Mixing and mastering are critical phases in the production of any song.
They can elevate your tracks from good to great, adding polish and cohesiveness.
However, if you don’t know the vital differences between these two stages, or lack the know-how to execute them properly, your beats may end up sounding basic.
Not to mention super unprofessional and lackluster.
To truly make your music stand out, it’s essential to understand what each process entails and how they complement each other.
That’s why we’re going to cover all the essential mixing vs mastering processes.
In today’s article, we’ll be breaking down:
- The components of a song ✓
- What is mixing ✓
- What is mastering ✓
- Mixing vs mastering ✓
- Why both are essential ✓
- Mixing and mastering tips (advanced) ✓
- Stereo audio files vs multichannel formats ✓
- Achieving the most balanced playback ✓
- Etc. ✓
After diving into this comprehensive article, you’ll walk away with a solid understanding of the distinctions between mixing and mastering.
As well as advanced techniques for both, and why each step is crucial for the success of your audio project.
Armed with this knowledge, you’ll be better equipped to make informed decisions in your music production journey and make your beats legendary.
So, let’s dive in…
Table of Contents
The Journey of a Song: From Composition to Mastering
Let’s kickstart our journey into the world of mixing vs mastering by first understanding the roadmap a song typically follows.
-
The Initial Music Composition Stage

The start of any great track is music composition.
Before you even begin to think about the mixing and mastering process, you need to nail your music composition.
This stage is where all the creativity flows 一 from brainstorming melodies to writing killer hooks.
Unlike in the mixing stage, here you’re not thinking about technical aspects like gain staging or balancing individual instruments.
Instead, you’re focused on the core musical ideas.
This involves things like:
- The overall vibe you’re aiming for
- The emotional impact you’re trying to convey
- Fine-tuning the sonic texture
- Ensuring the song translates well across various playback systems
It’s all about that final polish, making sure the track not only sounds good but feels complete and compelling.
The composing process lays the groundwork for the recorded tracks you’ll soon be laboring over in your home studio.
And trust me, the quality of your composition will massively impact how your music sounds after it’s been mixed and mastered.
-
Recording & Individual Tracks

Once your music composition set, you’re going to begin recording and combining individual tracks (whether at a professional studio or your home studio).
Each track is recorded separately, whether it’s your:
- Lead vocal
- Backup vocals
- Instruments
This separation into individual tracks allows mixing engineers to have better control during the mixing process.
Quality recording here is crucial, because a bad mix can often be traced back to poorly recorded tracks.
If the initial recording is top-notch, it’s like handing off a polished gem to the mixing engineer.
So make sure you get it right at this stage before moving on.
-
The Mixing Stage

Alright, so you’ve composed your music and recorded your individual tracks…
Now enters the mixing stage.
This is where your track begins to take shape as one cohesive song.
A mixing engineer takes over at this point, using a variety of techniques, audio effects, and sound design to balance out the:
- Audio levels
- Spatial positioning
- Frequencies of all the tracks
The goal is to make sure every element of your song (your entire mix) can be heard clearly and harmoniously.
NOTE: You don’t have to use mix engineers, of course, but it’s recommended when first starting out.
One essential part of the mixing process is gain staging.
It ensures that all the elements in your mix are at the right levels, so you don’t end up with any clipping or distortion when you move on to mastering.
Another important technique at the mixing stage is Equalization (EQ).
EQ can make or break your song’s clarity 一 making it a favorite tool among mixing professionals.
Subtle adjustments here can add the ‘oomph’ or ‘zing’ your track needs.
-
The Mastering Stage

Now, let’s talk about the final frontier in your music production process: the mastering stage.
At this point, your song should sound pretty darn good but it’s not quite ready for the world to hear yet.
A mastering engineer (if you’re using one) adds the final polish to your mixed song.
The aim here is to ensure your music will sound good on all playback systems 一 from high-end speakers to smartphone speakers.
The mastering process involves:
- Fine-tuning the track’s EQ
- Adjusting the stereo enhancement
- Adding some subtle broad strokes like multiband compression to bring out certain elements
It’s the final step in your audio production process, and it’s crucial for making sure your music has the most balanced playback across all systems.
NOTE: Remember, the mastering stage is not where you should fix any mistakes, that should be during the mixing stage.
Mastering is strictly for fine-tuning and polishing.
-
Final Playback & Distribution

At last, your song is complete and you should feel like a full-blown audio engineer.
However, that’s only once it’s been:
- Composed
- Recorded
- Mixed
- Mastered
Now, it’s time for the final playback and distribution.
Whether you’re releasing your own music on Spotify or sending your tracks to a record label, the mastering stage ensures that your music will sound its best on a multitude of playback systems.
As a digital music producer, understanding this entire journey gives you a bird’s eye view of the music production process.
And, most importantly, it underscores the significance of both mixing and mastering in the final product.
What Exactly is Mixing?
When we talk about mixing and mastering, the mixing stage often gets less glam but it’s where the magic really begins to happen.
-
The Mixing Process: From Start to Finish

Mixing is more than just adjusting volume levels.
The mixing process is a creative but complicated process involving multiple tracks, sound effects, and plugins.
You start by importing all the tracks into a Digital Audio Workstation (DAW).
Once everything is in there, you can begin the art of mixing.
Mixing involves tasks like:
All these contribute to how your final mix will sound.
Often in digital music production, mixing also includes Pitch FX for vocals 一 especially in genres like pop and EDM.
NOTE: If you’re going for that polished, radio-ready sound, don’t underestimate the power of good pitch correction.
At this stage, you’ll often find that the most subtle adjustments make the biggest impact.
Whether you’re a seasoned pro or just building your home studio, honing your mixing skills is a lifetime endeavor.
-
The Significance of Gain Staging
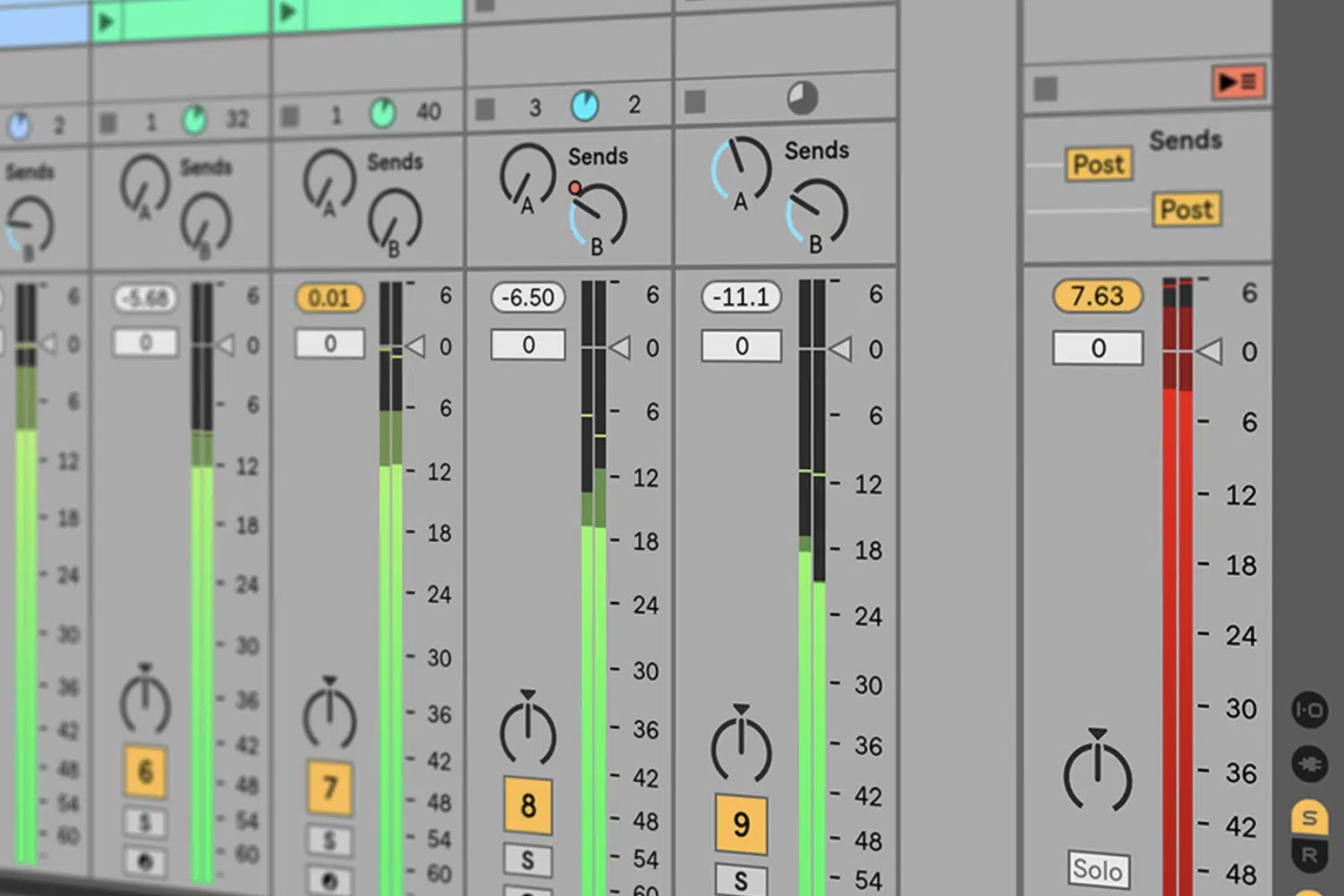
Alright, now let’s talk a little bit about gain staging, as it’s a vital part of the mixing process.
Gain staging is the process of setting the correct levels for your individual tracks before diving into the mixing process.
Gain staging ensures that all your tracks are at an optimal level, so you don’t clip and distort when you start adding effects and plugins.
You do this by carefully adjusting the input and output levels of each individual track and element within your mix.
This sets the stage (pun intended) for a clean, distortion-free sound.
And allows you the freedom to creatively apply effects and plugins without compromising audio quality.
Proper gain staging also provides a better dynamic range and ensures that your mix has room to breathe.
Trust me, there’s nothing worse than a bad mix caused by poor gain staging.
This is something often overlooked by newbies, but all the best mixing engineers pay meticulous attention to gain staging.
It sets the foundation for a quality master later on.
If you’re looking to nail your mixing stage, gain staging is your secret weapon.
-
Mixing Stage Tips, Tricks, and Techniques
To finish off this mixing section, let’s break down some advanced mixing techniques, tips, and tricks to help you along the way.
#1. Parallel Compression
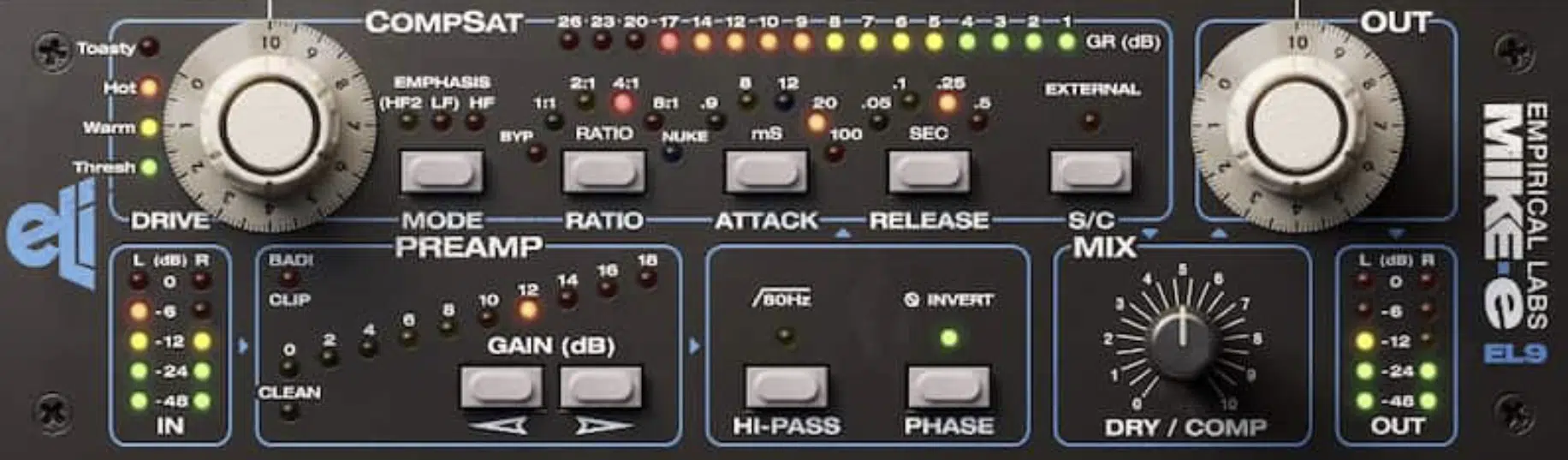
One advanced technique in the mixing stage is parallel compression, sometimes referred to as “New York Compression.”
This involves blending an unprocessed ‘dry’ signal with a heavily compressed version of the same signal.
It helps in maintaining dynamic range while still taming peaks and increasing the overall perceived loudness.
#2. M/S Processing
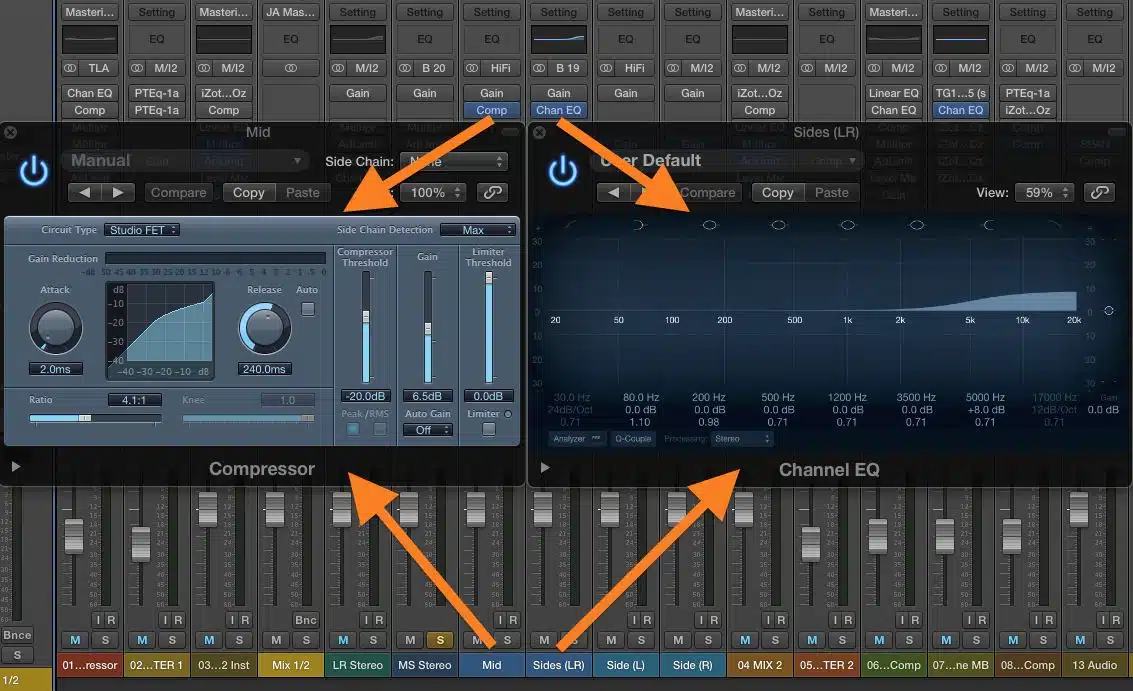
Mid/Side processing allows you to treat the center and sides of the stereo field independently.
This can be particularly useful for things like:
- Adding brightness to a vocal without affecting panned instruments.
- Applying different compression settings to the mid and side signals.
Some EQ plugins even have M/S mode for more intricate and precise tonal shaping, which is really beneficial.
If you’re looking for the absolute best EQ plugins, we’ve got you covered.
#3. Automated EQ Sweeps
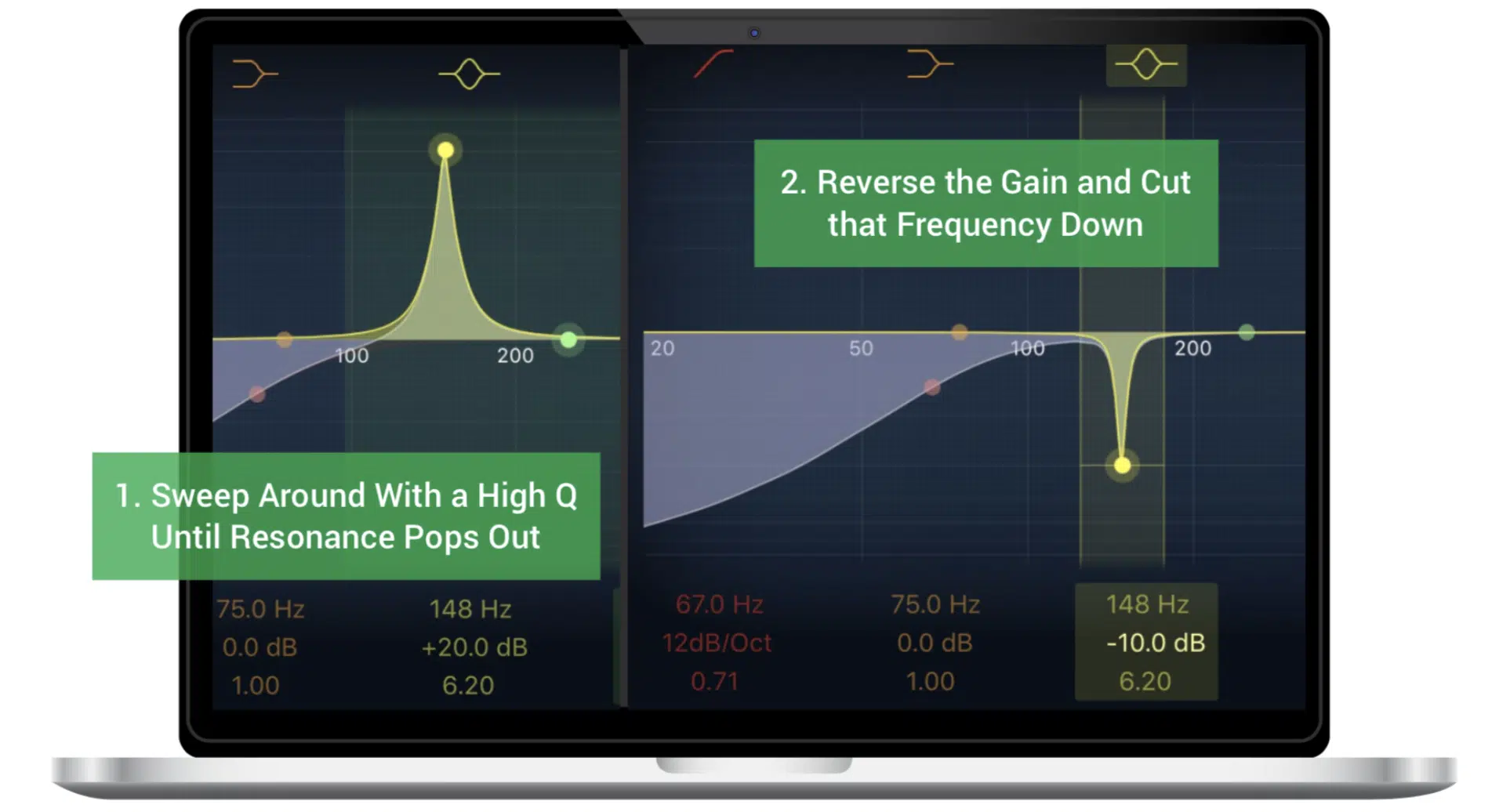
When you’re mixing, you might find certain frequencies that clash or resonate poorly at specific times.
Automated EQ sweeps enable you to attenuate these problem frequencies only when they become a nuisance, rather than cutting them out completely and affecting the overall tone.
#4. Dynamic EQ
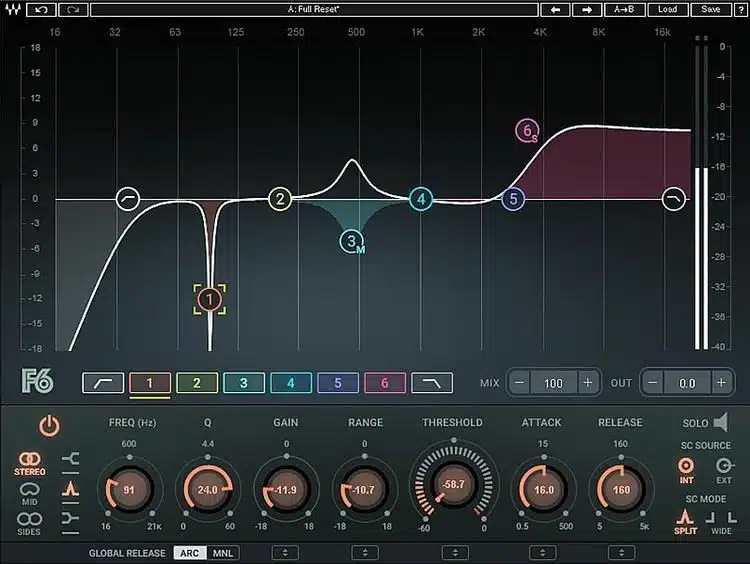
Unlike standard EQ, which impacts the entire track consistently, dynamic EQ only kicks in when the input level crosses a certain threshold.
It’s like a mix of EQ and compression and is especially useful for handling complex material with wide frequency ranges (like full mixes or mastering scenarios).
What Exactly is Mastering?
You’ve mixed your track to perfection, but your journey in the realm of mixing vs mastering isn’t complete.
Now comes the ultimate stage: mastering.
-
The Mastering Process

Okay, let’s dig into the mastering process.
This is where your music takes its final form, becoming that stereo audio file or multichannel format ready for playback on all types of audio systems.
The mastering engineer typically works with a single stereo file, making broad strokes that affect the sound of the entire song.
Certain things are commonly applied at this stage, like:
- EQ adjustments
- Compression
- Limiting
If your music involves multiple tracks, then your mastering engineer will sequence them in the desired order 一 ensuring the entire album has a consistent sound and volume.
Mastering also often involves stereo enhancement, making your music sound fuller, wider, and more engaging for the listener.
You can also think of mastering as the quality control phase of your music production process.
A good mastering engineer performs checks for any issues that may not have been evident during the mixing stage.
If you want a quality master, don’t skip this step.
-
Mastering Stage Tips, Tricks, and Techniques
Since we gave you some advanced mixing tips and tricks, it’s only right to include the same for the mastering stage, so let’s get into it.
#1. Stereo Imaging
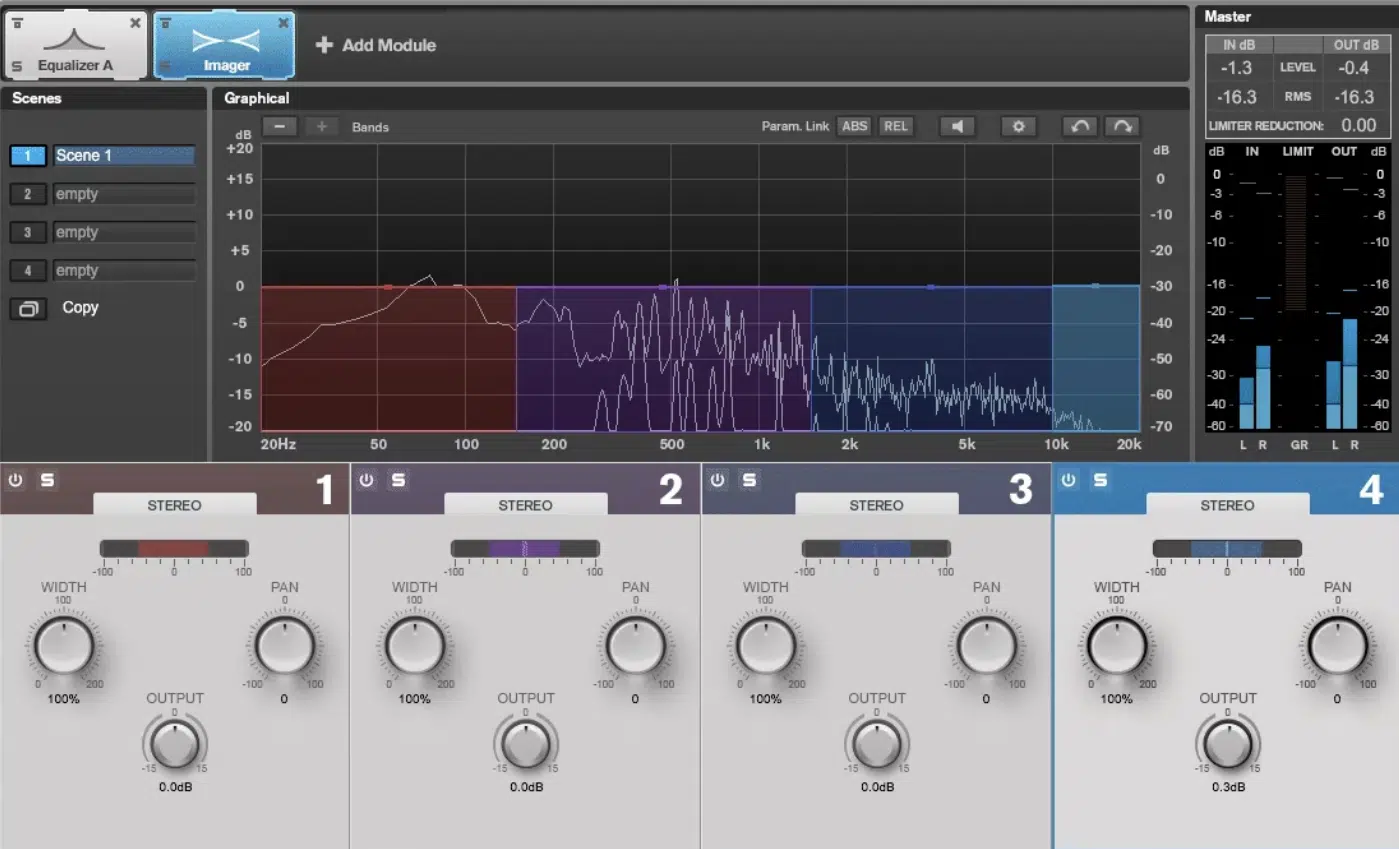
In the mastering stage, one advanced technique is the manipulation of stereo imaging.
This is not just about making everything wide 一 it’s about strategically placing elements in the stereo field for a fuller sound.
I recommend using specific tools like:
- The Haas Effect
- Mid-side processing
- Specialized plugins
This will help you further enhance or focus the stereo image.
Remember, it’s all about being strategic at this point, not to misplace anything.
#2. Harmonic Excitation
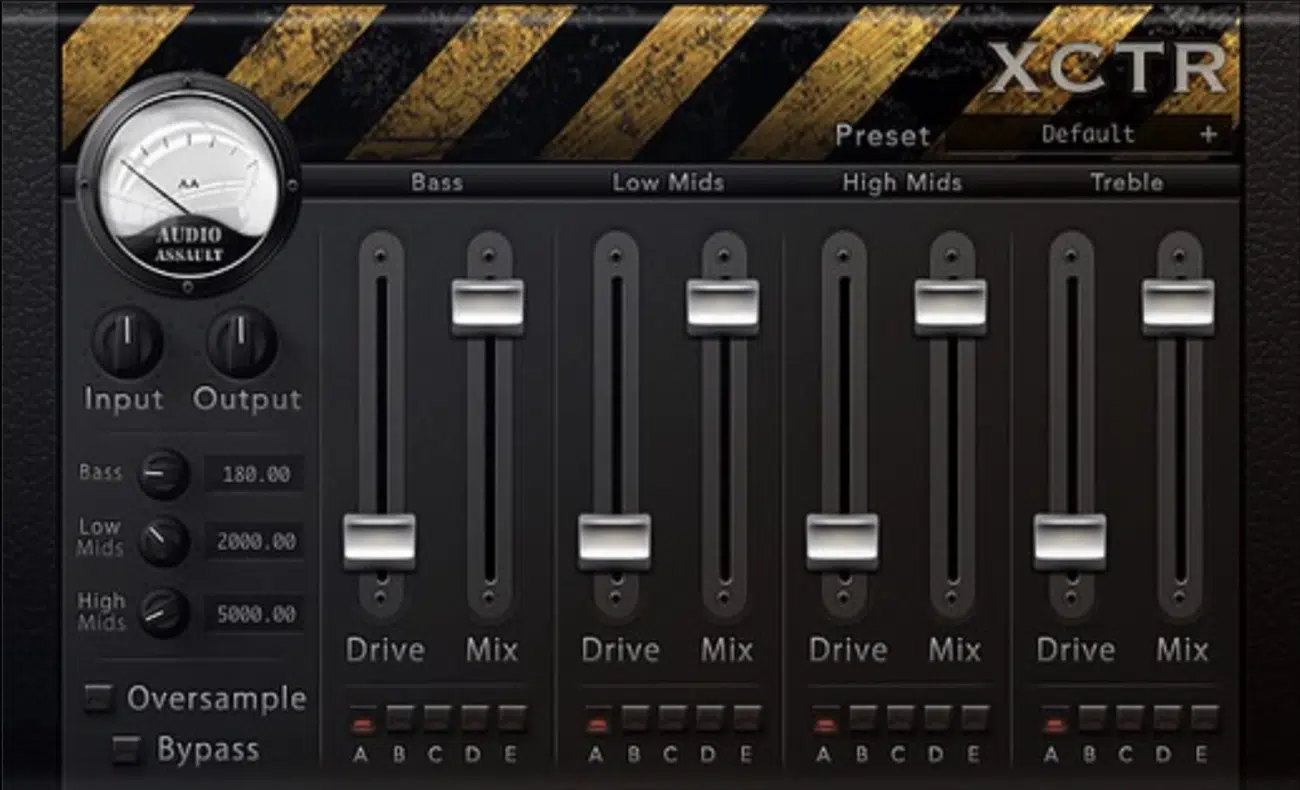
Mastering isn’t just about making things louder, it’s also about adding richness.
Harmonic exciters can impart pleasing overtones and harmonics, and typically add:
- Warmth” to the lower frequencies
- Sparkle to the highs
Without increasing the actual amplitude of those ranges, of course.
Do not get lost in the loudness war, as that could make your track unbalanced and irritating on the ears.
#3. Loudness Matching

It’s easy to think a louder track is a better track.
However, to critically assess the changes you’re making during mastering, use loudness matching to compare the mastered and unmastered versions at the same perceived volume.
Side note, if you’d like to learn everything about LUFs, we’ve got you covered.
#4. Dithering
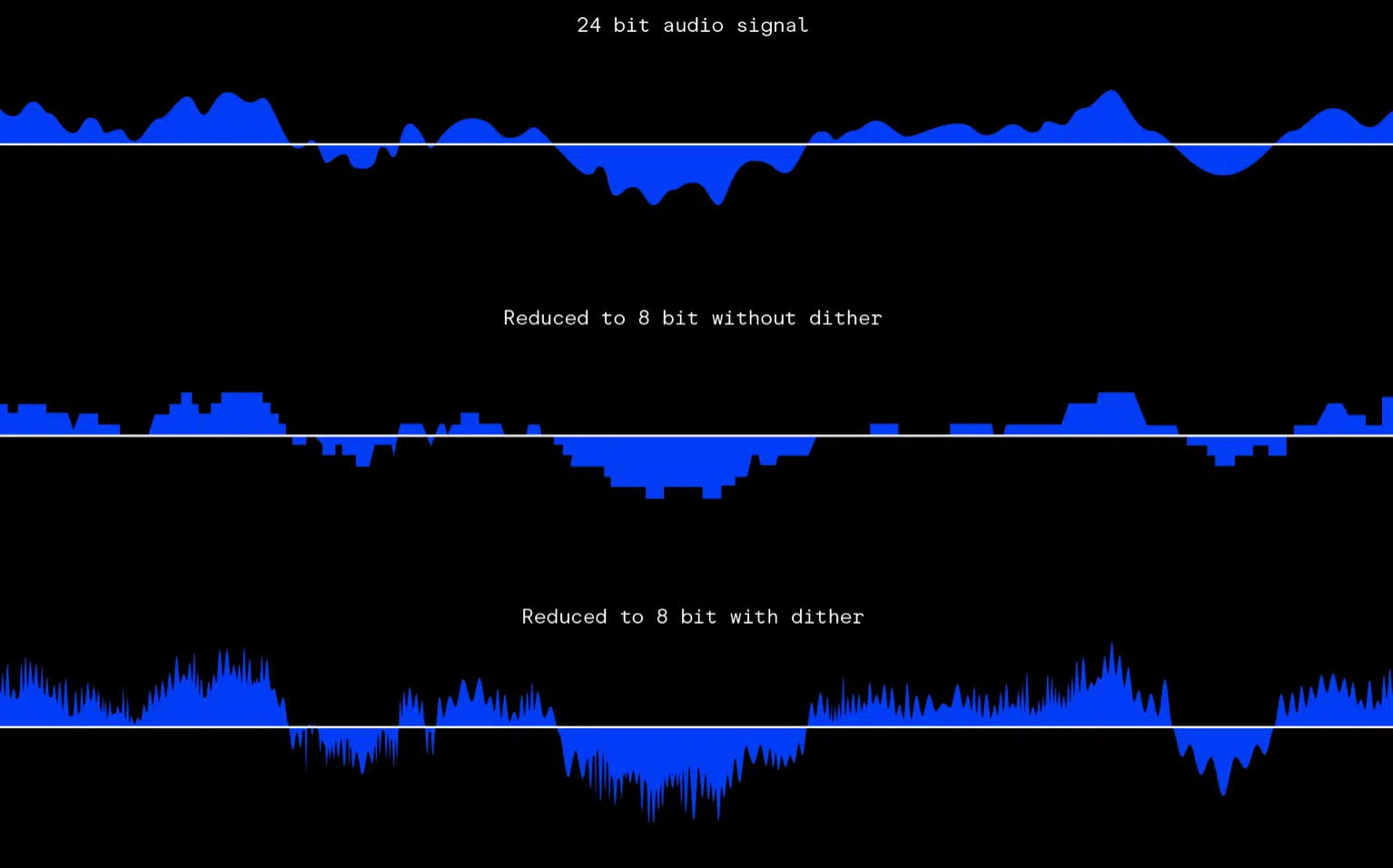
The last step often involves converting the high-resolution master down to a 16-bit format for distribution.
Dithering is a technique that adds a very low level of noise to the audio to minimize quantization errors and artifacts during this bit-depth reduction.
It’s a subtle effect but can improve the perceived audio quality of the final product.
The Elements of Mixing and Mastering: Key Differences
Ready to go a bit deeper?… Well, let’s delve into the very elements that make up both mixing and mastering.
Therefore, when you’re creating music, it will make sure your song sounds professional and pristine.
-
Individual Tracks vs Stereo Track

A crucial part of the music creation process is understanding the difference between working on individual tracks and a stereo track.
When you’re in the mixing stage, you’re dealing with separate tracks, like:
As an aspiring mixing engineer, you’ll make sure that all the tracks come together in harmony.
Techniques like gain staging, EQ, and even pitch FX (as we discussed earlier) are used to ensure that each track sits well in the mix.
NOTE: Once it gets to the mastering stage, however, the mastering engineer receives a stereo audio file.
They don’t deal with individual tracks anymore.
When mastering music, mastering engineers make the entire song sound cohesive and ready for public consumption.
-
Stereo Audio File vs Multichannel Format

In today’s digital age, the format of your music is more versatile than ever before.
Stereo audio files are the norm, but some artists and mastering engineers are experimenting with multichannel formats.
A stereo file is generally what you’ll use for most distribution channels, as its:
- Easy
- Accessible
- Plays well across all audio systems
Multichannel formats, however, provide a more immersive experience.
Think of it like the IMAX of music production…
It’s not commonly used in most genres, like Lo-fi, but it can provide a unique listening experience that sets your music apart.
-
Pro Tip: Mixing vs Mastering Quality Control

Quality control in mastering/mixing is not just an afterthought; it’s an integral part of both mixing and mastering.
One cannot overemphasize the need for multiple rounds of listening and adjustments.
In mastering, the overall quality control goes beyond just listening.
You should try using vistual tools to analyze your sound, like:
- Spectrometers
- VU meters
This will ensure the most balanced playback across various systems, which is key!
In mixing, quality control is about ensuring that each element (vocals, instruments, synths) plays well with each other.
The mixing process is like a complex puzzle, and each piece has to fit perfectly.
Why Both Mixing and Mastering Are Essential
So you now understand the essential nuts and bolts of both mixing vs mastering.
But why are both of these processes so crucial?…
Let’s delve into why you can’t afford to skip either (separate) process if you’re serious about music production and making your final sound professional.
Plus, it will help you achieve balance that match the professionalism and expertise of seasoned producers or audio engineer.
-
Achieving the Most Balanced Playback: Mixing vs Mastering
Achieving balanced playback is like finding the Holy Grail in music production.
It’s not just about volume levels 一 it’s about how the music feels across different platforms.
Mixing ensures that the sounds within the track are well-balanced against each other.
Mastering music takes it a step further by making sure the track holds its own when played back-to-back with other mastered tracks. It’s the final stage, as you know.
The process includes testing on different:
- Speaker systems
- Headphones
- Car stereos
The idea is to offer a universally pleasing auditory experience, ask all the mastering engineers you know, and they’ll tell you the same.
With both mixing and mastering, your track will sound not only good but also consistently good across a variety of platforms.
-
The Effect of Bad Mix and Mastering

A bad mix is like a movie with poor editing; people will most certainly notice.
It could have all the elements of a hit, but it will lost impact if:
- The levels are off
- The vocals are drowning in reverb
- The bass is overwhelming
Poor mastering can make your song sound dull, too quiet, or, at worst, unlistenable when placed next to other professional tracks.
A bad master is like a poorly framed great painting; it diminishes the entire experience.
Sometimes, it’s not just about the listener’s experience…
Poor mixing and mastering can also result in your track being rejected by platforms or recording labels.
It can act as a jumping off point for your career growth.
These errors are often irreversible, however, once the track is out there, first impressions cannot be taken back.
Hence, investing in good mixing and mastering can save you from future regrets and make sure your song sounds professional.
Mixing vs Mastering: Final Thoughts
Mixing and mastering are two distinct stages in the music production process that, as you can now see, serve different but complementary purposes.
The difference between mixing vs mastering is like sculpting vs polishing.
Mixing gets all your elements to play nice together; while mastering makes sure they shine as a cohesive unit.
If you’re really serious about taking your music production to the next level, mastering the intricacies of mixing vs mastering is essential.
And hey, if you’re on the hunt for high-quality resources to enhance your skills further, you need to look into the Free Black Friday Pack.
This isn’t just your run-of-the-mill sample pack 一 it includes 625 unique samples, MIDI’s, and presets that are pure gold for anyone diving deep into the world of music production.
Why are these samples and presets so special?…
Because they’ve been part of creations that have garnered over 2.2 billion plays and been featured in chart-topping tracks.
And the best part?
They’re mixed and mastered to perfection.
Therefore, analyzing these can offer you a hands-on education in mixing vs mastering and allows you to understand how pros handle the two distinct yet interconnected stages of music production.
Understanding the key differences between mixing vs mastering can truly be a game-changer for your music.
When you nail both, that’s when you produce tracks that not only sound good but also feel like complete, compelling stories.
Remember, both mixing and mastering are skills that take time to perfect.
However, with the right tools like the Free Black Friday Pack and the information you’ve gained here on mixing vs mastering, you’re well on your way to becoming a true master.
Until next time…







Leave a Reply
You must belogged in to post a comment.