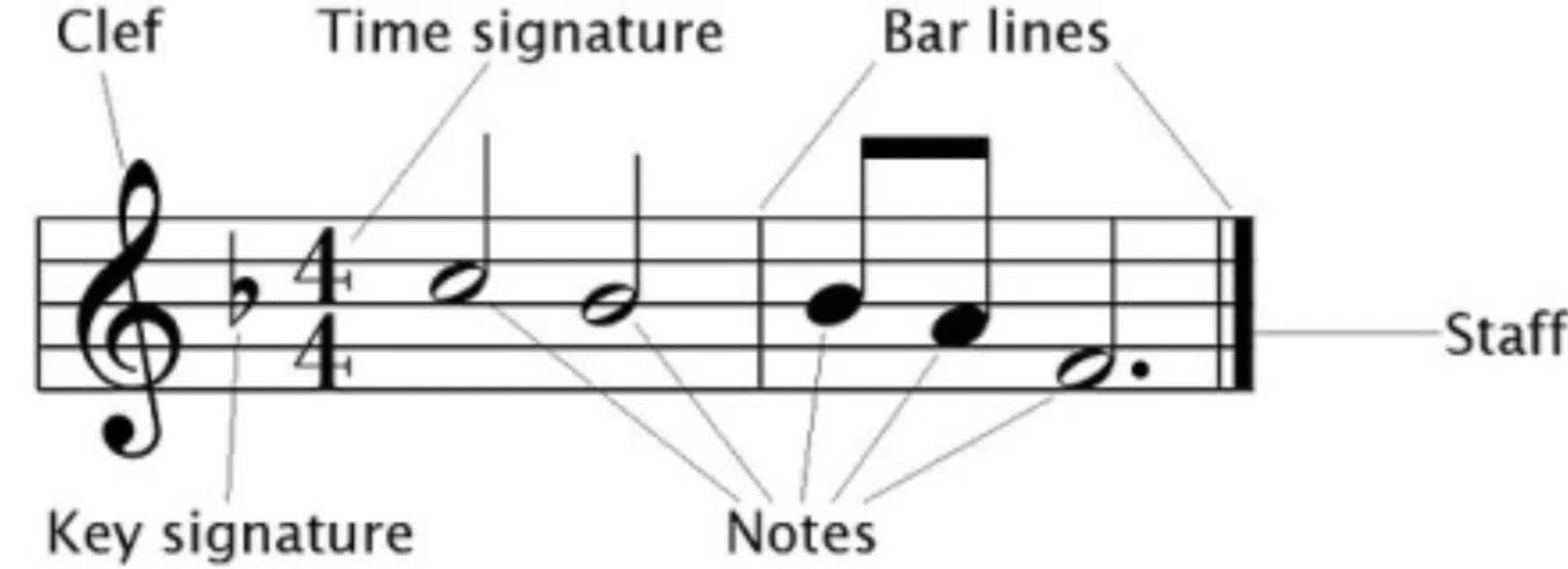
Writing music on a single staff requires a clear understanding of musical symbols and their correct placement.
This includes:
- Notes
- Rests
- Clefs
- Key signatures
- Time signatures
They keep notations neat and well-spaced, making the written music easier to read.
Software tools offer advanced features for writing and editing music notations.
These tools allow for precise control over every aspect of the notation, from note duration to dynamics 一 enabling the creation of detailed and accurate musical scores.
It’s also important to develop a personal style of notation, especially when transcribing original compositions.
This can include unique markings or annotations that make the music more expressive or easier to interpret during production.
What is a Staff in Music? Final Thoughts
The staff is not just a set of lines on a page, but a powerful tool that bridges the gap between traditional music theory and modern digital production.
Understanding “What is a staff in music,” from its basic lines and spaces to more complex elements like key signatures and clefs, is crucial for any digital music producer.
It enhances your ability to read, write, and conceptualize music, helping you translate musical ideas into digital formats with precision and creativity.
Whether it’s mastering the grand staff or interpreting complex rhythms, the knowledge you’ve gained here is invaluable.
To further aid your journey as a music producer, you have got to check out the legendary Free Project Files pack.
This indespensible resource contains three free project files, each available in Ableton, FL Studio, and Logic Pro formats.
These project files are not just templates 一 they are gateways to applying what you’ve learned about music staffs in a practical, hands-on manner.
For Logic users, there’s an additional benefit.
You can convert the MIDI data from these project files into score data, allowing you to see it represented on a staff.
This is a fantastic opportunity to compare the traditional staff notation with the piano roll data you’re used to, providing a tangible way to see the theory in action.
It can deepen your understanding and appreciation of music notation, which makes it an essential tool in your production toolkit.
Remember, the journey of music production is continuous, and each new piece of knowledge adds depth to your tracks.
Embrace the staff, experiment with the project files, and watch as your compositions evolve into richer, more nuanced creations.
Until next time…







Leave a Reply
You must belogged in to post a comment.