MIDI (Musical Instrument Digital Interface) is the language that allows electronic musical instruments, computers, and other related devices to communicate, control, and synchronize.
Essentially, it bridges the gap between human expression and digital precision.
Harnessing the power of MIDI instruments can completely revolutionize your sound and streamline your workflow.
And, as a music producer, they can also catapult your creative potential to new and unexplored heights.
That’s why we’re here to break down everything you need to know about MIDI instruments.
This way, you can navigate the MIDI landscape with confidence and expertise.
In today’s article, we’ll be breaking down:
- MIDI basics, techniques, and key components ✓
- The power of MIDI instruments ✓
- MIDI data, messages, files, and connections ✓
- The importance of MIDI controllers & MIDI keyboards ✓
- Virtual instruments and their significance ✓
- MIDI cables & MIDI ports ✓
- How to navigate your MIDI interface ✓
- Pro tips, tricks, and techniques for producers ✓
- Much more to help you master MIDI instruments ✓
Whether you’re an amateur dabbling in production or a seasoned professional, understanding MIDI is indispensable.
By the end of this journey, you’ll be crafting sonic masterpieces, manipulating intricate data, and optimizing your setups, all with the finesse of a seasoned professional.
So, let’s dive in…
Table of Contents
- What is MIDI (Musical Instrument Digital Interface)?
- MIDI Instruments: Breaking it Down
- MIDI Controllers: Ultimate Control
- The Role of MIDI Messages in Music Production
- Diving into Key MIDI Components
- Navigating Through MIDI Data and Connections
- MIDI Technology & Its Many Wonders
- MIDI in Electronic Instruments
- MIDI and the Digital Landscape
- Bonus: Unlocking Your Piano’s Potential with MIDI
- MIDI Instruments: Final Thoughts
What is MIDI (Musical Instrument Digital Interface)?

Introduced in the 1980s, the Musical Instrument Digital Interface (MIDI) revolutionized music production.
Unlike traditional audio recordings that capture and store sound directly, MIDI records the instructions for reproducing that sound.
Think of MIDI as the DNA of a track…
It doesn’t provide the sonic outcome but contains information on how it should be shaped and manipulated.
Within a standard MIDI file, certain elements are meticulously detailed, like:
- Every note
- Its pitch and duration
- Dynamics
Beyond just pitches and rhythms, MIDI dives deeper.
It encodes other nuances of a performance, capturing subtleties like the vibrato of a string or the intensity of a keystroke.
This makes it invaluable for music producers who want that unique sound.
Its universality ensures it acts as a bridge between various software and hardware, ensuring seamless communication.
This interconnectedness offered by MIDI (Musical Instrument Digital Interface) means a producer can craft intricate compositions.
It connects various devices and instruments in harmony so you can create the music you envision.
MIDI Instruments: Breaking it Down
When we think about MIDI, we often picture MIDI keyboards or MIDI controllers, but the world of MIDI instruments extends far beyond these familiar tools.
These devices are pivotal in translating our musical intentions into digital data, ready for any software or hardware to interpret.
Let’s dive deep into the intricate landscape of MIDI instruments and see how they have transformed music production.
-
The Anatomy of MIDI Instruments
MIDI instruments encompass multiple devices designed to send MIDI data when played.
This includes everything from traditional-looking MIDI keyboards to drum pads, wind controllers, and even stringed instruments explicitly designed for the digital age.
For instance, the Roland GR-55 Guitar Synthesizer allows guitarists to trigger synthesizer sounds, sample playback, and more right from their beloved six-string.
Each of these instruments is equipped with sensors or mechanisms to detect a player’s actions, like:
- Key presses
- String vibrations
- Breath intensity
These actions are then converted into corresponding MIDI messages, ready to be processed by software or other MIDI-compatible hardware.
-
MIDI Instruments: Their Role in Modern Production

The versatility of MIDI instruments has led them to be staples in studios worldwide, from home studios to professional recording environments.
You might use a MIDI drum pad like the Akai MPC series to punch in unique and intriguing drum patterns.
Or a MIDI wind controller such as the Yamaha WX5 to emulate a saxophone sound.
This adaptability means that, even if you don’t have access to a specific acoustic instrument, you can emulate its sound with a MIDI instrument.
And the right virtual instrument software, of course.
It’s like having an entire orchestra or band at your fingertips 一 displaying how beneficial MIDI instruments truly are.
-
Integration with DAWs & Virtual Instruments

MIDI instruments are crucial in the realm of digital audio workstations (DAWs).
Once connected, instruments like the Novation Launchkey can be mapped to control various functions within a DAW 一 from playing virtual instruments to adjusting mix levels or turning audio effects on and off.
The real magic happens when MIDI instruments are paired with virtual instruments (VSTs).
With software like Native Instruments’ Kontakt or Spectrasonics’ Omnisphere, a single MIDI keyboard can emulate anything, like a:
- Grand piano
- Pulsating synth
- Ethereal choir
The possibilities are virtually limitless, and you set the bar.
If you’re going to become a MIDI master, you must recognize its impact when played within a DAW and combined with virtual instruments.
MIDI Controllers: Ultimate Control

MIDI controllers, often mistaken for MIDI instruments, play a pivotal role in the music creation process.
MIDI controllers act as intermediaries; converting physical actions into digital data in order to be manipulated.
For example, a press on a MIDI controller’s key doesn’t produce sound…
Instead, the MIDI controller dispatches a series of MIDI messages (detailing the note’s attributes) to a sound-producing device or music production software.
This could be:
- A synthesizer
- A digital audio workstation
- Virtual instruments
But MIDI controllers extend beyond keyboards.
The MIDI controller realm includes drum pads, fader boards, and wind controllers.
Each offers unique methods of interaction 一 enabling you to articulate your creativity with different MIDI controller techniques.
Integrating MIDI keyboard controllers into your music production setup can be transformative.
It can quicken processes, offer hands-on interaction, and seamlessly bridge imagination and creation.
NOTE: We’ve got you covered if you’d like to learn about the Novation Launchpad X and other MIDI controllers.
The Role of MIDI Messages in Music Production
If MIDI is the language of music production, then MIDI messages are its profound words.
MIDI messages relay instructions that detail:
- How a note should sound
- Its duration
- Intensity
- Much more
Beyond simple note-on or note-off commands, MIDI messages delve much deeper.
From modulation and pitch bends to aftertouch and velocity, these commands capture the essence of a performance.
Mastering MIDI messages is paramount for music producers.
It allows you to harness the true potential of their gear 一 ensuring every nuance, every subtle change in intensity, and every modulation is captured and conveyed as intended.
It’s this granularity (this detailed instruction set) that empowers you to craft tracks that resonate, evoke emotions, and stand out in a crowded musical landscape.
Diving into Key MIDI Components
MIDI is like the intricate cogs and wheels inside a watch; every component has its unique role.
Diving deeper into these elements can offer insights that, when harnessed, can elevate your music production workflow.
-
MIDI Keyboard Madness
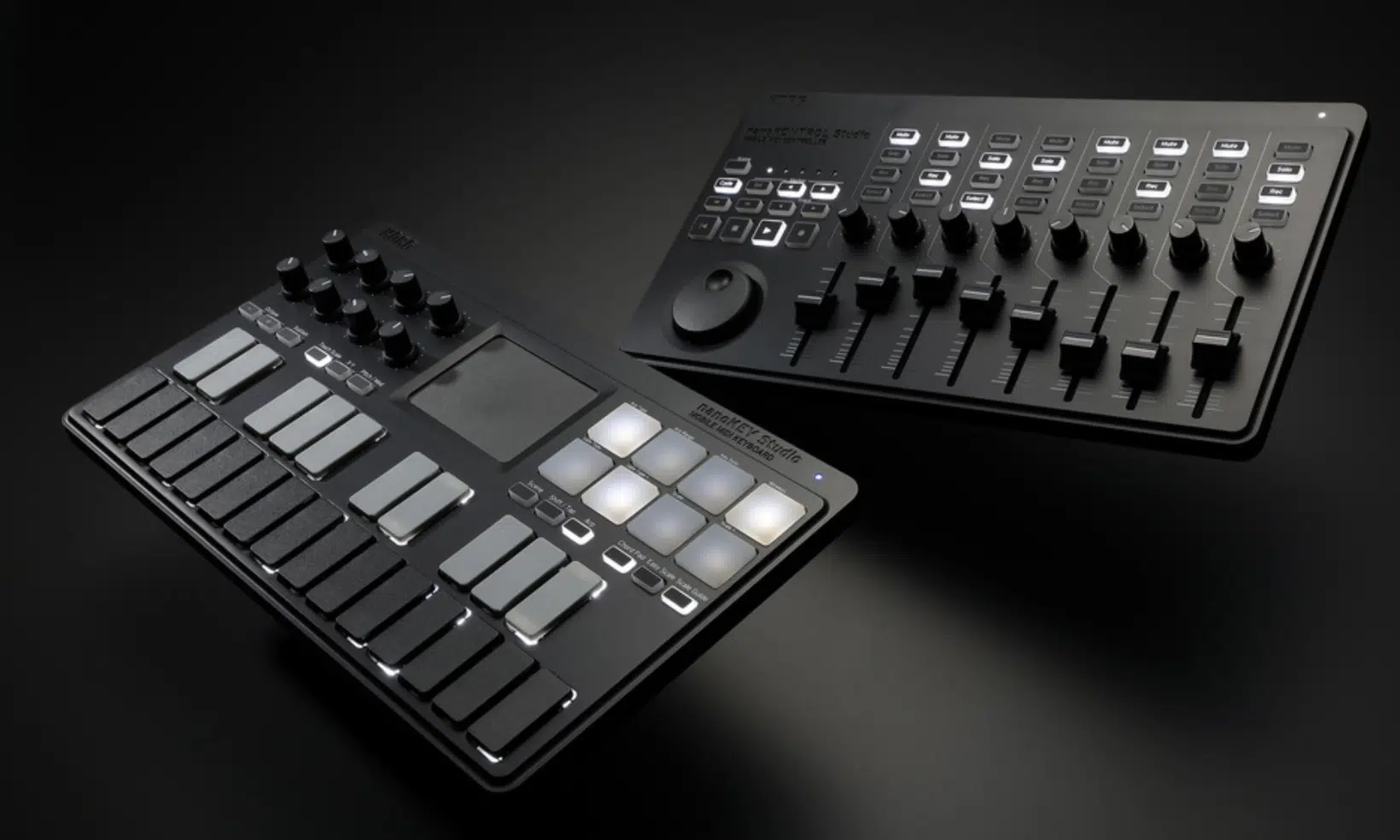

The MIDI keyboard, often considered the cornerstone of many studios, serves as both an instrument and a controller.
Its familiar layout makes it pleasantly accessible and easy to navigate, especially when transitioning from traditional acoustic piano playing to digital instruments.
When you strike a key, the MIDI keyboard translates that action into MIDI data 一 detailing specifics like which note was hit, how hard, and its duration.
As we discussed, MIDI data doesn’t produce sound on its own.
Instead, it communicates with sound modules software synthesizers, and digital audio workstations.
Just like with MIDI controllers, it instructs them on which unique sound to produce.
Interestingly, many MIDI keyboards now include additional features like pads, knobs, and sliders.
These not only trigger drum sounds but also:
- Modulate effects
- Control volumes
- Tweak software parameters
If you’d like to adjust the resonance on a synth or the reverb on a track, you can do so (plus much more) with MIDI keyboards.
NOTE: With the advent of touch-sensitive keys and aftertouch, the expressive potential has skyrocketed.
A gradual press might introduce a vibrato, or pressing harder post-note can introduce modulation.
Such subtleties infuse life into digital tracks and can help your music skyrocket.
-
Importance of MIDI Notes
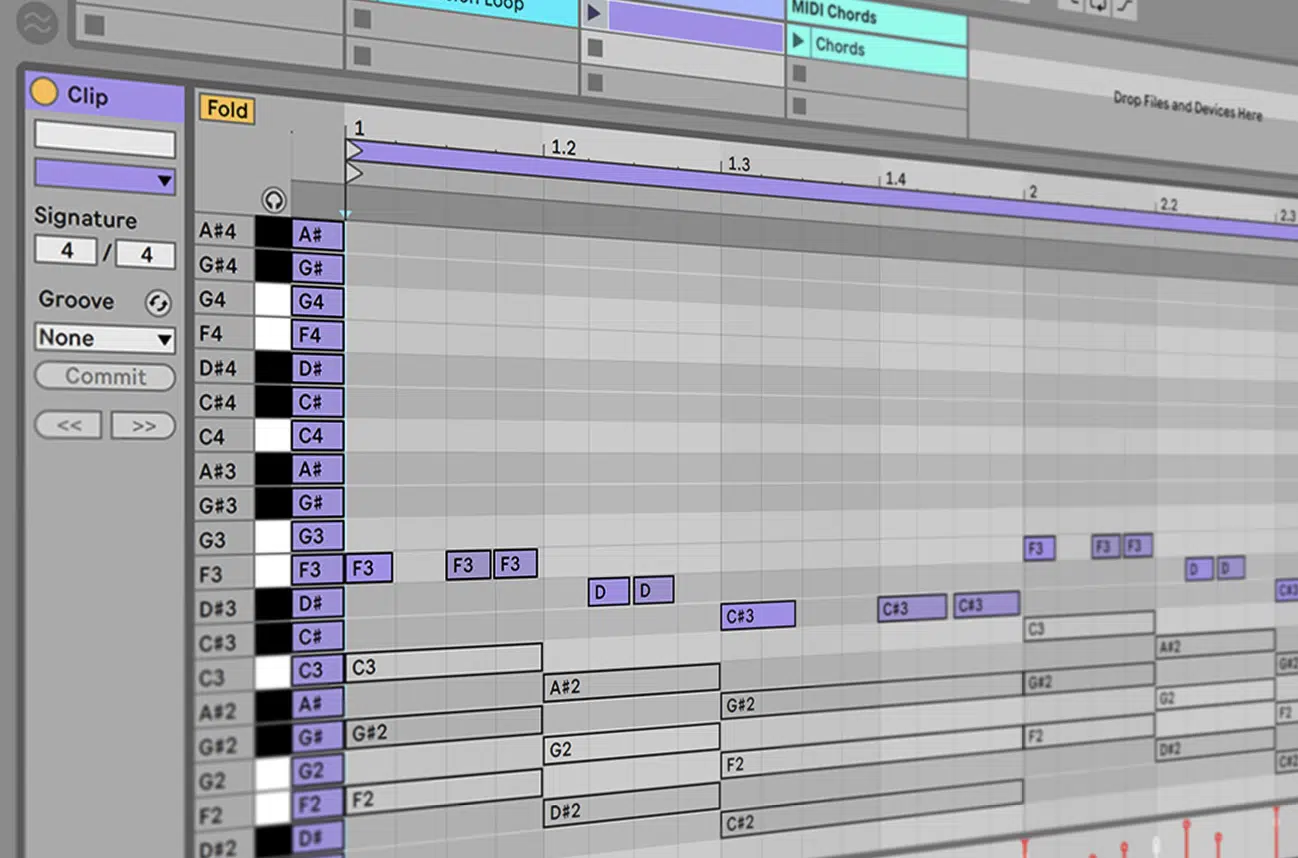
MIDI notes are the heartbeats of any alluring track.
They’re not just instructions on which pitch to play but encapsulate the rhythm, dynamics, and expressiveness of a piece.
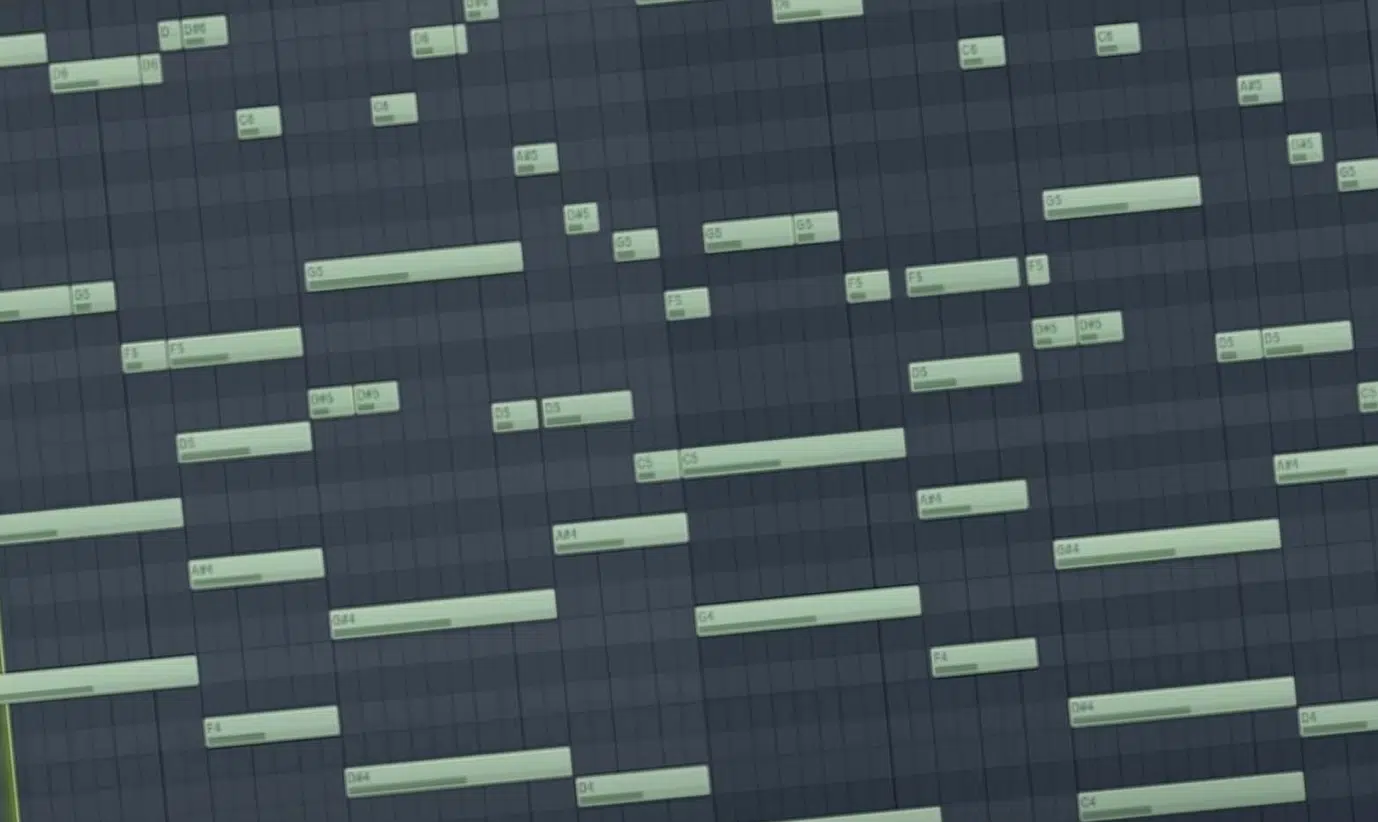
In software parlance, when you observe the piano roll in a digital audio workstation (DAW), each block or line is a visual representation of a MIDI note.
This grid system allows for easy editing 一 changing pitch is as simple as dragging the note up or down.
The length of these blocks represents the note’s duration, and their vertical placement corresponds to pitch.
In essence, the entire song’s melody, harmony, and rhythm can be tweaked, transposed, or transformed without ever recording another note.
The implications and capabilities provided by MIDI notes are profound.
Meaning, on the fly, you’re able to test out different:
- Chord progressions
- Melodies
- Rhythms
Meaning that if you’d like to change a C to a C# or extend a quarter note to a half, it becomes a matter of a few clicks.
MIDI notes are pivotal in your journey to mastering MIDI instruments.
-
Virtual Instruments: The Sound Behind the Silence

Virtual instruments (VSTs) are computer software emulations of real or imagined instruments.
A MIDI note that reads “C3” with a certain velocity might be interpreted by a piano VST as a medium-strength middle C.
The same note could transform into a thumping bass hit if routed to a synthesizer VST.
The universe of VSTs is vast and varied, and with them, you can create sound previously unheard of.
- Some virtual instruments 一 Emulate grand pianos, capturing their nuances.
- Other virtual instruments 一 Night produce ethereal, otherworldly sounds.
With them, one can transform a simple MIDI pattern into an orchestral ensemble, a jazz trio, or a futuristic soundscape.
Producers often have a collection of carefully chosen VSTs based on their sonic needs.
NOTE: It’s not uncommon to layer multiple VSTs, where a single MIDI pattern triggers a piano, a synth pad, and a string ensemble simultaneously.
As we journey further into the world of MIDI, understanding the intricacies of its data and the web of connections it forms is pivotal.
These foundational insights can transform complex setups into seamless, intuitive workflows; let’s get to it.
-
The Power of MIDI Data in Song Creation
MIDI data is like the DNA of your track, encoding every musical nuance into a digital format.
But it’s more than just note information and MIDI information; it’s a narrative of the song’s progression.
A significant component is the control change data.
Imagine wanting to slowly introduce a filter sweep in a synthesizer or gradually decrease the volume of a track.
These dynamic changes (often seen in automation lanes in DAWs) are all transmitted as you guessed it, MIDI data.
Pitch bend is another crucial element.
The sweeping sound of a guitar dive bomb or the gentle glide between notes in a vocal line can be recreated in digital instruments, thanks to the pitch bend data in MIDI.
Plus, the program change function can automatically switch between instrument patches, which is super cool.
For instance, a keyboardist could transition from a piano sound to strings with a single command 一 enhancing live performances without manual intervention.
-
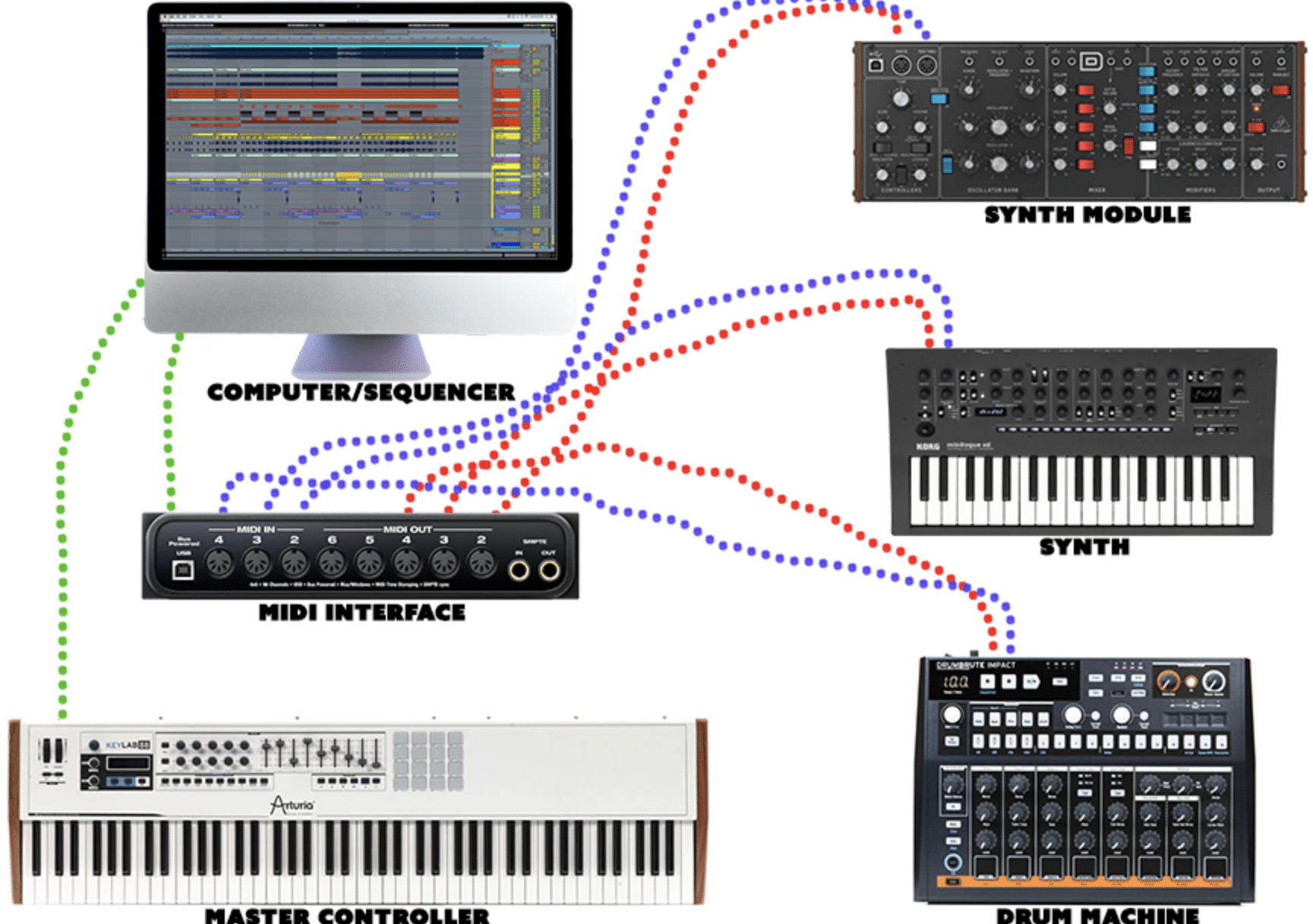
Connectivity Through MIDI Cables and MIDI Ports
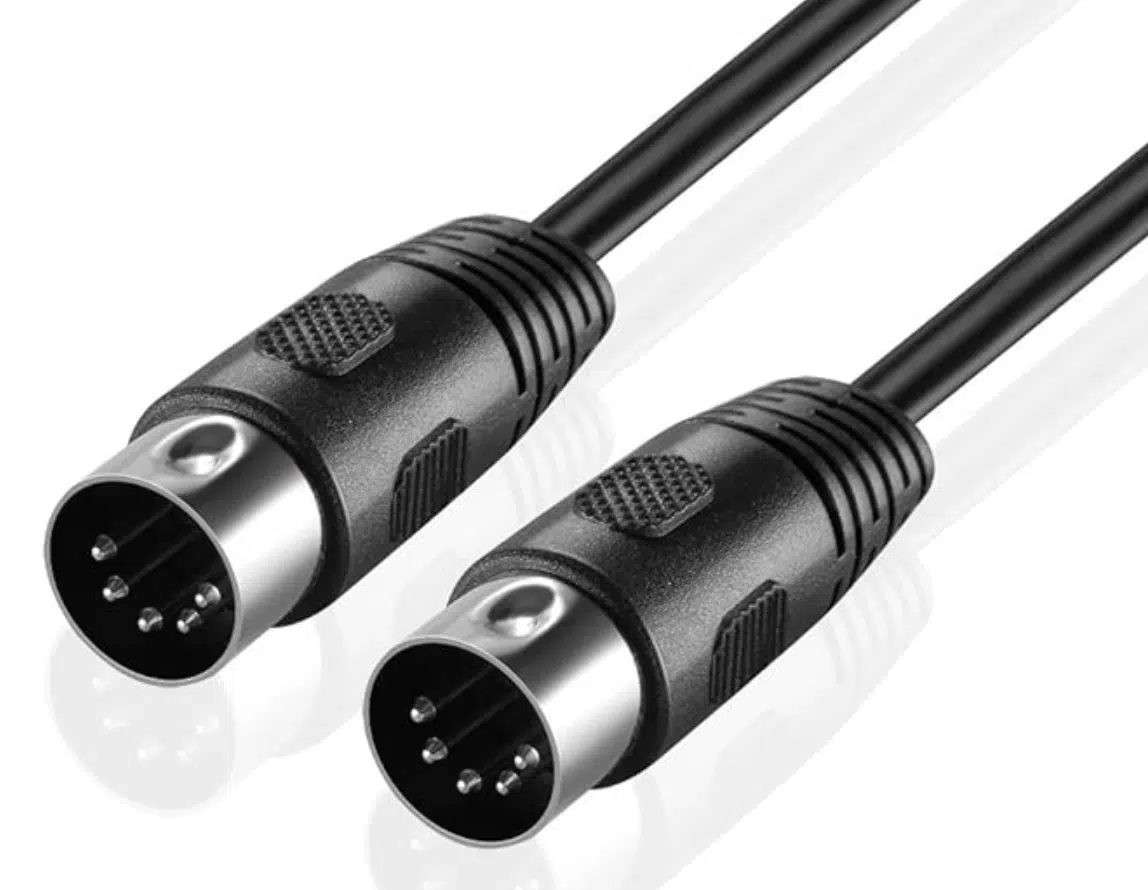

The traditional MIDI setup involves 5-pin DIN cables (a specific MIDI cable) that connect multiple devices.
Two main MIDI ports to remember are the:
- MIDI In
- MIDI Out
When you wish to send data from one device to another, it usually goes from the “Out” of the transmitting device to the “In” of the receiving device.
However, some MIDI devices also feature a MIDI “Thru” port, which is vital for chaining multiple MIDI devices.
If you’re going to master MIDI instruments, you’ll undoubtedly need to be familiar with MIDI cables and the multiple devices in which they can connect.
This port sends out a copy of the incoming MIDI data 一 enabling it to pass the same data to several instruments without latency.
In today’s setups, though the traditional MIDI cable is still widespread, many modern devices use USB for MIDI communication.
This is because they reduce clutter and offer faster data transmission.
-
The Role of Your MIDI Interface
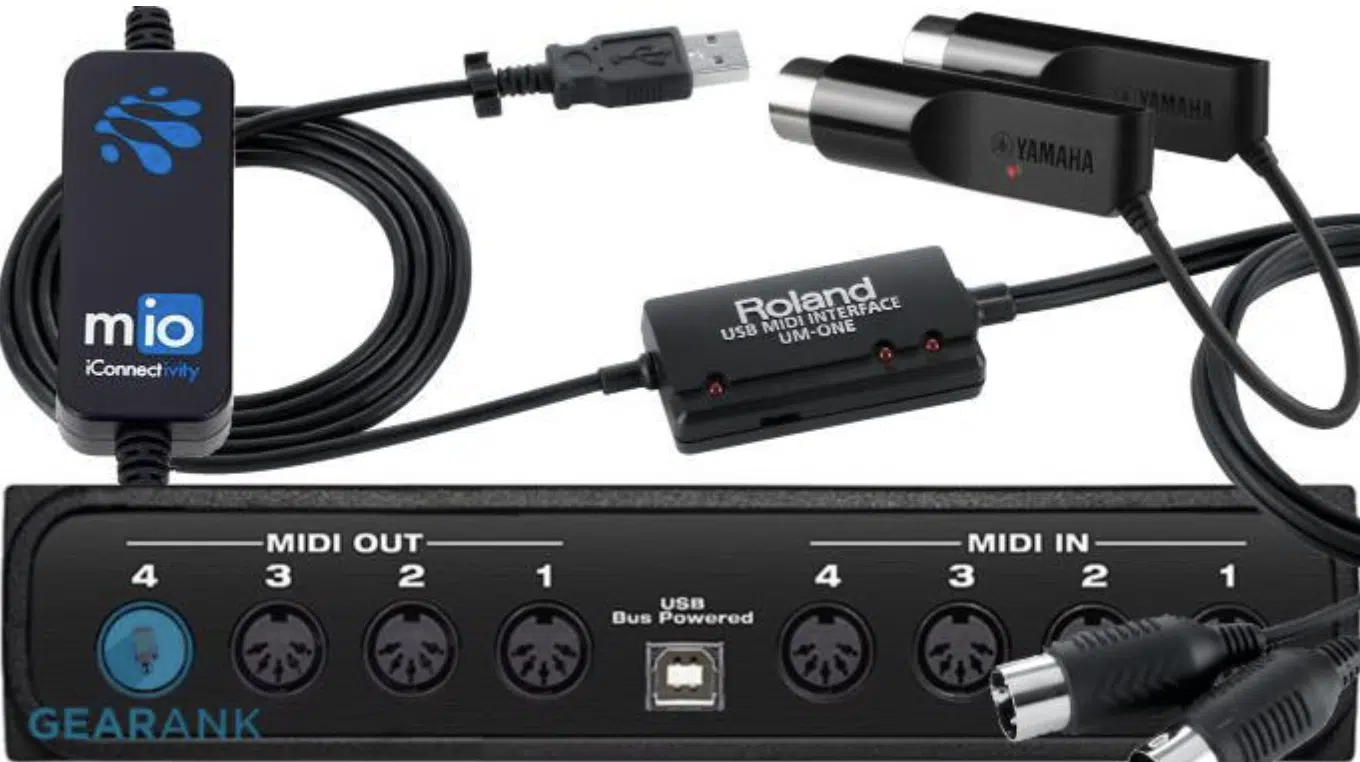

The MIDI interface, often an overlooked component in a producer’s toolbox, is the staple of a smooth MIDI setup.
This is especially true for comprehensive studio arrangements where many instruments and controllers coexist.
A MIDI interface acts as a nexus, channeling data between devices and a computer.
It’s not just a traffic director but a helpful translator.
The intricate web of MIDI communication finds coherence through the interface.
It translates MIDI signals between 5-pin DIN or USB formats and the language a computer’s DAW comprehends.
Diverse in form and function, MIDI interfaces range from compact units with a single input/output pair to more elaborate rack-mounted models boasting over 16 MIDI channels.
Their primary purpose is to ensure every piece of MIDI equipment (be it a decades-old synth or a contemporary digital workstation) interfaces in harmony.
For the modern producer, MIDI interfaces bridge the gap between the past and present.
Consider a studio that houses a vintage 1980s synthesizer alongside a cutting-edge MIDI controller…
While both are MIDI-compatible, their connection modalities might differ.
The MIDI interface seamlessly integrates such diverse equipment 一 producing a consistent, reliable data flow.
NOTE: In setups where latency is a concern, high-end MIDI interfaces can be a game-changer.
By ensuring rapid data transmission and minimizing delay, they can be pivotal in live performance scenarios where timing is paramount.
MIDI Technology & Its Many Wonders
Delving deeper into the world of MIDI technology is like discovering an intricate dance of digital communication.
So, let’s get right into it.
-
Unlocking MIDI Protocols and MIDI Standards

The essence of MIDI communication hinges on protocols (MIDI protocol), a standardized set of rules ensuring interoperability between devices.
MIDI standard allows a sequencer from the early days of MIDI to command a brand-new virtual instrument on a contemporary computer.
Each MIDI message is a cocktail of bytes.
Typically, a status byte initiates the message 一 indicating its nature, whether it’s a note being played, a knob turned, or a pedal pressed.
This byte is followed by one or two data bytes that carry the specifics:
- Which note
- At what velocity
- To what degree a parameter has changed
Think of MIDI protocols as the grammar rules of the MIDI language.
They maintain structure and coherence, and ensure that when a command is given, the receiving device comprehends and executes it as intended.
Knowing the MIDI standard and MIDI protocol is vital in mastering MIDI instruments and taking the music industry by storm.
-
Compatibility: What Makes Instruments MIDI Compatible

Compatibility in the MIDI realm goes beyond mere connectivity.
True compatibility implies a physical connection and a shared understanding of the MIDI messages being exchanged.
When an instrument or software claims MIDI compatibility, it asserts the ability to not only receive MIDI data but to interpret and act upon it in a standardized manner.
For example, a “note on” command might be universally recognized, but how a device responds is where individual character shines through.
A digital drum pad could trigger a crisp snare, while a synthesizer might emanate a lush chord.
This distinction is key in understanding the versatility of MIDI and MIDI instruments.
It’s a language where the words (commands) are standardized, but the accent (the resulting sound or effect) is unique.
-
The Magic of MIDI Channels and Sequencing Software
Channels in MIDI are not about stereo soundscapes but about multitasking.
The standard MIDI protocol supports up to 16 distinct MIDI channels 一 allowing a single MIDI device to handle multiple sounds or instructions simultaneously.
Consider a multitimbral workstation or synthesizer that’s capable of emulating an entire orchestra.
Using MIDI channels, you can assign each section of the orchestra to a distinct channel:
- Violins on Channel 1
- Brass on Channel 2
- Percussion on Channel 3
- So forth
When sequencing in a DAW (with sequencing software), these single-channel assignments ensure the correct instrument sound is triggered.
Additionally, MIDI channels play a vital role in live scenarios.
A keyboardist with a multi-channel setup can switch between a piano on Channel 1 and an organ on Channel 2 with sequencing software.
This enables dynamic live performances without the need for multiple instruments.
MIDI in Electronic Instruments
Electronic instruments have long embraced the magic of MIDI, marrying sonic capabilities with intricate control options.
This alliance has paved the way for transformative music-making experiences.
-
Synthesizers, Drum Machines, and Sound Modules

If you’re going to understand the intricacies of MIDI and MIDI instruments, you’ll need to be familiar with synthesizers, drum machines, and sound modules.
Synthesizers, like analog synthesizers, with their vast sound-shaping capabilities, are an iconic representation of MIDI’s sheer versatility and flexibility.
A synthesizer can receive MIDI data and transmute it into lush soundscapes (a growling bassline, ethereal pad, or searing lead).
Drum machines, dedicated to rhythm and percussive sounds, have embraced MIDI for more refined control over their patterns and grooves.
By interfacing with a DAW or an external sequencer via MIDI, drum patterns can be easily:
- Programmed
- Edited
- Synchronized with other instruments
This is vital because a mind-blowing drum sequence can make or break your track.
Sound modules, often seen as the silent workhorses of the MIDI world, are essentially synthesizers minus the keyboard.
These are often rack-mounted and produce sound when fed MIDI data.
A single sound module could house an entire orchestra, a bank of vintage synthesizer emulations, or specialized sounds, all ready to be triggered via MIDI.
-
The Rise of MIDI-Compatible Electronic Instruments
The adoption of MIDI in the electronic music realm is not just a coincidence; it’s the result of recognizing the unmatched flexibility MIDI offers.
Contemporary instruments are increasingly being designed with general MIDI compatibility at their core.
This compatibility isn’t just limited to hardware.
Software synthesizers, commonly known as VST (Virtual Studio Technology) instruments, simulate hardware instruments’ behavior (and internal sounds).
When connected to a MIDI controller, virtual instruments offer tactile interaction with sounds that exist only digitally.
The surge of MIDI-compatible virtual instruments signals a paradigm shift.
Musicians and producers aren’t bound by the physical limitations of a physical instrument.
Instead, we’re empowered to shape, mold, and generates sound limited only by imagination with the use of virtual instruments.
-
Why USB is Revolutionizing MIDI Connectivity

Historically, 5-pin DIN connectors (MIDI cable) were the primary, traditional mode of MIDI connection.
But as technology evolved, USB emerged as a transformative force in MIDI connectivity.
USB MIDI connections offer simplicity.
A single USB cable can carry MIDI data and power, making it efficient for smaller setups and portable MIDI controllers.
The plug-and-play nature of USB-MIDI devices ensures they’re recognized swiftly by:
- Personal computers
- Tablets
- Smartphones
Furthermore, the bandwidth of USB exceeds that of traditional MIDI cables.
This means faster data transfer rates, leading to reduced latency 一 an essential factor for real-time performances using MIDI instruments.
With USB, integration between modern DAWs, plugins, and instruments has never been more seamless.
MIDI and the Digital Landscape
In the evolving realm of music technology, the digital landscape has embraced MIDI as its cornerstone.
As we venture into the intricate relationship between MIDI and modern digital platforms, it’s essential to recognize the synergy they create together.
-
Using MIDI with Computer Software
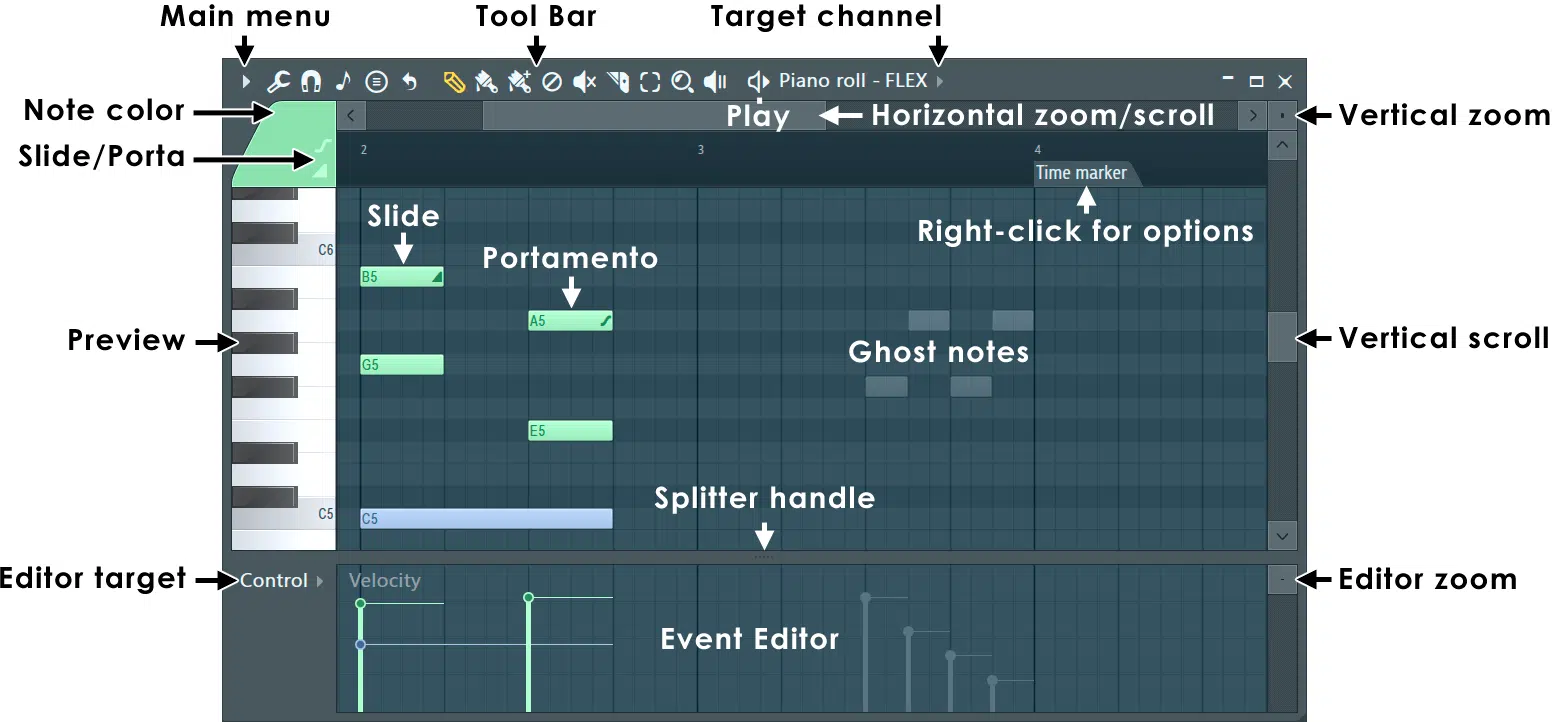
Moving beyond mere sound creation, MIDI’s interaction with software offers a refined level of arrangement and sequencing.
Consider the convenience of FL Studio’s legendary piano roll.
NOTE: A piano roll is simply a digital representation of a piano-style keyboard where you can draw or click to input notes 一 creating intricate melodies and chord progressions.
This visual approach to music composition allows for an intuitive workflow; where seeing and hearing go hand in hand.
Plus, the live performance capabilities of DAWs, particularly evident in platforms like Ableton Live, showcase the potential of MIDI.
DJs and live performers can use general MIDI controllers to trigger:
Such controllers, grid-based like Novation’s Launchpad or key-centric like Akai’s MPK Mini, translate tactile actions into software responses.
They bridge the physical and the digital in real time.
-
The Role of MIDI Files in Modern Production
The humble MIDI file (typically bearing the “.mid” extension) plays a pivotal role in contemporary music creation.
Like all things MIDI, these MIDI files, at their core, don’t store sound.
Instead, standard MIDI files capture your song’s ‘blueprint,’ like the included:
- Note sequences
- Durations
- Velocities
- Instrument data
Imagine a digital music sheet that any MIDI-compatible instrument can interpret and reproduce…
This unique characteristic of MIDI files presents diverse applications.
You can exchange ideas without sending bulky audio files 一 retaining the flexibility to alter notes or instruments.
For instance, collaborating artists might share a “.mid” file (standard MIDI file) of a melody.
This allows both parties to experiment with different synthesizers or sound timbres while retaining the original note pattern.
Additionally, MIDI files serve as valuable educational resources.
If you’d like to decipher the magic behind iconic tracks, you can delve into MIDI recreations and dissect each musical layer.
Can someone say beneficial!
MIDI files offer a window into the structural anatomy of songs across genres, from understanding the intricacies of a complex chord progression to mimicking rapid arpeggios.
If you’d like to learn everything about MIDI files, we’ve got you covered.
Bonus: Unlocking Your Piano’s Potential with MIDI

When we think of pianos, classical tunes, and elegant grand instruments come to mind.
However, in today’s digital age, even traditional pianos can become MIDI powerhouses, revolutionizing how beneficial MIDI instruments can be.
With general MIDI retrofitting, pianos can transform into dynamic MIDI controllers.
MIDI-equipped pianos can also interact with various sound modules and virtual instruments.
Instead of being limited to the piano’s inherent timbre, you can harness sounds ranging from ethereal pads to aggressive basses.
For instance, playing your piano’s keys could activate a lush string section from a VST like Native Instruments’ Kontakt or a striking lead from Spectrasonics’ Omnisphere.
Using MIDI also empowers pianists to compose and arrange with surgical precision.
Through the piano roll in DAWs, you can fine-tune their performances 一 correcting misplays or adjusting note velocities for enhanced dynamics.
Let’s say you recorded a heartfelt ballad on your piano, but a few notes felt lackluster…
With MIDI, you can revisit those notes and make granular adjustments without ever having to re-record.
NOTE: If you’re passionate about layering sounds, MIDI opens the gates to multi-timbral performances.
One could play a chord progression on a MIDI-enabled piano and, with software or hardware layering, simultaneously trigger a deep bass, a shimmering pad, and a vibrant arp sequence.
Such layered orchestrations can enrich live performances and studio recordings alike.
MIDI Instruments: Final Thoughts
As we’ve journeyed through the complexities and nuances of MIDI, it’s evident that this technology remains an indispensable tool for modern music production.
From the foundational basics to the myriad ways it integrates into the digital domain, MIDI continues to shape the soundscape of contemporary music.
It can help you transform basic melodies into rich sonic tapestries, streamline your creative workflow, and give life to the musical ideas that exist in your mind’s ear.
But understanding the theory and mechanics is just the beginning…
To truly leverage the power of MIDI, you need the most innovative, reliable resources, like the free Essential Advanced MIDI Chord Progressions.
Packed with 24 unique, professionally-crafted MIDI chord progressions, this collection is your ticket to elevating your tracks to professional standards.
These aren’t just ordinary progressions 一 they’ve been designed by professional music producers with a deep understanding of music theory.
Meaning, every chord sequence has been expertly crafted to ensure your music stands out.
By incorporating these expertly designed progressions into your compositions, you’re not just adding chords.
You’re successfully infusing your music with the knowledge and expertise of industry professionals.
So, as you move forward in your music production journey, remember that with the right tools and techniques, you’re not just staying in tune with the industry, you’re setting the pace.
Dive in, explore, and let MIDI instruments unlock your music’s true potential.
Until next time…







Leave a Reply
You must belogged in to post a comment.