MIDI, or Musical Instrument Digital Interface, is the unsung hero behind countless billboard-topping hits.
It gives you the power to transform ideas into sonic masterpieces.
MIDI can elevate your tracks, breathe life into virtual instruments, and provide unparalleled control over your musical creations.
However, you risk missing out on its full potential if you don’t understand how MIDI operates.
That’s why we’ll dive deep into all things MIDI to ensure you unlock every ounce of its versatile capabilities.
In today’s article, we’ll be breaking down:
- What MIDI is and how it works ✓
- How to enhance your tracks with MIDI ✓
- MIDI messages and their significance ✓
- MIDI keyboards & controllers ✓
- Navigating MIDI channels ✓
- Studio gear integrating MIDI ✓
- Bridging devices with MIDI interfaces ✓
- MIDI’s role in virtual instruments ✓
- Advanced MIDI features ✓
- MIDI tips, tricks, and secrets ✓
- MIDI Thru, MIDI Mapping, and MPE ✓
- Much more ✓
By the end of this article, you’ll know all the ins and outs of MIDI.
This way, you can enhance your tracks and navigate the digital music world like a professional.
You’ll never have to ask yourself, “How does MIDI work?” again 一 you’ll have all the answers right at your fingertips.
So, let’s dive in…
Table of Contents
- What is MIDI & How Does It Work?
- How MIDI Can Enhance Your Tracks
- How Does MIDI Differ From Audio Signals?
- MIDI Data: Everything You Need to Know
- The Significance of MIDI Messages
- MIDI Controllers vs MIDI Keyboards: What’s The Difference?
- Navigating Through MIDI Channels
- Understanding MIDI Devices & Digital Music Gear
- MIDI Interfaces: Bridging the Gap
- Virtual Instruments and MIDI: A Powerful Pair
- MIDI’s Advanced Features: Beyond the Basics
- How Does MIDI Work? Final Thoughts
What is MIDI & How Does It Work?

MIDI stands for ‘Musical Instrument Digital Interface.’
This might sound like an alien term to some, but it’s the backbone of modern music production.
It isn’t an audio file but a protocol: a set of rules allowing different digital devices to communicate successfully.
When discussing MIDI in music production, we’re referring to a specific language.
Picture a piano for a minute…
When you press a key, a hammer hits a string, producing sound.
Now, in the digital world, when you press a key on a MIDI keyboard, instead of sound, it sends a message to a computer or synthesizer telling it:
- Which key was pressed
- How hard it was pressed (velocity)
- For how long it was pressed (duration)
So, to answer “How does MIDI work?” it’s a way devices convey and interpret specific instructions, not sounds.
These instructions, often termed “MIDI data,” determine how an instrument should sound in terms of pitch, velocity, and duration, among other parameters.
The beauty of MIDI lies in its flexibility.
Since it only sends instructions and not audio, you can easily modify these instructions post-recording.
Change the instrument, adjust timing, modify the pitch 一 the possibilities are immense.
How MIDI Can Enhance Your Tracks
For digital music producers, MIDI is a game-changer, as you’re no longer confined to the sounds you’ve recorded.
If you’ve laid down a melody but feel it might sound better on another instrument, MIDI allows you to switch it out effortlessly.
Here are just some of the ways it can enhance your tracks and get your music the recognition it deserves:
-
Dynamic Control

At the heart of MIDI’s capability is its invaluable dynamic control.
Every note played can have a specific velocity, pitch, modulation, and duration.
For example, while recording a keyboard part, MIDI will capture the notes and how hard or soft each key was struck.
-
Virtual Instrument Arsenal

With MIDI, you’re no longer confined to the sounds of the instruments you physically own.
MIDI tracks can trigger various virtual instruments 一 from rare vintage synths to orchestral samples.
For instance, a simple MIDI controller can transform into a grand piano, violin, or even an entire brass section.
It all depends on your selected virtual instrument and intended vibe.
-
Easy Editing & Quantization
Did you make a minor mistake during your recording? With MIDI, there’s no need to redo the entire take.
Individual notes can be moved, deleted, or changed in your DAW.
If your timing isn’t perfect, MIDI allows for quantization, automatically aligning your notes to the grid.
This ensures that drum beats or melodic runs are on time.
-
Layering and Soundscapes
MIDI enables easy layering of tracks.
Imagine recording a melody and then duplicating it to be played simultaneously by strings, brass, and woodwinds.
This would create a lush orchestral sound that completely transforms your original sound.
-
Endless Experimentation
The non-destructive nature of MIDI means you can experiment endlessly.
Change keys, swap MIDI instruments, or alter rhythms without permanently altering the original recording.
For example, a guitar riff can be easily converted into a flute solo or even a bassline, giving you endless musical possibilities.
And remember, the piano roll is a visual interface in many DAWs 一 allowing you to plot out MIDI notes and make the composition process more intuitive/precise.
If you’d like to learn professional piano roll secrets, tips, and tricks, we’ve got you covered.
How Does MIDI Differ From Audio Signals?

At first glance, MIDI and audio might seem similar… both are used in creating music, right?
Well, while both are crucial in the realm of digital music, they serve very different purposes and functions.
MIDI is all about instructions (MIDI protocol).
Think of it as a music sheet, telling the player what note to play, when to play it, and how to strike it.
Audio signals are the actual sound; if MIDI is the metaphorical music sheet, then audio signals are the recorded performance of that sheet.
This distinction is crucial when producing.
- With MIDI 一 You’re working with flexible data, easily adjusted and modified.
- With audio 一 You’re working with fixed sounds.
It’s worth noting that while audio gives the raw, organic texture (especially for vocals), MIDI offers unparalleled flexibility for beats, synths, and effects.
The balance of both brings out the best in digital music.
Therefore, you’ll need to understand their intricacies to master them and take full advantage.
MIDI Data: Everything You Need to Know
Diving deeper, “MIDI data” is the heartbeat of the MIDI language.
These are the specific instructions we keep discussing; the details that an electronic instrument sends to a computer or another device.
Imagine pressing a key on a MIDI keyboard for a minute.
The keyboard then sends MIDI data to your production software 一 indicating which key was pressed, how hard, and how long it was held.
This data doesn’t contain sound but acts as a trigger for the software to produce the correct note.
MIDI data isn’t just confined to notes…
It encompasses a range of musical information, from pitch bend to modulation, from sustain pedal actions to the intensity of the hit on a drum pad.
In the music production realm, thoroughly understanding MIDI data is essential.
When refining your tracks, It’s this MIDI data that you’ll be:
- Editing
- Tweaking
- Rearranging
Especially in genres like hip-hop and trap, where precision and beat layering play a huge, pivotal role.
To genuinely understand “How does MIDI work?” you must get acquainted with MIDI data, as that’s the key to creating unique music.
The Significance of MIDI Messages
Transitioning from the basic understanding of MIDI, you must explore the core: MIDI messages.
These are the ‘messages’ that give the instructions 一 making the magic of MIDI possible.
-
What are MIDI Messages?
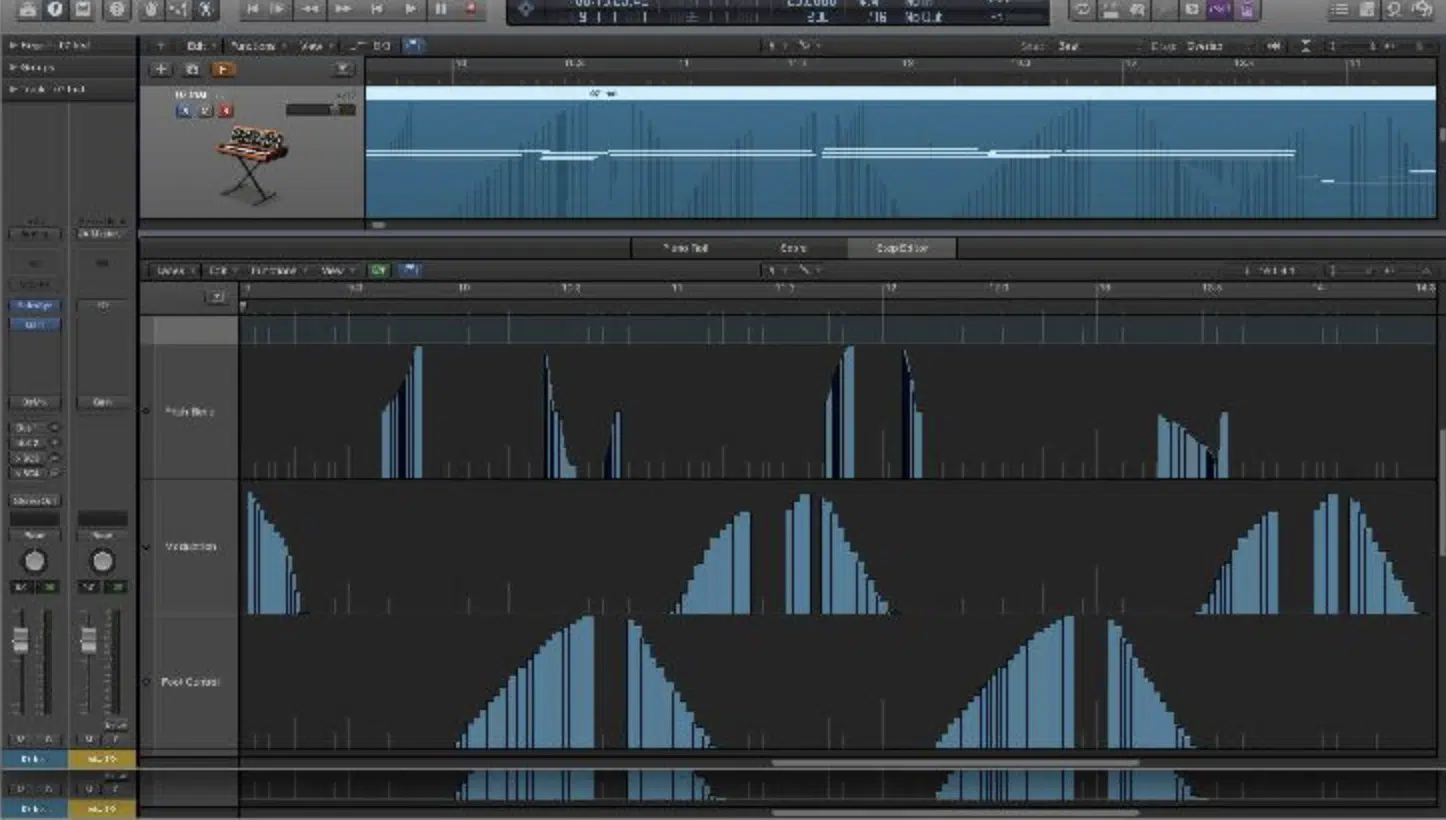
The essence of MIDI’s functionality lies in MIDI messages.
While “data” is the information, “messages” are the structured instructions that deliver this information from one device to another.
These MIDI messages are crucial because they ensure uniformity.
No matter what equipment or software you’re using, if it’s MIDI-compatible, it understands these messages.
It’s a universal language in the world of digital music.
MIDI messages allow for granular control over every track element for producers of any genre.
This level of detail (from the attack of a note to the modulation of a sound) helps craft the nuances that define great tracks.
NOTE: MIDI messages are indispensable when dealing with intricate genres like hip-hop and trap.
They offer the precision required to create those layered beats, staccato rhythms, and textured synths that are the signature of these genres.
-
Types of MIDI Messages
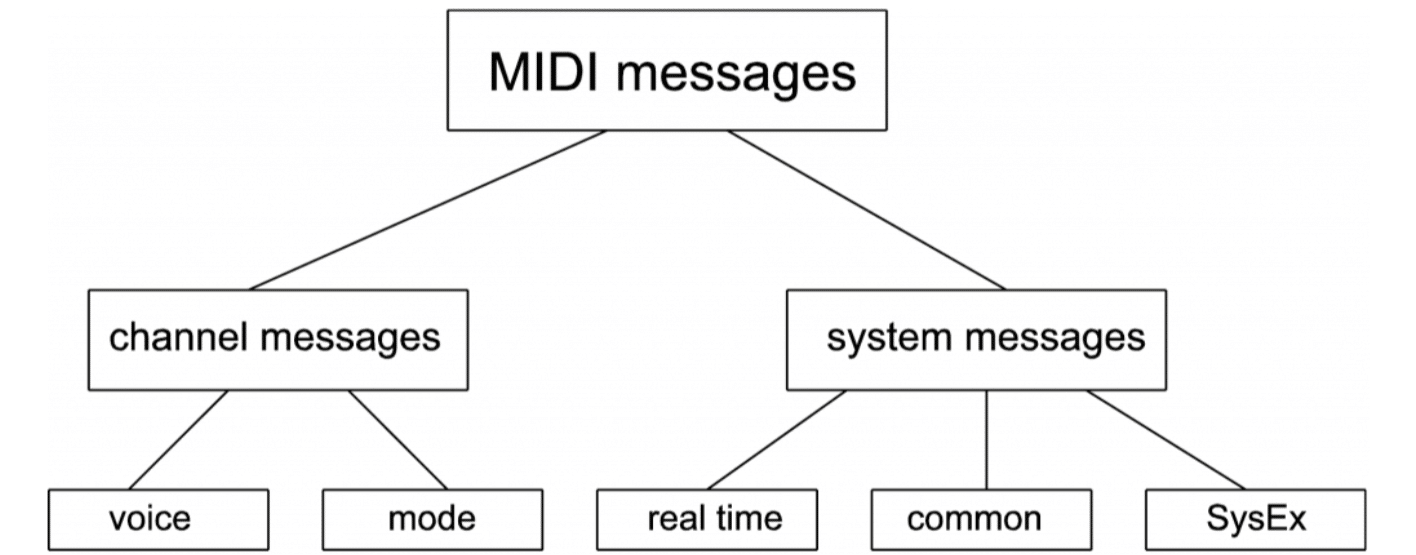
In the MIDI protocol, you’ll need to familiarize yourself with two different categories of messages.
These two message-types are:
- Channel Messages 一 Pertains to individual channels (instruments).
- System Messages 一 Relates to the system as a whole (or multiple systems).
There are “Voice” and “Mode” within Channel Messages.
Voice messages include Note On/Off, Program Change, and others that determine how an instrument sounds.
Mode messages, on the other hand, affect the mode of operation of an instrument.
System Messages can further be broken down into “Common,” “Real-Time,” and “Exclusive.”
While “Common” and “Real-Time” messages are standardized (like song position or start/stop commands), “System Exclusive” messages are manufacturer-specific.
They enable unique functionalities for specific equipment.
Understanding these message types isn’t just for tech aficionados; it’s essential for music producers aiming for intricate control and customization in their music.
Which is safe to say covers all of us.
It allows for a much broader palette of musical expressions, which is key to creating unique, memorable, legendary tracks.
MIDI Controllers vs MIDI Keyboards: What’s The Difference?
As we deepen our exploration, let’s focus on the physical equipment that harnesses the power of MIDI to bring your musical visions to life.
-
MIDI Controllers

At its core, MIDI controllers are hardware devices that sends MIDI data to computers or other musical equipment.
Unlike traditional instruments, a MIDI controller doesn’t produce sound independently but controls other devices that generate sound.
Controllers come in various shapes and forms.
- Some MIDI controllers 一 Are keyboard-based.
- Other MIDI controllers 一 Have pads, knobs, sliders, or touch-sensitive screens.
Their primary purpose is to successfully offer a tactile way to input MIDI data into a DAW or sound module.
For digital music producers, pad-based controllers are particularly popular.
These pads allow for rhythmic input, essential for crafting signature, chart-topping, mesmerizing beats.
Plus, they offer the ability to sample sounds; further expanding creative possibilities.
As the realm of digital music evolves, so do MIDI controllers.
Modern controllers now offer features like aftertouch 一 where the pressure applied to a key after its initial press can modulate the sound.
This opens up dynamic new avenues for musical expression.
-
MIDI Keyboards

A subset of MIDI controllers, MIDI keyboards, resemble traditional keyboards but, like controllers, don’t produce sound themselves.
Instead, they send MIDI data based on the keys played, which a computer or sound module then translates into sound.
MIDI keyboards often come with additional features like:
- Pitch bend wheels
- Modulation controls
- Sometimes pads
Such additions allow for a broader range of expression 一 making MIDI keyboards indispensable for many producers.
NOTE: Sizes vary, from compact 25-key MIDI keyboards perfect for on-the-go setups to expansive 88-key models that replicate the range of a grand piano.
Selecting the right size often involves workspace, portability needs, and the musical range they typically work within.
Given the versatility and intuitive design of MIDI keyboards, they’ve become a staple in many home studios.
Whether laying down a melody or programming a complex synth line, they bridge the gap between the tactile feel of an instrument and the digital realm.
When one thinks of channels in MIDI, it’s not about the numerous radio stations we flip through.
Instead, MIDI channels are pathways that transmit specific data.
Let’s delve into their mechanics.
-
Introduction to MIDI Channels
MIDI channels serve as individual lanes for transmitting MIDI data.
The MIDI protocol provides 16 separate channels 一 allowing multiple instruments or commands to be controlled independently from a single device.
Think of these channels as separate tracks on a mixing board.
Each individual MIDI channel can carry its own:
- Unique sequence of notes
- Control changes
- Other MIDI data
This gives you the capability to orchestrate complex arrangements.
A single MIDI device (like a keyboard) can transmit data on one channel (monophonic) or multiple channels (polyphonic).
For instance, in a layered sound, the bass might be on channel 1, while the melody occupies channel 2.
Recognizing which instrument or sound is assigned to which MIDI channel becomes paramount for clarity and pristineness.
This is especially true when orchestrating multiple-layer compositions or integrating various MIDI devices.
-
How Many MIDI Channels Do You Need?
The required number of MIDI channels varies based on a project’s complexity; one channel may suffice for a simple setup with a single instrument.
However, intricate arrangements or live performances with multiple instruments demand multiple channels.
Remember, MIDI offers 16 channels, but not all must be utilized.
It’s advised that you designate channels based on the role of instruments, like:
- Percussions on one
- Bass on another
- Melodic elements on yet another
- So on and so forth
Assigning channels isn’t just a random choice.
Consistency across projects (especially when using the same instruments or sounds) can streamline the workflow and reduce the chances of errors or overlaps.
For those into electronic music genres or any form demanding extensive sound layering, maximizing channel usage becomes crucial to maintaining distinct sounds.
As well as prevent muddiness in tracks, which is always the goal.
Understanding MIDI Devices & Digital Music Gear
Diving into the technological side, it’s essential to break down the gear that empowers MIDI to master it fully.
-
Common MIDI Devices in a Studio

In the recording studio, you’ll undoubtedly encounter various digital music devices, like a MIDI sequencer, designed to enhance and refine the music production process.
Among the most crucial of these tools are MIDI devices 一 each serving a unique purpose in the intricate dance of sound creation.
Here’s a quick run down as we cover these MIDI devices in detail throughout the article.
Sequencers: These devices or software applications allow for the recording, editing, and playback of MIDI data. Many digital audio workstations have built-in sequencers.
Sound Modules: Often rack-mounted, these devices produce sounds when they receive MIDI data. Think of them as instruments awaiting instructions.
Drum Machines: Specifically designed to emulate drum sounds, drum machines can be programmed via MIDI to produce rhythms.
Synthesizers: Instruments that generate audio signals, synths can be hardware units or software plugins. They play sounds based on the MIDI data they receive.
Understanding the diverse range of MIDI devices is paramount 一 not just for technical proficiency and creative mastery.
By doing so, you can unlock an expansive sonic palette and tweak your setup to the needs of each unique project.
As well as ensure your creative vision is fully realized, naturally.
-
The Evolution of Digital Music Gear with MIDI

MIDI revolutionized digital music production by introducing a standardized protocol.
One that paved the way for devices from different manufacturers to communicate seamlessly.
With the rise of home studios, MIDI enabled producers to have vast orchestras or entire bands at their fingertips (all via synthesizers and sound modules).
Modern developments include:
- Wireless MIDI controllers
- Touch-sensitive control surfaces
- Highly specialized devices
As technology progresses, the boundary between traditional instruments and MIDI devices blurs.
Instruments like MIDI guitars exemplify this fusion 一 integrating age-old musical expression with digital versatility.
NOTE: Consulting a MIDI implementation chart for your devices can streamline your MIDI setup process.
It ensures that each component communicates efficiently and as intended.
MIDI Interfaces: Bridging the Gap
Mastering MIDI requires a robust understanding of MIDI interfaces – the bridge that ensures seamless communication between your devices.
-
The Role of a MIDI Interface

A MIDI interface acts as the mediator between devices that don’t have standard MIDI ports and computers or other devices.
It bridges the gap and accurately relays MIDI data between the connected units.
Modern music production computers, for instance, don’t typically come with standard 5-pin MIDI ports.
Therefore, a MIDI interface becomes essential when working with traditional MIDI hardware devices.
MIDI interfaces can range from simple 1-in/1-out units to complex multi-port devices 一 which should be determined based on the studio setup or live performance rig.
Choosing the right MIDI interface is, needless to say, crucial.
It’s not just about transferring notes, as MIDI interfaces handle factors such as:
- Timing data
- Control changes
- Ensuring every nuance of a performance is captured/relayed
The evolution of interfaces now includes a USB cable, FireWire, and even wireless connectivity.
Each offers unique benefits; with USB being the most common for its simplicity.
-
Connecting Your MIDI Interface
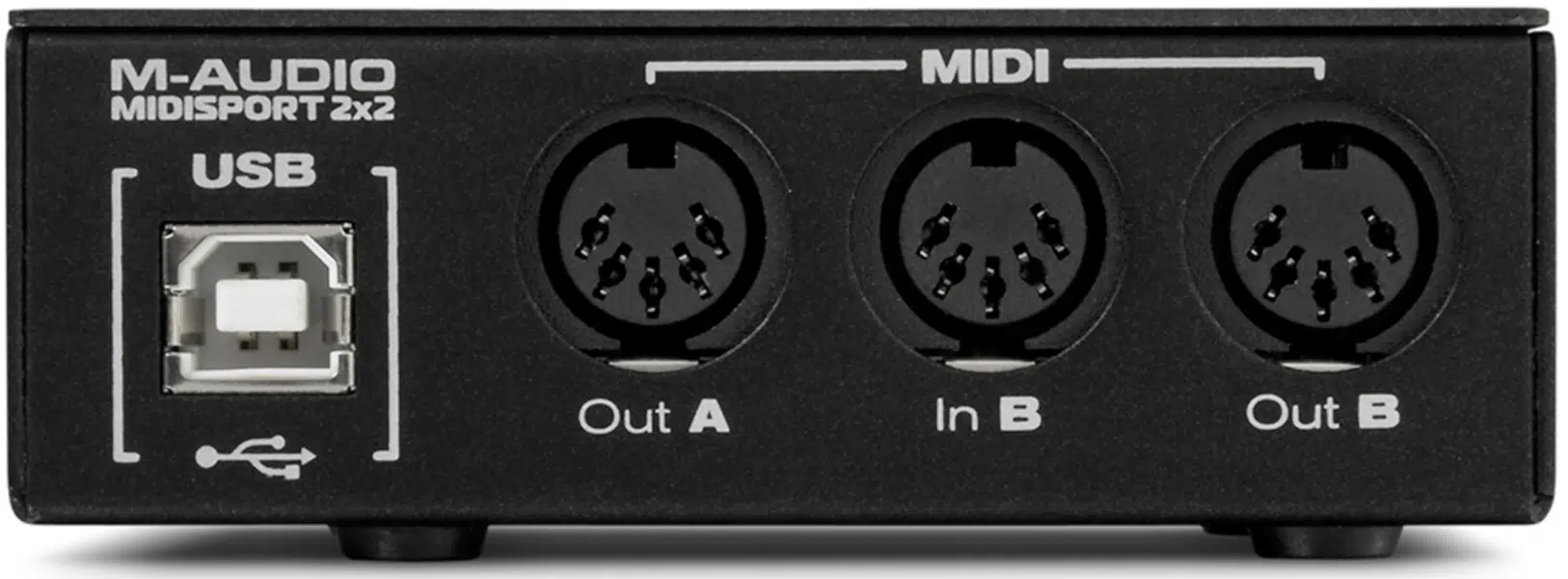

At its most basic, connecting a MIDI interface involves plugging the “MIDI IN” of the interface into the “MIDI OUT” of your instrument or controller (and vice versa).
Modern interfaces typically connect to computers via USB or FireWire.
Once connected, computers recognize them as MIDI devices, and they can be selected within DAWs or other software.
For multi-port interfaces, meticulous labeling and organization become key.
Knowing which instrument corresponds to which port can streamline the creative process and troubleshooting.
Understanding the MIDI signal flow is paramount, given the variety of devices in a typical setup.
Establishing a robust MIDI connection between your devices is crucial for musical data transmission and synchronization.
Instruments, controllers, and software need to sync seamlessly for optimal results, so ensure it matches.
NOTE: Data lag, or latency, can be a musician’s nightmare, as the time between pressing a key and hearing the sound should be virtually instantaneous.
Choosing a high-quality interface can significantly minimize latency issues.
Also, picking out the right MIDI cable (or MIDI cables) is essential to ensure uninterrupted data transfer between devices without lag or interference.
Virtual Instruments and MIDI: A Powerful Pair
MIDI and virtual instruments have formed an inseparable bond in today’s digital age, elevating music production to new horizons.
So, let’s dive right in.
-
MIDI and the World of Virtual Instruments

When you’re trying to decipher ‘How does MIDI work?’ it’s essential to get familiar with virtual instruments.
Virtual instruments (VSTs) are software emulations of traditional instruments, and MIDI is their lifeblood.
These instruments can be played, sequenced, and controlled with MIDI data.
VSTs replicate sounds with stunning accuracy and precision, from grand pianos and guitars to intricate synthesizers.
With MIDI, you can control these instruments in real time or sequence them in a DAW.
The flexibility of VSTs means they can be successfully:
- Layered
- Combined
- Modified
This flexibility, powered by MIDI, has democratized music production 一 making high-quality soundscapes accessible to bedroom producers.
With the evolution of technology, many virtual instruments now incorporate artificial intelligence, learning from MIDI input to offer more expressive and realistic performances.
Given the vast world of available VSTs, MIDI provides a standardized protocol.
This ensures that integration remains smooth and flawless regardless of the instrument or software brand.
-
Tips for Using MIDI with Drum Machines

Drum machines, both physical or virtual, rely heavily on MIDI for sequencing beats.
When using MIDI with drum machines, it’s crucial to understand the layout, like which pad or key triggers which sound.
#1. Quantization
Quantization is a handy tool in digital audio workstations.
If your beats aren’t perfectly in time, quantizing can snap them to the nearest beat or subdivision 一 ensuring a tight rhythm.
#2. Utilizing Velocity Sensitivity
Utilizing velocity sensitivity can make beats feel more dynamic.
Instead of every hit having the same intensity, MIDI allows for nuanced performances, where some hits are softer or harder based on the input.
#3. Experiment with MIDI Effects
Arpeggiators, for example, can turn a simple beat into a complex rhythm and expand the possibilities of your drum patterns.
#4. Remember That the Human Touch is Irreplaceable
In your journey to discovering ‘how does MIDI work,’ it’s vital to remember that while machines and software offer precision, the human touch is irreplaceable.
Sometimes, you should intentionally avoid quantization to replicate the human imperfections of playing live instruments.
-
MIDI Sequencing for More Intricate Beats
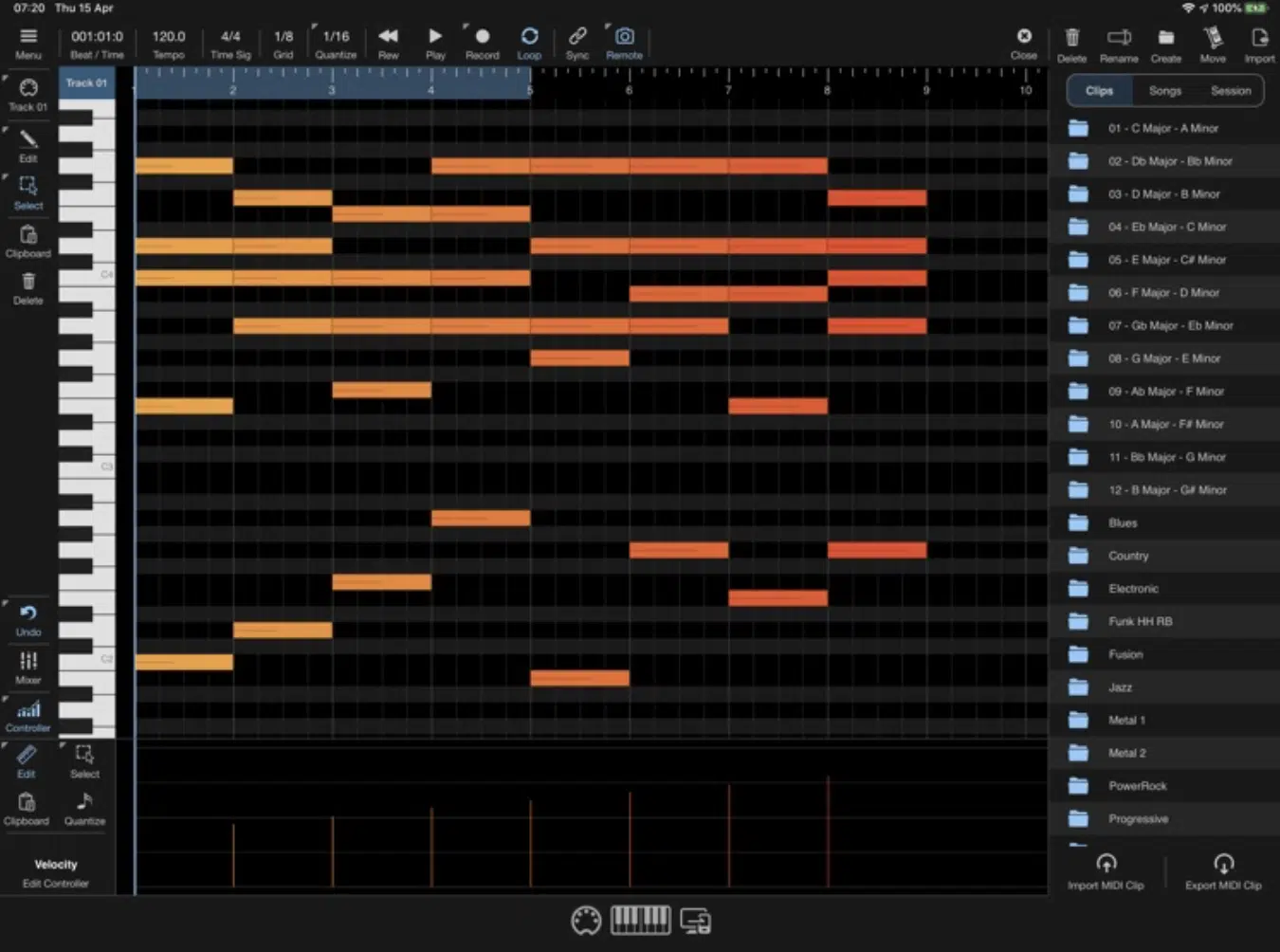
MIDI sequencing involves arranging MIDI notes to form patterns, melodies, or rhythms.
This can lead to intricate and layered drum patterns in the context of beats.
Advanced MIDI sequencers allow for polyrhythms, where multiple rhythms coexist, creating a rich tapestry of sound.
With MIDI, you can effortlessly experiment with varying time signatures and syncopations.
The beauty of sequencing in a DAW is the visual aspect; you can see the beats, making it easier to identify:
- Gaps
- Overlaps
- Sections that might need embellishment
Using MIDI controllers with built-in sequencers can also enhance live performances.
By triggering sequences on the fly, dynamic and evolving beats can be crafted in real time for unique results.
Remember, sequencing is as much about silence as it is about sound.
Strategic placement of pauses or breaks in MIDI sequences can provide moments of tension or release in a track.
MIDI’s Advanced Features: Beyond the Basics
Venturing deeper into MIDI, a whole world of advanced features presents itself.
These functionalities provide more control, versatility, and precision to music enthusiasts and professionals alike.
-
MIDI Thru
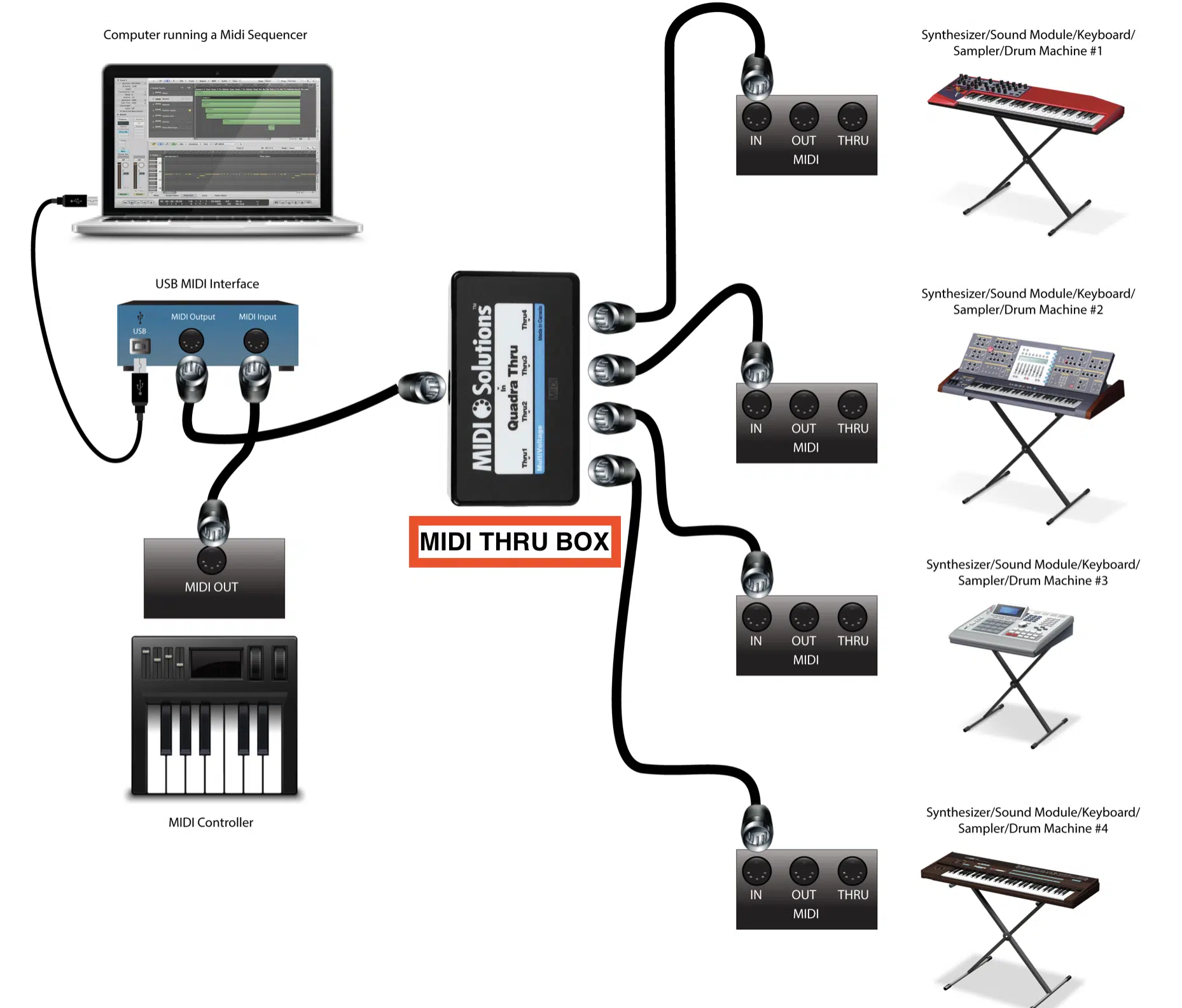
At its core, MIDI Thru might sound simple, but its practical application is very important in a digital music setup.
Unlike MIDI Out (which sends MIDI data from one device to another), MIDI Thru replicates the exact MIDI data it receives from the MIDI In port.
Then, it passes it to the next device without delay or change.
This feature is incredibly beneficial when linking multiple MIDI devices in a daisy chain configuration.
Imagine you have a MIDI keyboard, a drum machine, and a digital synthesizer, and you want to control all three with a single MIDI controller.
Using the MIDI Thru port, the data from your controller can pass unchanged through each device 一 guaranteeing they all receive the same MIDI information.
Think of it as a relay in a race…
The first runner (the initial MIDI device) hands the baton (the MIDI data) to the next runner (the subsequent MIDI device).
Each device in the chain gets an identical message.
This ensures that every part of your MIDI setup remains synchronized and harmonious.
NOTE: While using MIDI Thru, it’s important to remember the order of devices in your chain, as it will influence how they react.
For instance, if you’re sending a command to adjust the pitch on your synthesizer, but your drum machine is the first in the sequence and doesn’t recognize that command, it simply passes it on.
So, ensure your devices are ordered correctly so every piece of gear understands and responds to the messages it’s supposed to.
-
MIDI Mapping and Its Significance
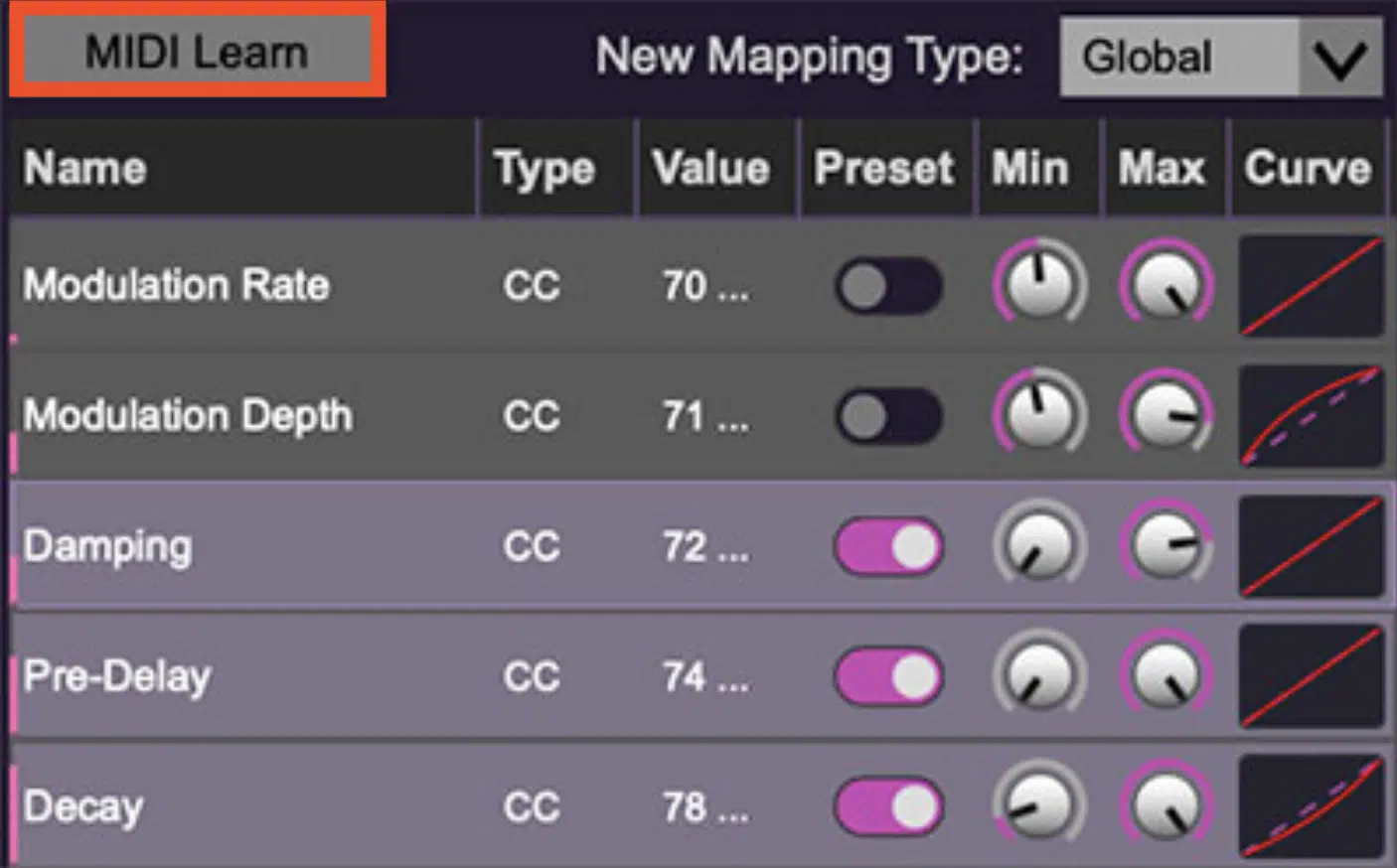
MIDI mapping is the process of assigning specific MIDI messages to specific functions within software or digital music hardware.
For example, mapping a knob on a controller to control the filter frequency in a synthesizer.
MIDI mapping provides immense flexibility, especially in live performances.
Therefore, you can customize controls however you’d like to ensure an efficient and expressive setup.
NOTE: Many DAWs and software instruments come with ‘Learn’ functions (as shown above), making MIDI mapping easier.
When activated, the software awaits a MIDI control action and automatically maps the triggered function to it, which is super beneficial.
Revisiting and refining your MIDI mapping setup can lead to more intuitive and dynamic performances.
-
MIDI 2.0: Dive into MIDI Polyphonic Expression (MPE)

Traditional MIDI systems send data so that all notes on a channel share certain controls, like pitch bend.
MPE (MIDI 2.0) redefines this by assigning each note its own MIDI channel, allowing individual:
- Pitch
- Timbre
- Expressive control
MPE devices can detect multidimensional touch aspects.
For instance, the ROLI Seaboard captures pressure, finger position, and slide direction.
Altering their touch allows you to introduce vibratos, swells, or timbral changes to individual notes.
The world of synthesizers has embraced MPE, with companies like Moog, Arturia, and more introducing MPE compatibility.
This means these synths can interpret the intricate details sent by MPE controllers 一 producing evolving soundscapes that were previously difficult to achieve.
NOTE: DAWs have begun integrating MPE support.
Ableton Live, Logic Pro X, and Bitwig are examples of DAWs that cater to the detailed expression MPE offers.
Within these software platforms, you can draw, edit, and manipulate MPE data to further harness the full potential of MPE for groundbreaking sound design.
How Does MIDI Work? Final Thoughts
MIDI, as we’ve explored, isn’t just about transferring data…
It’s about revolutionizing how music is made, offering a dynamic range of sound options, and elevating tracks in epic ways.
Deciphering the question “how does MIDI work” places you leaps and bounds ahead of many producers.
As well as equips you with the tools and knowledge to craft chart-topping hits.
To further enhance your understanding of MIDI and to help you delve deeper into its creative application, you have to check out the Free MIDI Box (Free Teaser).
This invaluable pack contains 55 MIDI files, designed to elevate your tracks and provide a practical experience.
With 10x MIDI Melodies, 10x MIDI Chord Progressions, 10x MIDI Basslines, and 25 MIDI drum patterns, it’s an indispensable tool for any serious producer.
As you experiment with these MIDI files, you’ll gain hands-on understanding and insight into the power of MIDI 一 solidifying the techniques we’ve discussed.
The next time someone asks, “How does MIDI work?” not only can you provide an answer, but you can also demonstrate its power in your music.
So, go ahead and harness the magic of MIDI to propel your tracks to professional heights.
Until next time…







Leave a Reply
You must belogged in to post a comment.