There’s something magical about electronic music.
The ability to manipulate sound waves into harmonies and rhythms, painting sonic landscapes with just your computer and a MIDI controller.
It’s an experience that’s hard to put into words.
Electronic music production takes you into a world where you’re the creator of your own universe, where every sound, every rhythm, and every melody is at your fingertips.
It gives you the tools to explore, innovate, and create music that is uniquely yours.
So, what does it mean to learn electronic music production?…
Well, that’s what we’re breaking down for you right now, so you’ll have all the knowledge you need moving forward.
In today’s article, we’ll be covering:
- The basics of electronic music production ✓
- The tools & skills you’ll need to claim your spot ✓
- MIDI controllers & MIDI keyboards ✓
- Sound design tips & tricks ✓
- Mastering Ableton Live ✓
- Synthesis techniques ✓
- Electronic genres & subgenres ✓
- Advanced electronic music production methods ✓
- So much more ✓
By the end of this article, you’ll be able to be confident in your electronic music production skills.
This way, you can get back to what you really love: pushing your creativity to its limits and creating legendary tracks for the world to enjoy.
Let’s dive in…
Table of Contents
- Getting Started: How To Produce Electronic Music
- Software Applications for Music Production
- Finding Your Unique Sound in Electronic Music
- Mastering Ableton Live: An Electronic Music Producer Must
- Electronic Music Tracks: Breaking it Down
- Expanding Your Electronic Music Production Knowledge
- Mastering Synthesis for Electronic Music Production
- Electronic Dance Music Arrangement & Composition Techniques
- BONUS: Advanced Tips to Help You Become an Electronic Music Production Master
- Electronic Music Production: Final Thoughts
Getting Started: How To Produce Electronic Music

Let’s begin by defining electronic music production.
It’s the process of creating music using electronic instruments and computer software.
It involves:
- Composing
- Arranging
- Recording music
- Creative sound design
- Mixing & mastering music using a Digital Audio Workstation (DAW)
The beauty of electronic music production lies in its versatility.
From ambient soundscapes to pulsating EDM tracks, you have the power to create a wide range of music.
This flexibility makes it an exciting and rewarding field to delve into.
Electronic music production, in essence, gives you complete control over the music creation process.
You decide the tempo, the pitch, the rhythm, and the melody.
You can create complex arrangements, experiment with different sound textures, and create music that is truly yours.
To become an electronic music producer, you need to understand and master various aspects of music production.
This includes sound design, music theory, composition, mixing, mastering, and more.
This knowledge will enable you to create high-quality music that resonates with your audience.
-
The Essential Role of Digital Audio Workstations

Central to your journey into electronic music production is the Digital Audio Workstation (DAW).
This is where all the magic happens.
It’s where you’ll create, arrange, mix, and master your tracks 一 serving as your canvas, your palette, and your brush.
DAWs come in different shapes and sizes, from Ableton Live to Pro Tools.
Each offers a unique workflow and a set of tools that cater to different production styles.
For instance, Ableton Live (which we’ll cover later) is favored by many electronic music producers for its intuitive design and powerful features.
Using a DAW, you can:
- Arrange sound samples
- Program MIDI sequences
- Apply effects
- Create complete/complex arrangements
For instance, with Ableton Live, you can use the session view to sketch out ideas quickly, or you can jump into the arrangement view to flesh out your track.
It’s a versatile tool, making it great for both live performances and studio work.
Investing time in mastering your DAW is key.
Make sure to learn the keyboard shortcuts, understand the signal flow, and explore the stock plugins for a smoother workflow.
For example, Ableton Live comes with impressive native plugins like Operator for FM synthesis, or Wavetable for modern sound design, which can be excellent tools in your music production process.
NOTE: We’ll be breaking down these synthesis methods further along in the article.
-
Picking the Right Tools: MIDI Controller & MIDI Keyboard
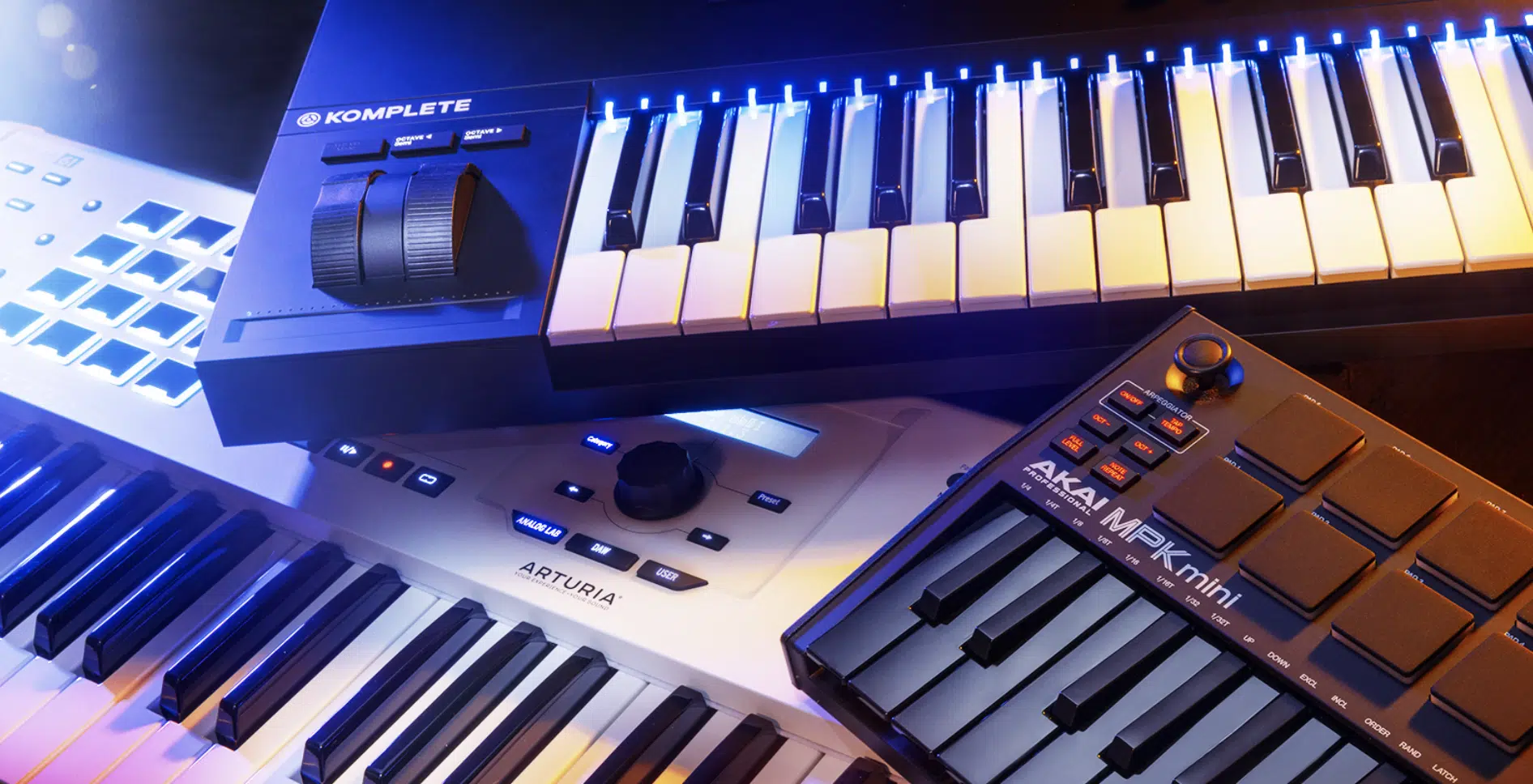

In electronic music production, your DAW is the center of operations 一 but it’s your tools like the MIDI controller and MIDI keyboard that bring your ideas to life.
These tools provide tactile control that helps in making electronic music more intuitive and engaging.
A MIDI controller allows you to control different parameters within your DAW.
You can use it to play virtual instruments, tweak knobs and faders, and trigger samples.
Some MIDI controllers even have pads that you can use for drum programming or triggering clips.
For example, the Akai MPD218 has 16 velocity-sensitive pads, perfect for finger drumming or triggering samples.
A MIDI keyboard, on the other hand, is used mainly for playing melodies, chords, and basslines.
It’s a vital tool for any producer, even if you’re not a keyboardist.
The Novation Launchkey Mini, for example, offers 25 mini keys, 16 pads, and 8 knobs, all of which can be mapped to your DAW.
Remember, it’s not about having the most expensive gear but understanding how to get the most out of what you have.
Learning how to use these tools efficiently can take your electronic music production to the next level.
-
Sound Design in Electronic Music

Sound design is one of the key elements that set electronic music apart from other genres.
It’s about creating your custom sounds, which can make your tracks addicting and alluring.
Whether it’s designing a punchy kick drum, a screaming lead, or a lush pad, sound design is an essential skill for any electronic music producer.
The first stage of sound design is understanding synthesis.
There are different types of synthesis, like:
- Additive
- Subtractive
- Wavetable
- Granular
- FM
Each of these provides a unique way to create sounds.
For example, Serum (a popular wavetable synth) allows you to morph between different waveforms and create complex and evolving sounds.
On the other hand, a synth like Massive, also a wavetable synth, different from a ROMpler, is known for its fat and powerful sounds 一 which is a staple in genres like Dubstep and Trap.
Next, we have sampling, a technique where you record or import audio to manipulate it and create new sounds.
You can pitch-shift a sample, reverse it, chop it, or even stretch it to create something completely unique.
For instance, Ableton Live’s Simpler & Sampler are excellent tools for sample manipulation, providing a world of possibilities at your fingertips.
Sound design might seem daunting at first, but with time and practice, it becomes an enjoyable part of the music production process.
Start with basic patches, understand how different parameters affect the sound, and slowly move towards more complex designs.
Remember, there’s no “right or wrong” in sound design; it’s all about what sounds good to you personally.
-
The Power of Music Theory in Electronic Music

Now, let’s talk about Music Theory…
While you can create great beats without knowing music theory, understanding it can give you a new perspective and tools to create more complex, interesting compositions.
If you’re attempting to learn electronic music production, Theory can seriously help excel the process tenfold.
Music theory provides you with the building blocks of music, like:
- Scales
- Chords
- Progressions
- Melodies
- Rhythms
- Harmonies
It helps you understand why certain notes sound good together, how to create tension and release in your song, and how to structure your track.
For instance, knowing that a minor chord can add a sad or melancholy feel to your song, while a major chord can evoke happiness or excitement, can be super beneficial.
Similarly, understanding different scales can open up a world of melodic and harmonic possibilities.
There are several resources available to learn music theory 一 from YouTube videos to dedicated music theory courses like the ones provided by Berklee Online.
Even if it seems complex at first, learning it at your own pace can bring significant improvements to your music production skills.
Software Applications for Music Production
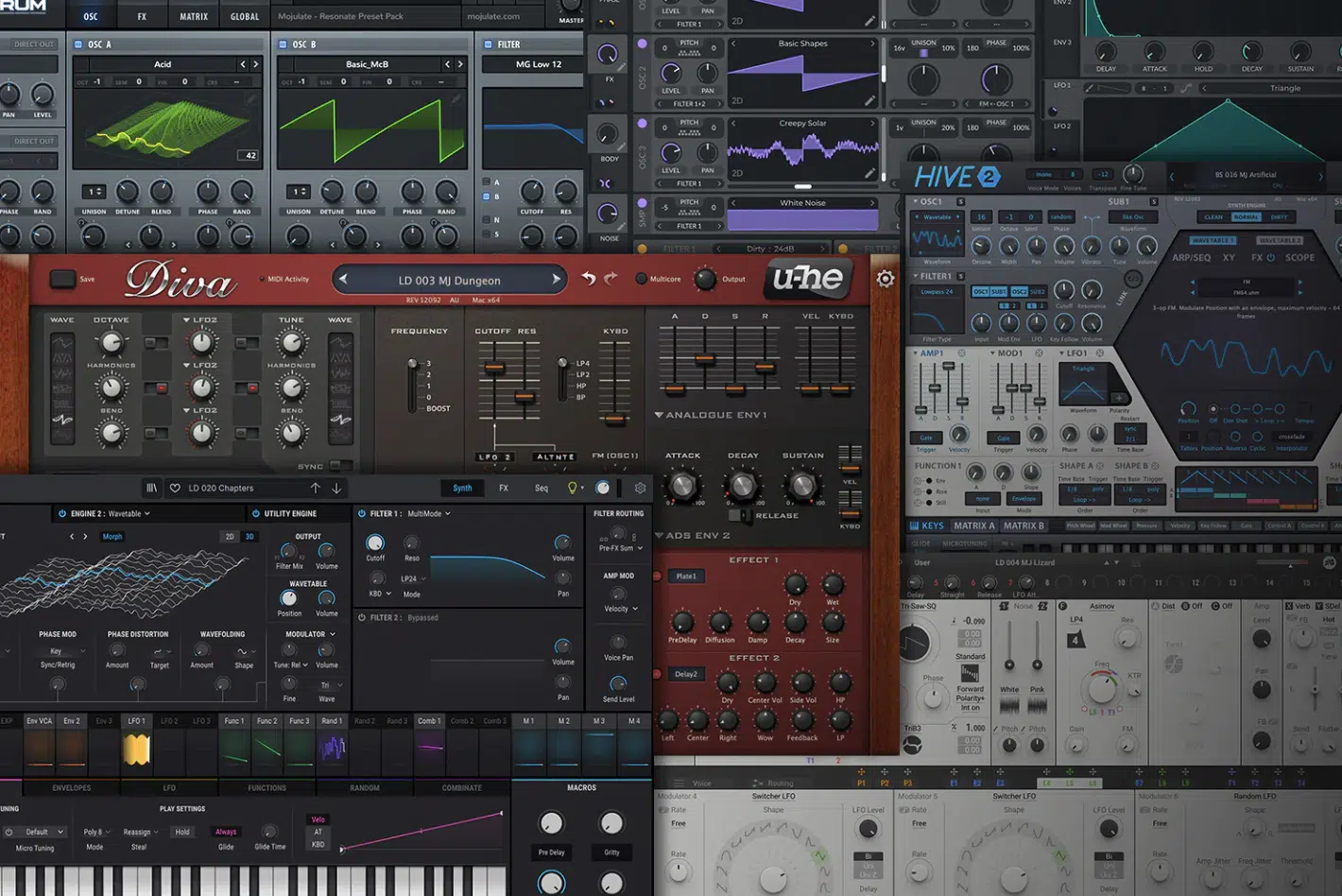
Electronic music production involves a wide array of software applications that can significantly enhance your workflow and production capabilities.
While your DAW remains the core platform for music creation, additional software can aid in sound design, editing, mixing, and mastering.
Virtual Studio Technology (VST) plugins are a type of software that integrates seamlessly with your DAW.
These plugins can be instruments (VSTi), like Serum or Massive, that allow you to create or modify sounds.
Others are effects (VSTfx) plugins, such as reverb, delay, EQ, and compression, which help shape and polish your mix.
FabFilter, for instance, offers a suite of high-quality plugins used by professionals worldwide for tasks like EQing, compression, and more.
Aside from plugins, there are standalone software applications that complement your DAW.
For example, software like Mixed In Key can analyze the key of your samples 一 helping you maintain harmonic consistency throughout your tracks.
Similarly, Melodyne (one of my favorites) is a powerful tool for pitch correction and creative melody manipulation.
Each software application adds a different flavor to your electronic music production process.
NOTE
Acquiring countless plugins won’t necessarily make you a better producer.
It’s all about understanding the tools you have and using them effectively to enhance your music.
Finding Your Unique Sound in Electronic Music

One of the ultimate goals for many producers is finding their unique sound in the music industry 一 a sonic signature that sets them apart from others.
This is what makes artists like Flume, Deadmau5, or Aphex Twin instantly recognizable.
But how do you find your sound?…
Finding your unique sound is a process that evolves over time, it won’t just appear after a few tracks or one full length song.
It’s the result of your influences, your musical preferences, your production techniques, and even your personality.
It’s about exploring different genres, techniques, and tools and seeing what resonates with you.
Don’t rush this process: let it happen organically.
As you keep producing and improving, you’ll start to notice certain patterns or elements in your music that you gravitate towards.
This could be:
- A certain type of chord progression
- A unique way you design your sounds
- A particular rhythm pattern you often use
While developing your unique sound, don’t be afraid to experiment and step outside your comfort zone.
Challenge yourself to try new techniques, create a track in a different genre, or use an instrument you’ve never used before.
The beauty of electronic music production is in its limitless possibilities.
But remember, it’s a learning curve, so don’t beat yourself up if it takes a little longer than other producers or other artists.
Maybe try a music production career path and invest in your first course, like this super beneficial affiliate program.
Mastering Ableton Live: An Electronic Music Producer Must
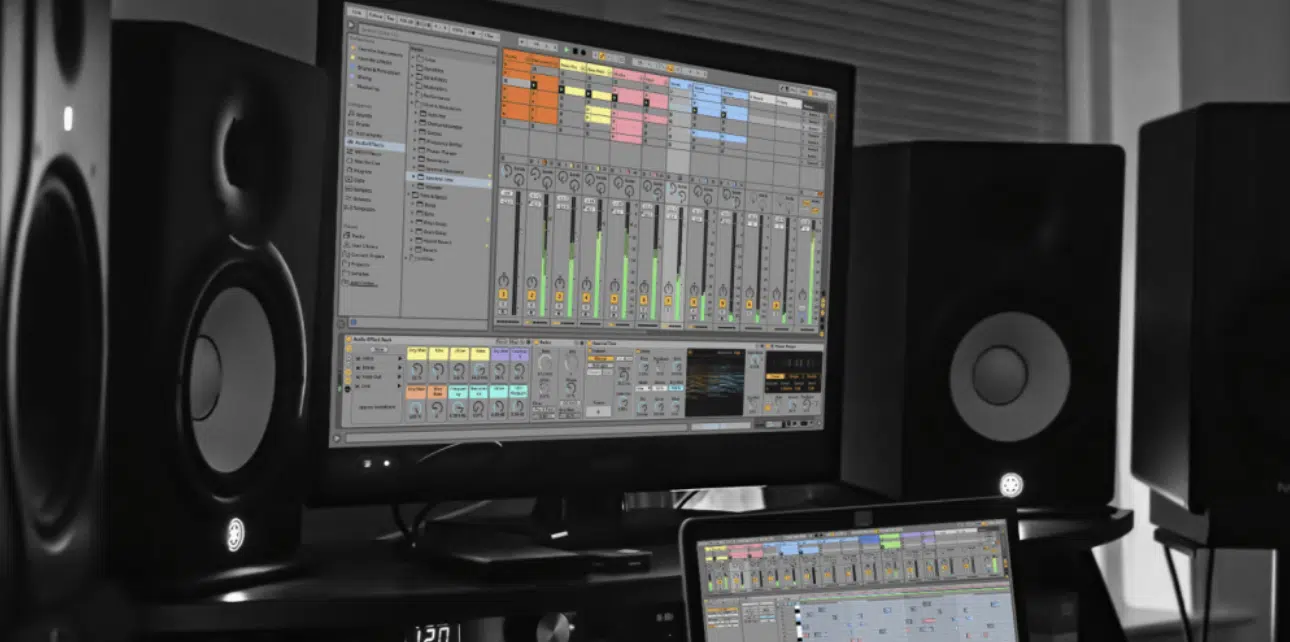
Now let’s talk about Ableton, a DAW that many electronic music producers swear by… and for good reason.
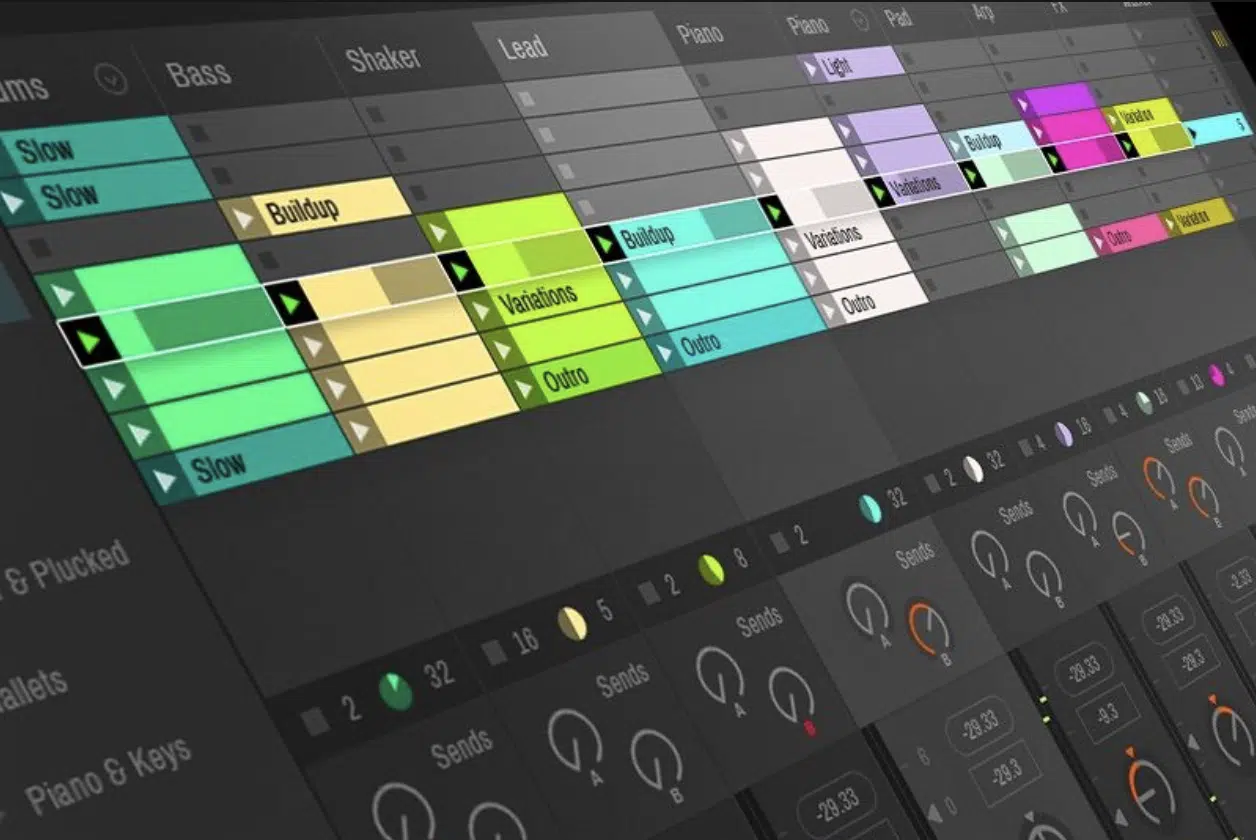
Ableton Live is an incredibly powerful DAW, but its interface can be intimidating for new users.
Luckily, we’ve got you covered, so you don’t feel frustrated or overwhelmed, and make sure you continue to learn electronic music production.
The Ableton Live workspace is divided into two main views:
- The Session view 一 A grid-like workspace that allows for improvising and experimenting with different clips, making it great for live performances.
- The Arrangement view 一 A timeline-based workspace where you can arrange your clips along a timeline, perfect for finalizing the structure of your track.
Each view serves a unique purpose in your music production workflow.
For instance, you could start by sketching out ideas in the Session view, playing around with different melodies, drum patterns, and basslines.
Once you’re happy with the ideas you’ve come up with, you can record them into the Arrangement view and start structuring your track.
Understanding Ableton Live’s interface is the first step toward mastering this highly-regarded DAW.
Spend some time exploring the software, and get familiar with its different sections 一 the Browser, the Control Bar, the Mixer, and so on.
The more comfortable you are navigating the interface, the smoother your production process will be.
-
Making the Most of Your MIDI Controller
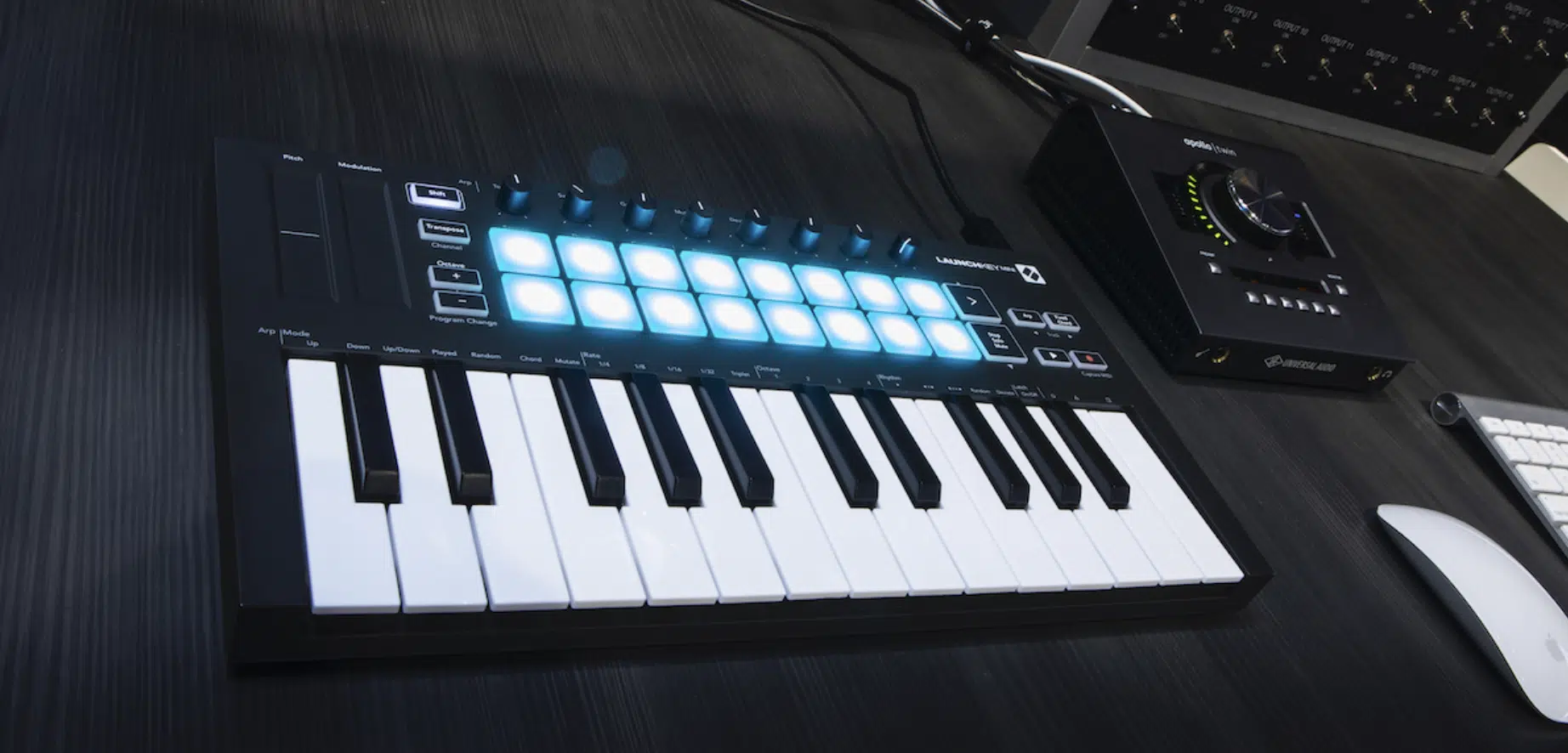

A MIDI controller can significantly enhance your workflow in Ableton Live.
Ableton Live features extensive MIDI mapping capabilities 一 allowing you to assign different parameters to your MIDI controller for tactile control.
A common use of a MIDI controller is playing virtual instruments.
You can use your MIDI keyboard to play melodies, basslines, and chords, which can often be more intuitive than drawing notes in the MIDI editor.
Moreover, with velocity-sensitive keys, you can add a human feel to your performances.
Ableton Live’s MIDI mapping feature allows you to assign different parameters to the knobs, faders, or buttons on your MIDI controller.
For instance, you could map a knob to a filter cutoff in a synth which allows you to perform filter sweeps live.
Or, you could map your controller’s faders to the track volumes in Ableton Live for hands-on control over your mix.
Some MIDI controllers (like Ableton Push) are specifically designed for Ableton Live and provide a tightly integrated workflow.
These controllers offer a grid of pads that correspond to the clips in your session view, allowing you to launch clips and even perform live.
Regardless of the MIDI controller you use, it’s about making the most out of it.
Learn about its features, understand how to map it to Ableton Live, and explore how it can enhance your music production process.
Electronic Music Tracks: Breaking it Down
Now let’s talk about how to create an electronic music track, from start to finish.
-
Creating a Track: From Idea to Arrangement
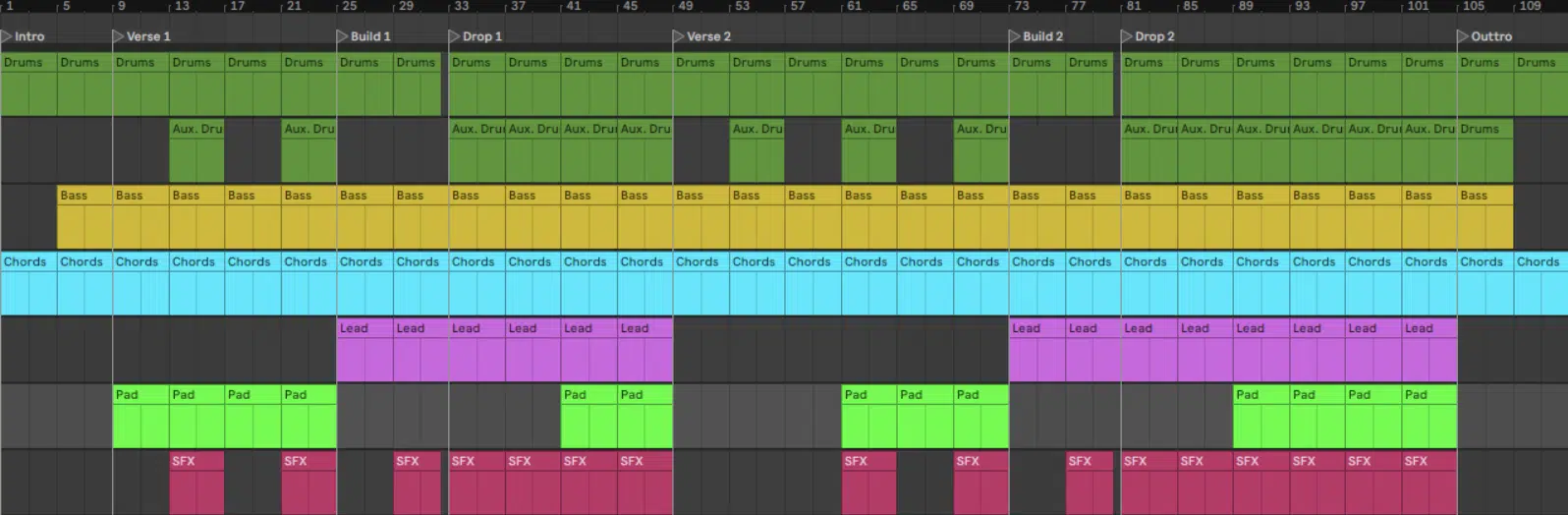
The journey of creating an electronic music track begins with a simple idea.
It could be a catchy melody you thought of, a unique sound you designed, or a rhythm pattern that got stuck in your head.
Once you have your idea, it’s time to start fleshing it out.
- If your idea is a melody 一 Try finding a suitable sound for it in your synth
- If it’s a rhythm 一 Start programming it into your DAW
Experiment with different sounds and instruments, and don’t be afraid to tweak and refine your idea.
As you start to build around your initial idea, other elements of your track will start to take shape.
Maybe your melody inspired a chord progression, or your rhythm suggested a bassline… slowly but surely, your track will start to grow.
The final step of creating a track is arranging it.
This is where you decide the structure of your track 一 where your intro starts, where the drop hits, how long the breakdown is, and so on.
A good arrangement can take your listener on a journey, building tension and releasing it at just the right moments.
-
Using Reference Tracks for Improved Production
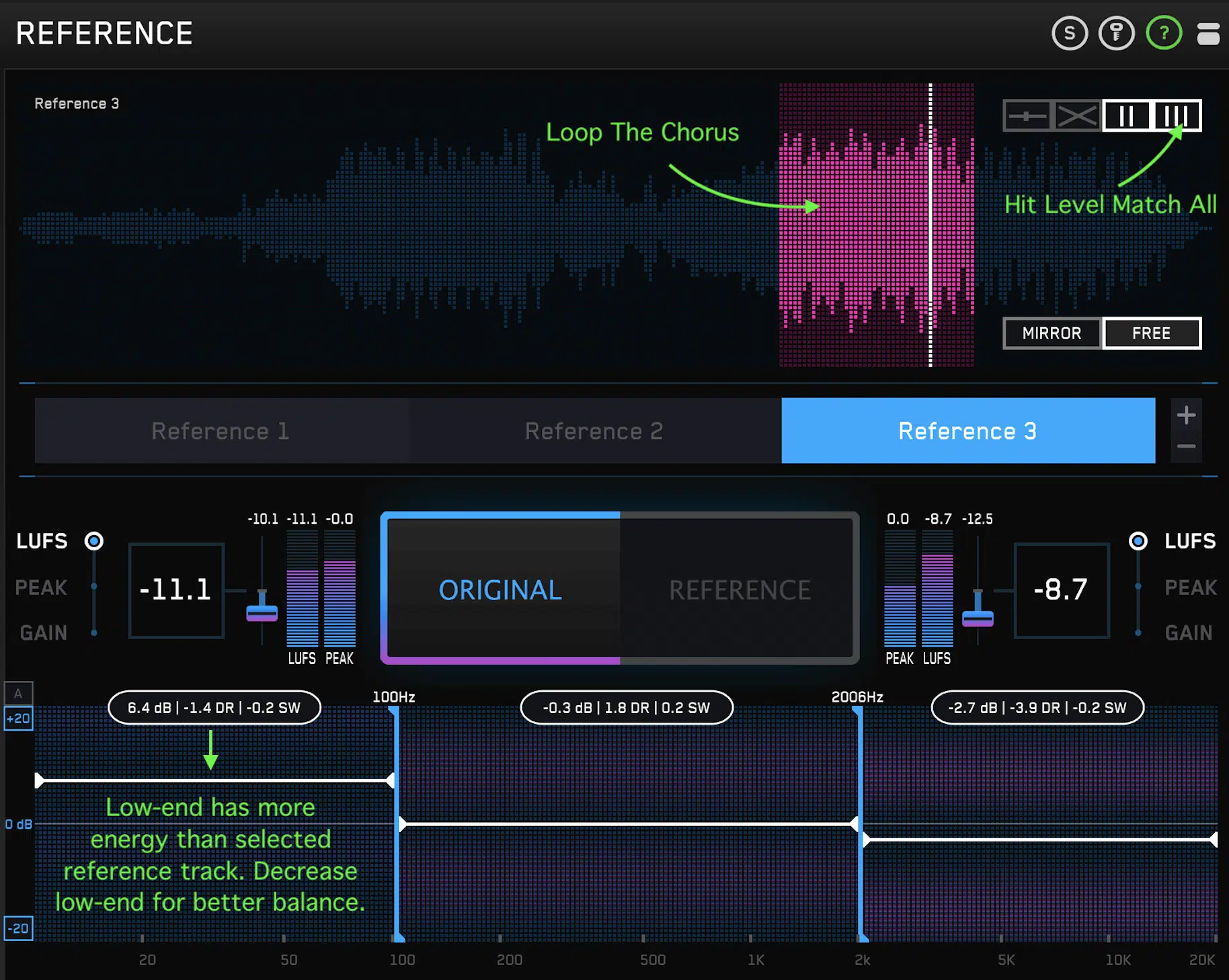
Reference tracks are professionally produced songs that you use as a guideline during your production, and mixing & mastering stages.
These tracks serve as a benchmark of quality 一 helping you make informed decisions about your sound design, arrangement, mix balance, and overall sonic quality.
If you want to learn electronic music production, it’s super important to take advantage of reference tracks.
When selecting a reference track, choose a song that is similar to the one you’re working on in terms of:
- Genre
- Instrumentation
- Vibe/mood
It’s important that your reference track is a song you admire and aspire to sound like, but remember, the goal isn’t to copy it, but to learn from it.
In the production stage, a reference track can provide insights into sound design, song structure, and arrangement.
By listening closely, you might understand:
- How the producer designed their sounds
- How they structured their song
- How they transitioned between different sections
Truthfully, there is no better way to grow and learn on your electronic music production journey than utilizing reference tracks.
During mixing, a reference track can help guide decisions about levels, panning, EQing, and more.
By comparing your mix to the reference, you can identify if your bass is too loud, if your mix lacks stereo width, or if your track needs more high-end.
During mastering, a reference track can provide a target for loudness, dynamics, and overall tonal balance.
However, it’s essential to remember that every song is unique, and what works for one might not work for another.
Use reference tracks as a guide, not a rulebook.
-
Mixing & Mastering Your Track
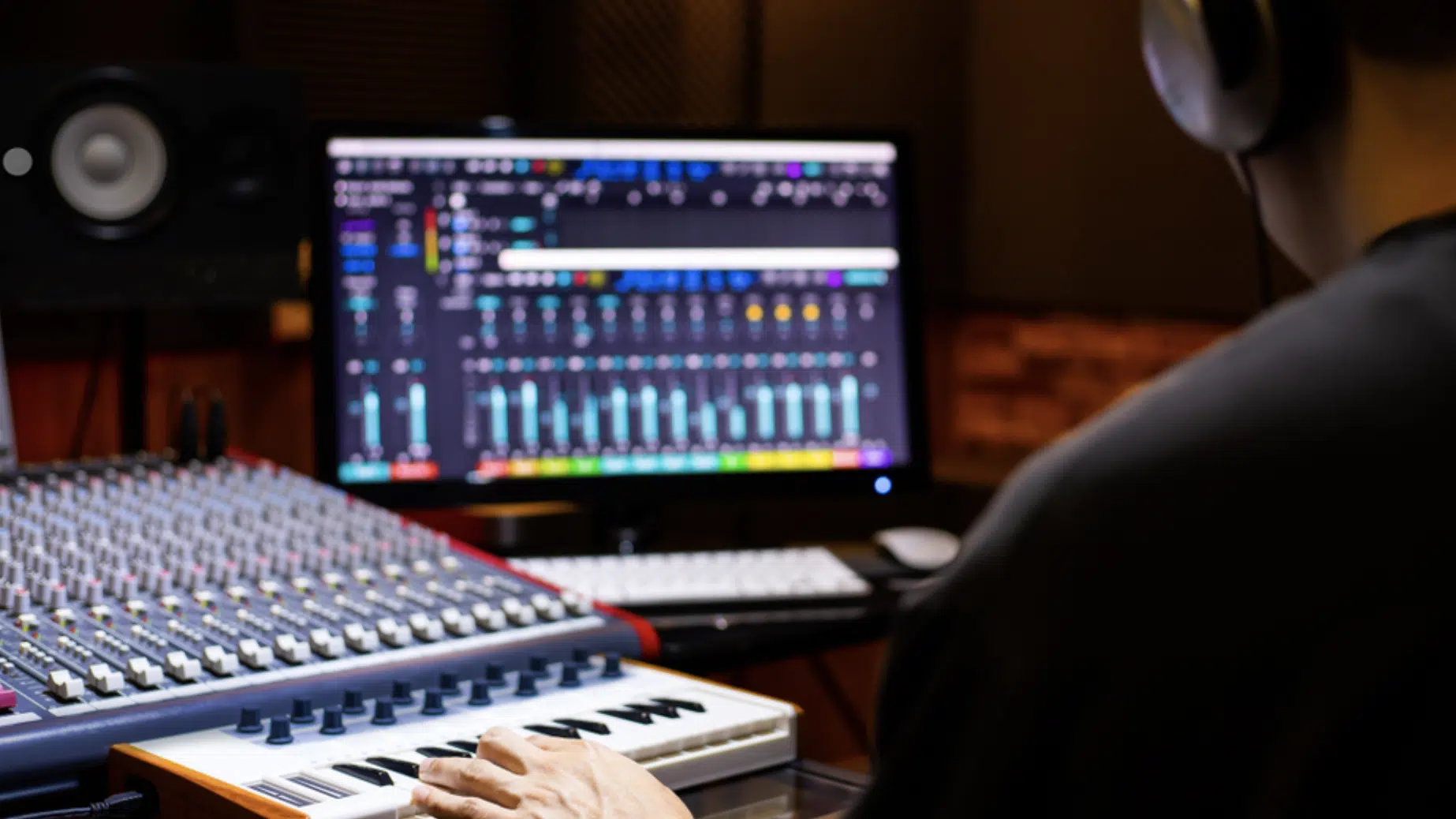

Once your track is arranged and your sounds are designed, it’s time to mix and master your track.
Mixing and mastering are critical stages in music production; ensuring your track sounds cohesive and polished across different playback systems.
Mixing involves:
- Adjusting the levels of your different tracks
- Panning them across the stereo field
- Using tools like EQ and compression to make sure every element has its own space in the mix
For instance, you might carve out some low-end frequencies from your synths to allow your kick and bass to cut through the mix.
After you’ve finished mixing, it’s time to master your track.
Mastering involves:
- Putting the final touches and polishes on your song
- Ensuring it sounds balanced across different playback systems and matches the loudness level of other commercial tracks
Tools used in mastering often include EQ, compression, stereo-width processors, and limiters.
For instance, a limiter can help increase the overall loudness of your track without clipping.
While mixing and mastering can be done in your home studio, they require a good understanding of audio processing and a well-treated space for accurate monitoring.
You might consider hiring a professional engineer for these tasks, especially for important releases.
However, there’s a wealth of resources online if you choose to learn and do it yourself.
NOTE: During mixing, always remember to check your mix on different systems 一 your studio monitors, headphones, car speakers, or even your smartphone.
This practice, known as reference monitoring, will give you an idea of how your mix translates on various systems.
Also, remember that even the better master can’t fix a bad mix, and take frequent breaks (for ear fatigue’s sake).
Pro Tip:
Once you have your track mixed and mastered, it’s time to give it the final polish.
This stage involves refining details that make your track sound complete and professional.
This stage could involve automating certain elements to create movement and interest in your track.
For instance, you might automate the filter cutoff on a synth to create a sweeping effect or automate the reverb on a vocal to make it sound distant at certain points (popular in hip-hop).
It might also involve fine-tuning your transitions to ensure they’re smooth and natural.
Maybe a reverse cymbal could make a transition smoother, or a white noise sweep could build more tension before a drop.
Pay attention to every detail, no matter how small it seems, as it could help you up your skill level fast.
Expanding Your Electronic Music Production Knowledge
Now that you’re aware of the basics, let’s expand your knowledge of electronic music production by talking about different genres, and mastering synthesis, arrangement, and composition.
-
Exploring Sub-genres in Electronic Music: From Techno to Ambient
In electronic music production, it’s super important to diversify your knowledge across the spectrum of its various sub-genres.
Each has its defining characteristics and unique production techniques 一 which can all enrich your electronic music production skills.
Techno, for example, is a genre known for its repetitive beat structures and pulsating basslines.
Techno relies heavily on the intelligent use of drum machines and synthesizers to create a hypnotic atmosphere.
If you want to create hard-hitting techno, you’d need to master the art of crafting tight, resonant kick drums.
As well as learn to experiment with sounds on the lower end of the frequency spectrum.
Ambient music, on the other hand, is all about creating a mood or atmosphere.
It often makes use of reverb and delay to create a sense of space and depth.
Long, drawn-out pads, slowly evolving synth textures, and the absence of a pronounced beat are hallmarks of this sub-genre.
Let’s not forget about sub-genres like house, trance, drum and bass, dubstep, and more.
Each of these brings unique elements and techniques to the table.
From the rhythmic shuffle in house music to the wobble bass in dubstep 一 understanding these stylistic nuances can give you a broader palette of ideas.
The idea here is not to box yourself into one sub-genre, but to learn from them all.
By dissecting and understanding the elements that define these genres, you can incorporate these techniques into your unique sound.
Or even fusing elements from different genres to create something entirely new!
Mastering Synthesis for Electronic Music Production
One cannot overstate the importance of mastering synthesis in electronic music production.
Synthesizers are at the heart of electronic music, creating everything from pounding basslines to ethereal pads.
Understanding different types of synthesis can open up a world of sonic possibilities.
-
Subtractive synthesis (common in analog synths)
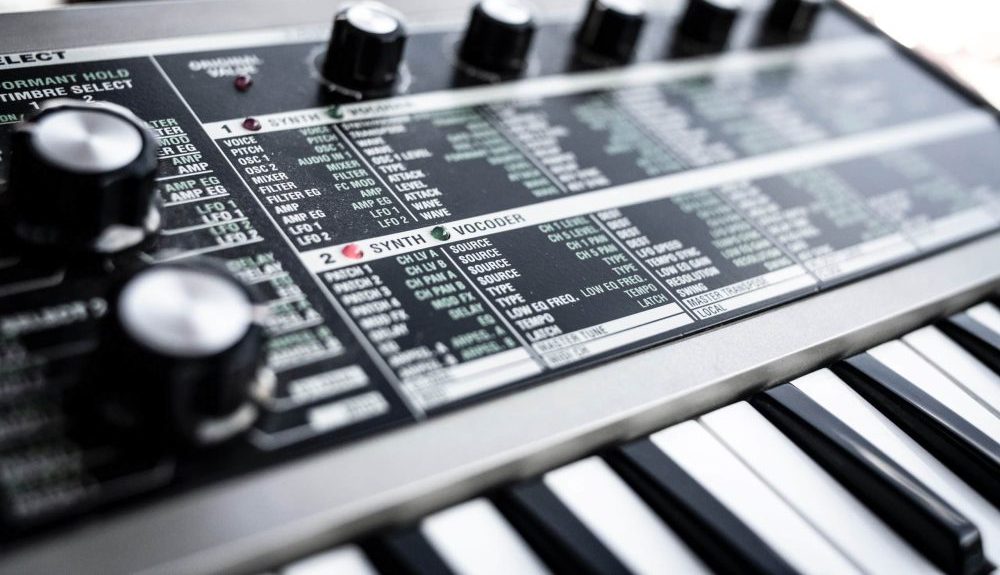

Subtractive synthesis involves filtering a harmonically rich oscillator to create a wide variety of sounds.
It’s great for creating warm, resonant basses and sharp leads.
-
FM (Frequency Modulation) synthesis
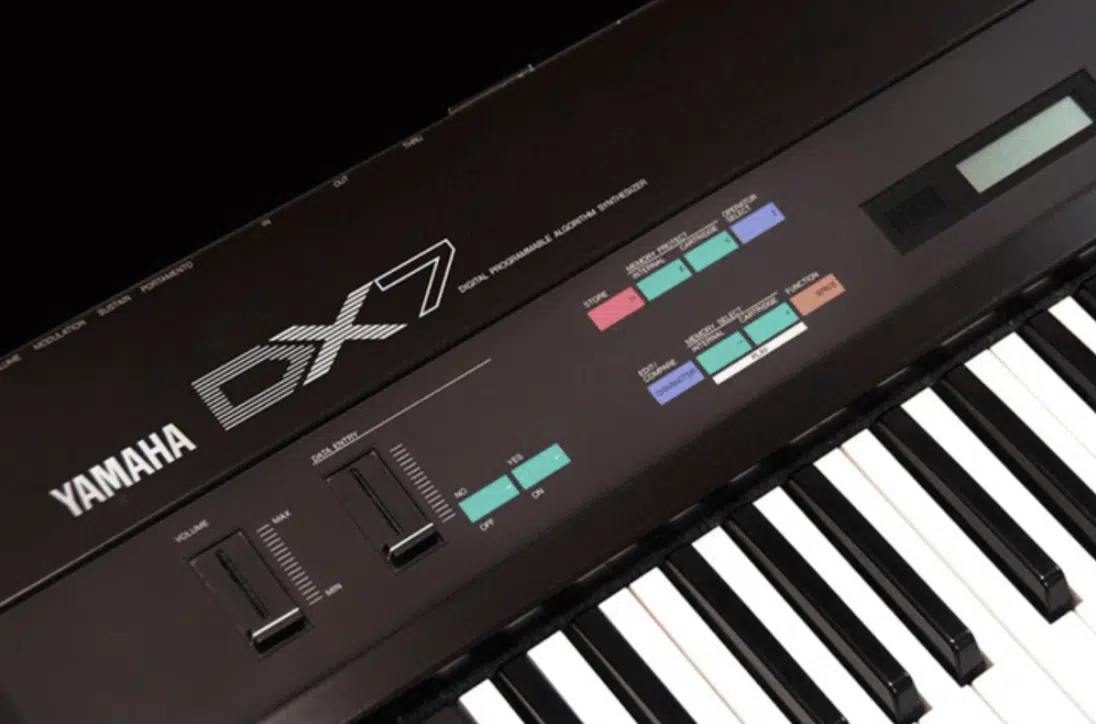

FM synthesis is a more complex form of synthesis.
It involves the modulation of one oscillator (carrier) with another (modulator).
This synthesis method can create complex, evolving sounds, often used for creating bell-like tones, sharp leads, or deep basses.
-
Granular synthesis
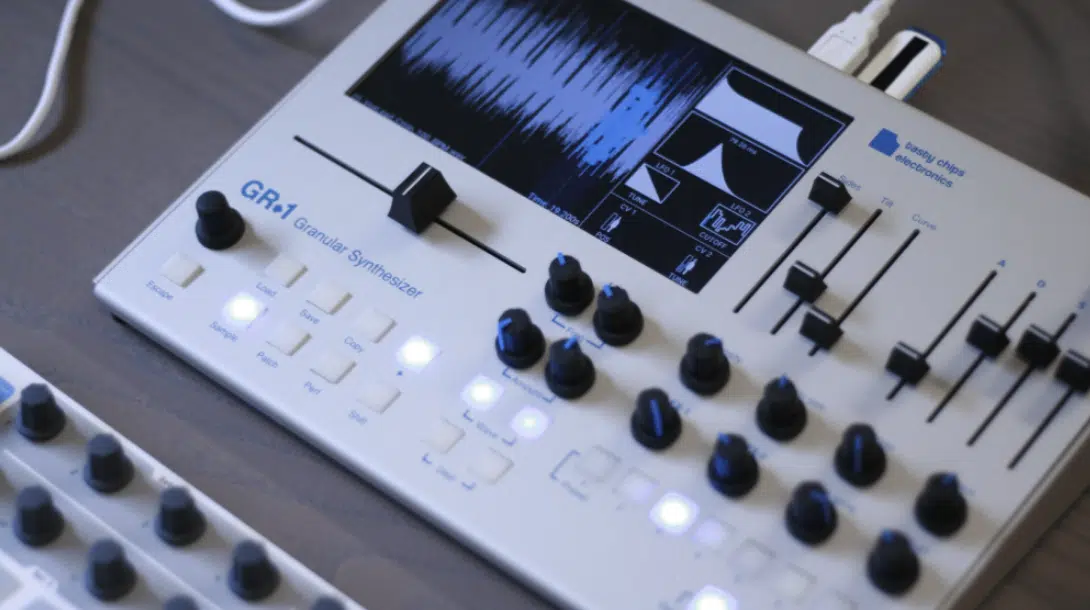

Granular synthesis is a method that involves breaking up the audio into tiny grains and manipulating them.
It’s fantastic for creating ethereal, otherworldly textures.
-
Additive synthesis
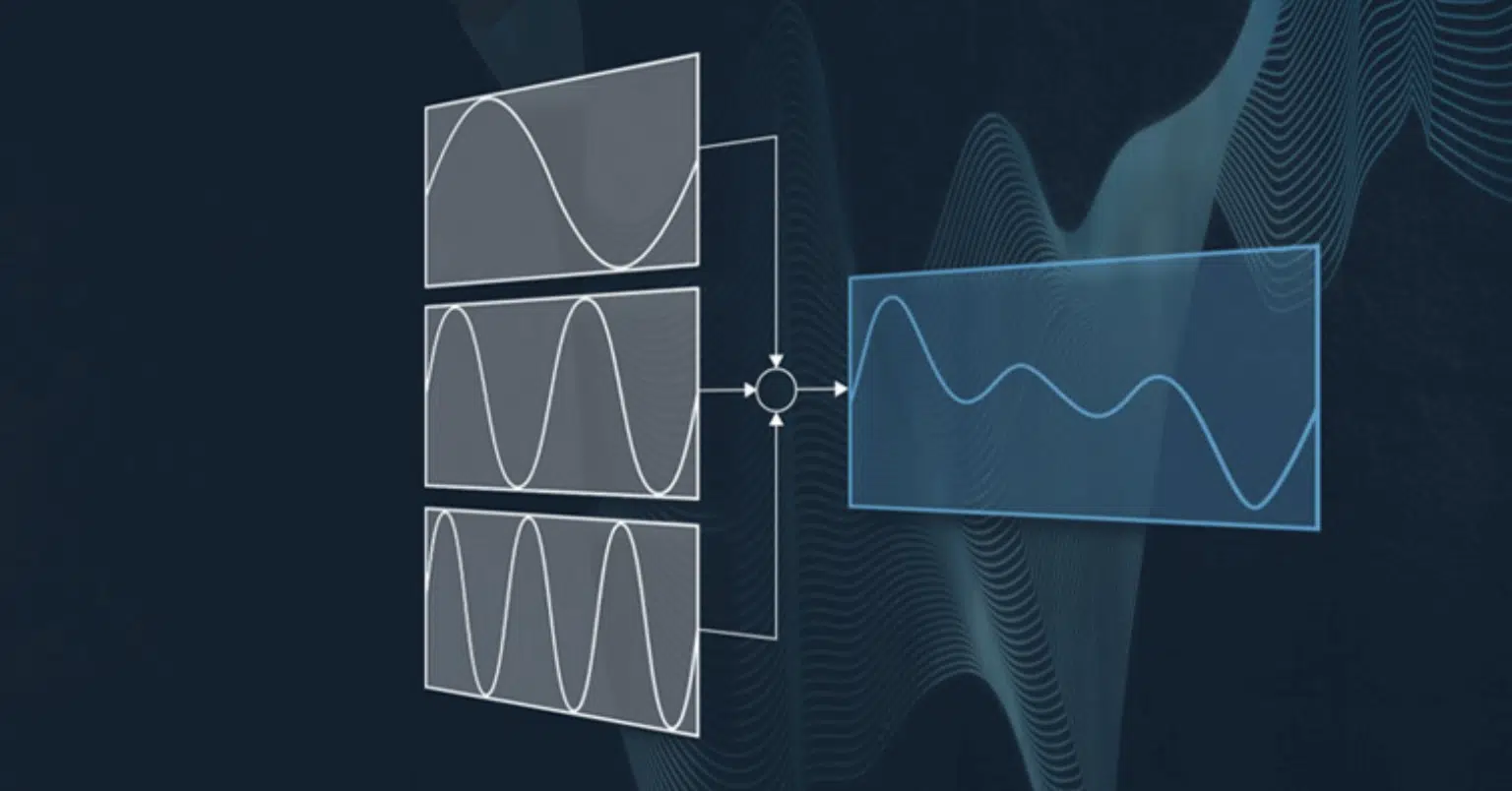
Additive synthesis involves combining simple waveforms (sine waves) at different frequencies to create complex tones.
You can manipulate the amplitude and phase of each component (or “partial”) to create intricate and evolving sounds, from lifelike electronic instruments to entirely synthetic textures.
-
Wavetable synthesis

Wavetable synthesis involves scanning through a ‘wavetable’ (a series of waveforms) to create rich, dynamic sounds.
You can morph smoothly between different waveforms within a wavetable, leading to a moving, evolving sound.
Each of these methods offers a unique set of possibilities when you’re making electronic music.
Understanding them can significantly expand your sound design capabilities and help you learn electronic music production like a boss (at your own pace, of course).
Electronic Dance Music Arrangement & Composition Techniques

Now, let’s talk about arrangement and composition in electronic music.
Unlike traditional music forms that might follow a verse-chorus structure, electronic music offers a lot of flexibility when it comes to arrangement.
However, there are certain techniques that have proven effective over the years.
Consider the concept of tension and release, a fundamental element in many types of music but especially vital in electronic music.
This might involve:
- Building up elements gradually
- Adding more percussion
- Introducing new melodic elements
- Increasing volume or intensity
All are applied before a drop or breakdown, which provides the release.
The drop itself (a signature moment in most electronic music tracks especially in genres like house, dubstep, or trance) is often marked by a shift in energy, melody, or rhythm.
Mastering the art of crafting impactful drops is a vital part of electronic music production.
Another notable arrangement technique in electronic music is the use of evolving soundscapes.
This could involve:
- Slowly changing a pad’s timbre over time
- Gradually introducing or removing elements
- Modulating effects parameters to keep the listener engaged
This technique is prevalent in ambient or minimal techno tracks 一 where the evolution of sounds over time maintains interest despite a lack of traditional melodic/rhythmic structures.
The beauty of electronic music production lies in its boundless possibilities.
You can compose a complex melodic piece, create a rhythm-focused track, or build an atmospheric soundscape based on layered textures.
It all depends on how far you’re willing to push the boundaries and discover what your music is truly capable of.
BONUS: Advanced Tips to Help You Become an Electronic Music Production Master
As a bonus, here are 3 super beneficial tips, tricks, and techniques that can help you become an electronic music production master in no time.
1. Advanced Sound Design Techniques
Sound design is the heart and soul of electronic music production.
As you progress and develop your skills, delving into advanced sound design techniques can enable you to create truly unique and innovative sounds.
Modular Synthesis is one such technique.
While this can seem intimidating at first, the world of modular gives you the ultimate freedom to create custom sounds from scratch.
Modular synthesis involves connecting different ‘modules’ in an electronic instrument to create complex and evolving sounds.
Many popular DAWs like Ableton Live offer virtual modular environments like Max for Live where you can experiment and create your own patches.
Multiband Processing is another advanced technique.
It allows you to process different frequency ranges of a sound separately.
You could, for instance, compress the low-end of a bass sound while distorting the high-end, giving you greater control over the final sound.
Resampling is also great for some added allure and creativity.
It’s a technique where you bounce a sound to audio and then manipulate that audio to create something new.
You can stretch it, pitch it down, chop it up, or add effects to turn a simple sound into something complex and unrecognizable.
It’s a fantastic way to discover new sounds and textures you wouldn’t have come up with otherwise.
2. Going Beyond Basic Music Theory

Music theory is not just for traditional composers or musicians, it’s just as crucial in electronic music production.
It can help you create compelling melodies, harmonies, and chord progressions that resonate with your listeners.
You can begin by exploring advanced concepts like,” also known as borrowed chords.
This is where you borrow chords from a parallel key to your own 一 leading to unexpected and interesting harmonic changes.
For example, if your track is in C major, you might borrow the iv (F minor) chord from C minor to add a different color to your progression.
Another powerful concept to explore is ‘polyrhythm‘, the simultaneous use of two or more conflicting rhythms.
This can add a unique and interesting groove to your tracks.
For instance, you might have a 3:2 polyrhythm, where one rhythm is playing triplets while another is playing straight quarters.
Lastly, consider learning more about ‘counterpoint‘, the relationship between two or more melodies that are independent in contour and rhythm but harmonically interdependent.
This can add depth and complexity to your electronic compositions.
3. Professional Mixing and Mastering Strategies
Let’s move on to advanced mixing and mastering strategies.
One pro tip that can really help your mixes shine is using mid/side processing.
This allows you to process the mono (middle) and stereo (sides) parts of a sound separately.
For example, you might apply EQ to clean up the mid frequencies while adding width to the sides with some gentle boosting in the high frequencies.
Next up is parallel processing.
This is when you duplicate a track (or send it to a bus/auxiliary track) and process the copy differently.
This allows you to blend the processed and unprocessed signals for greater control over the balance.
NOTE: This technique is often used with compression (parallel compression) or reverb (parallel reverb) when heard in popular music.
An advanced mastering technique is using multi-band compression.
Unlike a regular compressor, a multi-band compressor allows you to compress different frequency ranges separately.
It’s actually a very popular technique within the music industry.
This gives you greater control over the dynamics of your mix and can help to balance out any inconsistencies in your frequency spectrum.
Finally, let’s touch upon the mastering limiter, the last plugin in your mastering chain.
It ensures your music doesn’t clip by setting a ceiling for the output level.
But more than preventing distortion, when used subtly, it can add a level of saturation and loudness that can make your track punchier.
Mastering is a delicate process that requires careful listening and adjustments… the goal is to enhance your mix, not alter it drastically.
Electronic Music Production: Final Thoughts
In the fascinating journey of electronic music production, we’ve delved into everything from the foundations to the more advanced skills that can truly set you apart.
We’ve navigated the intricacies of DAWs, explored different genres, immersed ourselves in sound design, and ventured beyond basic music theory.
Yet, the journey is far from over…
The field of music production is constantly evolving, and there’s always something new to learn.
As we wrap up this guide, there’s one more thing to discuss that will give your tracks that professional edge and tie everything together: these expertly crafted, super unique free bass loops.
These loops are the secret weapon many professional electronic music producers have in their arsenal.
They are perfectly tailored for electronic music and are designed to give your tracks the depth, punch, and character that can take them from basic to legendary.
Plus, they’ll make your tracks powerful, catchy, and irresistible.
Think of the endless possibilities: a bassline that syncs perfectly with your drum groove, driving the rhythm forward.
A sub-bass loop that adds warmth and depth to your mix.
Or a complex, modulated bass pattern that becomes the centerpiece of your track.
Well, these bass loops have it all, plus some.
Whether you’re producing house, techno, drum & bass, or any other electronic genre, you’ll find loops that fit your style perfectly.
You can drop them into your project as is, or use them as a starting point for your own bass sound design.
Either way, they’re a great way to kickstart your creativity and get your tracks sounding their best.
Becoming an electronic music production master is no small feat 一 it requires dedication, patience, and a deep passion for music.
But with the right tools and knowledge at your fingertips, like everything within this article, you’ll be a master in no time.
Remember, in the world of music production, every sound is an opportunity.
Until next time…







Leave a Reply
You must belogged in to post a comment.