EQing is the heartbeat of music production.
Dive into any chart-topping hip-hop track, and beneath those fiery bars and addictive hooks, you’ll discover the art of Equalization.
The art of manipulating frequencies to carve out space for every instrument, vocal, and sound in a mix is paramount for a clean and professional-sounding track.
And at the core of this art is the EQ frequency chart 一 a visual representation of the audio spectrum that can guide your mixing decisions.
However, without an understanding of the EQ cheat sheet, understanding the intricacies of frequencies might seem like a daunting task.
But don’t worry, we’ll be breaking down every aspect of the EQ frequency chart and providing insights that will make your mixes shine.
In today’s article, we’ll be covering:
- The frequency spectrum ✓
- EQ cheat sheets ✓
- Different instruments & frequencies ✓
- Navigating the EQ chart ✓
- Mastering frequency ranges ✓
- Various frequency charts ✓
- Advanced EQ techniques ✓
- Common EQ challenges & how to solve them ✓
By the end of this read, you will fully understand the EQ frequency chart inside and out.
Plus, be ready to EQ your tracks like a champ; ensuring every beat, lyric, and melody sits perfectly in your mix.
So, let’s dive in…
Table of Contents
What is the Frequency Spectrum?

Imagine a vast canvas where every shade of color represents a unique sound… that’s the frequency spectrum for you.
A vast array of frequencies; from the deep rumbles to the high-pitched shrills.
Each frequency has its place and unique signature.
The human hearing spectrum generally ranges from 20Hz to 20kHz.
In this range, every instrument, every voice, and every beat finds its sweet spot.
From the sub-bass region that vibrates your very soul to the treble that provides the shimmer 一 every sound is a frequency.
Digital music (and more so hip-hop) thrives on manipulating this spectrum.
A kick might need more punch, a vocal might require clarity, and so on.
All of this is achievable by understanding and manipulating the frequency spectrum.
By doing so, you can master EQ like a true professional.
Decoding the Frequency Range
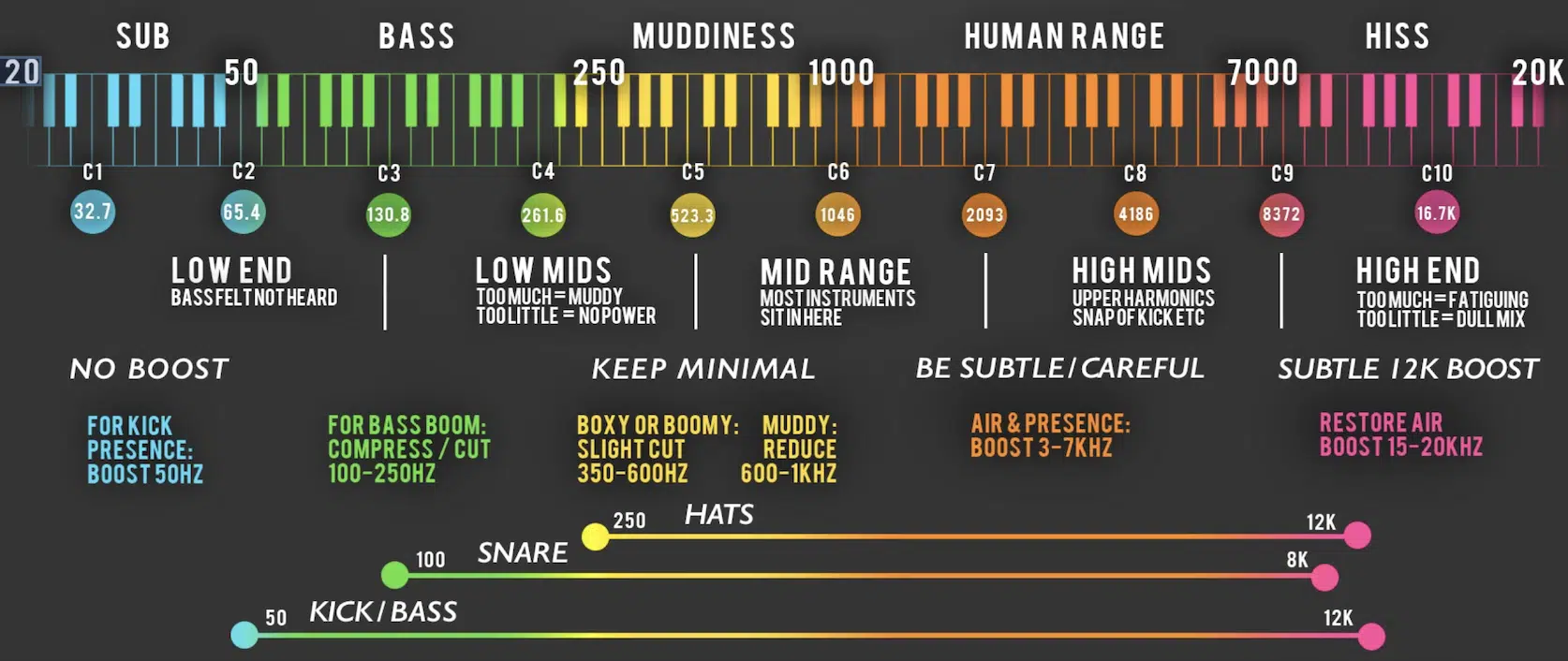
Every sound you hear falls into a specific frequency range.
The rumble of thunder or the roar of an engine lies in the lower frequencies.
On the contrary, the chirping of birds or the tinkle of a bell lies in the higher frequencies.
These frequency ranges play a crucial role in mixing music, where each element has its unique space.
For instance:
- A snare 一 Might pop in the mid-range.
- The hi-hats 一 Sizzle in the higher frequencies.
In turn, EQ frequency charts have become the key to decoding these ranges.
It not only shows where a particular sound might reside but also helps identify spaces where sounds can be layered or isolated.
Instruments are the soul of a track; in the frequency spectrum, each instrument carves out its niche.
A piano might sprawl across multiple frequency bands, while a flute might nestle comfortably in the mids to highs.
Understanding where an instrument sits in the frequency spectrum can make or break a mix.
This is especially important when layering multiple instruments.
No one wants a muddy mix where the bass guitar is clashing with the kick drum.
Whether it’s creating space for a sample or ensuring that the 808s don’t overwhelm the vocals, knowing your instrument’s frequency is paramount.
NOTE: The “fundamental frequency” refers to the lowest, most dominant tone produced by any musical instrument or sound source.
It’s the exact frequency that gives a note its recognizable timbre and pitch in a mix.
A Deeper Dive into EQ Cheat Sheets
While the frequency spectrum is the canvas, EQing is the art of painting on it.
But what if you had a cheat sheet to master this art?
Enter: EQ Cheat Sheets.
-
What Exactly is an EQ Cheat Sheet?
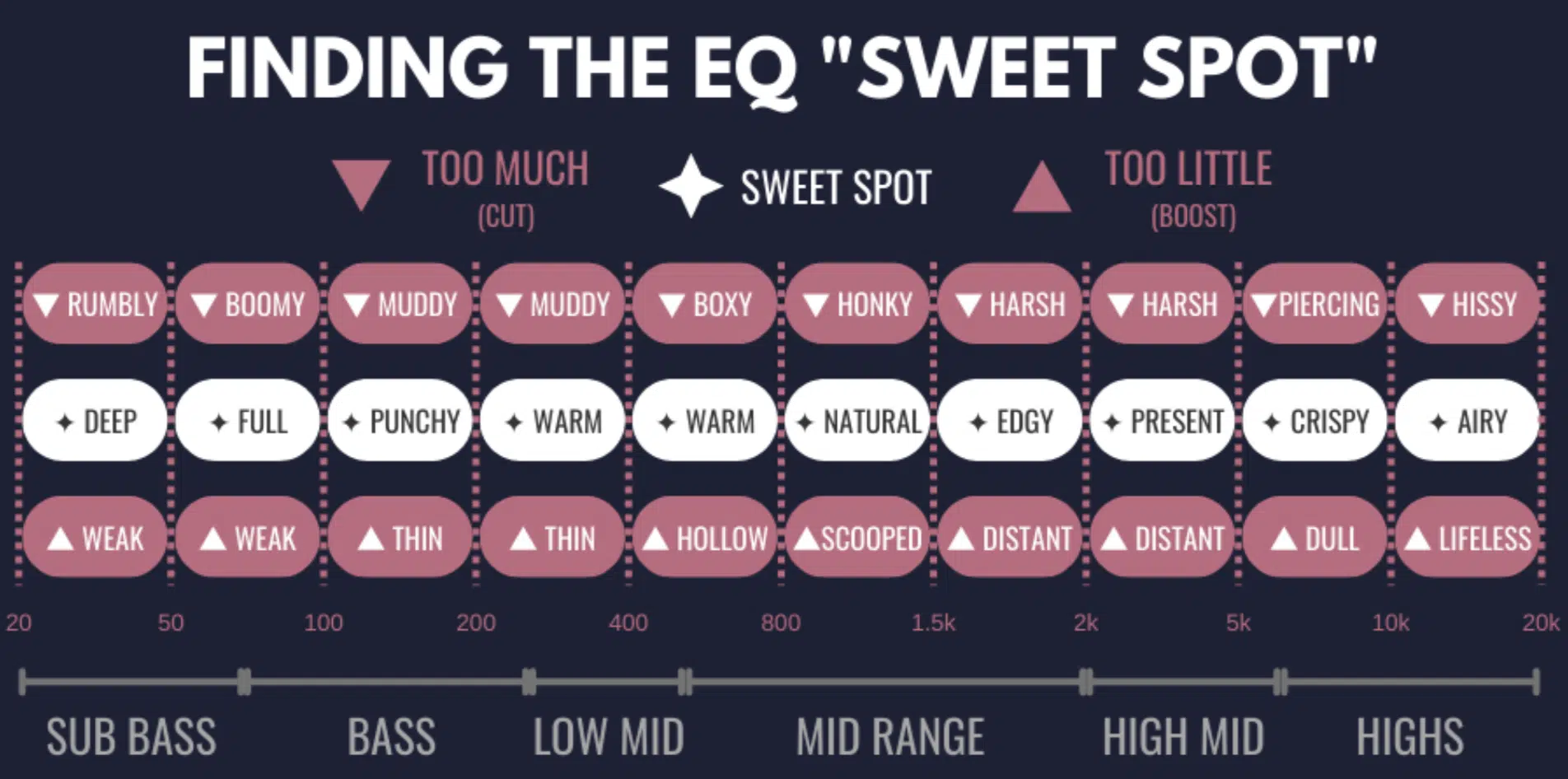
Think of the EQ cheat sheet as a reference guide that breaks down the complex world of frequencies into bite-sized chunks.
It’s a tool that showcases the fundamental frequencies of various instruments; helping you identify where each instrument typically sits within the frequency spectrum.
For instance:
- Kick Drums 一 Often, they have a punchy thud around the 50-100Hz mark.
- Vocals 一 For a typical male rapper, you might find the richness lies somewhere between 85-155Hz, while the clarity or presence might shine through around 4kHz-9kHz.
When you’re juggling multiple sounds in a mix, the EQ cheat sheet can act as a roadmap.
By comparing the frequency ranges of different instruments, you can make sure that they don’t clash.
Ever noticed how a bass guitar and kick drum might fight for the same space?..
A glance at the EQ cheat sheet will show that they often occupy similar frequency ranges, nudging you to carve out unique spaces for both.
By highlighting where each instrument usually sits and pointing out potential frequency overlaps, it offers clues to where issues might arise.
In essence, the EQ cheat sheet demystifies the process of mixing 一 making it less of an overwhelming task and more of a strategic game of placing every piece.
With this tool in hand, you’re already several steps ahead in the mixing game.
-
EQ Cheat Sheets vs. The Traditional EQ Frequency Chart
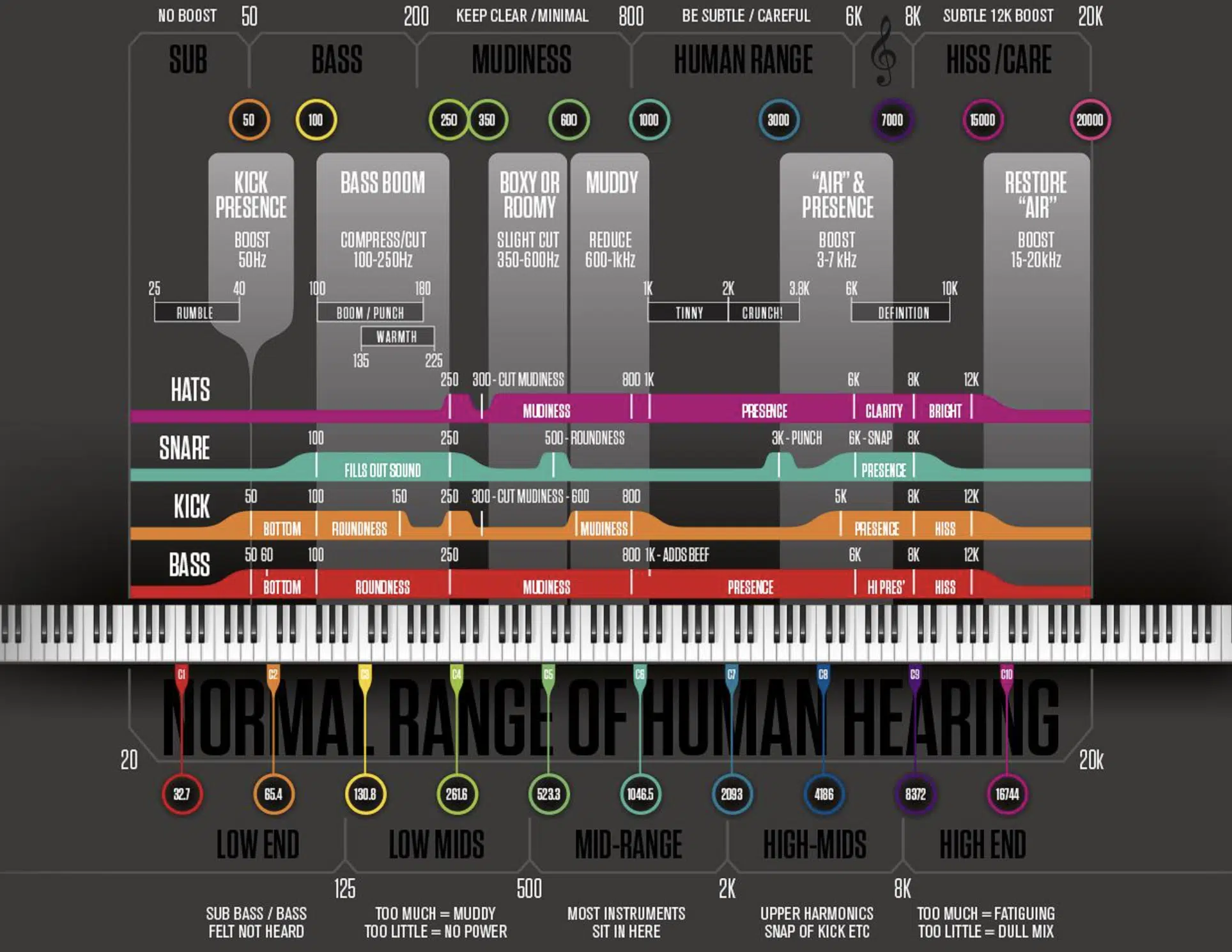
While both the EQ cheat sheet and the traditional EQ frequency chart are rooted in the frequency spectrum, they serve different purposes.
An EQ frequency chart is like a map (showing the terrain) and the EQ cheat sheet is the GPS (guiding you to your destination).
A traditional EQ frequency chart will show you the frequencies, maybe even where certain instruments typically reside.
While an EQ cheat sheet tells you where to:
- Boost in order to add warmth to your bass
- Cut to remove the muddiness from your mix
For a hip-hop producer, especially in the digital realm, time is essential.
While understanding the traditional EQ frequency chart is foundational, having a cheat sheet is like having a mentor guiding your EQ moves.
It ensures that every beat, sample, and loop is in its prime sonic space.
Learning the differences between the EQ cheat sheet and EQ frequency chart is vital to mastering EQ as a whole.
Instruments & Their Frequencies
Recorded instruments and digital instruments, with their varying tones and textures, paint the musical canvas.
But to truly appreciate and harness their power in a mix, we must understand where they sit on the frequency spectrum.
-
Acoustic Guitar

The acoustic guitar, with its rich harmonics and vibrant strumming, has a broad presence in the frequency spectrum.
Its low end can start from around 80Hz, going up to a bright 5kHz or even higher.
However, the “magic spot” for an acoustic guitar often lies in the mid-range (around 200Hz to 1kHz).
This is where the body and warmth of the instrument shine through.
Think of the intro to “Blackbird” by The Beatles… the depth and resonance you hear are primarily emphasized in this magic spot.
But there’s also the sparkle, the shimmer of the acoustic guitar.
This can be found in the higher frequencies 一 between 2kHz to 5kHz.
Boosting these frequencies can bring out the clarity of individual plucked strings, making every note stand out.
-
Bass Region: Where Acoustic Bass and Bass Guitar Lie

The bass region, ranging roughly from 20Hz to 250Hz, is where the heartbeat of most songs lie.
Acoustic bass and bass guitar mainly occupy this region 一 providing the foundational groove.
An acoustic bass, such as the one you might hear in a jazz ensemble, usually has a more rounded and full-bodied sound.
Its sweet spot tends to lie in the 60Hz to 100Hz range.
Therefore, boosting these frequencies can give the acoustic bass a more pronounced presence.
In contrast, the electric bass guitar in hip-hop tracks (especially when slapped or plucked) can have pronounced frequencies around 200Hz to 500Hz.
This is where the “pluck” or the “snap” of the bass string stands out.
A great example would be the iconic bassline in “Billie Jean” by Michael Jackson; the clarity of each note is achieved by emphasizing these mid-bass frequencies.
-
Percussion Instruments: Finding the Rhythm’s Frequency

Percussion is the backbone of rhythm.
From the deep thud of a bass drum to the sharp crack of a snare, each percussion instrument occupies a unique space on the spectrum.
The kick drum (especially the sought-after 808) usually has a dominant frequency around 60Hz for that sub-bass feel.
However, it also has a ‘click’ or ‘snap’ often around the 2kHz-4kHz range.
This helps it cut through in dense mixes.
Snares and claps, staples in hip-hop beats, typically pop around the 200Hz for body 一 but their crispness and snap are emphasized around the 2kHz to 4kHz range.
Take, for instance, the snare in Dr. Dre’s “Still D.R.E.”
It’s sharp, clear, and slices through the mix, primarily due to its presence in the higher mids.
-
The Vital Presence of Vocals & Their Frequencies
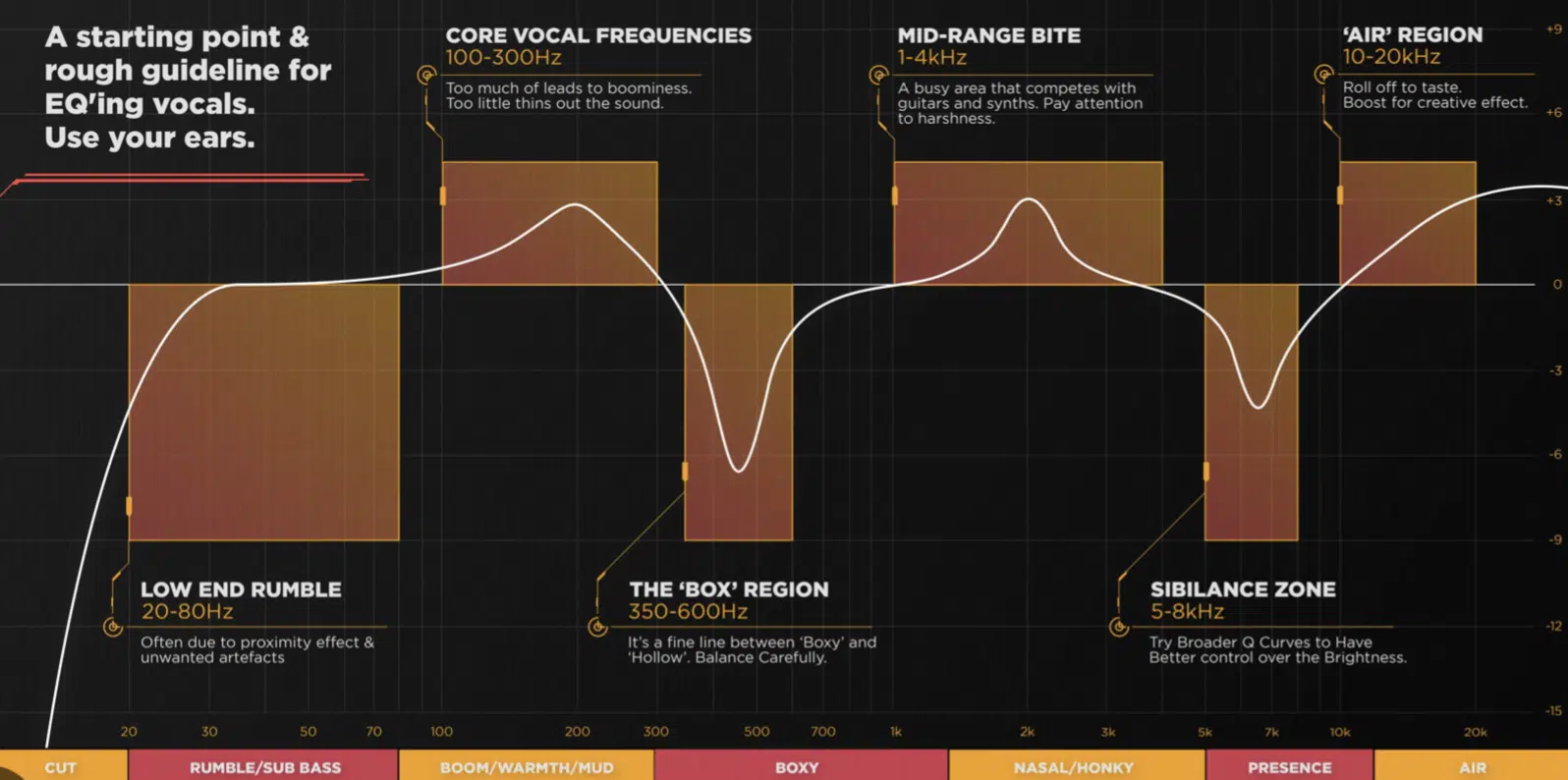
Vocals are the soul of hip-hop.
Whether it’s the lyrical prowess of Kendrick Lamar (male vocals) or the melodic flows of Ariana Granda (female vocals), vocal presence carries the message and emotion of the genre.
In terms of frequency, vocals primarily lie between 300Hz and 3kHz.
However, they can extend well into the upper mids an higher frequencies due to sibilance and airiness.
The challenge is ensuring the vocals are crisp, clear, and central in the mix; especially with dense instrumentals or powerful beats.
EQ techniques for vocals can vary:
- A slight boost around the 1kHz to 3kHz range 一 Can add clarity.
- A dip in the lower mids 一 Might reduce muddiness.
Cutting problematic high frequencies can reduce harshness, ensuring the vocals sit perfectly in the mix.
If you’d like to learn how to EQ vocals like an expert, we’ve got you covered.
‘
The EQ chart is the map of the sonic world.
With it, artists and producers (like you) can navigate the intricate landscapes of sound and make informed decisions to craft their masterpieces.
-
Importance of the Instrument Frequency Chart
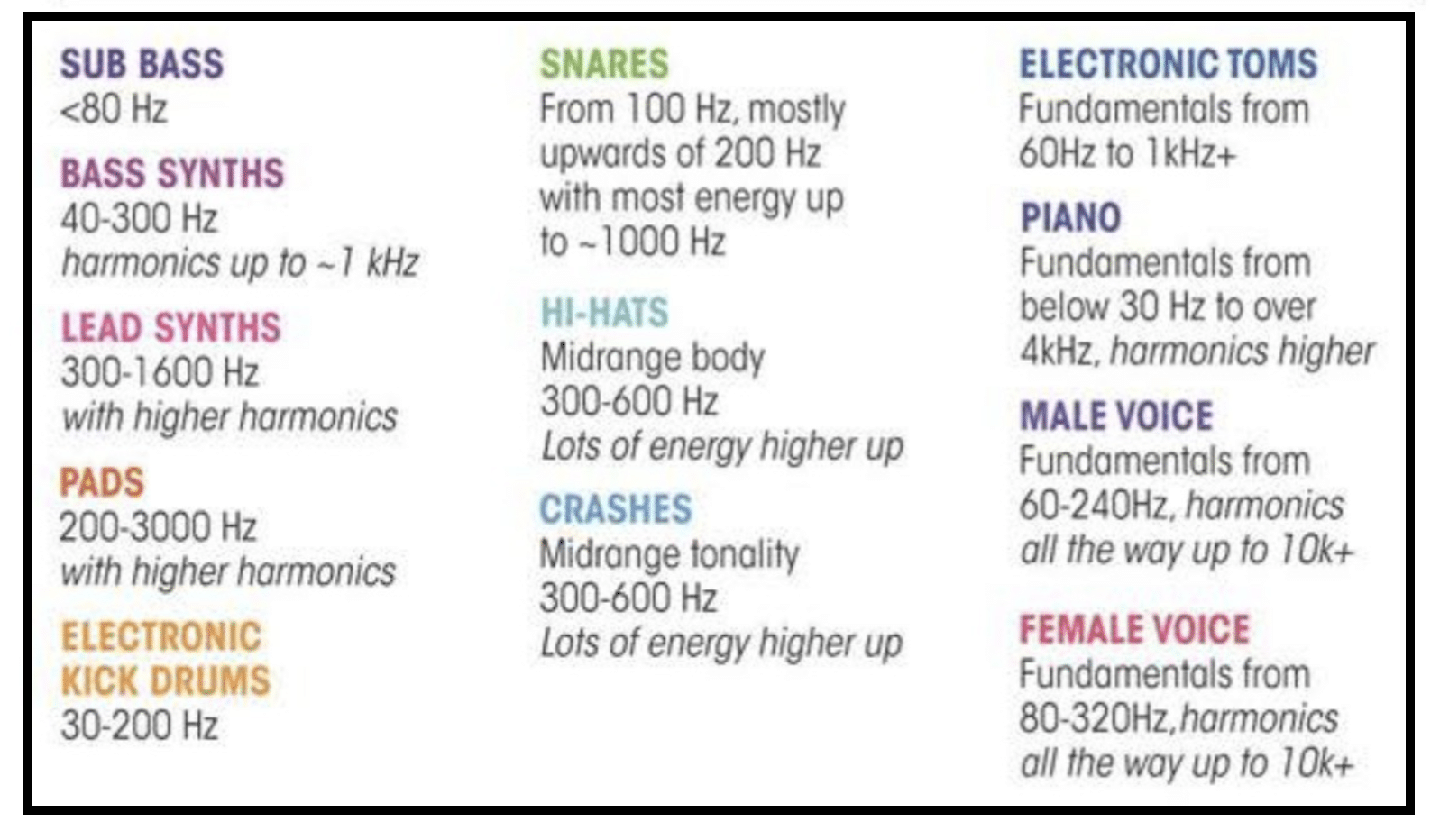
As many instruments as there are, every single one, from the delicate flute to the roaring rock guitars, has a distinct frequency profile.
The instrument frequency chart is a visual representation of these profiles 一 guiding producers and sound engineers in their mixing decisions.
For instance, when looking to layer a violin over a piano in a hip-hop track, you might consult the chart to ensure there’s minimal frequency clashing.
The violin, with its prominence in the 200Hz to 1kHz and brilliance around 2kHz to 5kHz, should complement the broad-ranging frequencies of the piano.
The chart becomes even more crucial in complex mixes.
Imagine a hip-hop track infused with elements of jazz, including different instruments like:
- Saxophones
- Trumpets
- Double bass
Each instrument has its unique frequency footprint.
Balancing them to achieve clarity without sacrificing the vibe becomes a task made manageable with the instrument frequency chart.
-
Recognizing Different Frequencies
Training one’s ear to recognize different frequencies is a skill that comes with time and practice.
It’s about listening actively and understanding how different frequency boosts or cuts impact the overall sound.
For example, a muddy mix might often be attributed to an accumulation in the 200Hz to 500Hz range.
Similarly, if vocals sound too harsh or piercing, there might be an excess of frequencies in the 2kHz to 5kHz zone.
By identifying these nuances you can take corrective actions.
Tools like spectrum analyzers (which we’ll delve into next) can aid in this recognition process.
But nothing beats the trained ear!
Listening to tracks critically, maybe even using reference tracks, and experimenting with EQ adjustments can fast-track this learning process.
-
The Power of a Spectrum Analyzer
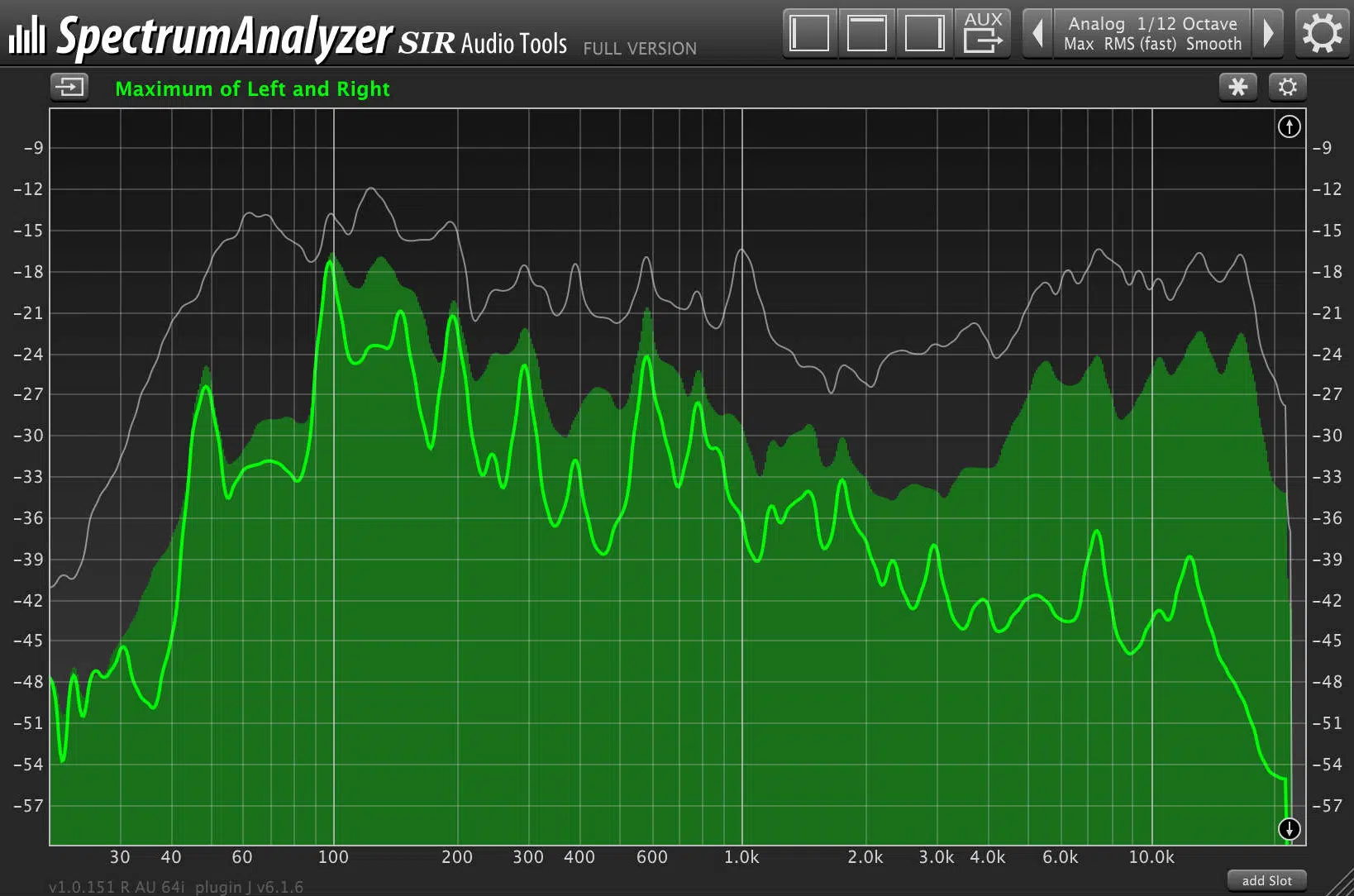
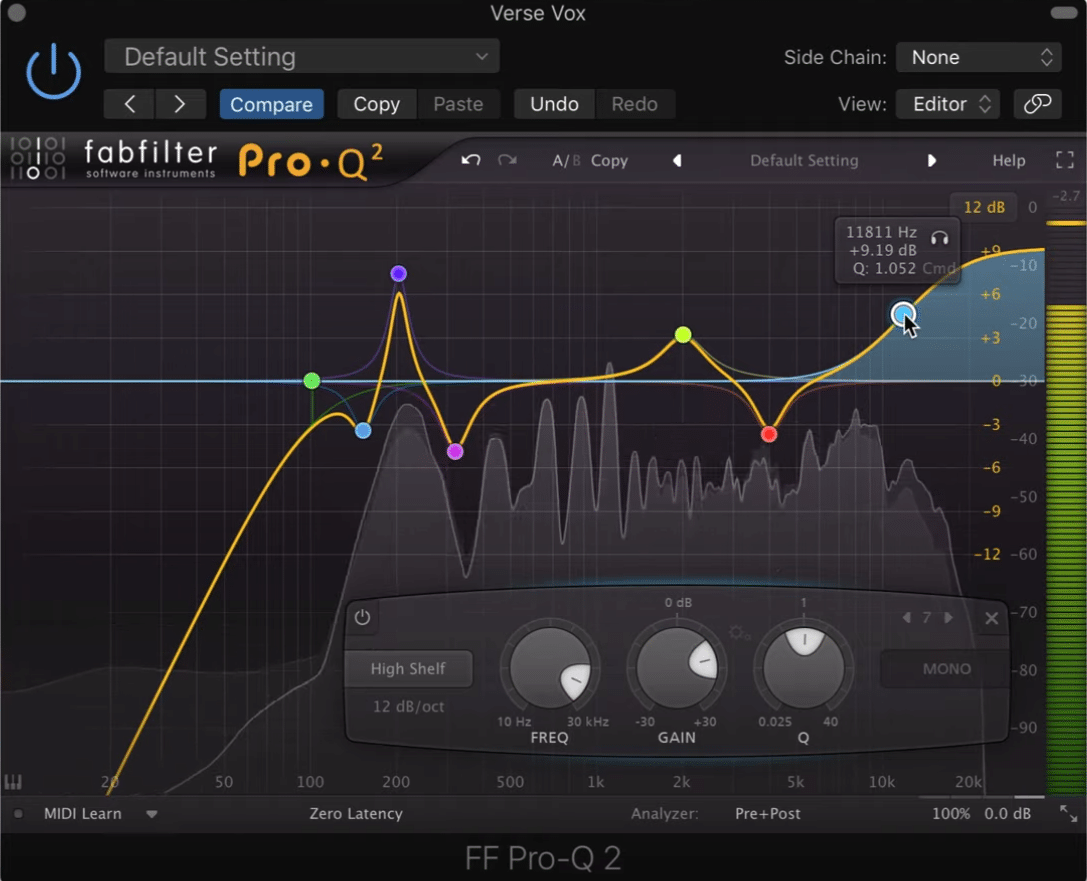
A spectrum analyzer is a visual tool that shows the amplitude of different frequencies in real-time.
By using a spectrum analyzer during the mixing process, you can:
- Spot problematic frequency build-ups.
- Identify areas that don’t have too much energy.
A spectrum analyzer is a resource that sound engineers (or a mixing engineer) utilize all the time.
If, for instance, there’s a peak consistently appearing at 3kHz, and it’s making the mix sound shrill, it can be tamed using EQ.
For hip-hop producers, where samples from various sources are often integrated into a single track, a spectrum analyzer can be a lifesaver.
This valuable tool helps ensure that the sample sits well in the mix 一 without overwhelming existing elements.
Consider Kanye West’s use of samples in his tracks…
The seamless integration (where every element has its space) is achieved with tools like spectrum analyzers guiding the way.
Mastering the Different Frequency Ranges
To achieve a balanced and full-bodied mix, it’s essential to understand and master the intricacies of different frequency ranges.
So, let’s dive right in:
-
The Sub Bass
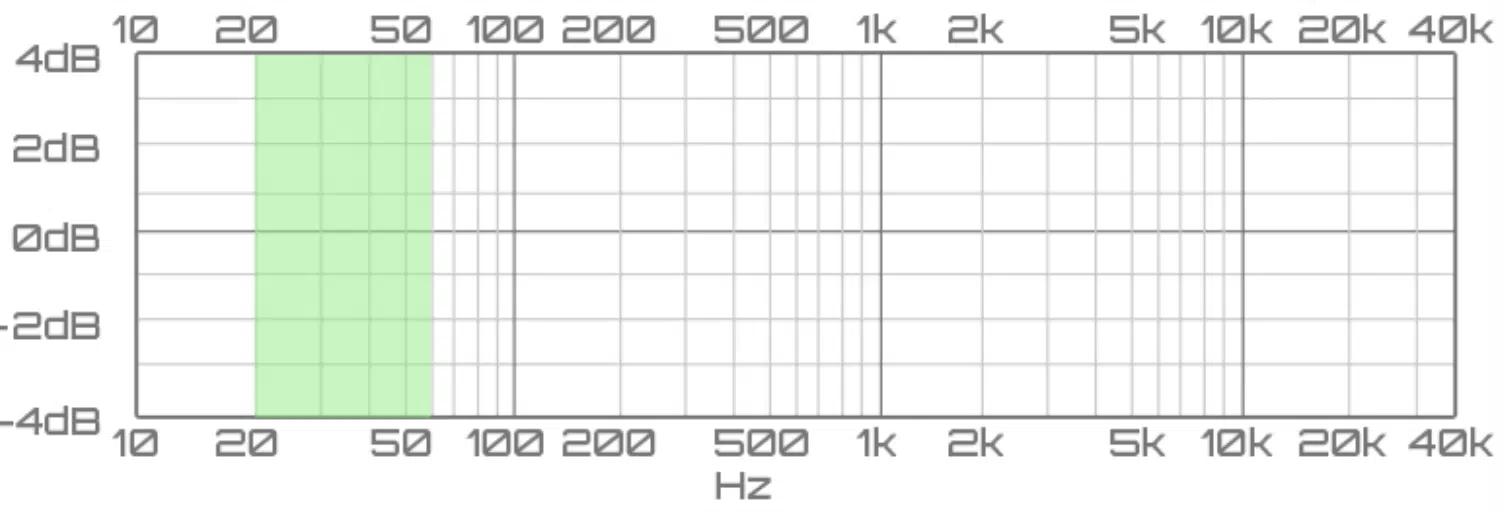
The sub-bass range, typically between 20Hz and 60Hz, is all about the deep, chest-rattling bass that underpins many tracks.
It’s the feeling you get more than the sound you hear.
This frequency range is fundamental in genres like trap or southern hip-hop, where 808 bass drums dominate.
Think of songs like “Low” by Flo Rida or “Mask Off” by Future.
That rumbling that you feel (and most likely love) is the sub-bass in action.
NOTE: Caution is needed. Too much emphasis here can drown a mix, making it sound muddy or boomy.
Proper side-chaining, where the sub-bass ducks under kicks or other significant elements, can maintain clarity.
We’ll break it down a little further along.
-
The Low-Mids
Ranging from 250Hz to 500Hz, the low-mids contain a lot of the warmth and body of instruments 一 from guitars to pianos to vocals.
But this certain frequency is also a common culprit for muddiness in a mix.
Overemphasis here can overshadow other frequency ranges, which leads to a mix that lacks definition.
A practical tip for hip-hop producers is to carve out a small notch in this range for vocals.
This ensures that the rapper or singer’s voice stands out clearly, without being masked by underlying beats or instrumentals.
-
The Upper Mids
Frequencies between 2kHz and 5kHz give presence and clarity.
It’s where the human ear is most sensitive, and it’s essential for the intelligibility of vocals.
Certain instruments also have significant content in this area, like:
- Electric guitars
- Keyboards
- Snare drums
When a snare drum hits hard and cuts through a mix, it’s often thanks to a boost in the upper mids.
However, caution is again super crucial.
Over-doing it can result in a mix sounding harsh or fatiguing.
In hip-hop, where vocals need to shine, it’s about finding the balance to ensure the voice doesn’t clash with other instrumental elements.
-
High Frequencies
Anything above 5kHz enters the ‘high frequency’ range of the frequency spectrum.
It’s where the sparkle, air, and brilliance of a track lie.
Cymbals, hi-hats, and the sibilance in vocals (the ‘sss’ sounds) exist prominently here.
In hip-hop tracks, a crisp hi-hat pattern, like in Migos’ “Bad and Boujee”, derives its clarity from these high frequencies.
While they add life to the mix, too much can result in a piercing sound.
A de-esser, which reduces excessive sibilance in vocals, is a handy tool for managing high frequencies.
EQ Techniques & Tricks
Like a painter with brushes, EQing offers techniques to craft the perfect sonic picture.
Let’s dive in to a few of my personal favorites..
-
Subtractive EQ
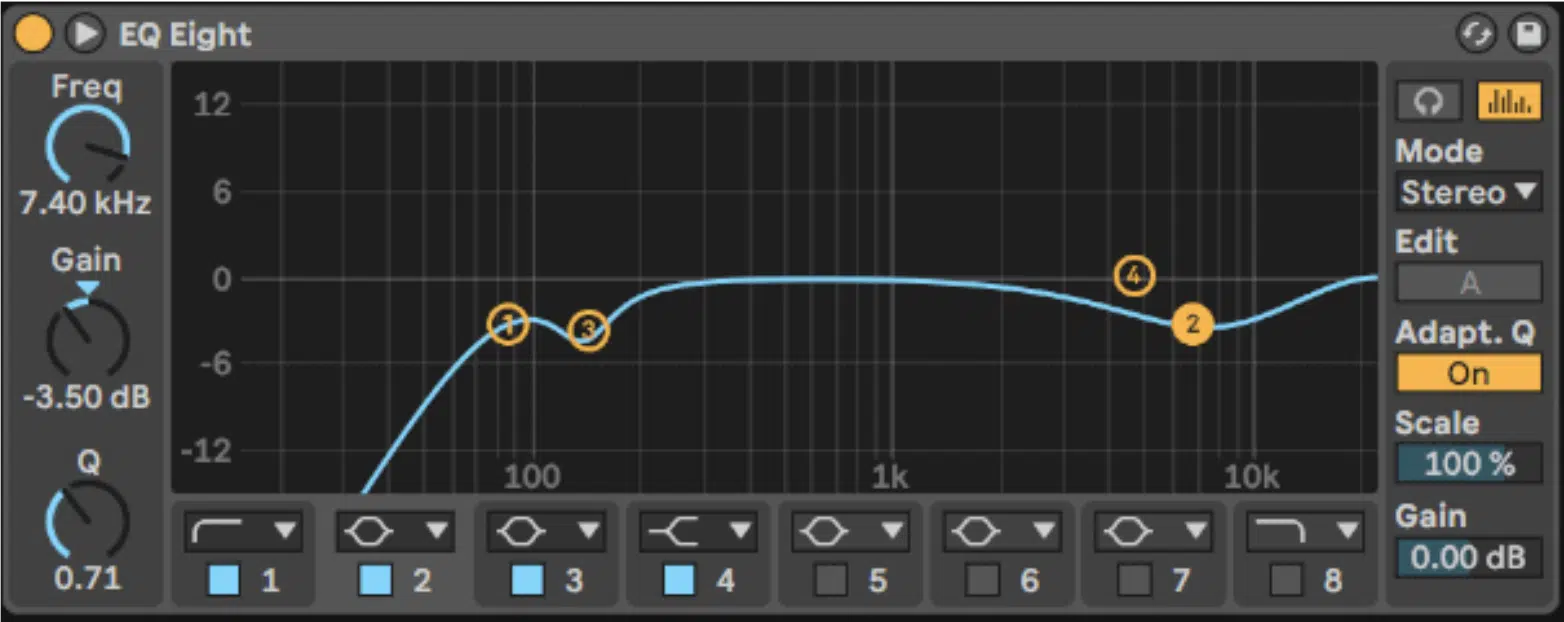
Subtractive EQ involves cutting frequencies rather than boosting.
It’s about carving space in the mix and ensures every element has room to breathe and sound good.
For instance, if a vocal feels buried beneath a guitar, rather than boosting the vocal’s frequencies, you could cut frequencies (those same frequencies) from the guitar track.
This gives the vocals space without adding unnecessary energy.
This approach often leads to much cleaner mixes.
By reducing frequency clashes, subtractive EQ minimizes the risk of a mix sounding cluttered or overloaded.
-
Using a Parametric EQ
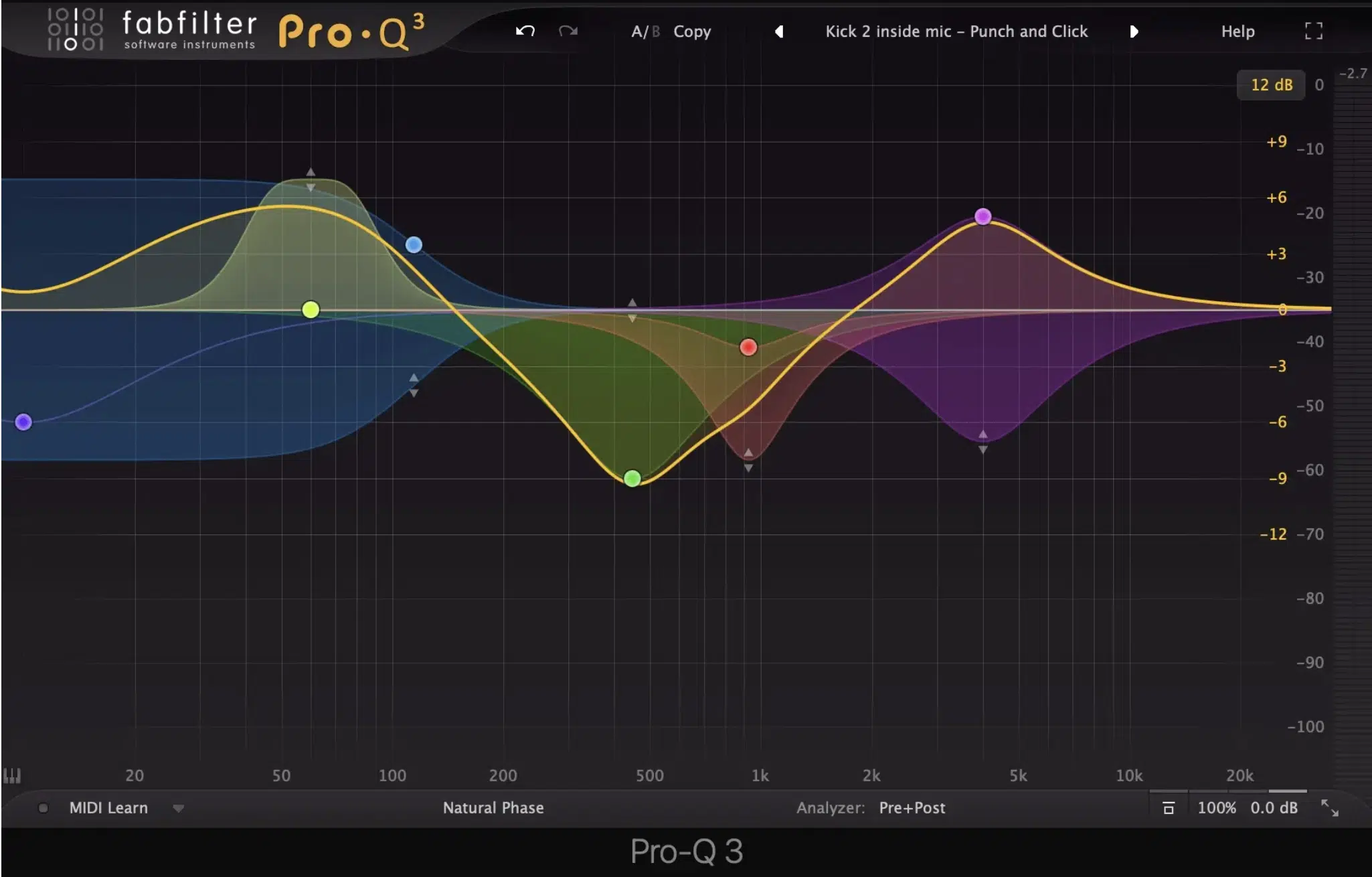
A parametric EQ is super beneficial, and allows you to successfully:
- Select a specific frequency
- Adjust its bandwidth (or ‘Q’)
- Then boost or cut
It essentially serves as the surgical scalpel of EQing.
Say a snare drum lacks punch…
With a parametric EQ, you can zero in on the 2kHz range, narrow the Q to focus just on that band, and give a slight boost.
In hip-hop, where samples might come with unwanted frequencies, a parametric EQ can be invaluable.
It allows for precise cuts to ensure the sample fits seamlessly into the mix.
-
Mixing Techniques for the Perfect Sound
Mixing is as much art as it is science. It involves knowing when to:
- Pan instruments
- Adjust levels
- EQ, of course
Also, reference tracks can be invaluable.
By comparing their mix to a professionally mixed song in the same genre (like r&b, lofi, or pop), you can spot areas for big improvement.
High-pass filtering, where everything below a certain frequency is cut, can be applied to non-bass instruments.
This clears up the low end, ensuring the bass and kick drum remain dominant.
Many hip-hop tracks use this technique to achieve a clear and powerful low end.
Addressing Common EQ Challenges
Even seasoned producers encounter challenges; recognizing and addressing them is half the battle.
So, let’s cover a few common EQ challenges and how to get around them.
-
Identifying & Correcting A Problematic Frequency Range
Every room (like your home studio) and every speaker has its own unique frequency response.
This means a mix might sound different in two settings.
Room modes, or resonant frequencies in a given space, can exaggerate certain frequencies.
Calibration tools and room treatments can help with a problem frequency, but ear training remains invaluable.
One method is the “sweep technique.”
This techniques involves boosting a narrow bandwidth and sweeping it across the frequency spectrum.
When an unpleasant resonance is found, it’s a potential trouble spot to address.
-
Using EQ to Add Clarity and Presence
More clarity ensures each specific instrument and vocal can be heard distinctly.
This oftentimes involves judicious EQing to carve space for each element.
Presence, especially for vocals in hip-hop, is crucial to reduce sibilance and include more fullness.
A slight boost around 3kHz to 5kHz can make a vocal pop 一 ensuring lyrics are clear and upfront.
But be careful about over-EQing, as it can strip the life from a track, like an annoying finger sound on a chalkboard.
It’s about making subtle adjustments and frequently referencing against the un-EQed version.
-
The Balance of Cutting Frequencies To Add Fullness
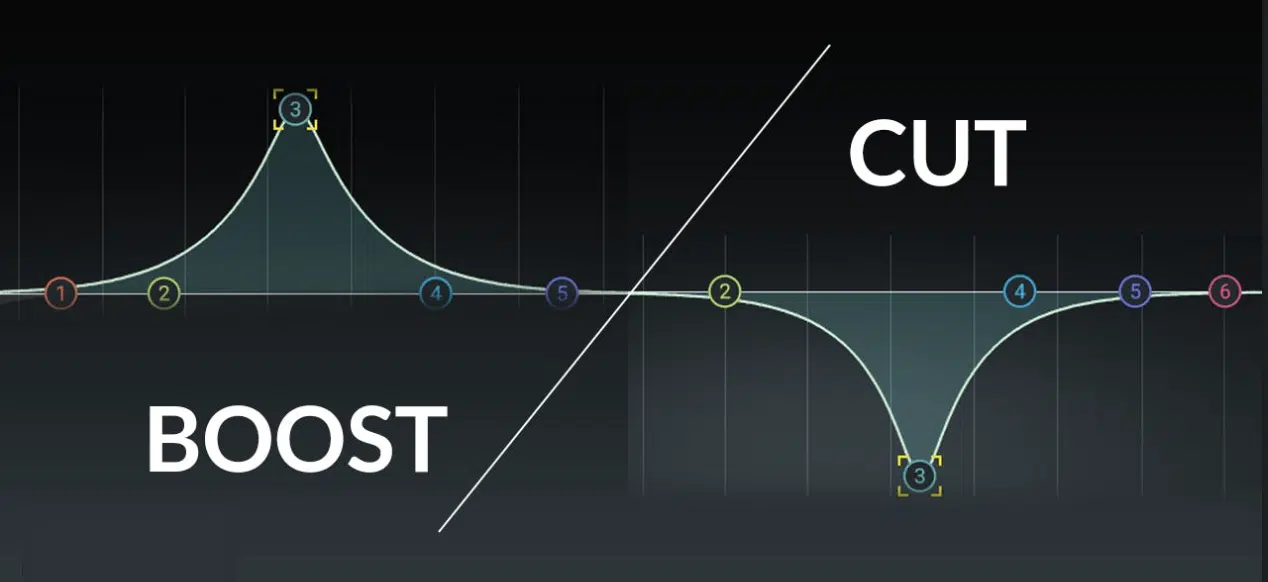
While subtractive EQ is a favored technique, sometimes a whole mix needs added fullness or warmth.
This might involve:
- Boosting the low-mids
- Adding some sparkle in the high end
Parallel processing can be a very successful and innovative solution.
By processing a duplicate track (like a vocal or string instruments) with heavy EQ and blending it with the original, one can add body without overloading the primary track.
In hip-hop, where beats and vocals are paramount, it’s a balancing act.
For instance, a beat might need more low-end thump, but this shouldn’t overshadow the vocals.
It’s about weaving elements together cohesively so everything sounds good and has its very own space.
EQ Frequency Chart: Final Thoughts
Throughout this deep dive, we’ve unpacked the complexities of the EQ frequency chart.
As well as explored the nuances of frequencies, instruments, and techniques specific to the realm of hip-hop production.
Grasping these concepts ensures that every layer of your mix (from the lowest sub-bass to the crispest high-end) finds its perfect place in the soundscape.
Speaking of bass, while we’ve emphasized the importance of knowing where each instrument lies on the EQ frequency chart, having top-quality sound sources can be equally crucial.
If you’re looking to elevate their hip-hop tracks, you have got to check out these free Essential Bass Loops.
This collection boasts 12 unique, fire basslines, designed to infuse your tracks with the energy and depth they deserve.
Pairing a solid understanding of the EQ frequency chart with premium assets like these can be transformative for your music production journey.
Understanding the EQ frequency chart isn’t just about adjusting knobs and carving out spaces.
It’s also about intentionality in every decision you make to ensure each element of your track truly shines.
With the knowledge you’ve gained today, you’re well on your way to not only producing with precision and mastering the EQ frequency chart, but crafting sonic masterpieces.
Until next time…







Leave a Reply
You must belogged in to post a comment.