Modular synthesis represents the pinnacle of sound design flexibility.
It offers an endless landscape of sonic possibilities, literally.
From the outside, the complex patch cables and modules may seem overwhelming, a maze of options with limitless potential…
However, fear not!
We’re about to demystify the world of modular synthesis for you.
By the end of this comprehensive guide, you’ll have a firm grasp of the fundamentals and more advanced topics.
This knowledge will empower you to conquer the digital world of modular synthesis with confidence, and most importantly, start creating your own epic sounds.
In today’s article, we’ll be breaking down:
- The limitless world of modular synthesis ✓
- Principles & inner-workings of a virtual modular synth ✓
- Comparison between digital modular synths & traditional synths ✓
- Exploration of digital modular systems ✓
- The magic behind virtual modular synthesizers ✓
- The role of voltage-controlled amplifiers ✓
- Understanding the virtual Eurorack format ✓
- Mastering the signal path in your virtual modular system ✓
- Crafting professional sounds with digital modular systems ✓
- Decoding control voltage in the digital domain ✓
- The role of virtual patch cables ✓
- So much more ✓
After reading this article, you’ll be able to navigate this fascinating sound design landscape in no time.
Let’s dive in…
Table of Contents
- The Modular Synthesizer: Breaking it Down
- Comparing Digital Modular Synth to Traditional Synths
- Breaking Down Digital Modular Systems
- Understanding the Virtual Eurorack Setup
- Mastering the Signal Path in Your Virtual Modular System
- Deep Dive into Digital Signal Input, Audio Signal & Signal Flow
- Harnessing Your Virtual MIDI to CV Converter
- Create Electronic Sounds with Your Digital Modular System
- Different Virtual Modules & Their Role in Sound Shaping
- Using Multiphonics CV-2 by AAS for Addition Sonic Possibilities
- The Role of Virtual Patch Cables
- Incorporating Software Synthesizers in Virtual Modular Systems
- Virtual Eurorack Modules: Enhancing Your Modular Journey
- Modular Synthesis: Final Thoughts
The Modular Synthesizer: Breaking it Down

When working with a virtual modular synthesizer, understanding its fundamental principles is crucial.
At its core, a virtual modular synth operates much like a traditional analog modular synth.
You have a collection of independent modules, each performing a specific function, and you connect these modules using virtual patch cables to create your signal flow.
A typical module could be:
- An oscillator (generating the raw sonic material)
- A filter (shaping the timbre of the sound)
- And/or a VCA & envelope generator (controlling the amplitude of the sound over time)
- An LFO or another modulator (for movement)
By patching these together in different ways, you create your own unique instrument.
For example, you might start by patching an oscillator to a filter 一 allowing you to control the harmonic content of your sound.
You could then add an envelope generator, using it to modulate the filter cutoff over time and add movement to your sound.
Comparing Digital Modular Synth to Traditional Synths
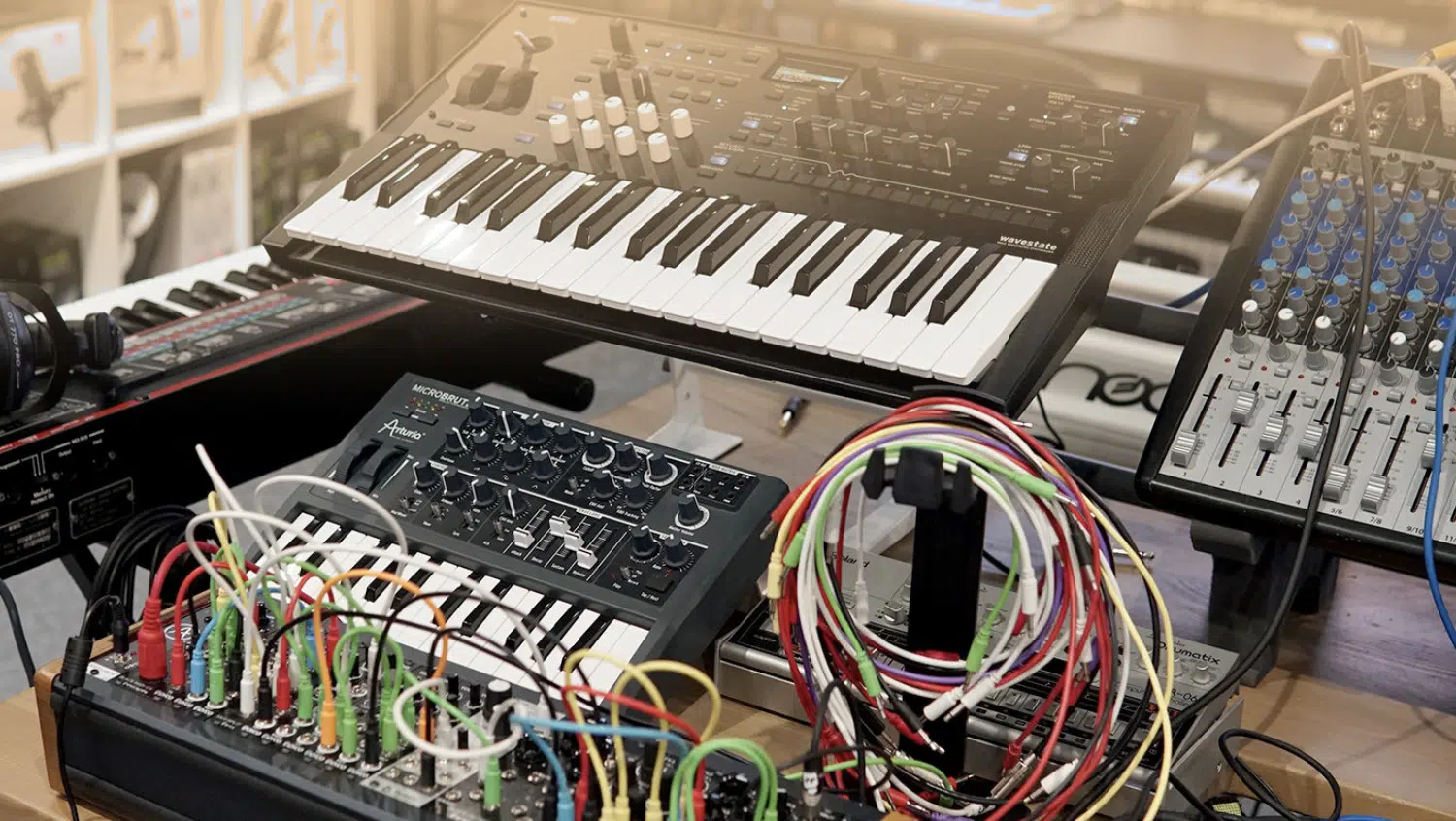

Comparing digital modular synthesizers and traditional synths can help highlight their unique strengths.
Traditional synthesizers (whether hardware or software) often come with a pre-defined signal path.
They usually feature a set of oscillators, filters, and envelope generators 一 with fixed routing and a certain degree of modulation possibilities.
This can be advantageous for quickly creating sounds and is usually more approachable for beginners.
Digital modular synthesizers provide complete freedom to define your own signal path.
Instead of being confined to a fixed architecture, you can:
- Add modules
- Remove modules
- Rearrange modules as you please
This creates complex patches that can produce sounds unlike anything possible with a traditional synth.
For instance, you could create a patch where an LFO modulates the rate of another LFO, which then modulates an oscillator 一 resulting in a sound that evolves and changes over time in unpredictable ways.
This flexibility and depth are what make modular synthesizers, including their digital counterparts, an invaluable tool.
NOTE: Since its signal path is predefined, any output module is continuously running internally, even if it’s not connected.
Meaning, when it comes to envelopes, they need to be patches first in order to prevent the output of your oscillator to be heard at times (e.g., when it’s not triggering notes).
Breaking Down Digital Modular Systems
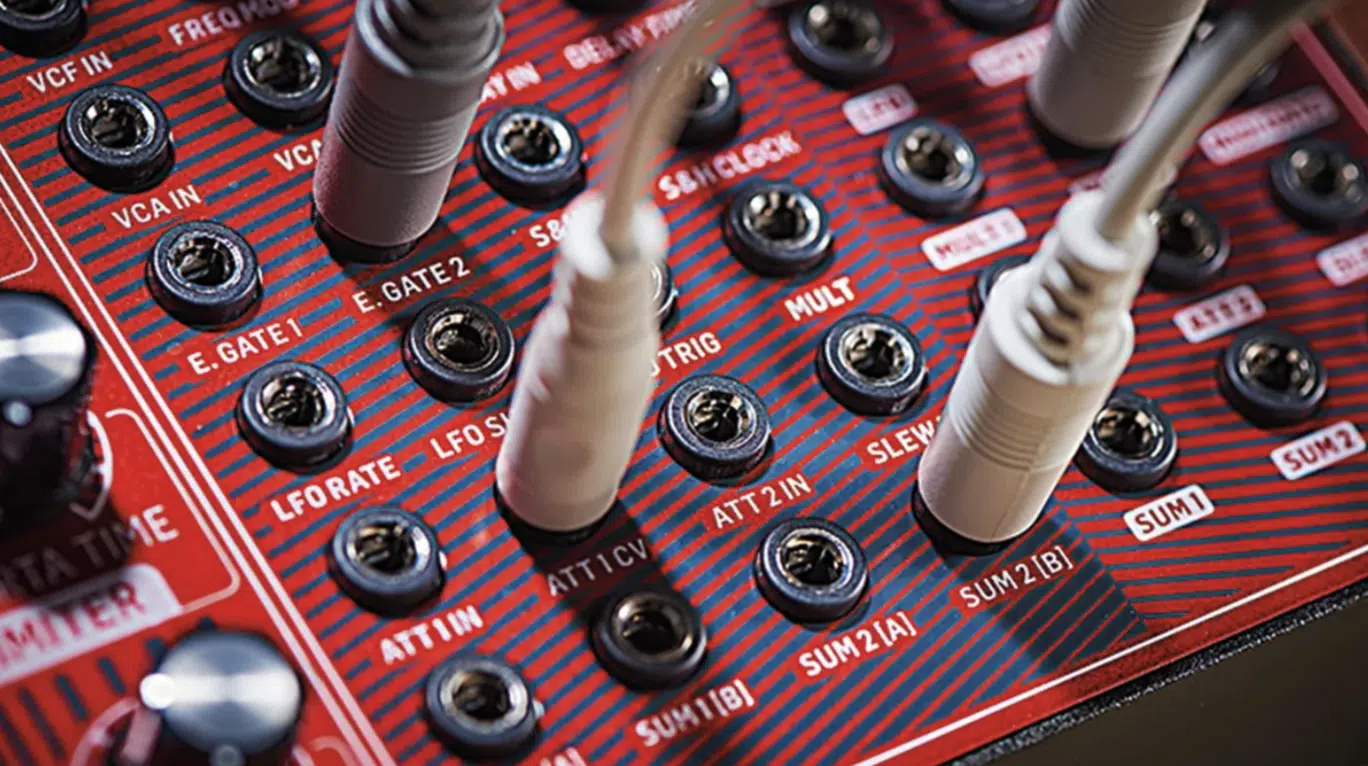

In a digital modular system, you have the same building blocks you’d find in a traditional synthesizer:
- Oscillators
- Filters
- Envelope generators
- Etc.
But unlike traditional synthesizers, these modules aren’t pre-connected in any fixed order.
They’re separate entities that you connect as you please.
And each connection you make is a decision point that shapes your sound in unique ways.
Let’s take an oscillator, for example… in a traditional synth, it would generate a simple waveform, like a sawtooth or square wave.
But in a digital modular system, an oscillator could do so much more.
You could:
- Patch it into a filter module to shape its tone
- Feed it into another oscillator to achieve frequency modulation
- Even both simultaneously
Digital modular systems often include a broader range of modules than you’d find in a traditional synth.
You might come across modules like:
- Dedicated sequencers
- Sample-and-hold modules (S&H)
- Quantizers
- Gates
- Triggers
- Complex Envelopes
All of which allow you to add rhythmic elements, manipulate audio samples, or shape your sound in intricate ways.
The beauty of digital modular systems lies in this limitless potential for exploration and customization.
-
Advantages of Using Digital Modular Systems
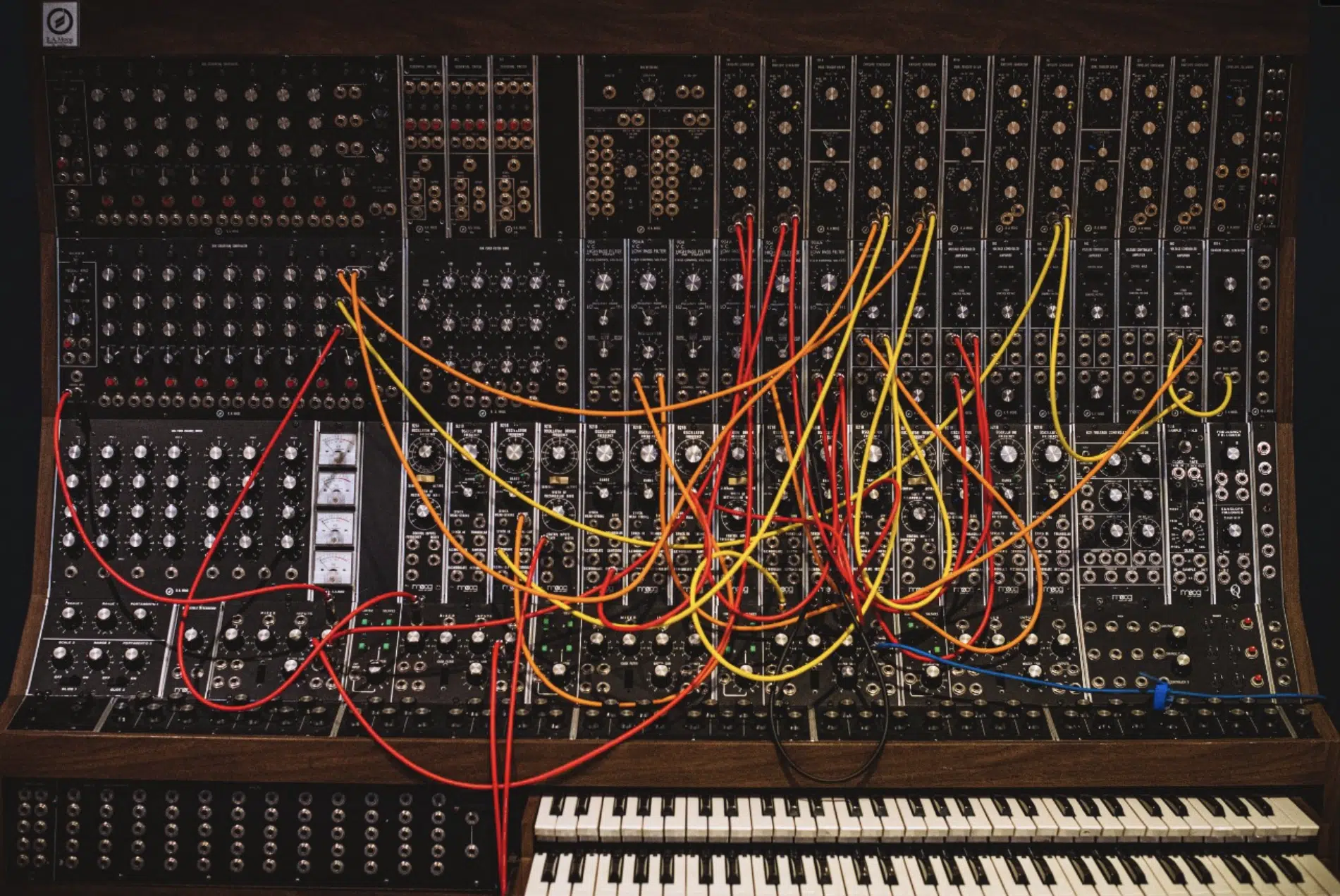

Digital modular systems offer several advantages over their physical counterparts.
#1. They’re significantly more accessible.
Physical modular synths can be incredibly expensive, and they also require a lot of space in your home studio.
But digital modular synths are much more affordable, and they don’t take up any physical space at all.
#2. Digital modular systems allow for more experimentation.
Most software allows you to save and recall patches, something that’s impossible with a physical modular synth.
This makes it easier to return to ideas and continue refining them.
#3. Undo & redo commands are often available.
This enables you to fearlessly experiment without worrying about losing your work.
-
Essential Virtual Modules in Your Digital Modular Systems
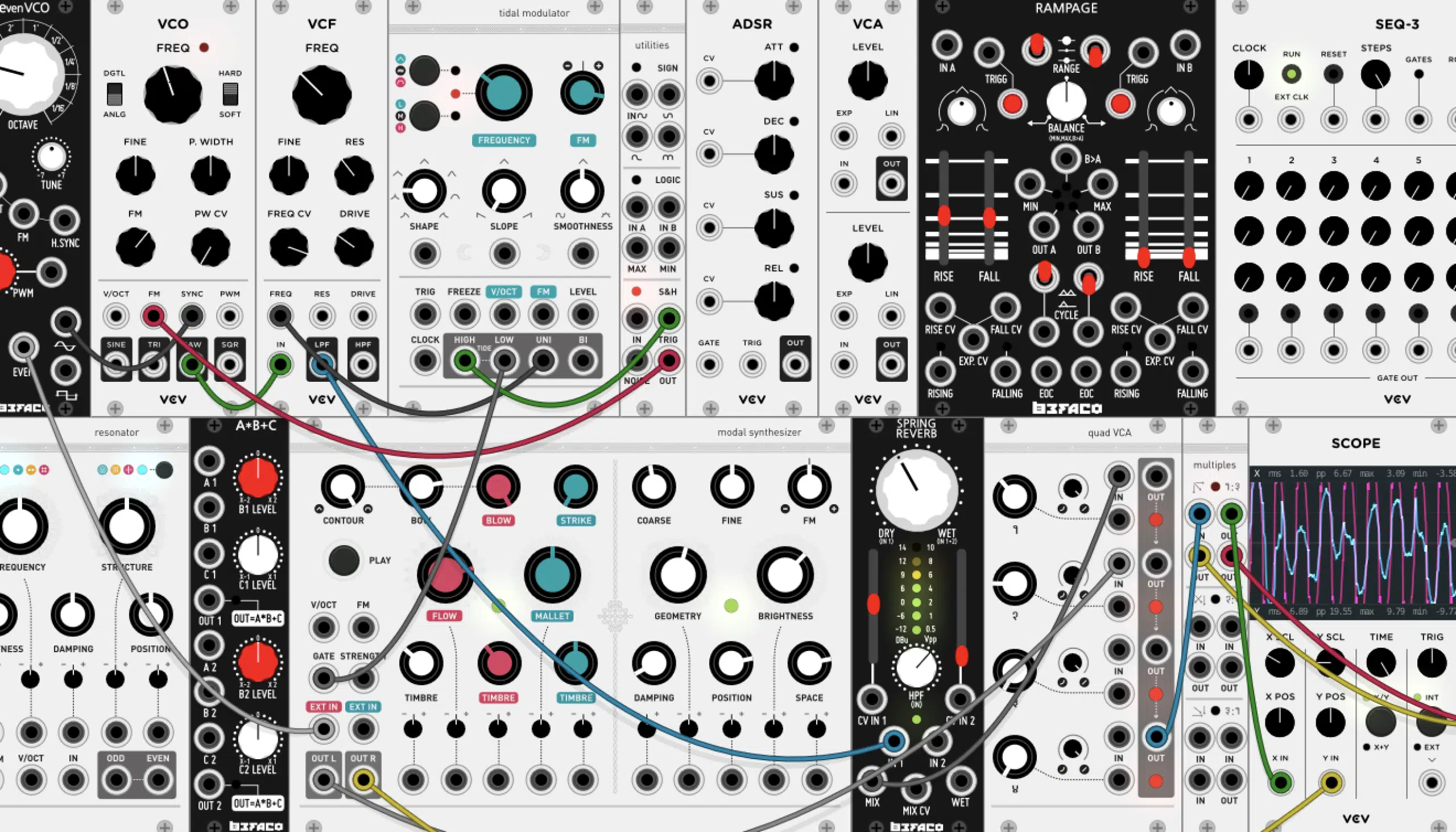

Just like a physical analog modular synth, there are certain essential modules you’ll want in your digital modular system.
An oscillator, a filter, an envelope generator, and a VCA are the most basic modules you’ll need to create a wide range of sounds.
But the beauty of modular synthesis is that you’re not limited to these basics!
There are many more modules available in the digital realm.
- Sequencers and sample-and-hold modules 一 Add rhythmic elements to your sounds.
- LFOs 一 Create slow/fast rhythmic changes in sound parameters.
- Complex envelope modules 一 Give you intricate control over how your sound evolves over time.
You’re limited only by your imagination and your willingness to explore.
NOTE: One thing about these LFOs (and all modulators in general) are they’re ran at an audio rate.
Meaning, they go fast enough for amplitude and frequency modulation; some even generate a tone and can be used as oscillators.
-
What is a Voltage-Controlled Amplifier (VCA)?
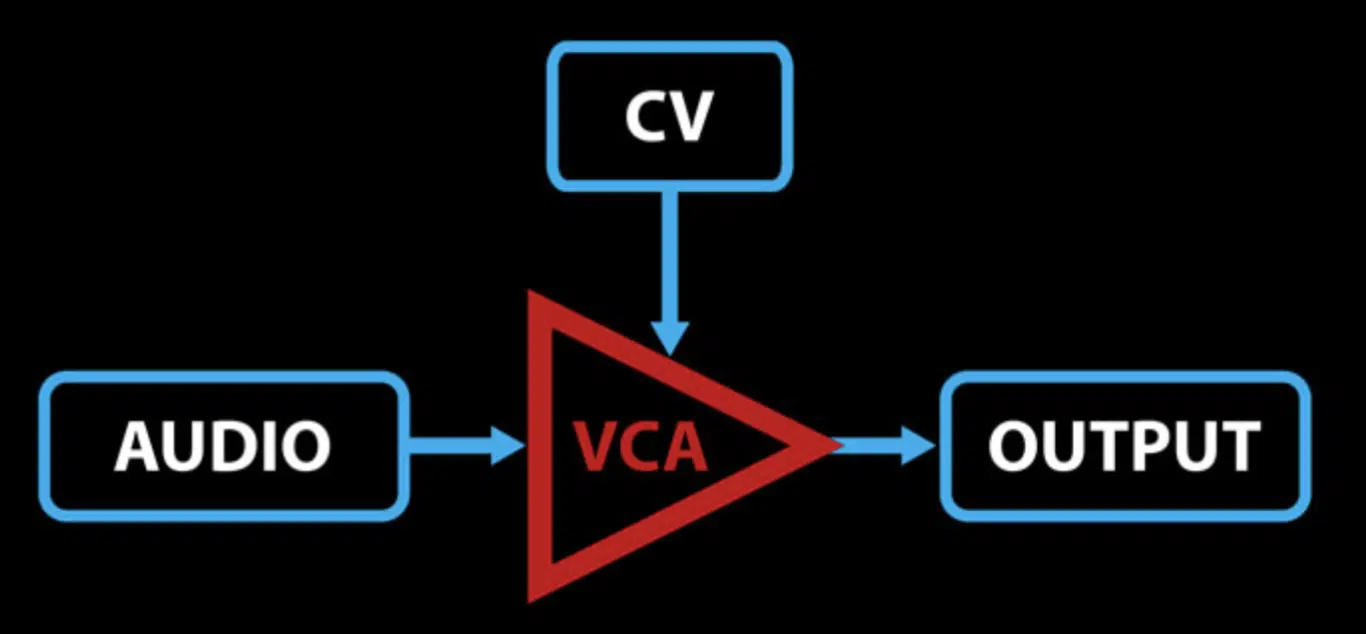
Voltage-Controlled Amplifiers (or VCAs) play a crucial role in modular synthesis, both analog and digital.
In the simplest terms, a voltage-controlled amplifier allows you to control the volume of a sound.
But in a modular synth, they serve a much more versatile purpose.
In a digital modular system, a VCA could be used to control the volume of your audio signal, sure, but it could also be used to shape a modulation signal.
For instance, you could use an envelope to control a VCA 一 which in turn controls how much a certain parameter (like filter cutoff or oscillator pitch) is modulated.
This allows you to create sounds that evolve and change over time, adding movement and life to your patches.
NOTE: A voltage-controlled filter (VCF) is a processor within a modular synthesizer that modifies the timbre of the audio signal by selectively boosting or cutting certain frequencies based on the control voltage it receives.
-
Refining Your Sound with Digital Envelope Generators

Envelope generators are another key element of a digital modular system.
They shape the amplitude of your sound over time, defining how your sound starts, evolves, and ends.
Think of a piano note:
- It starts abruptly (fast attack)
- Sustains as long as you hold the key (sustain)
- Then fades out when you release a key (the release)
That’s an envelope.
In a digital modular synth, envelope generators can do much more than just shape volume.
You can use them to modulate any parameter in any module.
For example, you could use an envelope to sweep the cutoff frequency of a filter, creating a “wah-wah” effect.
Or you could use it to modulate the pitch of an oscillator, creating a “dive bomb” effect.
The possibilities are truly endless.
They also ‘output’ and accept CV (control voltage) signals in addition to dedicated CV modules (which we’ll break down later).
Understanding the Virtual Eurorack Setup
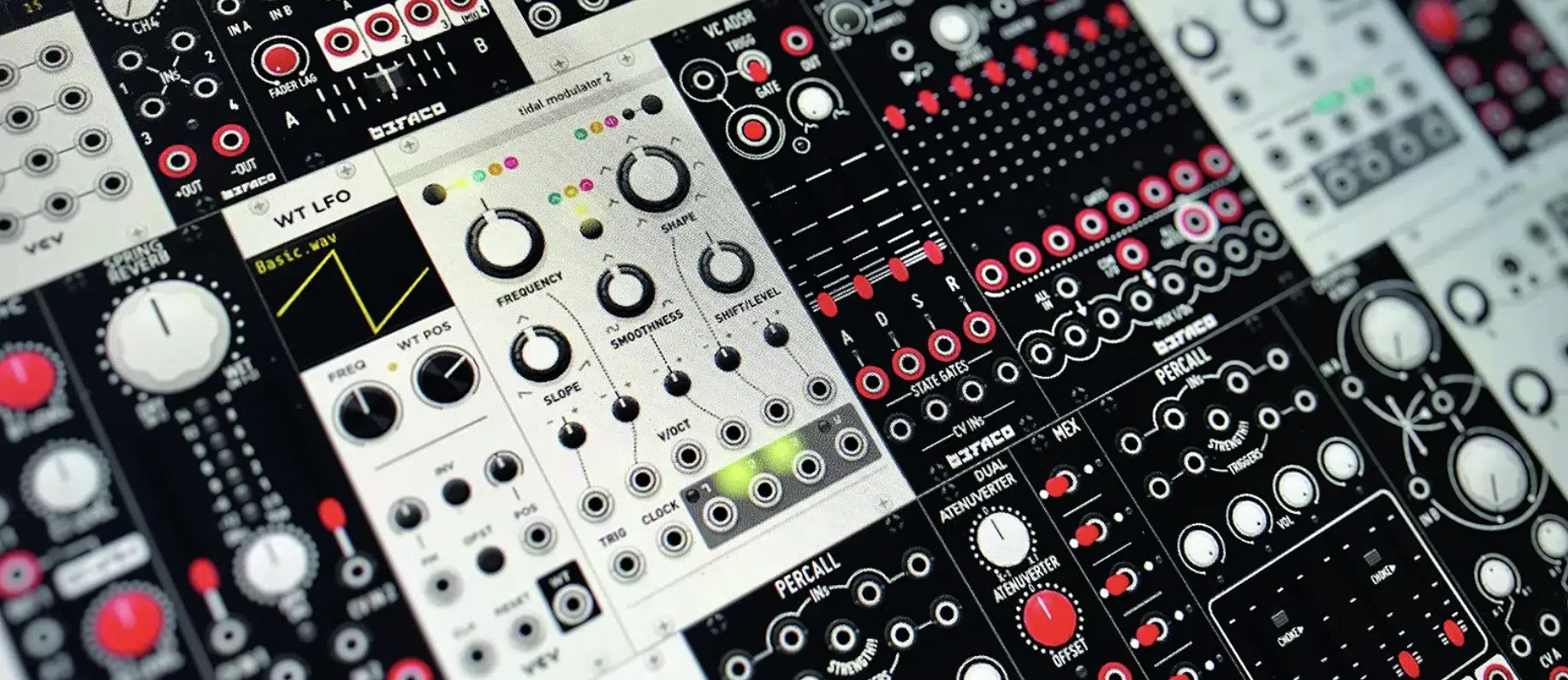

The Eurorack format, a standardized system for modular synths, has been virtually adapted in software like VCV Rack and Softube Modular.
In the digital realm, the Eurorack format (roughly) defines the way modules are visually represented and how they connect and interact with each other.
The virtual Eurorack format aims to provide an authentic modular experience within the digital space.
NOTE: Most of the voltage standards are also virtually adapted.
Just like in the physical world, digital Eurorack modules are represented as individual components that you can add to your rack.
Each module has inputs & outputs that you can connect using virtual patch cables, and you can adjust the parameters of each module using virtual knobs and switches.
- In the digital space 一 You can add, remove, and rearrange modules with a simple drag and drop. You can also add as many of these moduals until your CPU can’t handle it.
- In the analog world 一 You’re limited to the available moduals and the amount you physically own.
Also, the Eurorack format extends to how modules are designed and how they behave.
Many virtual Eurorack modules are based on their physical counterparts; emulating their sound characteristics and quirks.
However, some virtual Eurorack modules take advantage of the digital medium to offer features that would be impossible in the physical world, such as:
- Virtually unlimited modulation sources
- Complex digital algorithms
- Visual feedback of the signal flow
NOTE: The virtual Eurorack format allows you to experiment with different configurations without any physical limitations.
In a physical Eurorack system, rearranging modules can be a time-consuming process.
But in a virtual system, you can easily drag & drop modules to try out different setups.
This encourages exploration and experimentation 一 making it easier to discover new and exciting sound possibilities.
Mastering the Signal Path in Your Virtual Modular System
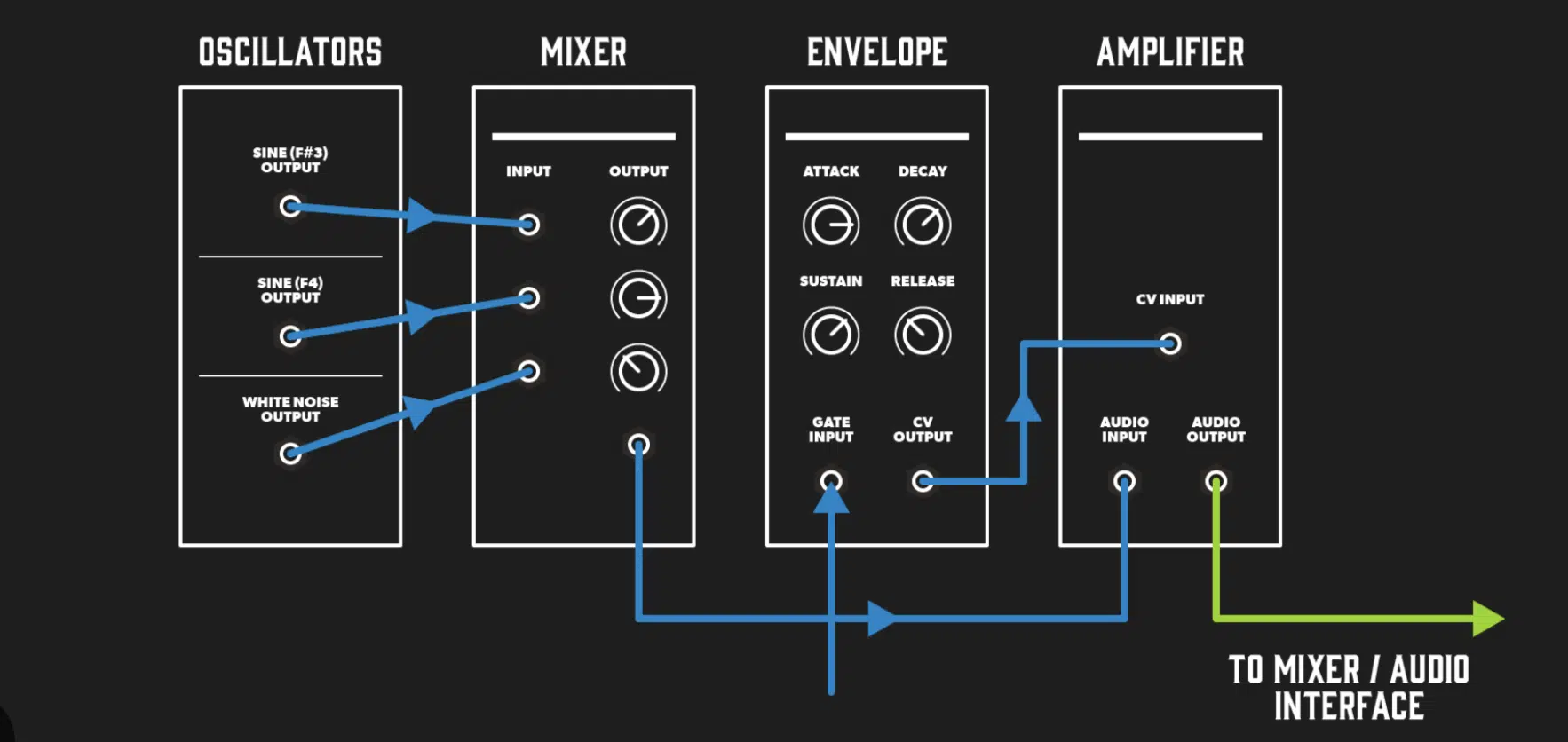
Signal path is a fundamental concept in modular synthesis.
It’s the route that your audio and control signals follow through your modular system.
Understanding signal path is crucial because it determines how your sound is shaped and how your modules interact with each other.
In a digital modular system, the signal path is determined by how you connect your modules with virtual patch cables.
By changing the connections, you can drastically alter the character of your sound.
The freedom to design your own signal path is what makes modular synthesis, especially in a virtual environment, so versatile and powerful.
Deep Dive into Digital Signal Input, Audio Signal & Signal Flow
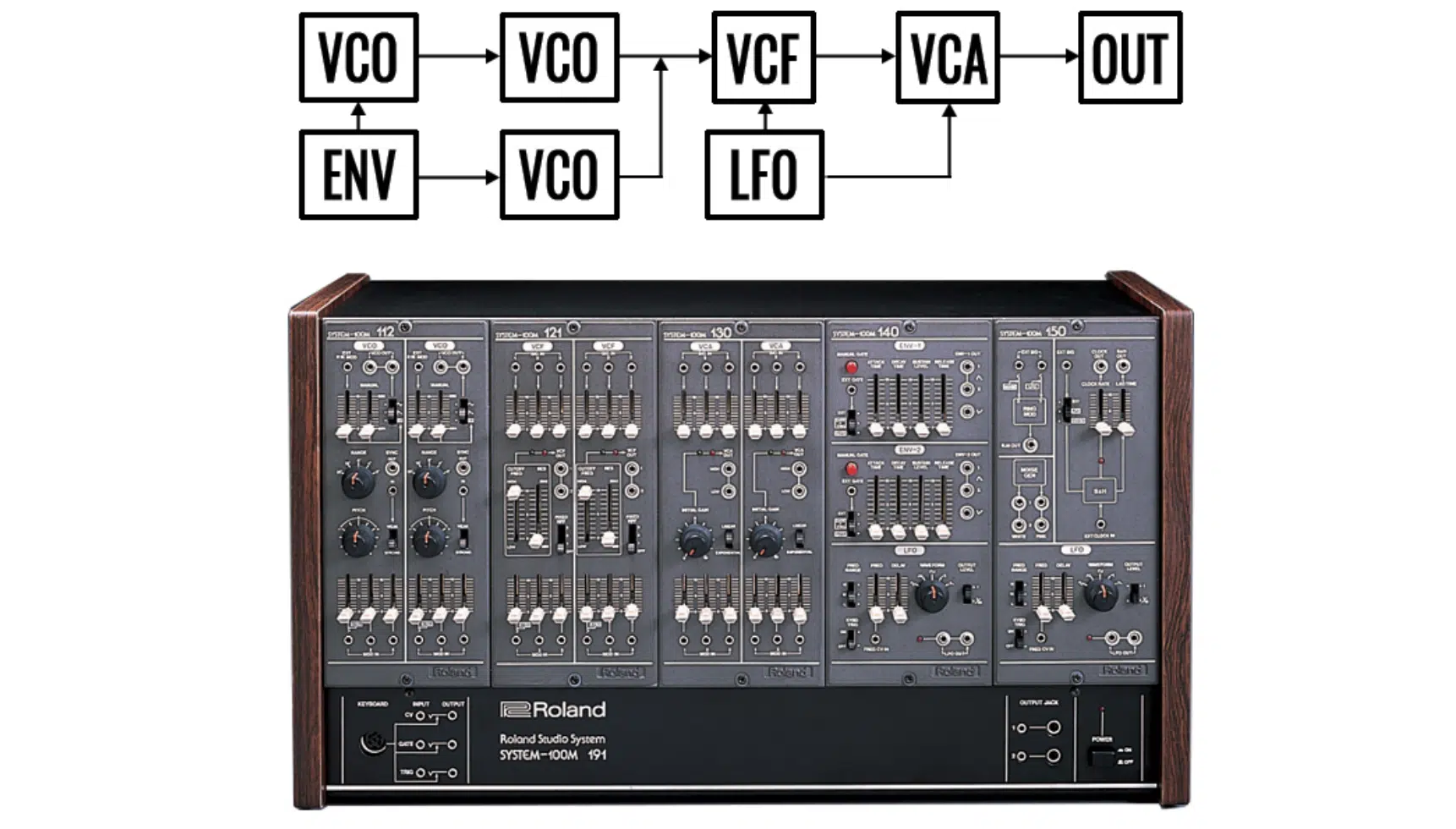
In a digital modular system, there are 2 main types of signals:
- Audio signals 一 What we hear as sound. They’re generated by oscillators or other sound sources and processed by filters, VCAs, and other modules.
- Control signals (CV/Control Voltage) 一 Used to modulate various parameters of your modules. They can come from envelopes, LFOs, sequencers, or a variety of other sources.
The signal input refers to where a signal enters a module.
For instance, an oscillator’s frequency input might receive a control signal from a sequencer, telling it to cycle through a series of pitches.
The audio signal, generated by the oscillator, would then be sent to the oscillator’s output.
This audio signal might then be patched into a filter’s input, and the filtered audio signal sent to the filter’s output.
NOTE: The cutoff usually modulated/controlled by another CV signal, and so on.
This sequence of connections 一 the journey of your signals through your modular system 一 is what we refer to as the signal flow.
Understanding signal flow allows you to sculpt your sound precisely and intentionally.
It’s what lets you turn a simple sawtooth wave into a growling bass, a soaring lead, or a rhythmic percussive pattern.
And the beauty of a digital modular system is that you can redesign your signal flow at any time, experimenting with new ideas and discovering new sonic timbres, textures, and territories.
Harnessing Your Virtual MIDI to CV Converter
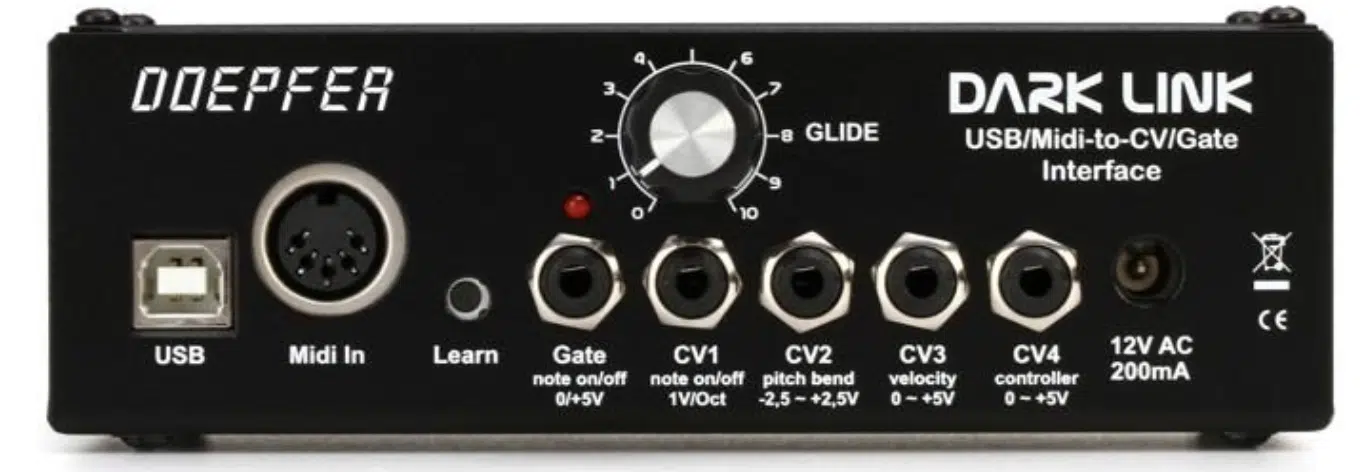

One crucial component in any digital modular system is the MIDI to CV converter.
- MIDI (Musical Instrument Digital Interface) 一 A protocol for communicating musical information, like notes and velocity, between electronic instruments
- CV (Control Voltage) 一 A way of controlling various parameters in a modular synth, such as pitch or filter cutoff (CV input and CV output).
A virtual MIDI to CV converter allows you to use your MIDI keyboard or DAW to control your digital modular synth.
You could, for instance, play notes on your external keyboard and have them control the pitch of an oscillator in your modular system.
Or you could use your DAW to automate the cutoff frequency of a filter, or to trigger a complex sequence of notes.
This integration between the digital and modular realms opens up a wealth of possibilities for performance and composition.
The MIDI to CV converter typically provides several outputs 一 each sending a different type of CV signal.
Common outputs include:
- Gate: (which sends a signal, aka ‘gate signals,’ when a key is pressed or a note is played)
- Pitch: (which controls the pitch of oscillators)
- Velocity: (which can be used to control any parameter, such as volume or filter cutoff, to add expressiveness to your playing)
Understanding how to harness your virtual MIDI to CV converter is key to integrating your digital modular system into your music production workflow.
Create Electronic Sounds with Your Digital Modular System
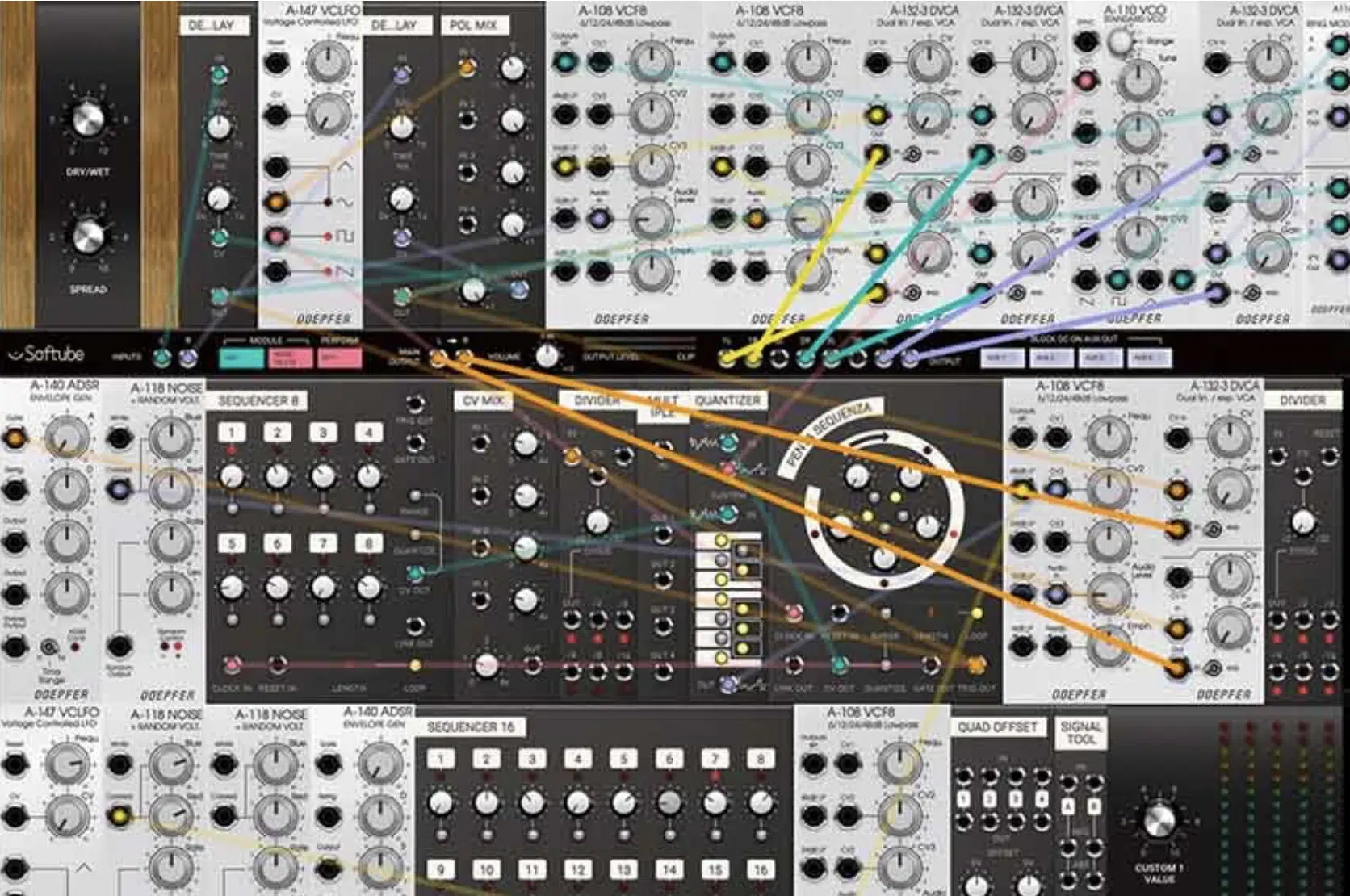
The ability to craft unique electronic sounds is one of the main draws of digital modular systems.
By connecting different modules in various ways, you can create everything from classic synth tones to complex, evolving soundscapes.
Whether you’re after fat basses, piercing leads, ethereal pads, or percussive hits, a digital modular setup can deliver.
You can:
- Generate raw waveforms with oscillators
- Shape these sounds with filters, VCAs, and envelope generators.
- Add in some LFOs to introduce movement
- Sequencers to create rhythmic patterns
- Throw in some effects like reverb and delay for added space and depth
The possibilities are nearly endless, and the beauty of it is that you’re creating these sounds from scratch.
Which gives them a unique character that’s hard to replicate with pre-set synths.
NOTE: A semi-modular synthesizer (semi-modular synth module) is a great place to start if you’re a beginner.
Semi-modular systems are a hybrid type of synthesizer that combines fixed signal paths of traditional synths with the flexibility of a modular setup.
They offer an excellent starting point for modular users to explore the world of modular synthesis.
Different Virtual Modules & Their Role in Sound Shaping

A digital modular system consists of numerous virtual modules, each serving a specific role in sound creation and shaping.
Let’s explore some of the key ones…
#1. Oscillators
Oscillators generate the raw sound in your system.
They produce waveforms like sine, square, triangle, or sawtooth, each with its unique tonal characteristic.
Oscillators can also be modulated 一 creating more complex waveforms for richer and more interesting sounds.
#2. Filters
Filters shape the sound by removing or emphasizing certain frequencies.
They can make your sound bright and buzzy, or dark and mellow.
Modulating the cutoff frequency of a filter can create sweeping effects or rhythmic patterns.
#3. Amplifiers
Amplifiers, controlled by envelopes or other modulation sources, determine the loudness of your sound and shape its dynamics.
#4. Envelopes
Envelopes, in turn, define how your sound evolves over time, controlling parameters such as attack, decay, sustain, and release.
#5. Modulators
Modulators, such as LFOs and sequencers, add movement and rhythm to your sound.
They can modulate virtually any parameter in your system 一 from pitch and volume to filter cutoff and effect parameters.
#6. Effect Modules
Effect modules, like delay and reverb add space and depth to your sound, helping it to sit better in a mix or creating lush, ambient textures.
They can be used subtly, for a touch of polish, or more drastically, as an integral part of your sound design.
Speaking of sound design, if you’d like access to all the most innovative and groundbreaking sound design secrets in the game, we’ve got you covered.
Together, these modules work in harmony to shape and sculpt your sound.
By learning how each one functions and how to patch them together effectively, you can start crafting your own unique sonic creations.
With the right knowledge, you can customize your virtual modular rig to a setup that perfectly matches your unique sound design requirements.
Using Multiphonics CV-2 by AAS for Addition Sonic Possibilities
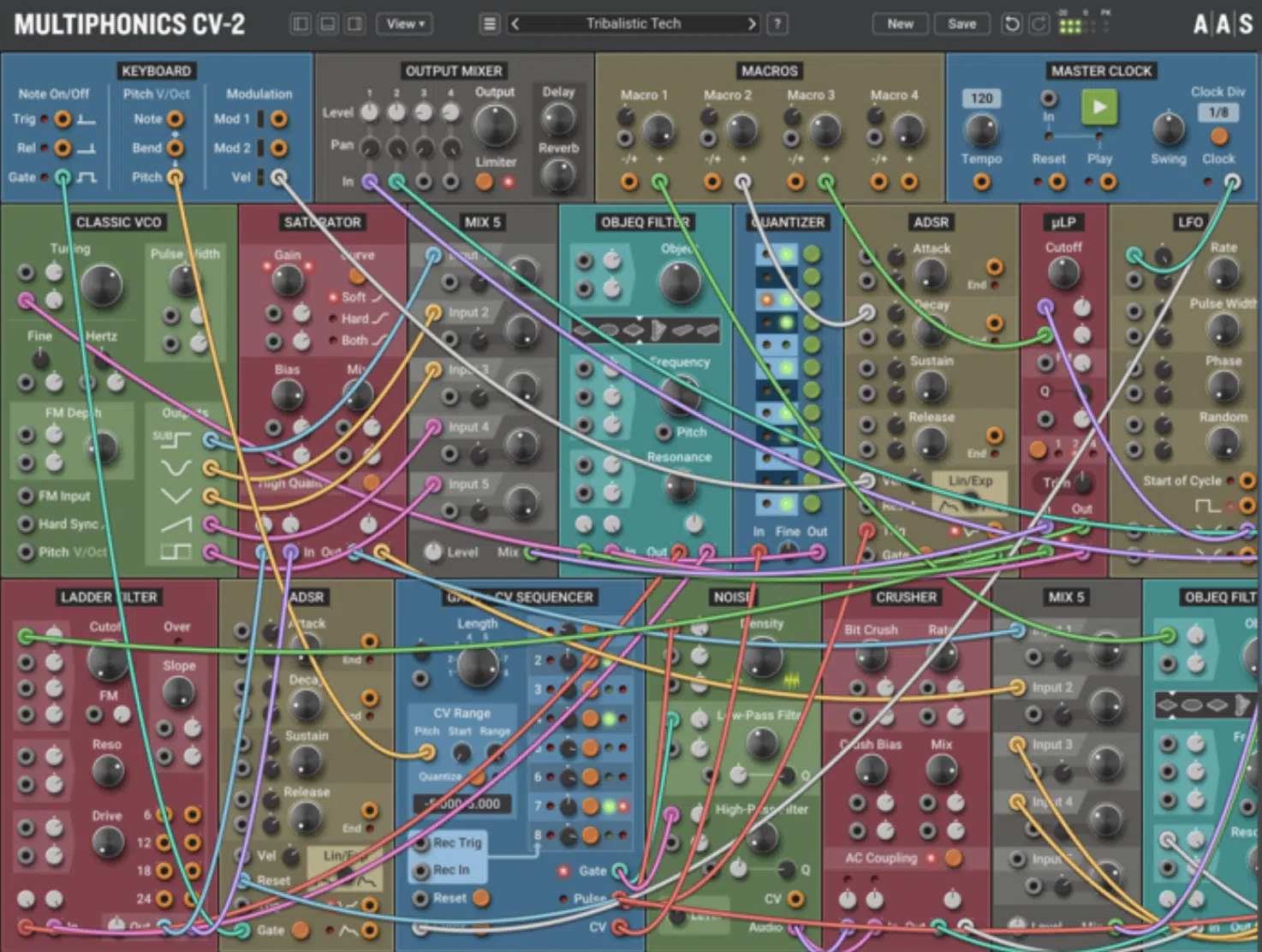
Some of these virtual modulator systems allow all developers to get in on the action.
While that has its benefits, when first learning modular synthesis, it can be a tad overwhelming.
This is why, regardless of your skill level, one of the best synths to use when you’re first getting your toes wet (or looking for a great new option) is Multiphonics CV-2 by AAS.
With its fixed set of unique and advanced moduals, you can quickly get up and running with unmatchable sound clarity.
They’re newest update even allows for it be run as an Effects plugin as well 一 further widening your sonic possibilities.
It’s rather unique physical modeling filter, adapted from the full version of the ‘OBJEQ’ filter, gives you unparalleled modeling expression (using any plugin as the Exciter source!).
The Role of Virtual Patch Cables

In a physical modular synth, patch cables are the lifelines that connect modules and direct the flow of audio and control voltages.
In a digital modular system, the same principle applies, but the cables are virtual.
You use them to connect the outputs of one module to the inputs of another 一 shaping your signal path and creating your unique sound.
These virtual patch cables work exactly the same way as their physical counterparts.
You click & drag from an output to an input, which creates a connection that allows signals to flow.
Through this process, you can build up complex patches that harness the full potential of your digital modular system.
Using virtual patch cables effectively is crucial to getting the most out of your digital modular system.
This involves not only understanding where to patch in order to create the sounds you want, but also managing your cables effectively to keep your patches understandable and manageable.
Many digital modular systems provide ways to keep your cables organized, such as:
- Color-coding
- Opacity controls
- Different routing views
You can use these features to reduce visual clutter and make it easier to understand your patch at a glance.
Incorporating Software Synthesizers in Virtual Modular Systems

The flexibility of virtual modular systems allows you to integrate them with other parts of your digital music production workflow, including software synthesizers.
By combining the distinct advantages of both, you can broaden your sound palette and achieve more complex and nuanced results.
For example, you can use a software synthesizer as a sound source within your virtual modular system, shaping and processing its output with your modular patches.
Alternatively, you can use your modular system to generate control voltages that modulate parameters in your software synth.
This brings the dynamic movement and unpredictability of modular synthesis to your software instruments.
Additionally, certain digital modular systems come with interfaces or modules designed to integrate with specific software synths.
These can provide seamless connections 一 letting you route audio and CV between your synth and your modular system with ease.
Virtual Eurorack Modules: Enhancing Your Modular Journey
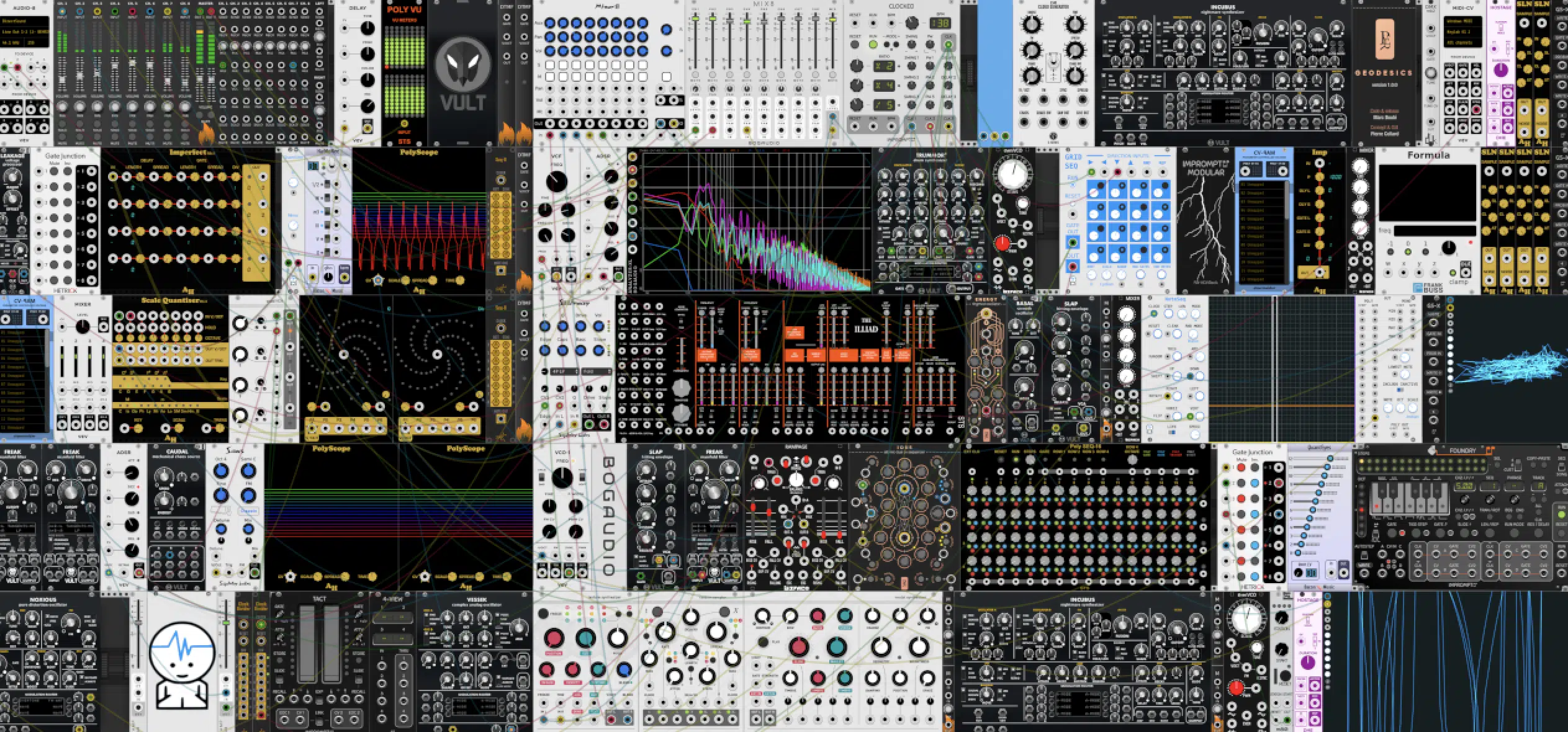
Eurorack is a format for modular synthesizers that has become the standard in both the physical and virtual world.
In essence, Eurorack refers to a standardized system of measurements and specifications that ensure different modules can work together in a single system.
NOTE: When we talk about virtual Eurorack modules, we’re referring to digital recreations of these modules that function within a virtual modular environment.
Eurorack modules retain the characteristics and functionality of their physical counterparts.
This includes:
- The layout and design of the module
- The types of inputs and outputs available
- The way the module processes and manipulates signals
There’s a vast array of virtual Eurorack modules available 一 covering everything from basic building blocks like oscillators and filters, to more complex and unique modules.
These modules can be mixed and matched in infinite combinations, which allow you to create a custom modular system that perfectly suits your needs.
-
Choosing the Right Virtual Eurorack Modules for Your Digital Modular Synths
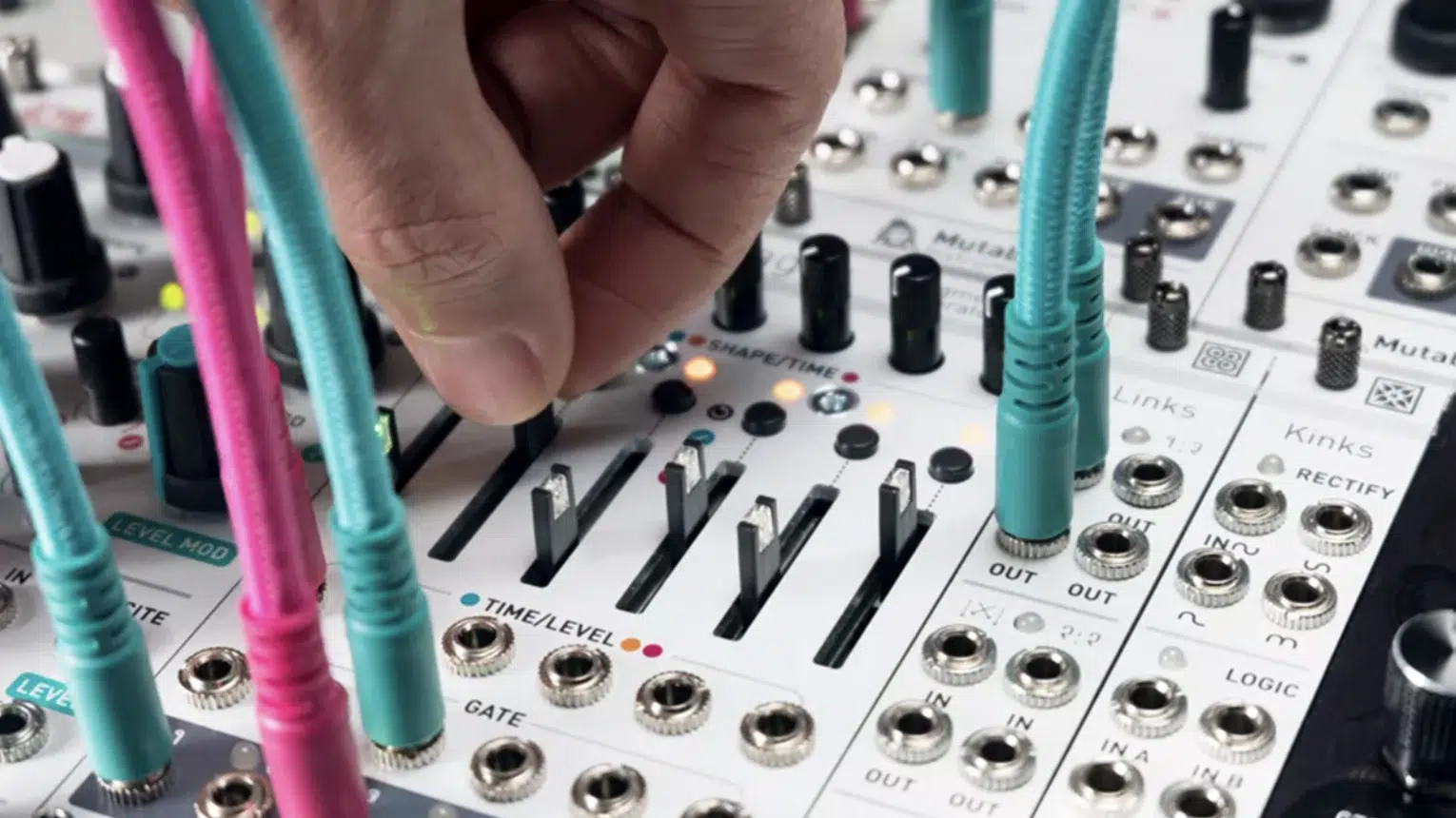

Choosing the right modules for your virtual Eurorack system is an important step in crafting your unique sound.
There are countless modules available, each with their own features and capabilities, so it’s crucial to understand what each one brings to the table.
Start with the basics:
- An oscillator to generate your raw sound
- A filter to shape the sound’s timbre
- An envelope generator to shape its amplitude over time
- A VCA to control the final output level
From there, you can start exploring more specialized modules.
Consider what kind of music you want to make, what genre, and what sounds you want to create.
Are you interested in creating complex, evolving pads? Look for modules like wavetable oscillators and granular synthesizers.
Do you want to make percussive techno? Consider adding some drum modules and sequencers to your setup.
It’s all about your personal preferences and what you feel comfortable working with.
Remember, it’s all a journey, so don’t get overwhelmed…
Take your time, get to know your equipment (physical or digital) and, most importantly, keep making epic music.
Modular Synthesis: Final Thoughts
After walking the corridors of digital modular synthesis, I trust you’re now full of inspiration and ready to start your modular synthesis journey.
This way, you can create sounds that are as unique as your musical identity.
The possibilities are as endless as your imagination when it comes to exploring and designing sounds with a digital modular synth.
Here’s a little secret sauce to add to your musical recipe: these mind-blowing, show-stopping free drum loops.
You can inject these premium quality loops into your modular systems to process and reimagine them in the most unique and intriguing ways 一 pushing the boundaries of your creative expression.
Use these loops as a starting point, twist them with the filter modules, sprinkle some voltage-controlled magic, or journey through complex patches in your digital modular setup.
In the realm of digital modular synthesis, these loops can be your treasure troves of sound design, acting as a perfect resource to experiment and learn.
So, let your sonic explorations begin!
With every knob tweak and patch cable routing in your modular system, remember, you’re creating not just sounds, but a reflection of your musical spirit.
Until next time…







Leave a Reply
You must belogged in to post a comment.