The world of synthesis is vast, diverse, and ever-evolving.
Every synth instrument, from humble analog options to advanced digital powerhouses, can help you create captivating music that keep people hooked.
As a music producer, understanding the intricate dance of oscillators, waveforms, and modulations is the first step to unlocking musical greatness.
That’s why we’ll break down everything you need to know about these intriguing electronic musical instruments.
In today’s article, we’ll be covering:
- The history and evolution of synthesizers ✓
- Analog synths vs. digital synths ✓
- Software synthesizers ✓
- Modular systems ✓
- Different synth types & their benefits ✓
- Professional synthesis techniques ✓
- Mind-blowing sound design tricks & tips ✓
- Everything you need to know about your favorite synth instrument ✓
By the end of this comprehensive guide, you’ll be able to harness the true power of synthesizers to make music with a real impact.
A solid grasp of most synthesizers (functions, history, potential) can be the difference between an average track and a mind-blowing one.
And we know you’re here to create mind-blowing tracks.
So, let’s dive into the synth world…
Table of Contents
Intro to the World of Synthesis
From the Moog’s powerful resonance to the modern VST’s endless digital landscapes, the synth instrument has irrevocably changed the face of music.
Let’s journey through its electrifying history and profound impact on today’s soundscape.
-
Brief History of Synthesizers
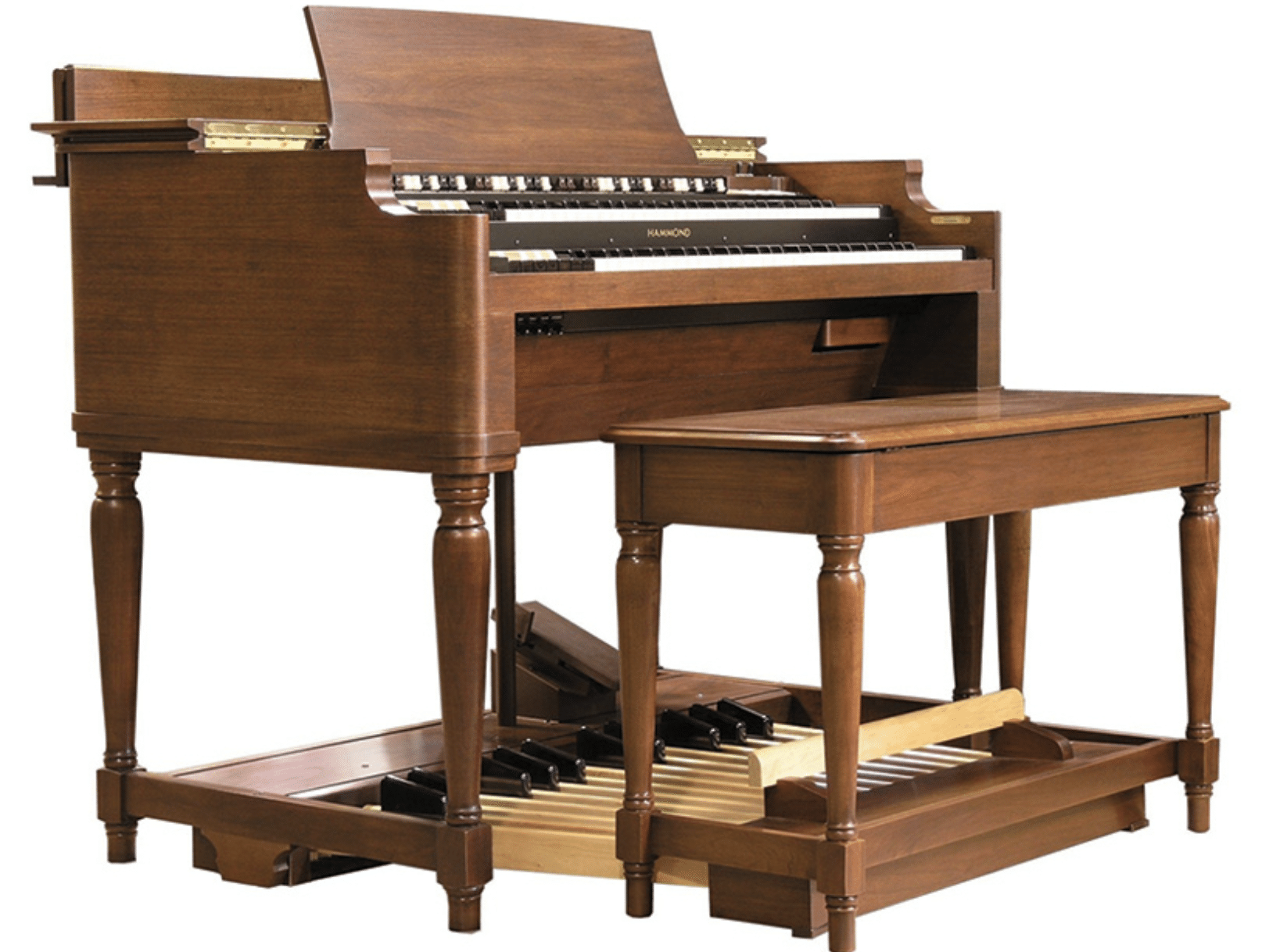

Imagine a world before electronic music and electronic instruments, where the concept of electronically generated sounds was completely foreign.
That’s the world into which the first synthesizers were born.
The Hammond Organ, for instance, was an early attempt to harness electronic components to replicate traditional instruments.
Robert Moog’s innovations in the 1960s changed everything.
His Moog synthesizer was groundbreaking and introduced some of the most innovative musical breakthroughs ever.
The Moog synthesizer actually brought the term “synthesizing” sounds into the limelight.
The ability of this electronic instrument to produce and manipulate sounds electronically was revolutionary.
With the 1970s and 80s came a synthesizer boom as artists from various genres embraced the musical instrument 一 pushing its boundaries like never before.
The evolution of synthesizers wasn’t just about the sound.
It was about accessibility, user interface, and the tactile experience that made them integral in live performances and studio sessions.
-
Modern Synthesizer Evolution in Electronic Music

As technology progressed, the analog circuits at the heart of the classic synthesizers started sharing the stage with their digital counterparts.
This digital transformation led to the rise of the first digital synthesizer.
The takeover of electronic music genres like EDM, house, techno, and, more recently, trap and hip-hop saw an insatiable demand for innovative sounds.
Digital synthesizers, with their vast sound libraries and editing capabilities, were more than up for the challenge.
Speaking of sound libraries, if you’d like access to the best free sound libraries of 2023, we’ve got you!
Today’s modern synthesizer is a testament to decades of innovation.
From emulating vintage tones to creating undiscovered sounds, synthesizers have become the backbone of electronic music production.
With artists constantly looking for that unique sound, the synthesizer market has exploded 一 offering many options, from compact MIDI controllers to extensive modular systems.
That’s where we learn the importance of synths in digital music production.
-
Importance of Synths in Digital Music Production

The digital synthesizer has moved beyond simply replicating acoustic instruments to offer a limitless palette of sounds.
The union of software synths with digital control allows for precision and complexity in sound design that was previously unattainable.
Different processes can now be done to your sounds, like:
- Layering
- Modulating
- Precise tweaking
With sampling technology, you can now capture any sound (from a chirping bird to a city street) and morph it into something entirely new through synthesizers.
This has broadened the horizons of genres like trap and hip-hop 一 allowing for richer, more layered compositions.
Plus, integrating synthesizers with other digital production tools and music production software means that physical limitations no longer bind the creative process.
A producer in Tokyo can seamlessly collaborate with another in New York, exchanging synth patches and sound design creations instantaneously.
This makes the creative possibilities quite literally endless.
NOTE: You’ll hear a synth instrument be characterized as either “monophonic synthesizers” or “polyphonic synthesizers;” it’s essential to know the difference.
Monophonic synthesizers are designed to produce a single note at a time, creating focused and singular tones.
Polyphonic synthesizers can generate multiple notes simultaneously, allowing for rich chords and layered soundscapes.
Now, let’s move on to one of my favorite topics: analog synths.
Analog Synthesizers: Where The Magic Began
The analog world has a confident, undeniable allure and the analog synthesizer is no exception.
There’s something magical about those weaving circuits and wires that an analog synthesizer is comprised of.
Whether you’re hands on or digitally inclined, knowing about analog synthesizers is pivotal.
-
The Charm of Analog Synths
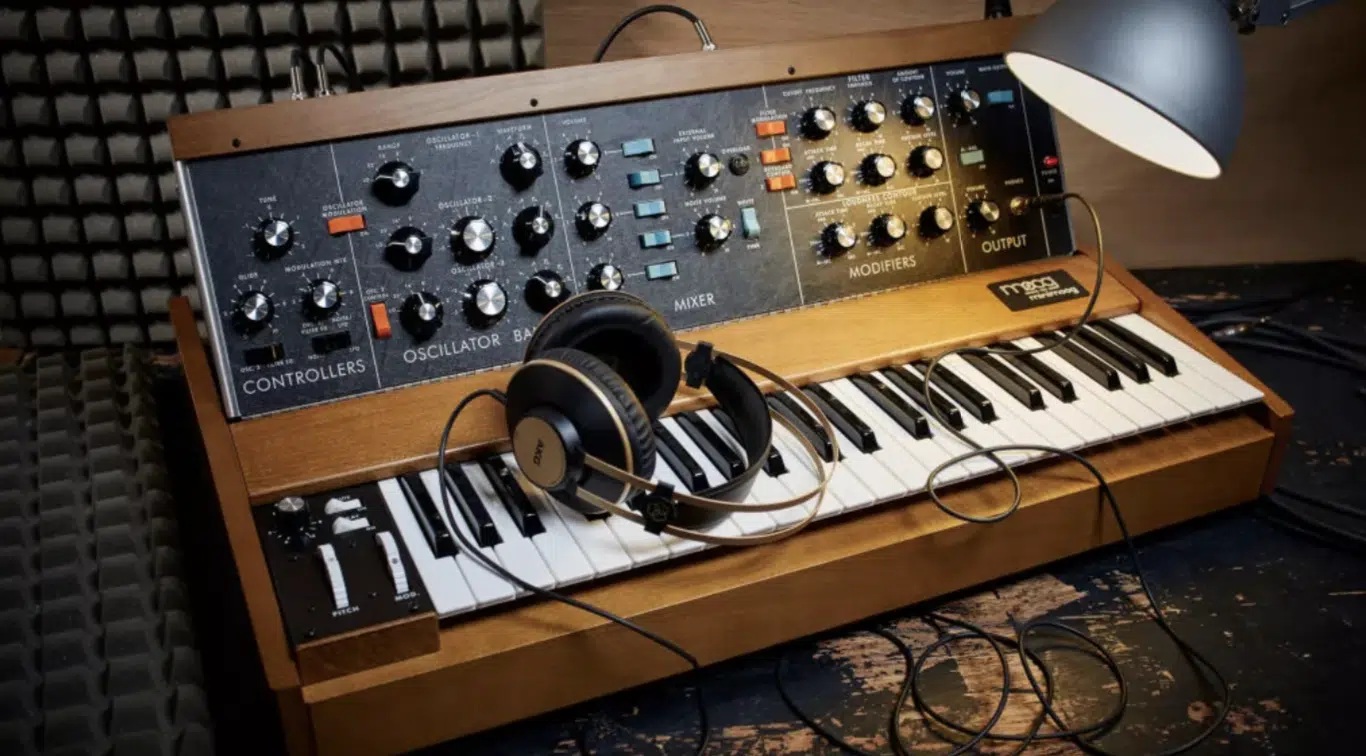

Analog synths: these electronic wonders transport us back to the roots of electronic music (and electronic instruments), where every note had a tangible warmth and depth.
Authentic Warmth: The warmth of analog synths is not just a phrase; it’s a genuine sonic character.
When you strike a note, the resulting sound envelops the listener, which makes it a favorite for many discerning ears.
Tactile Connection: In the world of touchscreens and digital interfaces, the hands-on experience with analog synths provides a direct, physical connection to the music.
Twisting a knob or sliding a fader results in immediate, palpable changes 一 creating an authentic experience.
Unique Personality: Every analog synth has its quirks and characteristics.
Two identical models might even sound slightly different, which is a fascinating concept when you think about it.
This uniqueness ensures that your compositions have a distinct flavor that’s hard to replicate with digital counterparts.
Timeless Appeal: While digital technology continually evolves, and AI is thrown in the mix, the foundational sound of analog synths remains a steadfast pillar in the music production world.
Their timeless tones can be found in tracks spanning decades, a testament to their enduring charm.
-
Analog Synthesis: The Science Behind It

At its core, analog synthesis is the art of manipulating electronic signals to generate sound.
Through various processes, these electronic signals, or sound waves, are sculpted into the tones we hear.
For instance, take subtractive synthesis: a staple of many analog synths.
Here, oscillators generate a rich sound wave, full of harmonics, which is then “carved” into the desired tone using filters.
Think of it as starting with a block of marble that you can chisel away at to create a true masterpiece.
Then, there are modulation methods like pulse width modulation (PWM).
By varying the width of a pulse wave, different harmonics can be emphasized 一 leading to a wide array of tonal possibilities.
Harmonious elements come together, each playing their unique part in shaping/refining the sound, like:
Think of analog synthesis as an orchestra…
Individual components (in this case, instruments) come together to produce an unmatched harmonious output.
NOTE: A few iconic examples of popular analog synths are Moog (named after the legend Robert Moog), the ARP Odyssey, and Sequential Circuit’s Prophet-5.
Digital Synthesizers: The New Age Revolution
Stepping into the digital synthesis realm, let’s explore how zeros and ones transformed our sound synthesizer horizons 一 unleashing a new era of musical digital technology.
We’ll dive into the new age revolution of digital synthesizers so you can explore your own sound and create music that leave a lasting impression.
-
The Rise of the First Digital Synthesizer

The Yamaha DX7, introduced in the early 1980s, marked a significant departure from the analog norm into digital recordings that defined a generation.
Utilizing Frequency Modulation Synthesis (FM synthesis), it could produce sounds that were complex, evolving, and unlike anything heard before.
FM synthesis, the heart of the DX7, involved modulating one waveform with another 一 resulting in many harmonically rich and intricate sounds.
NOTE: The iconic electric piano sound of the Yamaha DX7 became synonymous with the pop music of the era.
The DX7 wasn’t just a testament to digital’s potential in sound creation.
It also highlighted the advantages of:
- Presets
- Storage
- Recall capabilities
This gave music producers unprecedented flexibility that didn’t exist before (believe it or not).
This era marked a shift, with companies like Roland, Korg, and Casio venturing into digital territories.
These synthesizers combined the best of both analog warmth and digital precision.
-
The Benefits of Digital Synths For Creativity: Breaking it Down

Digital synthesizers opened the doors to vast soundscapes previously unimaginable.
Their ability to emulate real-world instruments, from grand pianos to string sections, with striking realism was groundbreaking.
Digital architecture also made way for innovations like wavetable synthesis.
Wavetable synthesis, which we’ll discuss later on, is where sounds evolve and morph over time, creating evolving:
- Pads
- Textures
- Atmospheres
The portability and affordability of digital synths democratized music production.
No longer was a synth instrument confined to big studios or elite musicians 一 they were now accessible to bedroom producers and hobbyists alike.
Additionally, integrating digital effects (from reverbs to modulators) allowed for an all-in-one sound design solution.
This further expanded the creative potential of any synth instrument you love today.
-
In a Nutshell: The Differences Between Analog Synths and Digital Synths
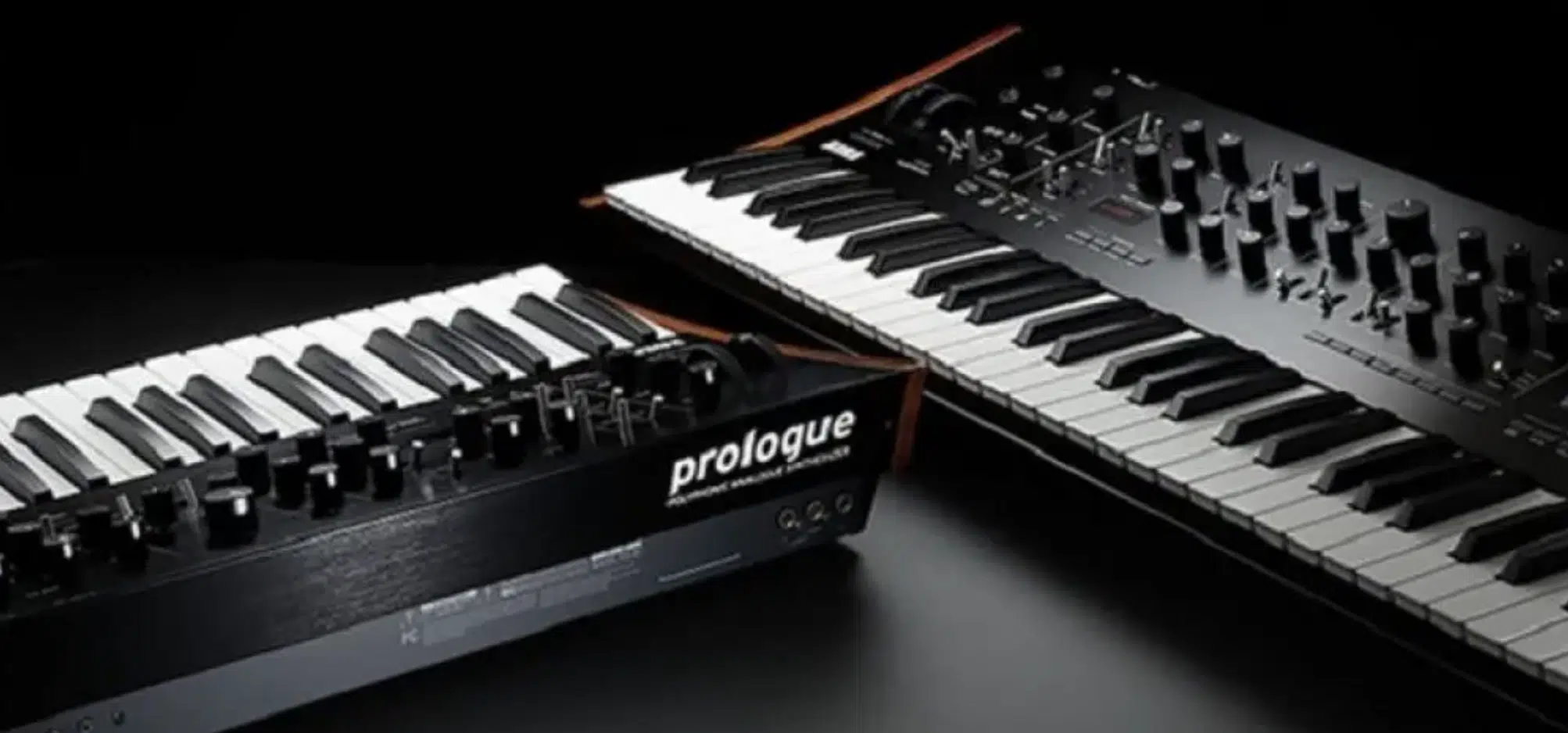

At its essence, the fundamental difference between analog synths and digital synths lies in how sound is generated.
Analog uses continuous electronic signals, while digital utilizes discrete numerical values (binary code).
- Analog synths 一 Have a warm, organic character, attributed to imperfections & nuances in the electronic circuitry.
- Digital synths 一 Can offer pristine clarity and precision.
From a user’s perspective, analog synthesizers often provide a hands-on, tactile experience, with each knob, fader, or switch dedicated to a specific function.
Digital synthesizers might employ multi-functional controls and digital screens.
While analog synths are often limited by their hardware, digital synthesizers can be expanded and updated with software.
This allowed, thankfully, for an ever-evolving sound palette.
Software Synthesizers
Transitioning from the tangible sound production world of knobs and faders, the digital age welcomes a realm where software synthesizers take center stage.
-
VST Synthesizers and the Software Realm
Virtual Studio Technology (VST) revolutionized music production.
These software plugins, compatible with most Digital Audio Workstations (DAWs), emulate the sounds and functions of hardware synths without physical constraints.
The true beauty of VST synthesizers lies in their adaptability.
With the power of modern computing, you can quickly and efficiently:
- Run multiple instances.
- Layer sounds.
- Integrate them with physical MIDI controllers.
Companies like Native Instruments, Arturia, and Spectrasonics have pushed the boundaries of software synthesis.
After all, they introduced products like Massive, Pigments, and Omnisphere to the world, which have become staples in studios worldwide.
Most likely, you own one of the three, am I right?
Software synths allow for quick updates and patches 一 ensuring you always have access to the latest features and sound libraries.
Which is super important if you want to stay ahead of the game and produce timeless tracks.
-
Advantages of Software Synths in Modern Music
The cost-efficiency of software synths cannot be overstated.
While acquiring a premium hardware synth can be a significant investment, many top-tier VSTs are available at a fraction of the cost.
They often come with comparable, if not superior, sound quality.
NOTE: If you’re looking for the best deals on software synths (all free), we’ve got you covered.
The ease of integration means producers can quickly swap between different synth engines, sound presets, or even automate parameters, all within the DAW environment.
With the power of software synths, the realm of possibilities expands exponentially.
A few of the most advanced methods in the digital domain are:
- Physical Modeling
- Granular Synthesis
- Spectral Synthesis
Storage and portability are also significant advantages.
Entire synth libraries can be stored on a laptop 一 making it easier for live musicians and producers to carry their sounds wherever they go.
-
Tips for Achieving Analog Sound with Software Synthesizers
Many software synthesizers offer analog emulation algorithms designed to replicate the warmth and character of vintage hardware.
Exploring these settings is essential, often found as “analog warmth” or “drive” features.
Don’t forget to utilize saturation and tape emulation plugins.
These can infuse digital sounds with the organic imperfections and harmonics associated with analog gear.
Also, it would help if you tried introducing factors like:
- Slight detuning
- Oscillator drift
- Even subtle noise layers
These can mimic the inherent instabilities of analog circuits 一 adding to the perceived warmth that can help your music become addicting.
Finally, consider pairing software synths with analog outboard gear like preamps or EQs.
Even the simple act of routing a digital sound through real-world circuitry can impart a unique character.
Modular Synthesizers: A Deep Dive
From the virtual domain, we pivot to a realm where creativity meets complexity: modular synthesis.
Modular synthesizers can introduce you to a world where signals flow freely and sound sculpting becomes an art, so let’s jump in.
-
The Basics of Modular Synthesis
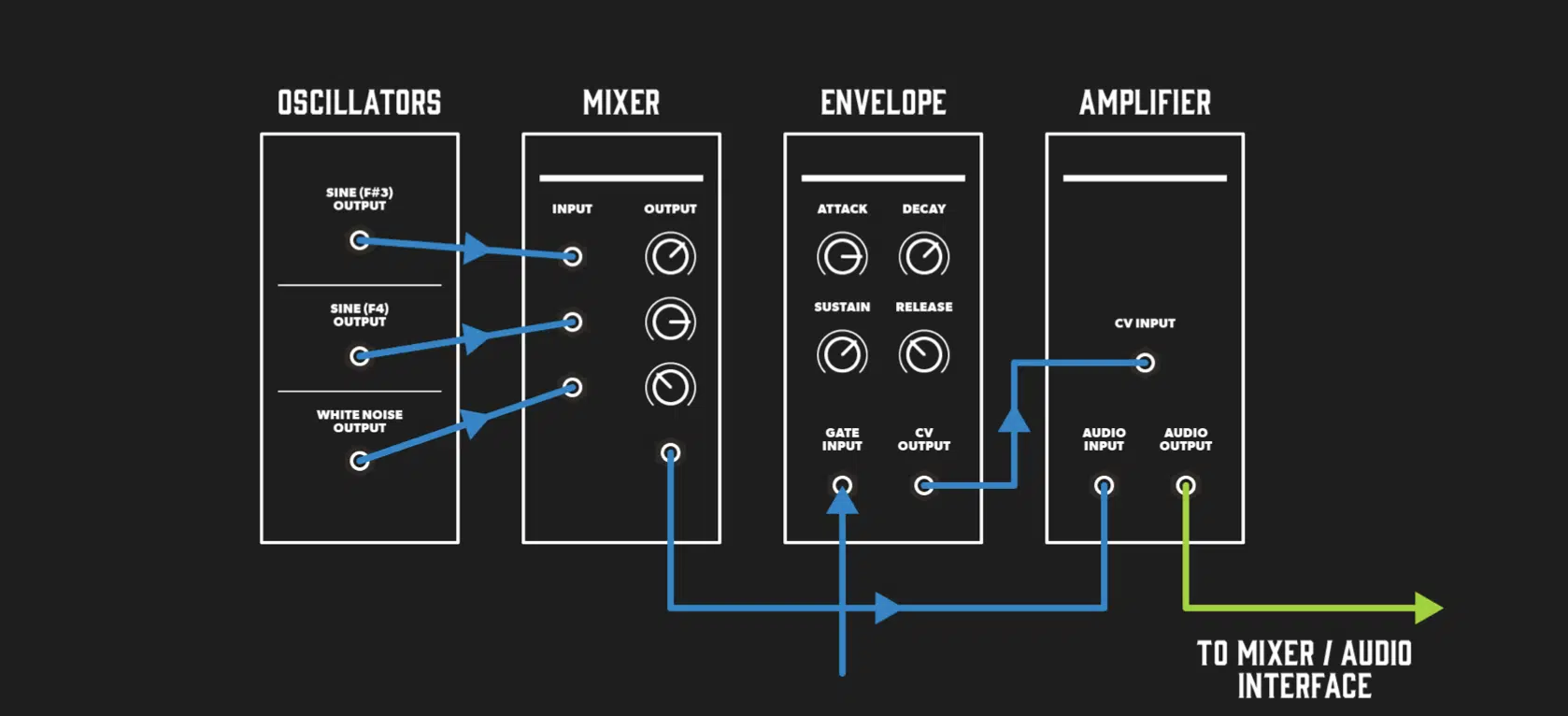
Modular synthesizers are essentially a collection of individual modules (oscillators, filters, envelopes, sequencers, etc.) that are patched together using cables.
These cables are used to create a custom signal path.
Unlike traditional synths, where the signal flow is predetermined, modular systems offer complete freedom.
An oscillator doesn’t necessarily have to connect to a filter 一 it could instead modulate an envelope or drive a sequencer.
The flexibility of the modular synthesizer (modular synths) allows for unique and often experimental soundscapes.
It’s not uncommon for modular synthesizer enthusiasts to discover new sonic textures and rhythmic patterns by accident, as the possibilities are endless.
However, with the great power modular synthesizers offer comes great responsibility…
The open-ended nature of modular synthesis demands a deep understanding of:
- Signal flow
- Audio synthesis
- The individual functions of each module
In today’s digital-dominated era, many producers still gravitate towards modular synthesis.
Its intricate patching and hands-on approach is a refreshing way to craft unique and innovative sounds for their tracks.
-
Using Patch Cables and Signal Flow for Sound Design

Patch cables are the lifelines of a modular system.
They carry audio or control voltage (CV) signals from one module to another 一 dictating how the system behaves.
An essential principle in modular synthesis is the distinction between:
- Audio signals 一 The sounds themselves.
- CV signals 一 Voltages used to control different parameters (pitch, filter cutoff, amplitude).
Creative patching can lead to intricate, evolving sounds.
For instance, routing an LFO (low-frequency oscillator) to modulate a filter’s cutoff frequency produces a rhythmic pulsing effect.
Feedback loops, where a signal is routed back into itself or another related module, can lead to exciting sonic results.
From drones to chaotic bursts of noise, feedback loops can unleash intriguing flair.
If you want to know everything about patch cables in detail, we’ve got you covered with the new article we just dropped.
-
The Allure of the Modular Synth in Trap and Hip-hop
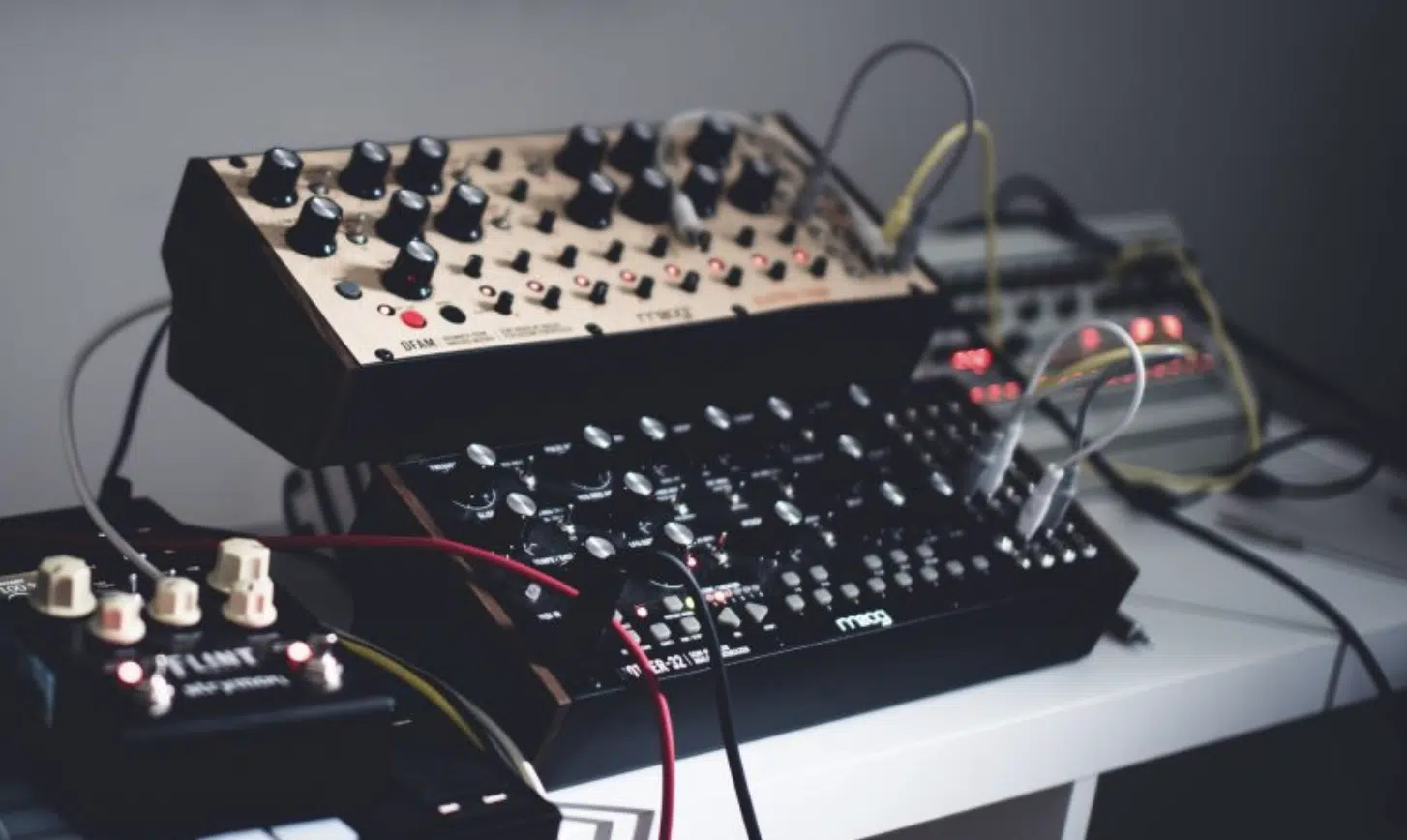

Modular synthesis is often associated with experimental or ambient music, but its influence has permeated mainstream genres like trap and hip-hop.
Producers like Kanye West and Travis Scott have incorporated modular textures into their beats 一 offering a fresh edge.
Modular systems excel at producing:
- Deep, resonant basses
- Glitchy sequences
- Atmospheric pads
These elements, proven to spark emotional interest, can elevate a trap beat or hip-hop instrumental from basic to epic.
The hands-on nature of modular synthesis also allows for real-time manipulation (like controlling pitch).
This makes any live performance dynamic and visually engaging.
Producers can be seen physically molding and shaping the sound, which is super dope.
While not as popular as some other synth instrument types, modular synths can open up a world of undiscovered soundscapes.
An Insight into Different Synthesis Types
The world of synthesis is diverse and deep, filled with many techniques and approaches.
You can better grasp how sounds are shaped and sculpted by understanding these methodologies.
-
Subtractive Synthesis
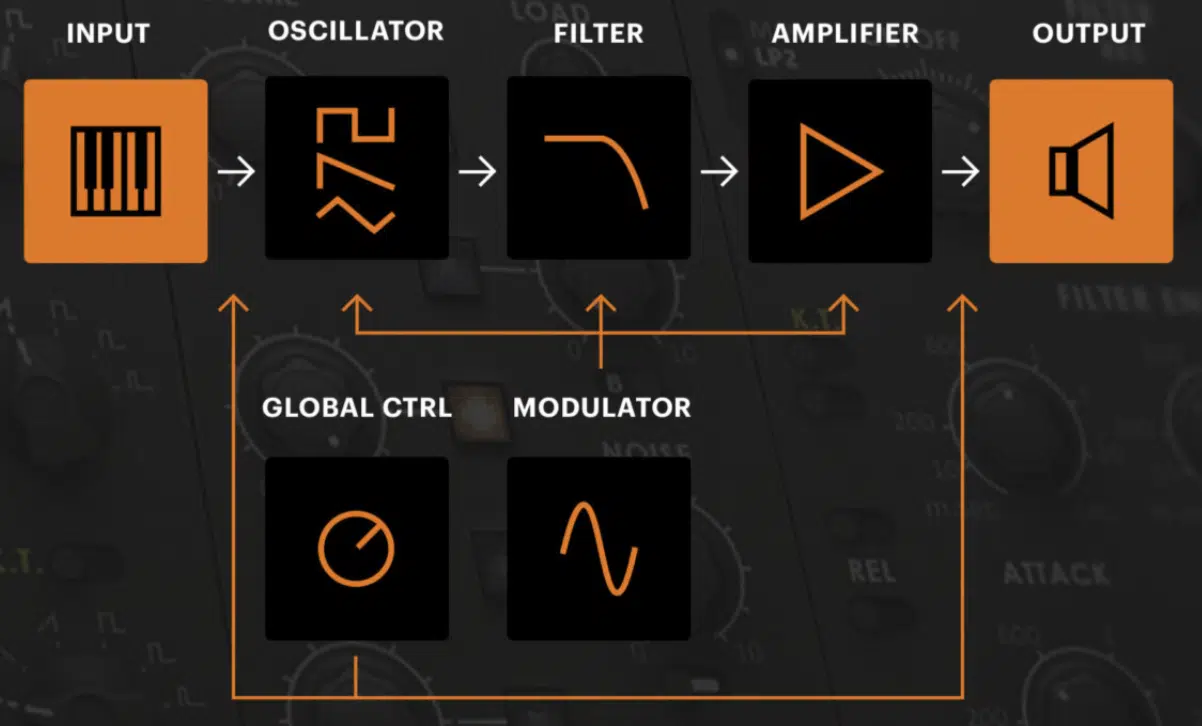
Subtractive synthesis, arguably the most common form, begins with a harmonically rich waveform, typically generated by an oscillator.
This raw sound is then shaped and sculpted by removing or “subtracting” certain frequencies using filters.
The main tool in subtractive synthesis is the filter type, like:
- Low-pass filters
- High-pass filters
- Band-pass filters
- Notch filters
Each filter type allows for a specific range of frequencies to pass through while attenuating others.
Envelopes and LFOs (Low-Frequency Oscillators) can dynamically control the filter’s cutoff frequency, where the magic happens.
This enables the creation of evolving sounds 一 such as the classic sweeping pad or a resonant bassline.
Classic synths like the Minimoog and Roland’s Jupiter series are quintessential examples of subtractive synthesizers.
They have successfully defined the sounds of multiple music genres over the decades with the help of subtractive synthesis.
-
Exploring Wavetable Synthesis: Electronic Music Madness

Wavetable synthesis employs a different concept: instead of starting with a single static waveform, it utilizes a series of waveforms or a ‘wavetable.’
By scanning or modulating through these waveforms, evolving timbres are achieved.
The key to wavetable synthesis is the ability to morph smoothly between different wave shapes in the table.
This creates dynamic, evolving sounds that are super captivating.
Synths like the Waldorf Blofeld or Serum by Xfer Records harness the power of wavetable synthesis 一 allowing users even to import or create their own custom waveforms.
This synthesis method is versatile, producing anything from lush pads to aggressive, metallic leads.
This makes wavetable synthesis a favorite among electronic music producers everywhere.
-
Delving into FM Synthesis and Sound Waves
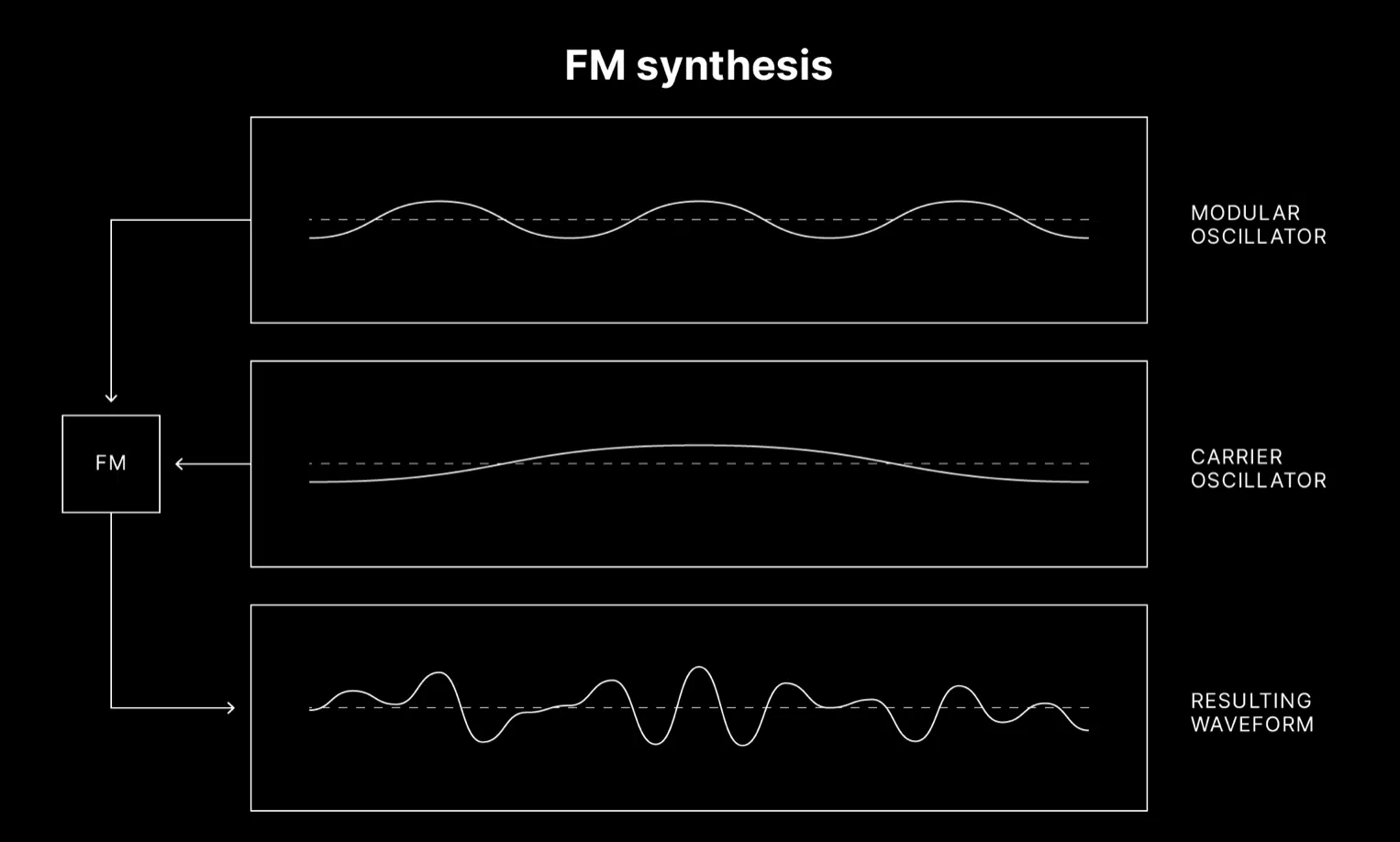
Frequency Modulation (FM) synthesis involves modulating the frequency of:
- One waveform (the carrier)
- With another waveform (the modulator)
This interaction produces complex timbral changes 一 resulting in unique sounds.
FM synthesis can be intricate due to its reliance on the interplay of multiple oscillators, but it can generate a vast range of timbres, from crystalline bells to growling basses.
Yamaha’s DX7, which we touched upon earlier, was introduced in the 1980s and brought FM synthesis to the forefront.
It shaped the sound of an entire decade with its characteristic electric pianos and punchy basses.
NOTE: Modern iterations, such as Native Instruments’ FM8, have made FM synthesis more accessible, offering intuitive interfaces and expanded capabilities.
This included advanced modulation matrices, integrated effects, and a broader range of waveform options for more profound sound sculpting possibilities.
-
Additive Synthesis and Sound Sculpting
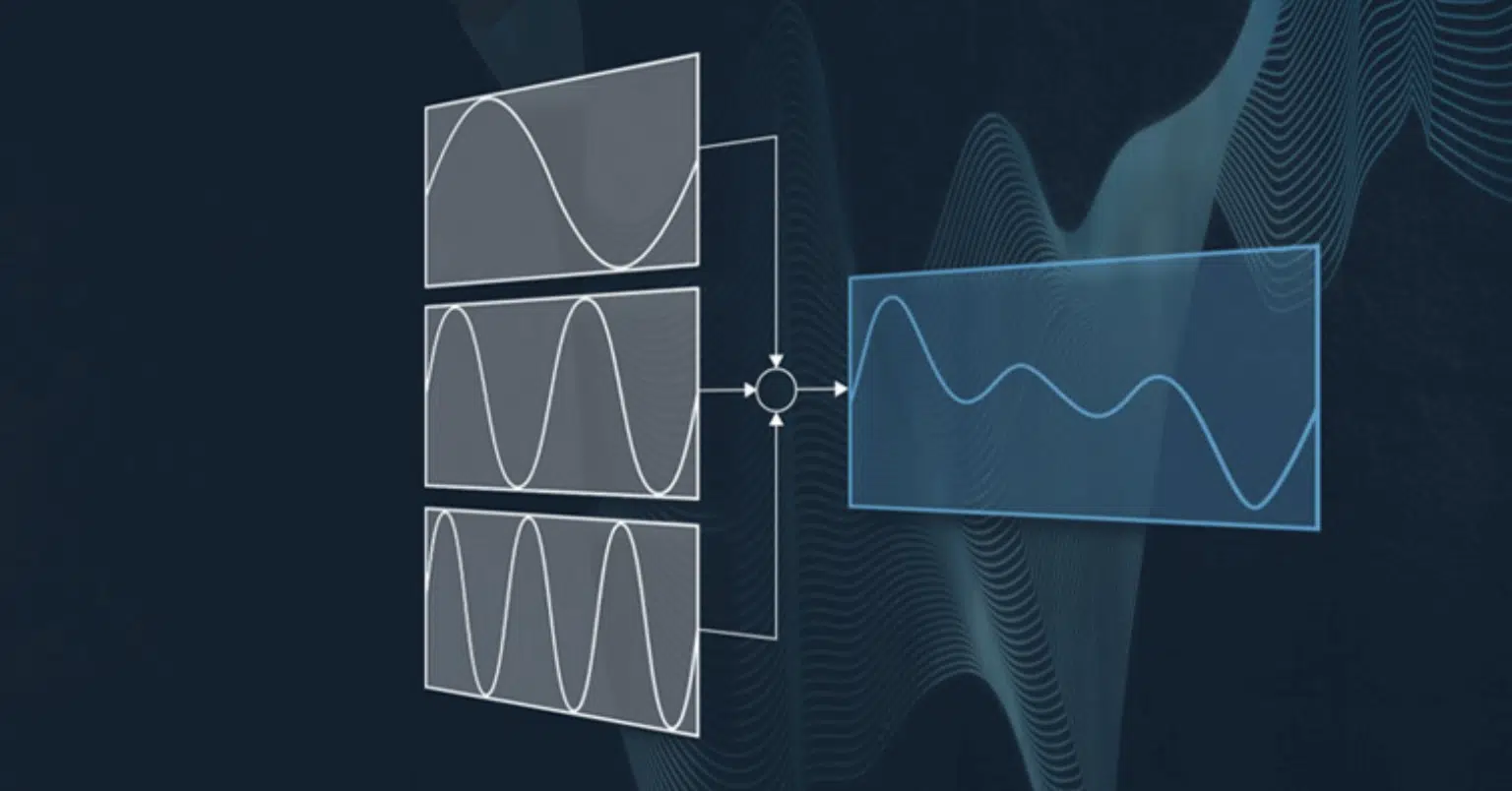
In contrast to subtractive synthesis, additive synthesis builds sound from the ground up.
Additive synthesis involves stacking individual sine wave harmonics at different:
- Frequencies
- Amplitudes
- Phases
This successfully produces a unique composite sound.
While theoretically capable of recreating any sound, additive synthesis can be computationally intensive due to the number of sine waves required.
Synth instruments like Loom by AIR Music Technology and Razor by Native Instruments exemplify modern additive synthesis.
They provide user-friendly interfaces and efficient algorithms.
This method excels at creating ethereal pads, evolving textures, and otherworldly sounds 一 making it a valuable tool for ambient and experimental music.
Enhancing Your Sound Design Techniques
Mastering the diverse world of synthesis involves understanding individual synth types.
As well as grasping the foundational elements that form the backbone of most synthesis techniques.
So, let’s dive into how you can deeply understand these elements to enhance your sound design techniques.
-
The Role of Pulse Waves and Sine Waves
If you’re going to emerge in the sound design world, you’ll need to be familiar with pulse waves and sine waves.
Pulse waves, a form of square wave with a variable duty cycle, are fundamental in many synthesis methods.
Their rich harmonic content can be sculpted into numerous timbres (especially when paired with filters).
Modulating the width of a pulse wave, known as Pulse Width Modulation (PWM), creates a phasing effect.
This is central to many vintage synth instrument sounds.
Sine waves, on the other hand, are the simplest waveforms, containing no harmonics.
They are the building blocks in additive synthesis and play pivotal roles in FM and wavetable synthesis.
Understanding the manipulation of these basic waveforms is crucial for any budding sound designer 一 laying the foundation for more advanced techniques.
-
Physical Modeling: Emulating Acoustic Instruments
Physical modeling synthesis doesn’t rely on traditional waveforms.
Instead, it mathematically models the properties and behaviors of real-world instruments, expertly recreating their sound.
Physical modeling can emulate the:
- Vibrations of a guitar string
- Resonant qualities of a drum head
- Complex interactions inside a wind instrument
Synths like Arturia’s Chromaphone or Logic Pro’s Sculpture offer physical modeling capabilities 一 delivering incredibly realistic emulations of acoustic instruments.
For producers seeking authentic acoustic sounds without recording them, physical modeling synthesis provides a great solution.
If nothing else, it will expose you to ultimate realism and flexibility.
Synth Instrument: Final Thoughts
In its many forms, the synth instrument has undeniably revolutionized music production.
From the warmth of analog synths to the intricacies of modular synthesis, understanding these tools is pivotal for any music producer aiming to innovate and stand out.
As creators, the possibilities available with your synth instrument is limitless.
You can craft signature basslines, design ethereal soundscapes, or even pioneer a new sonic trend.
Yet, to truly exploit the synth instrument’s versatility, top-tier presets can be a game-changer.
Enter: the Free Serum Essentials pack 一 a curated set of premium Serum presets, modeled after hit tracks.
Every preset is designed for adaptability, loaded with macros and tweakable parameters, allowing you to tailor each sound distinctively.
The included preset banks give you the most polished, professional Serum presets for each genre.
Needless to say, having access to these kind of vital elements will help you navigate your synthesis journey.
Mastering the art of the synth instrument is both a journey and an asset.
Paired with resources like the Free Serum Essentials, it empowers you to create, customize, and elevate your tracks to professional levels.
So, dive in, experiment, and let the synth instrument be the cornerstone of your creative expression.
Until next time…







Leave a Reply
You must belogged in to post a comment.