Music production is a fascinating blend of creativity and technical skill that’s becoming more popular every second.
It requires an ear for detail, an understanding of music technology, different techniques, and a deep passion for making music.
If you’re going to learn how to produce music like a pro, you’ll have to grasp the basics of mixing and mastering, sound design, and so much more.
Plus, you’ll need to know how to master breaking into the music industry so you can leave a lasting mark.
Luckily, that’s exactly what we’ll be breaking down today, like:
- What you’ll need to know to produce music professionally ✓
- Selecting the perfect DAW for your music ✓
- Essential gear for your first home studio as a music producer ✓
- Why you should learn music theory ✓
- Mastering sound design for unique tracks ✓
- Recording techniques that capture every detail ✓
- Advanced mixing and mastering techniques ✓
- Utilizing virtual instruments for dynamic sounds ✓
- Integrating MIDI controllers into your workflow ✓
- Breaking into the music industry with your tracks ✓
- Enhancing your music production skills ✓
- Much more about how to learn music production ✓
After this article, you’ll know everything about how to learn music production (and even be able to start producing music today if you want).
This way, you’ll be able to produce your own tracks with confidence and dominate the music production process with ease.
Whether you’re aiming to produce the next big hit or simply want to share your sound with the world, these insights will help you get there.
So, let’s dive in…
Table of Contents
How to Learn Music Production in 2024

Learning music production in the modern world involves more than just understanding how to operate software or play an instrument.
It’s all about diving deep into the world of different genres, sounds, effects, and techniques and exploring the endless possibilities digital audio offers.
Plus, make sure your music stands out and sounds professional, of course.
As a music producer, you’re at the heart of the music creation process 一 blending creativity with technology to produce music that can blow people’s minds.
And resonate with audiences worldwide, of course.
In order to learn music production, it’s essential to start with a solid foundation.
This includes:
- Setting up a conducive music production environment
- Choosing the right tools for your work
- Getting familiar with the fundamentals
Then, you’ll need to learn music theory, production techniques, and sound design in order to create those epic songs that (most likely) inspired you in the first place.
In turn, you can start making music/your own songs and become a better producer.
-
Setting Up Your Music Production Environment

If you’re going to be producing music and have a successful music production career, you’ll need to know how important your music production environment is (because it can make or break how you produce tracks).
It’s key to making music that will help you have a successful music production career.
A well-organized home studio, free from distractions, is the first step toward a successful music production career.
Your space should be comfortable and inspiring and stocked with the necessary gear to enhance your workflow and beat-making process.
The overall vibe and ambiance of your studio significantly affect your productivity, so you have to consider:
- Lighting
- Furniture
- Overall setup (to ensure a conducive environment for long hours of work)
Ergonomics plays a vital role in your setup 一 make sure your equipment is positioned to prevent strain or fatigue during those prolonged sessions.
Sound treatment is also a key aspect of setting up your home studio.
Proper acoustic treatment can drastically improve the sound quality of your recordings by minimizing room reflections and external noises.
Simple adjustments, such as adding acoustic panels or bass traps, can make a significant difference in achieving a clearer and more accurate recorded audio.
It’s all about the little details when you want to learn music production, audio engineering, or sound design.
-
Choosing the Right Digital Audio Workstation (DAW)

Selecting the ideal DAW is foundational for any great music producer, as it shapes the your whole music production process.
Popular DAWs include Ableton Live, known for its seamless live performance capabilities and intuitive loop-based composition workflow.
Needless to say, it’s a favorite among electronic music producers who want to start producing music.
FL Studio shines with its pattern-based sequencing 一 making it particularly appealing for producers in genres like hip-hop, trap, pop, and EDM.
Logic Pro offers a comprehensive set of recording, editing, and mixing tools, along with an extensive library of virtual instruments and loops.
It caters to producers and songwriters focusing on a wide range of different genres.
The choice of DAW can significantly influence your workflow (for good or bad)…
For instance, if sound design and synthesis is what interests you, you might love Ableton for its powerful native devices and Max for Live integration.
On the other hand, if you’re just starting in music production, FL Studio’s user-friendly interface and abundant online resources can provide a smoother learning curve.
Logic Pro’s all-in-one approach, with its sick mixing console and score editing features, might appeal to those with a background in music theory or live recording.
As a music producer, it’s all about the small, individual elements that can make a huge difference and impact (like picking the right DAW).
-
Essential Equipment for Your Home Studio

Building a functional home studio requires essential equipment that supports your music production journey from composition to final mix.
Here’s a rundown of music producer must-haves:
#1. Computer/Laptop: The centerpiece of your studio, a computer/laptop with sufficient processing power and RAM, is necessary for running your DAW and plugins smoothly. Whether it’s an Apple MacBook for its robust performance with Logic Pro X or a high-spec PC for FL Studio, ensure your system can handle multiple tracks and effects with ease.
#2. Audio Interface: An audio interface like the Focusrite Scarlett 2i2 or Universal Audio Apollo Twin provides high-quality analog to digital conversion 一 ensuring your recordings are crisp and clear. It’s your gateway to recording vocals and instruments, offering preamps for microphones and direct inputs for guitars or basses.
#3. Studio Monitors: Reliable monitors such as the Yamaha HS series or KRK Rokit provide accurate sound reproduction, essential for mixing and mastering. Make sure to position them correctly in an equilateral triangle with your listening position for the best stereo image. It’s not to be compromised when you want to make accurate, professional songs.
#4. MIDI Controller: A MIDI controller like the Akai MPK Mini or Native Instruments Komplete Kontrol opens up a world of virtual instruments and enhances your workflow with assignable pads, knobs, and faders for hands-on control of your DAW.
#5. Good Microphone: A versatile large-diaphragm condenser microphone, such as the Audio-Technica AT2020 or Rode NT1-A, is essential for recording vocals and acoustic instruments. It captures the nuances of performances. However, you should be familiar with all the microphone types when you’re learning how to produce music.
#6. Reliable Headphones: Closed-back headphones like the Audio-Technica ATH-M50x offer isolation for tracking, while open-back models like the Sennheiser HD 600 are preferred for critical listening and mixing.
If you knock down (and understand) all the items on this list, you’ll be in a great position to produce music like a real professional in no time.
-
Pro Tip: Optimizing Your Space for Optimal Sound Quality

The acoustics of your studio directly affects the accuracy of your mixes.
Positioning your studio monitors correctly and treating your room to address acoustic issues can lead to more balanced and professional-sounding productions.
Also, monitor placement is crucial for achieving a reliable stereo image.
NOTE: The ideal setup forms an equilateral triangle between you and the two speakers, with tweeters at ear level. This arrangement helps in accurately assessing panning, levels, and frequencies in your mixes.
Acoustic treatment, such as foam panels and bass traps, can help with unwanted reflections and standing waves 一 ensuring a more neutral listening environment.
Professional treatment can be expensive, so just know that there are cost-effective DIY solutions that can also significantly improve the sound of your room.
As a music producer, you might need to get a little creative at first, but it’s easy.
Fundamental Concepts in Music Production
When you want to learn music production and create your own songs, you’ll need to understand the core principles. This includes music theory, familiarizing yourself with the music production process, and mastering sound design.
-
Understanding Music Theory (Even Just So You Can Break the Rules)
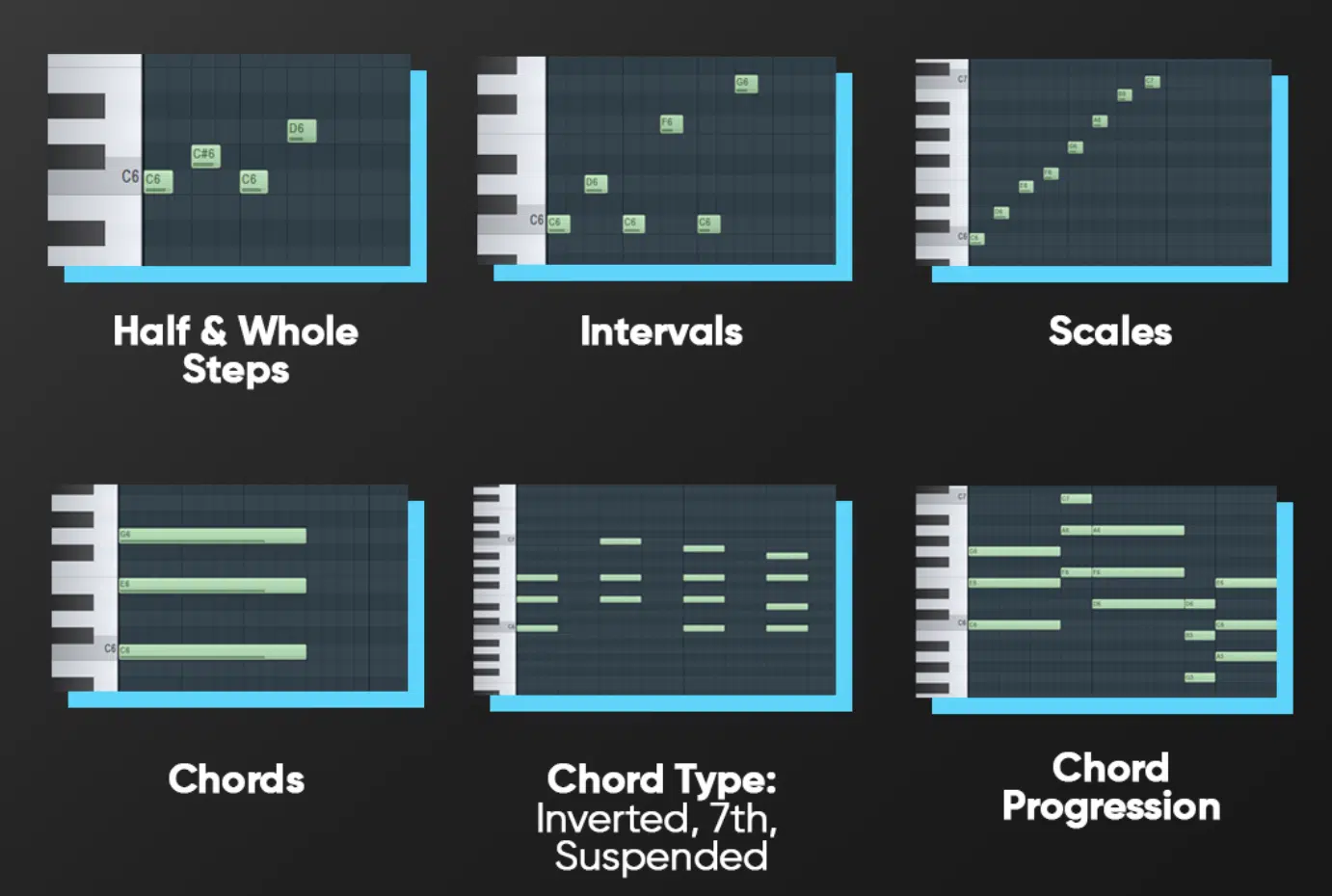
Music theory provides a blueprint for understanding the elements that make music sound good, whether you’re into trap, R&B, electronic music production or anything in between.
Basic knowledge of scales, chords, and rhythm can greatly enhance your ability to compose and arrange your tracks like a true music producer.
While it might seem daunting when you first start producing music, music theory is not about restricting creativity…
But rather, it gives you the tools to break the rules more effectively in your own projects.
Many successful producers (like you’re hoping to be) learn music theory as a foundation to experiment and innovate when they create music.
For instance, understanding chord progressions can help you create more emotional and impactful music, just like your favorite tracks.
A chord progression like the I-IV-V (in the key of C major, this would be C-G-Am-F) is timeless and you can listen for it in countless hit songs across various genres.
This knowledge will not only help you create enchanting melodies when writing music, but also in arranging song structures that keep listeners engaged.
For example, using borrowed chords from parallel minor scales can add an unexpected twist to your tracks 一 creating a your own sound that sets you apart.
Incorporating modal interchange, such as mixing elements from the Dorian mode into a primarily Aeolian (natural minor) based track, can introduce a fresh vibe to your songs.
These techniques, once you master them, allow you to bend/break the rules of traditional music theory and give you a unique edge as a music producer.
-
The Music Production Process: The Official Breakdown

The music production process can be broadly categorized into several stages:
Each stage helps transform your musical idea into a mind-blowing song.
For example, during the songwriting phase, a music producer might start with a simple melody or chord progression played on a MIDI keyboard.
Using a DAW like FL Studio to sketch out the idea, of course.
In the arranging phase of producing music, this basic idea is developed into a full song structure, with the addition of various elements like drums, bass, and synthesizers.
Virtual instruments and sample packs play an invaluable part of this stage because they provide you with various different sounds to play around with.
For instance, using a virtual instrument like Massive can add powerful synth lines, while a drum sample pack might provide the perfect drum loop to complement your track.
The recording stage of your song involves capturing performances, whether they’re live vocals, instruments, or additional synth lines.
NOTE: Techniques like multi-tracking, where multiple takes are recorded and layered to create a fuller sound, are commonly used.
Editing and mixing are up next, where the raw recordings are polished, balanced, and blended to achieve a cohesive sound.
During mixing, tools like EQ, compression, delay, and reverb come into play 一 each serving a specific purpose.
For example, EQ can be used to carve out space for each instrument in the mix which ensures clarity and prevents frequency overlap.
Finally, mastering ensures the track sounds consistent and impactful across all playback systems.
This might involve adjusting overall levels, applying limiting to achieve commercial loudness, and enhancing the stereo image for a wider sound.
Just keep in mind, when you start producing music, mixing is for intricate little details and mastering is for broad strokes.
As all audio engineers will tell you, you can’t fix problems in the mix when you master, so make sure everything is up to par before moving on.
-
The Role of Sound Design in Music Production

Sound design is the art of creating and manipulating audio elements to produce unique sounds.
As a future music producer, sound design is what’s going to help set your songs apart.
It involves, but isn’t limited to:
- Synthesizing sounds
- Sampling
- Audio processing
It will help you create everything from atmospheric pads to punchy basslines.
A well-designed sound can become the signature of any song (just think of your favorite tracks in the EDM category).
For example, the iconic bass sound in many of Daft Punk’s tracks is the result of, you guessed it, innovative sound design 一 combining synthesis with creative processing techniques.
Similarly, the lush, evolving pads in The Weeknd’s songs are achieved through a combination of synthesis, sampling, and tape processing.
It gives it that extra edge every time you listen that keeps you coming back.
-
Pro Tip
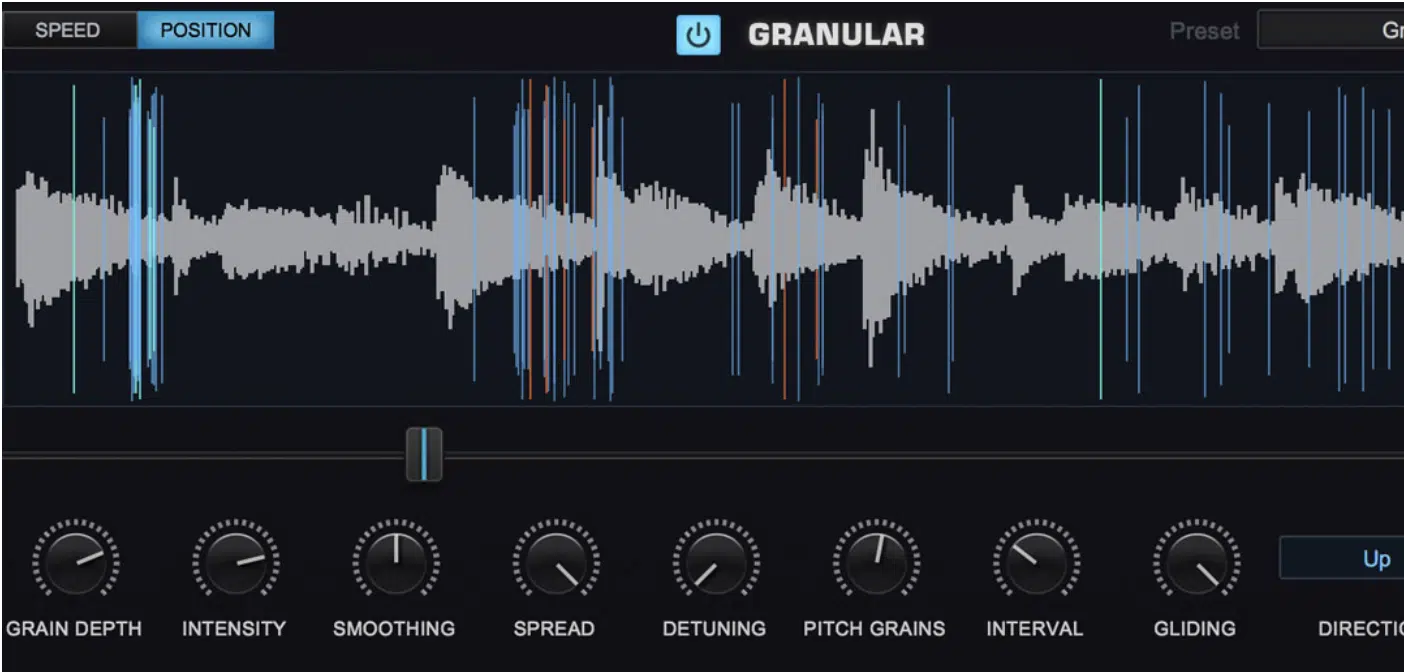
Sound design extends beyond musical elements to include ambient sounds and effects that can add depth and context to your tracks.
Field recordings, such as the sound of rain or city ambiance, can be manipulated and integrated into tracks to create a sense of place or emotion.
Also, tools like granular synthesis can transform these recordings into unrecognizable textures, which add a unique layer to your songs.
Plus, software like Ableton Live’s Sampler or Logic Pro’s Alchemy are powerful tools for sound design.
It offers extensive parameters for manipulating samples and synthesis to create new sounds from scratch.
Just remember, if you want to be making music that stands up to professional producers, sound design is definitely key.
The Technical Side of Music Production
When it comes to the technical aspects of music production, you need to become familiar with the tools and techniques that bring your songs to life. This means getting hands-on with your Digital Audio Workstation (DAW), understanding the ins and outs of audio interfaces, and mastering the recording, mixing, and mastering processes.
-
Getting to Know Your DAW & Audio Interface

Your DAW is going to be like your safety blanket and safe zone; it’s where you’ll arrange, edit, and mix your music for hours and hours.
Each DAW, whether it’s FL Studio, Ableton Live, or Logic Pro, has a unique workflow and set of features.
So, if you want to learn music production quickly and easily, choosing the right DAW upfront is going to save you endless hours of frustration.
For example, Ableton Live is renowned for its Session View, which allows for an intuitive approach to composing and performing music live.
This makes it a favorite among electronic music producers and audio engineers alike.
On the other hand, Logic Pro offers an extensive library of virtual instruments, effects, and instrument presets.
So, if you’re heavy into MIDI programming, sound design, and creative experimenting, this might be the right choice for you.
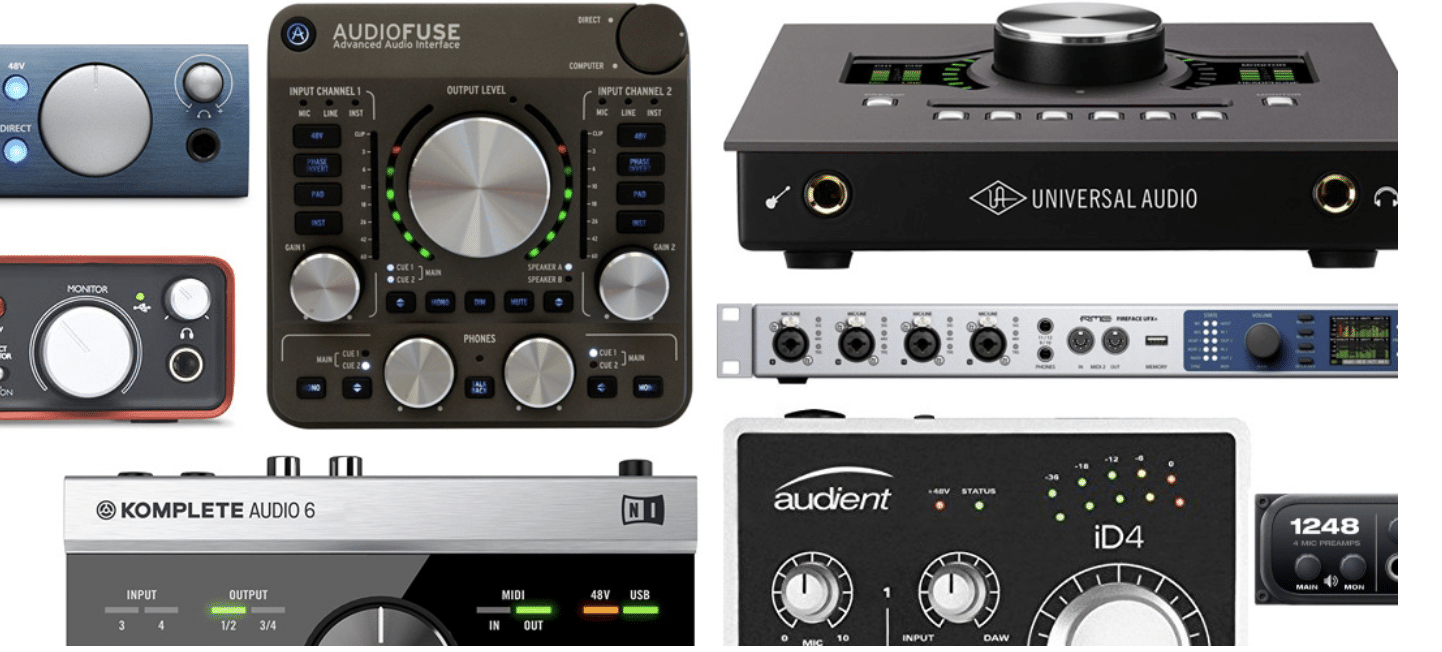
Your audio interface acts as the bridge between your various instruments or microphones and your computer.
It converts analog signals into digital audio that your DAW can process.
A quality audio interface, like those from Focusrite or Universal Audio, ensures that your recordings are captured with clarity and fidelity.
Ultimately, it will help you become a better producer.
It’s super important to understand the capabilities of your audio interface, as these factors significantly impact your recording quality and workflow efficiency.
This can include:
- Preamp quality
- Latency performance
- Input/output options
As a music producer, familiarizing yourself with the technical capabilities and, better yet, shortcuts of your DAW can drastically improve your productivity.
For instance, learning keyboard shortcuts for common tasks like splitting clips, quantizing MIDI, or applying fades can save countless hours in the long run.
Additionally, taking advantage of DAW-specific features, such as FL Studio’s Piano Roll or Logic Pro’s Smart Tempo, can enhance your creative process as well.
-
Recording Techniques: Capturing Your Sound

Effective recording techniques are essential for capturing pristine, high-quality audio.
This involves not only the right equipment but also an understanding of:
- Microphone placement
- Room acoustics
- Signal chain
For example, when recording vocals as a new music producer, using a cardioid condenser microphone in a well-treated room, positioned at the correct distance from the singer, can capture the nuances and dynamics of the performance.
It minimizes room reflections and background noise.
Experimentation with microphone placement and selection when you learn music production can lead to discovering unique sounds and textures.
For instance, recording a guitar amplifier with a dynamic microphone placed directly in front of the speaker cone captures a different tonal quality than placing a ribbon microphone slightly off-axis.
These subtle changes in technique can significantly impact the character and feel of your recordings, providing epic sonic options to choose from (during the mixing stage).
-
Mixing and Mastering

Mixing is the process of combining and balancing individual tracks within a project to create a cohesive and pleasing final product.
When you mix music, it involves critical listening and the strategic effects to enhance the clarity, depth, and dynamics of your music.
This includes:
- EQ
- Compression
- Reverb
- Delay
- Distortion
- Etc.
For example, applying a high-pass filter on non-bass instruments can clear up the low-end frequencies.
It makes room for the kick drum and bass to sit prominently in the mix without muddiness or any unprofessional slip-ups.
Mastering is the final step in the production process 一 preparing your track for distribution by ensuring it translates well across various playback systems and media formats.
Mastering involves subtle adjustments to the stereo mix’s overall EQ, compression, limiting, and stereo imaging to achieve a balanced, professional sound.
Tools like iZotope’s Ozone offer a comprehensive suite of mastering effects.
It allows each unique music producer to finalize their tracks with industry-standard loudness and polish.
Understanding the principles of mixing and mastering when you first learn music production is crucial, but so is knowing when to seek out a professional.
While many producers are capable of mixing their tracks, mastering often benefits from an experienced ear and an acoustically treated environment.
Collaborating with a professional mastering engineer or audio engineering specialist can bring a new level of clarity and professionalism to your music.
It ensures, when you’re making music, that it stands up against commercial releases.
Your songs will have that professional, pristine vibe that is necessary to become a professional, highly-respected music producer.
-
Exploring Virtual Instruments & Sample Packs

Virtual instruments and sample packs are invaluable resources for modern music producers and innovative sound designers.
It offers a wide range of sounds and textures to incorporate into your song.
From realistic piano and orchestral sounds to synthesized textures and drum samples, these tools can expand your production skills and inspire new creative paths.
When choosing virtual instruments, you’ll need to consider both the sound quality and the flexibility of the instrument/individual elements.
Similarly, synthesizers like Serum by Xfer Records provide a powerful platform for creating custom sounds, with intuitive interfaces that encourage experimentation and sound design.
Sample packs can also be a major source of inspiration 一 offering loops, one-shots, and vocal samples that can you tweak and play around with in your own tracks.
These samples can:
- Serve as the foundation for a track
- Provide complementary elements
- Inspire entirely new creations
For example, drum loops can quickly establish a groove that sets the tone for the entire track, while a unique vocal snippet can become a central hook of your song.
It’s essential to use virtual instruments and sample packs creatively when you learn music production 一 manipulating and customizing them all day.
-
Pro Tip

If you’re going to produce music that really stands out, you should try techniques like:
It will help you discover unique sounds that separte your music from the competition.
For example, layering a synthesized bass sound with a sampled acoustic bass can create a rich, complex tone that combines the best of both digital and analog worlds.
Additionally, integrating MIDI controllers into your workflow can enhance your interaction with virtual instruments.
It makes the production process way more intuitive and expressive.
A MIDI keyboard with velocity-sensitive keys and assignable knobs or faders can provide hands-on control over virtual instrument parameters.
In turn, dynamic performances and real-time sound manipulation are right in reach.
-
Understanding Song Structure
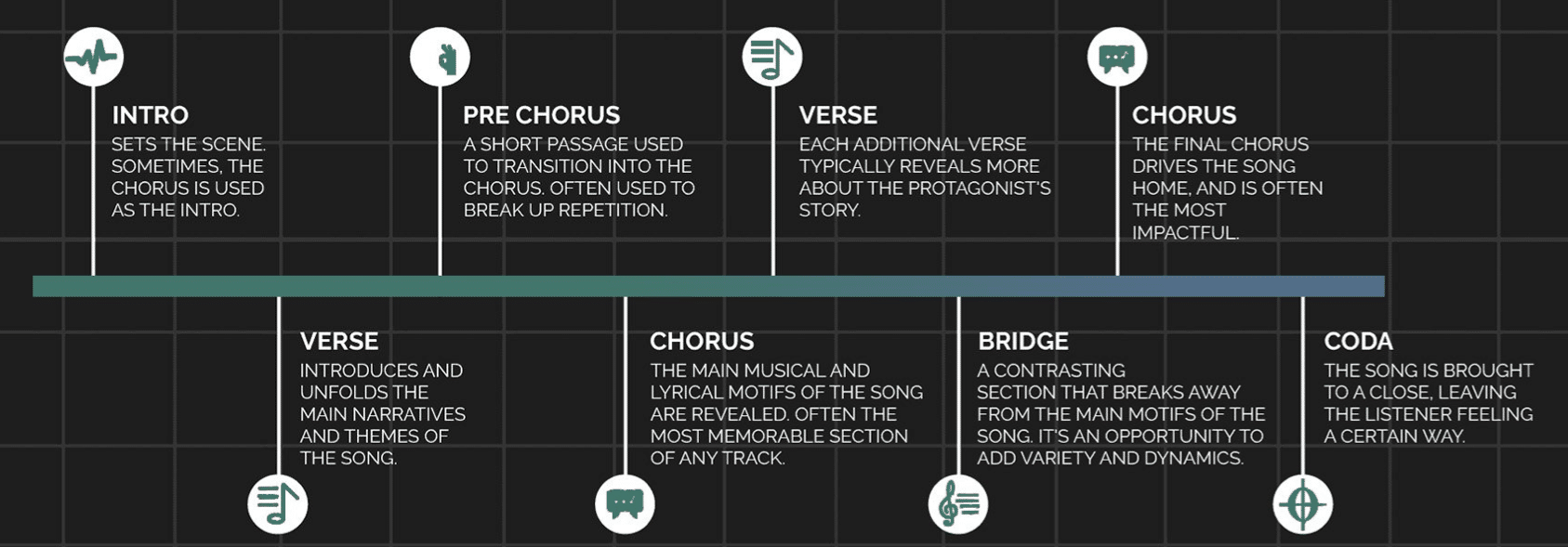
As a music producer, a solid grasp of song structure is key for creating your own music, especially if you want it to be engaging from start to finish.
Traditional structures like verse-chorus-verse provide a reliable framework, but exploring unconventional structures can lead to innovative tracks that stand out.
Understanding the function of each song structure section can guide your arrangement decisions, including:
- Verses introducing lyrical themes
- Choruses providing emotional peaks
- Bridges offering contrast
- Etc.
Analyzing the song structures of successful tracks (reference tracks) in your genre can provide valuable insights when you want to learn music production.
For example, many electronic dance music (EDM) tracks follow a structure designed to build energy and anticipation 一 leading to a sick drop that releases the tension.
In contrast, ambient or experimental tracks might eschew traditional structures in favor of evolving soundscapes that focus on texture and mood rather than hooks and choruses.
Experimentation with song structure can also involve playing with the length and order of sections and incorporating unexpected elements like tempo changes or key shifts.
Plus, blending genres to create a unique narrative flow.
Tools within your DAW, such as markers and arrangement views, can help visualize and manipulate the structure of your songs.
It helps with creative experimentation and refinement, which is everything.
Understanding (& Breaking into) the Music Industry

Making a name for yourself in the music industry as an up-and-coming music producer requires more than just talent (unfortunately).
It demands an understanding of the business side of music, from copyright laws to effective branding and networking.
Building a compelling brand around your music is the first step.
This could mean developing a unique visual identity that reflects your sound as a music producer, or creating a narrative that connects with your audience on a personal level.
Just think about legends like Marshmello and Tchami 一 they’ve successfully created an air of mystery around each song, which comes with intrigue.
Social media and streaming platforms are indispensable tools for reaching new audiences and get people talking about how good you produce music.
Regularly engaging with your followers through:
- Behind-the-scenes content
- Teasers for upcoming releases
- Live beat-making/Q&A sessions
- Etc.
It builds that familiarity, intrigue, and sense of community around your music.
Additionally, understanding the importance of playlist placements on platforms like Spotify can, obviously, increase your visibility in a big way.
Knowledge of music rights and monetization as a music producer is also critical (especially when you want to learn music production from the ground up).
Utilizing services like DistroKid for distribution or joining a performing rights organization can ensure you’re compensated fairly for each track.
Plus, networking within the industry can open up awesome opportunities, from collaborations to gigs.
Don’t underestimate the power of connecting with other artists who love music and industry professionals at events or through online platforms.
Bonus: Resources for Learning Music Production

Whether you’re a successful music producer or just wondering how to learn music production, the internet is always the perfect resource.
Online learning platforms offer courses taught by music industry professionals or another experienced tutor who specializes in music production and sound design.
They provide structured moves from basic techniques to advanced concepts and videos about music production.
YouTube is still (believe it or not) a great starting point to watch tutorials about producing music so you can become a successful music producer and experiment with different sounds.
From the creative production videos of Andrew Huang to the detailed music theory breakdowns of Rick Beato, these YouTube tutorials can provide both inspiration and music production education.
Also, participating in production forums, affiliate programs, and communities can offer support, feedback, and advice from other music producers who love music production as well.
These platforms can be a goldmine of information, whether you’re troubleshooting a technical issue or seeking feedback on your latest song.
Each DAW you produce in also includes a dedicated community of users and audio production professionals.
These communities often share tips, tutorials, and templates specific to the DAW to help you learn music production in no time.
They’re an excellent resource for both beginners and professional producers.
Engaging with these resources helps you stay updated on the latest trends and technologies in music production.
Plus, it also connects you with a global community of creators who share your passion for production and dedication to making music that leaves an impression.
Through these platforms, you can stay updated on the latest trends in the music industry, discover new production software, and refine your production skills.
All while being part of a global community of music creators that will build you up and help you produce music with confidence and edge.
How to Learn Music Production: Final Thoughts
If you want to know how to learn music production, it takes dedication, patience, and a willingness to explore new sounds and techniques.
Plus, as you now know, you’ll have to master the use of DAWs, equip your studio with essential gear, understand music theory, and dive deep into sound design, mixing, and mastering techniques.
This way, you’ll be able to create music that resonates with your audience and stands out in the industry.
As you’re starting your music production journey, it’s invaluable to see exactly how professional-quality tracks are made…
That’s where the #1 Free Project Files pack comes in.
It includes 3 professional free project files (each available in Ableton, FL Studio, and Logic Pro) that can break down everything we talked about today.
From intricate sound design to innovative mixing techniques and everything in between.
These project files are in the same styles as the biggest hit songs in modern music and were created by the world’s top producers.
It offers you an inside look at the processes behind creating chart-topping tracks which can seriously help kickstart the process.
With all these resources at your disposal and the knowledge you’ve gained today, you’re ready to run the production game and take over, so go do just that!
Until next time…







Leave a Reply
You must belogged in to post a comment.